Nutr Res Pract.
2023 Dec;17(6):1255-1266. 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.6.1255.
Classification and prediction of the effects of nutritional intake on diabetes mellitus using artificial neural network sensitivity analysis: 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kyung Hee University, Yongin 17104, Korea
- 2Department of Home Economics Education, Dongguk University, Seoul 04620, Korea
- KMID: 2548890
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2023.17.6.1255
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
This study aimed to predict the association between nutritional intake and diabetes mellitus (DM) by developing an artificial neural network (ANN) model for older adults.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
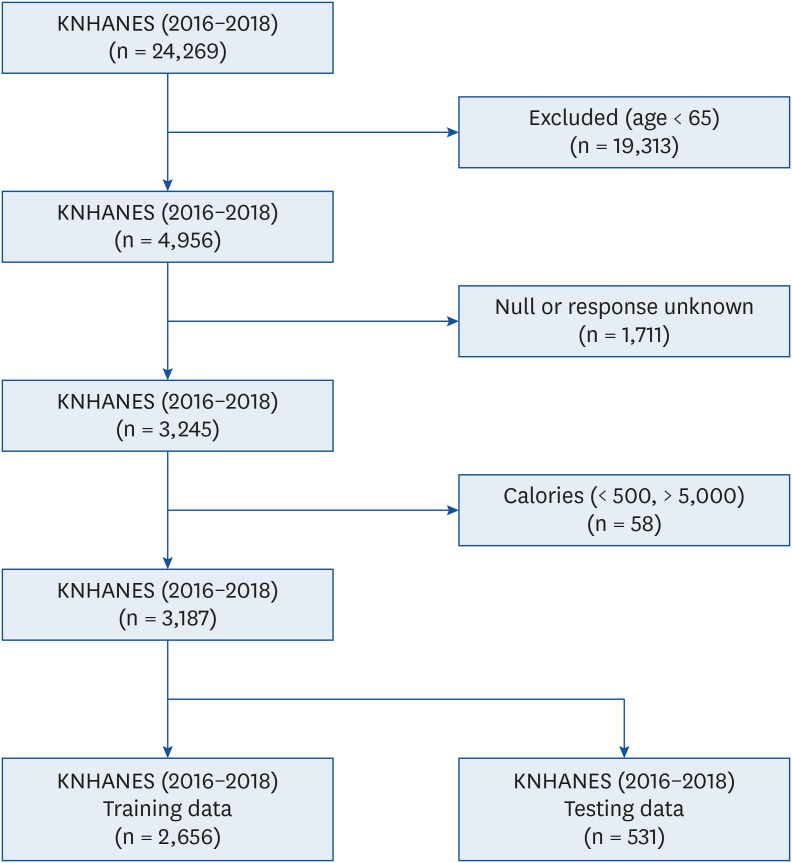
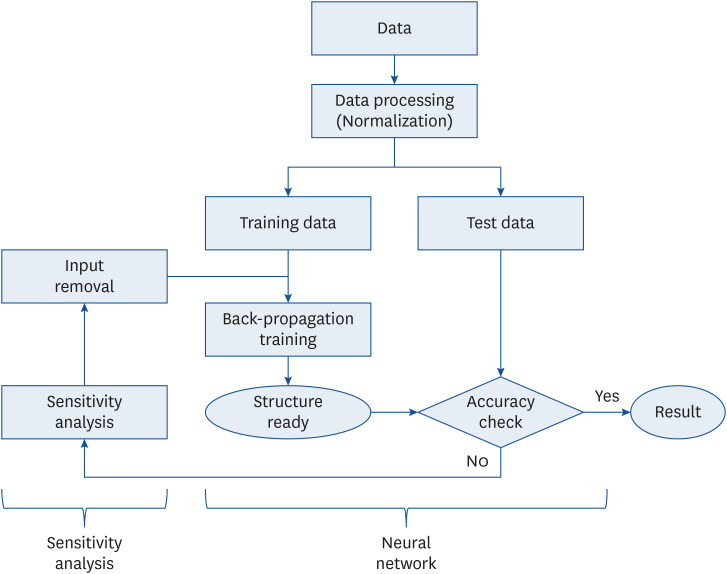
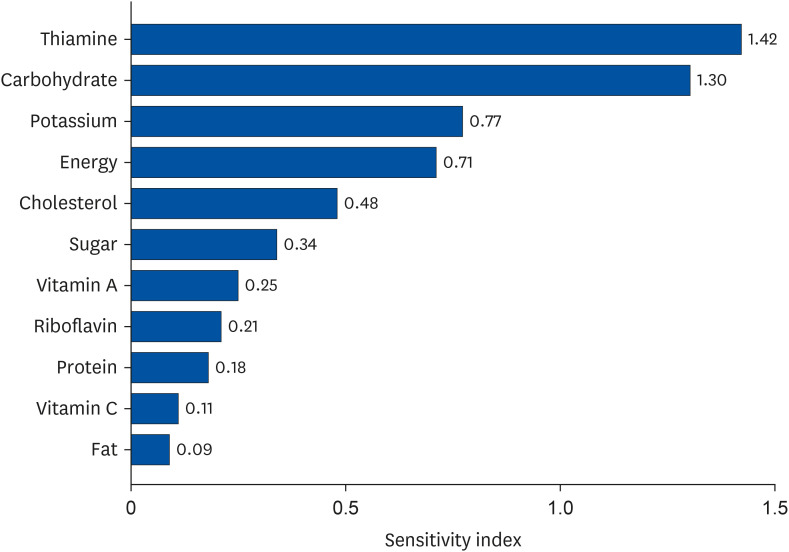
Participants aged over 65 years from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were included. The diagnostic criteria of DM were set as output variables, while various nutritional intakes were set as input variables. An ANN model comprising one input layer with 16 nodes, one hidden layer with 12 nodes, and one output layer with one node was implemented in the MATLAB ® programming language. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to determine the relative importance of the input variables in predicting the output.
RESULTS
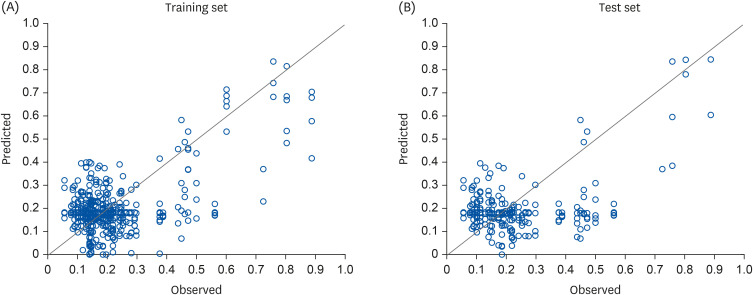
Our DM-predicting neural network model exhibited relatively high accuracy (81.3%) with 11 nutrient inputs, namely, thiamin, carbohydrates, potassium, energy, cholesterol, sugar, vitamin A, riboflavin, protein, vitamin C, and fat.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the neural network sensitivity analysis method based on nutrient intake demonstrated a relatively accurate classification and prediction of DM in the older population.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung CH, Son JW, Kang S, Kim WJ, Kim HS, Kim HS, Seo M, Shin HJ, Lee SS, Jeong SJ, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2020: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:1–10. PMID: 33434426.2. Chentli F, Azzoug S, Mahgoun S. Diabetes mellitus in elderly. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 19:744–752. PMID: 26693423.3. American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic targets. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:S48–S56. PMID: 27979893.4. Ma Y, Olendzki B, Chiriboga D, Hebert JR, Li Y, Li W, Campbell M, Gendreau K, Ockene IS. Association between dietary carbohydrates and body weight. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 161:359–367. PMID: 15692080.5. Frimpong EA, Oluwasanmi A, Baagyere EY, Zhiguang Q. A feedforward artificial neural network model for classification and detection of type 2 diabetes. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020; 1734:012026.6. Soh DCK, Ng EYK, Jahmunah V, Oh SL, Tan RS, Acharya UR. Automated diagnostic tool for hypertension using convolutional neural network. Comput Biol Med. 2020; 126:103999. PMID: 32992139.7. Zhang Q, Liu Y, Liu G, Zhao G, Qu Z, Yang W. An automatic diagnostic system based on deep learning, to diagnose hyperlipidemia. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019; 12:637–645. PMID: 31118725.8. Isin A, Ozdalili S. Cardiac arrhythmia detection using deep learning. Procedia Comput Sci. 2017; 120:268–275.9. Wagner JM, Shimshak DG. Stepwise selection of variables in data envelopment analysis: procedures and managerial perspectives. Eur J Oper Res. 2007; 180:57–67.10. Pizarroso J, Alfaya D, Portela J, Muñoz A. Metric tools for sensitivity analysis with applications to neural networks. arXiv. Forthcoming. 2023.11. Nourani V, Fard MS. Sensitivity analysis of the artificial neural network outputs in simulation of the evaporation process at different climatologic regimes. Adv Eng Softw. 2012; 47:127–146.12. Cao M, Alkayem NF, Pan L, Novák D. Advanced methods in neural networks-based sensitivity analysis with their applications in civil engineering. Rosa JLG, editor. Artificial Neural Networks. Rijeka: IntechOpen;2016. p. 335–353.13. Delen D, Walker G, Kadam A. Predicting breast cancer survivability: a comparison of three data mining methods. Artif Intell Med. 2005; 34:113–127. PMID: 15894176.14. Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S. Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecol Modell. 2003; 160:249–264.15. Borzouei S, Soltanian AR. Application of an artificial neural network model for diagnosing type 2 diabetes mellitus and determining the relative importance of risk factors. Epidemiol Health. 2018; 40:e2018007. PMID: 29529860.16. Agliata A, Giordano D, Bardozzo F, Bottiglieri S, Facchiano A, Tagliaferri R. Machine learning as a support for the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24:6775. PMID: 37047748.17. Liu Q, Zhou Q, He Y, Zou J, Guo Y, Yan Y. Predicting the 2-year risk of progression from prediabetes to diabetes using machine learning among Chinese elderly adults. J Pers Med. 2022; 12:1055. PMID: 35887552.18. World Health Organization. Classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization;2019.19. Olaniyi EO, Adnan K. Onset diabetes diagnosis using artificial neural network. Int J Sci Eng Res. 2014; 5:754–759.20. Ebrahim OA, Derbew G. Application of supervised machine learning algorithms for classification and prediction of type-2 diabetes disease status in Afar regional state, Northeastern Ethiopia 2021. Sci Rep. 2023; 13:7779. PMID: 37179444.21. Niedbała G, Kurasiak-Popowska D, Piekutowska M, Wojciechowski T, Kwiatek M, Nawracała J. Application of artificial neural network sensitivity analysis to identify key determinants of harvesting date and yield of soybean (Glycine max [L.] merrill) cultivar augusta. Agriculture. 2022; 12:754.22. Jeczmionek E, Kowalski PA. Input reduction of convolutional neural networks with global sensitivity analysis as a data-centric approach. Neurocomputing. 2022; 506:196–205.23. Kowalski PA, Kusy M. Sensitivity analysis for probabilistic neural network structure reduction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2018; 29:1919–1932. PMID: 28422668.24. Franceschini S, Tancioni L, Lorenzoni M, Mattei F, Scardi M. An ecologically constrained procedure for sensitivity analysis of artificial neural networks and other empirical models. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0211445. PMID: 30699204.25. Choi SK, Park CG. The study of blood glucose level prediction model using ballistocardiogram and artificial intelligence. J Digit Converg. 2021; 19:257–269.26. Singla V, Singla S, Feizi S, Jacobs D. Low curvature activations reduce overfitting in adversarial training. In : Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision; 2021 Oct 11-17; Montreal, Canada. Scarsdale (NY): Computer Vision Foundation;2021. p. 16423–16433.27. Güldoğan E, Zeynep T, Ayça A, Çolak C. Performance evaluation of different artificial neural network models in the classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cogn Syst. 2020; 5:23–32.28. Ryu KS, Lee SW, Batbaatar E, Lee JW, Choi KS, Cha HS. A deep learning model for estimation of patients with undiagnosed diabetes. Appl Sci. 2020; 10:421.29. Pizarroso J, Portela J, Muñoz A. NeuralSens: sensitivity analysis of neural networks. J Stat Softw. 2022; 102:1–36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- On the Use of Neural Networks for the Risk Factor Analysis of NIDDM
- Intake of Fruit and Glycemic Control in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- The Current Status and the Perspectives of Nutrition Survey
- A Hybrid Bayesian Network Model for Predicting Breast Cancer Prognosis
- Analysis of Dietary Factors of Chronic Disease Using a Neural Network