J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2023 Dec;49(6):365-368. 10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.6.365.
Setback genioplasty with rotation for aesthetic mentolabial soft tissue: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550301
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.6.365
Abstract
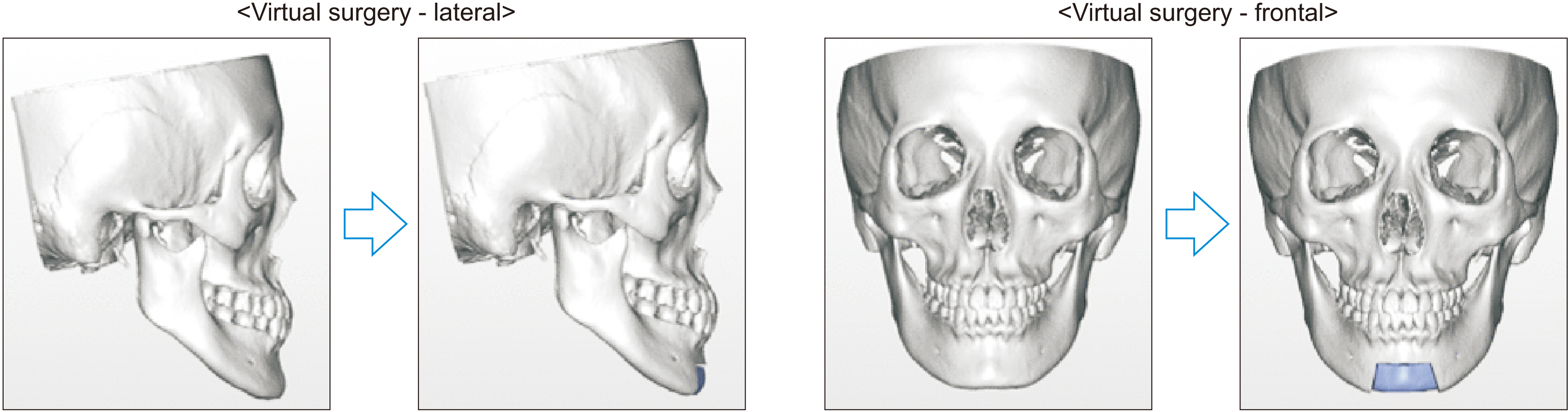
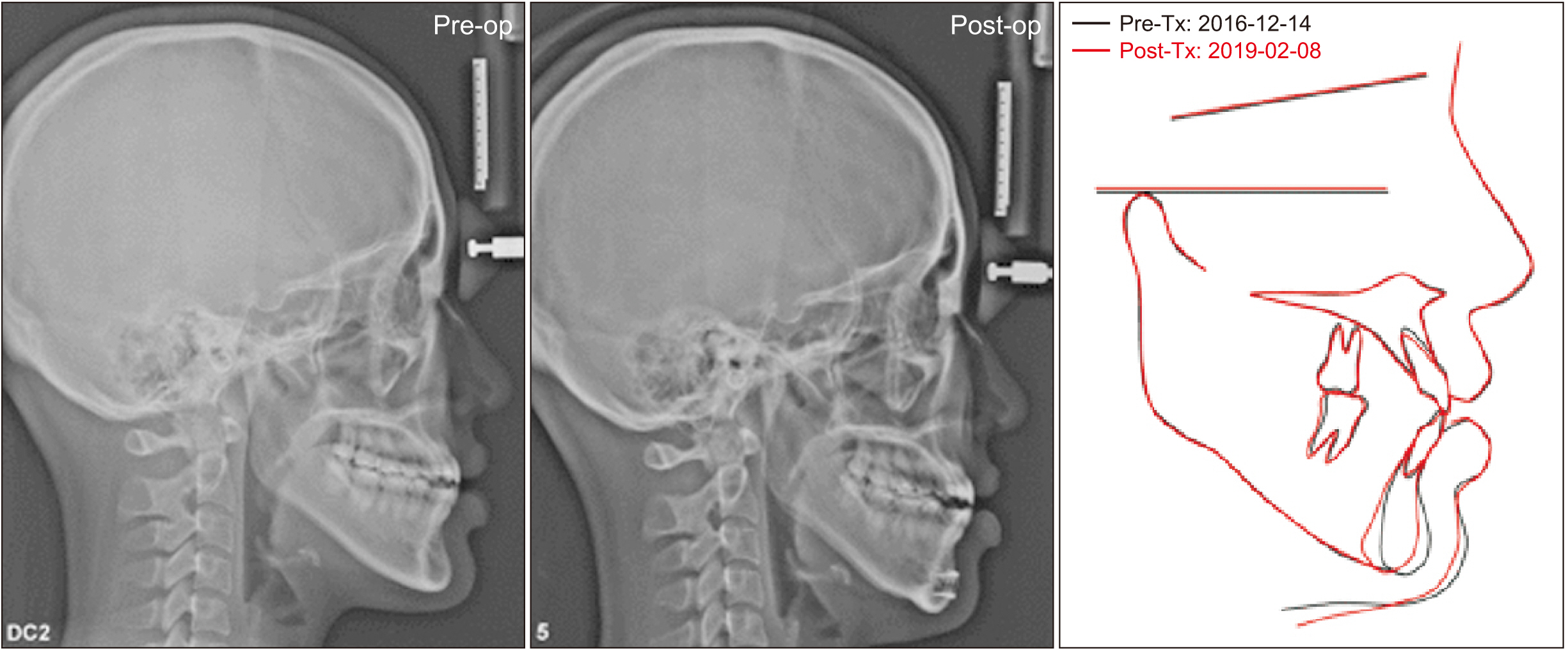
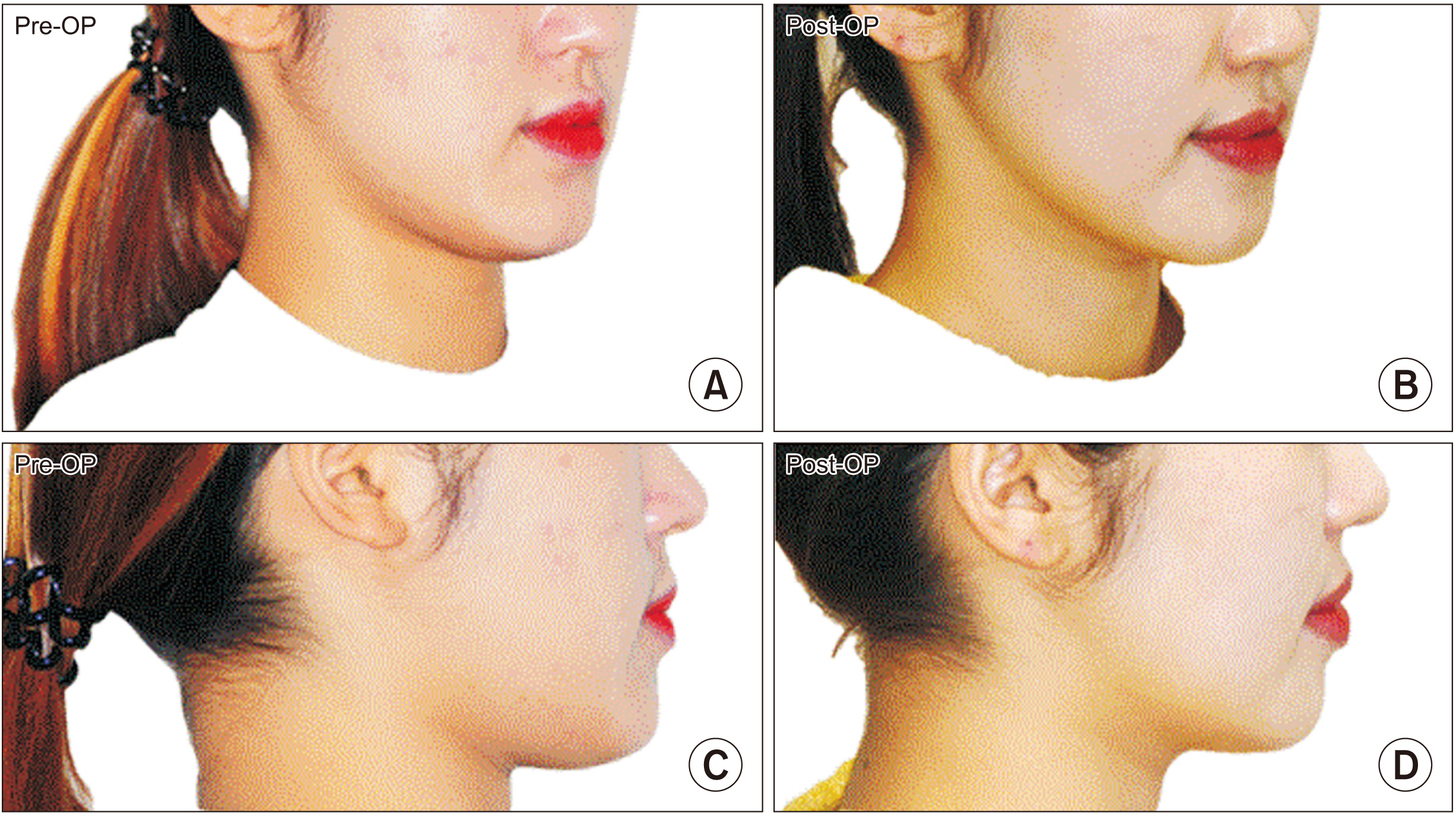
- The mentum plays an important role in the aesthetics of the face, and genioplasty is performed to improve an unbalance of the mentum. Among the various surgical approaches, setback genioplasty is used to create an aesthetic jaw-end appearance by moving the mentum backward when it protrudes more than normal. However, conventional setback genioplasty may be aesthetically disadvantageous because the profile of the mentum could become flat. This case study attempted to overcome the limitations of conventional setback genioplasty by rotating the position of the menton and pogonion. We devised a new method for setback genioplasty by rotating the segment anteroinferiorly. Using virtual surgery, we were able to specify the range of surgery more accurately and easily, and the surgery time was reduced. This case report showed the difference in chin soft tissue responses between conventional setback genioplasty and setback genioplasty with rotation.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lagos OAV, Montenegro L, Colucci G, Amarista FJ. 2022; Sagittal reduction genioplasty: technical note. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 123:576–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2022.02.015. DOI: 10.1016/j.jormas.2022.02.015. PMID: 35240341.2. Park JY, Kim MJ, Hwang SJ. 2013; Soft tissue profile changes after setback genioplasty in orthognathic surgery patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 41:657–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2013.01.005. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.01.005. PMID: 23395297.3. Möhlhenrich SC, Heussen N, Kamal M, Peters F, Fritz U, Hölzle F, et al. 2015; Influence of setback and advancement osseous genioplasty on facial outcome: a computer-simulated study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:2017–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.10.017. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.10.017. PMID: 26603107.4. Deschamps-Braly J. 2019; Feminization of the chin: genioplasty using osteotomies. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 27:243–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2019.01.002. DOI: 10.1016/j.fsc.2019.01.002. PMID: 30940390.5. Hama Amin OS, Abdulrahman SW, Altom A, Hasan BA, Khdhir RH, Zorab RH, et al. 2022; Facial deformity correction and genioplasty; a case report and literature review. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 79:104088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104088. DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104088. PMID: 35860134. PMCID: PMC9289503.6. San Miguel Moragas J, Oth O, Büttner M, Mommaerts MY. 2015; A systematic review on soft-to-hard tissue ratios in orthognathic surgery part II: chin procedures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43:1530–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.032. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.032. PMID: 26321067.7. Brindha MS, Ramya R, Bharanidharan R, Govindaram D, Rajkumar K. 2019; Mentolabial sulcus and malocclusion: facial esthetics in ethnic Tamil population. SRM J Res Dent Sci. 10:209–13. https://doi.org/10.4103/srmjrds.srmjrds_64_19. DOI: 10.4103/srmjrds.srmjrds_64_19.8. Glorion A, Perrillat A, Foletti JM, Cristofari S. 2022; Surgical techniques used in chin feminization: literature review and knowledge update. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 123:e883–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2022.07.015. DOI: 10.1016/j.jormas.2022.07.015. PMID: 35870794.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Various Osseous Genioplasty Combined with Orthoganthic Surgery
- A Study on the Prediction of Hard and Soft Tissue Changes after Setback Genioplasty
- Current concepts in genioplasty: surgical techniques, indications, and future perspectives
- A Study on the mandibular setback osteotomy and reduction genioplasty in mandibular prognathism with long anterior facial height
- Soft tissue changes associated with advancement genioplasty in skeletal class III individuals receiving mandibular set-back surgery