Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2023 Nov;27(4):350-365. 10.14701/ahbps.23-025.
Surgical outcome of extrahepatic portal venous obstruction: Audit from a tertiary referral centre in Eastern India
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Surgical Gastroenterology, School of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Kolkata, India
- KMID: 2548501
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.23-025
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
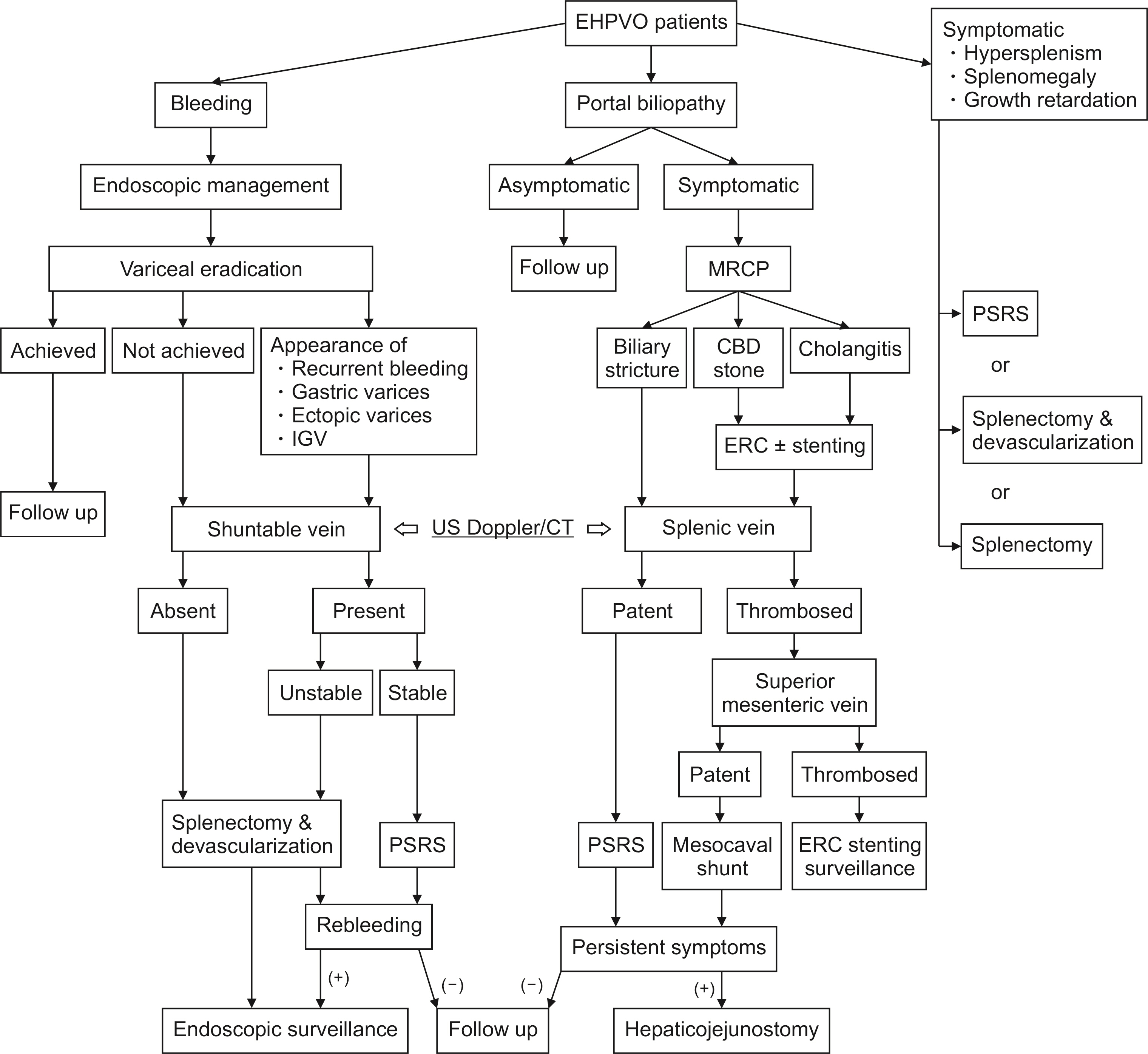
Extra hepatic portal venous obstruction (EHPVO) is the most common cause of portal hypertension in Indian children. While endoscopy is the primary modality of management, a subset of patients require surgery. This study aims to report the short- and long-term outcomes of EHPVO patients managed surgically.
Methods
All the patients with EHPVO who underwent surgery between August 2007 and December 2021 were retrospectively reviewed. Postoperative complications were classified after Clavien–Dindo. Binary logistic regression in Wald methodology was used to determine the predictive factors responsible for unfavourable outcome.
Results
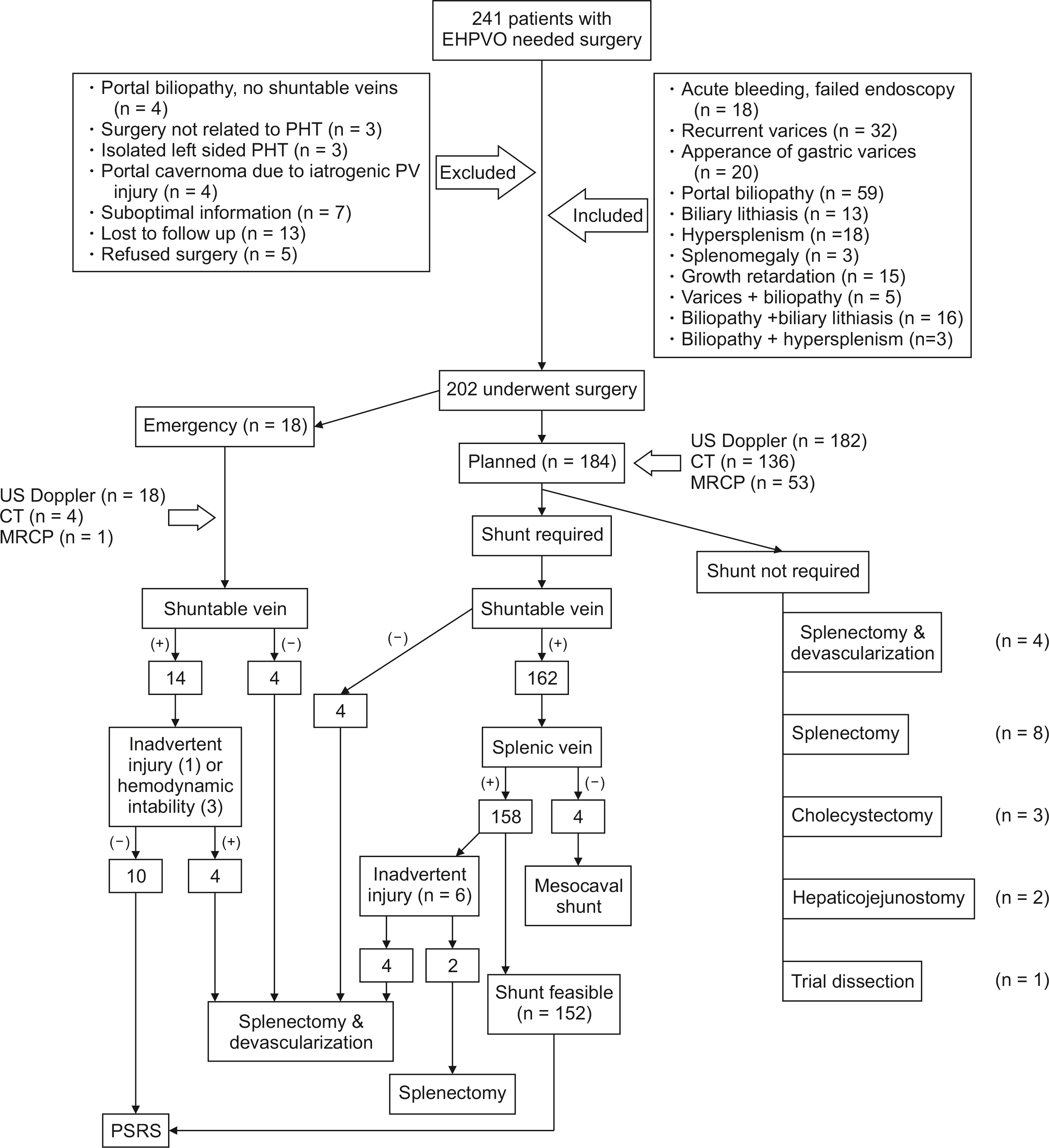
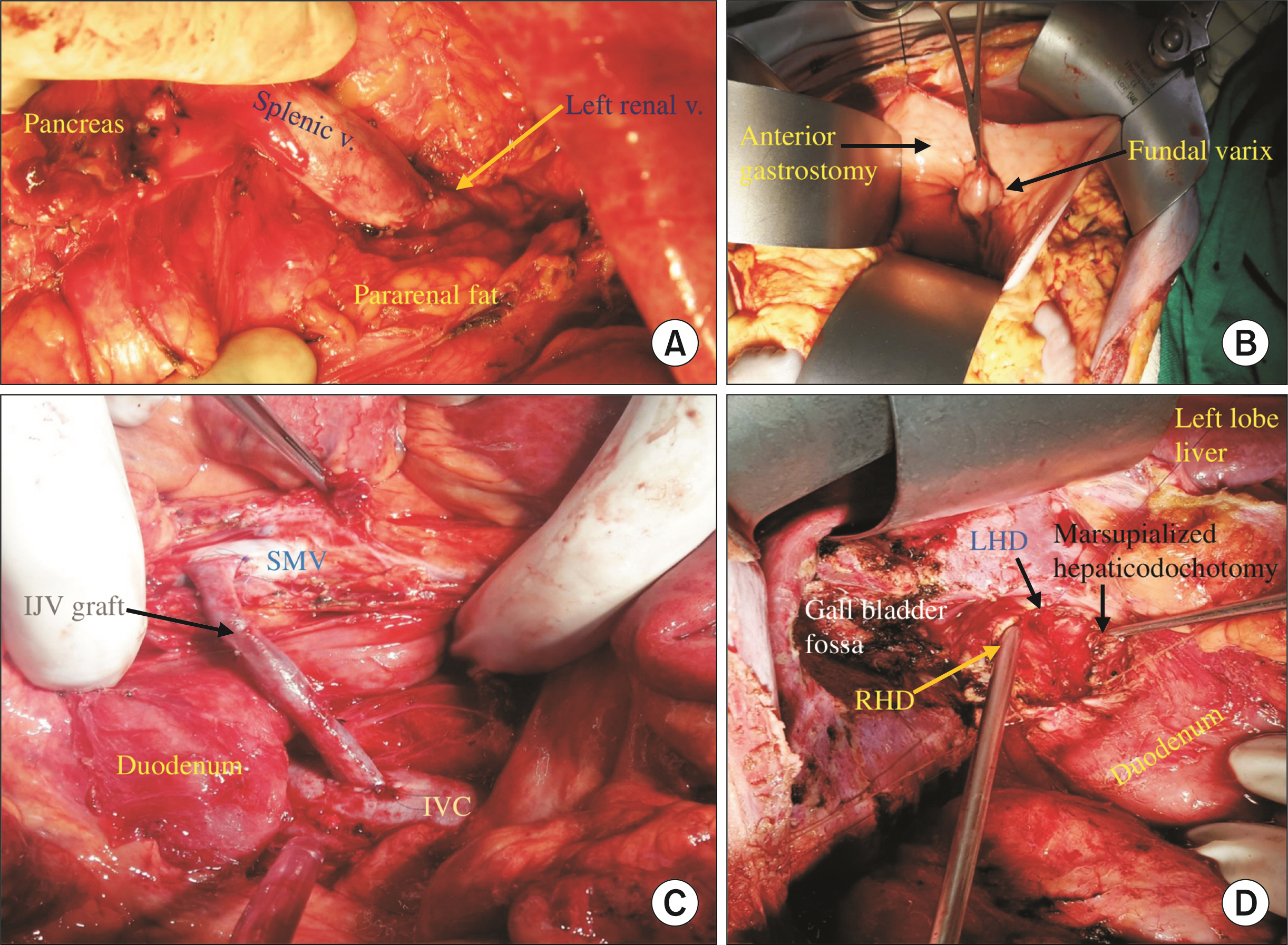
Total of 202 patients with EHPVO were operated. Mean age of patients was 20.30 ± 9.96 years, and duration of illness, 90.05 ± 75.13 months. Most common indication for surgery was portal biliopathy (n = 59, 29.2%), followed by bleeding (n = 50, 24.8%). Total of 166 patients (82.2%) had shunt procedure. Splenectomy with esophagogastric devascularization was the second most common surgery (n = 20, 9.9%). Nine major postoperative complications (Clavien–Dindo > 3) were observed in 8 patients (4.0%), including 1 (0.5%) operative death. After a median follow-up of 56 months (15−156 months), 166 patients (82.2%) had favourable outcome. In multivariate analysis, associated splenic artery aneurysm (p = 0.007), isolated gastric varices (p = 0.004), preoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiography and stenting (p = 0.015), and shunt occlusion (p < 0.001) were independent predictors of unfavourable long-term outcome.
Conclusions
Surgery in EHPVO is safe, affords excellent short- and long-term outcome in patients with symptomatic EHPVO, and may be considered for secondary prophylaxis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sahni P, Parde GK, Nundy S. 1990; Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Br J Surg. 77:1201–1202. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800771102. PMID: 2252992.
Article2. Jena SK, Mohanty M, Patra UC, Behera S. 2017; A study on demographic and clinical profile of children with extra hepatic portal venous obstruction and with special reference to thrombophilic factors. Int J Community Med Public Health. 4:640–645. DOI: 10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20170468.
Article3. Dhiman RK, Behera A, Chawla YK, Dilawari JB, Suri S. 2007; Portal hypertensive biliopathy. Gut. 56:1001–1008. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.103606. PMID: 17170017. PMCID: PMC1994341.
Article4. Premkumar M, Dhiman RK. 2021; Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy: Indian perspective. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 18:127–137. DOI: 10.1002/cld.1130. PMID: 34691399. PMCID: PMC8518339.
Article5. Mise Y, Vauthey JN, Zimmitti G, Parker NH, Conrad C, Aloia TA, et al. 2015; Ninety-day postoperative mortality is a legitimate measure of hepatopancreatobiliary surgical quality. Ann Surg. 262:1071–1078. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001048. PMID: 25590497. PMCID: PMC4633391.
Article6. Sarin SK, Sollano JD, Chawla YK, Amarapurkar D, Hamid S, Hashizume M, et al. Members of the APASL Working Party on Portal Hypertension. 2006; Consensus on extra-hepatic portal vein obstruction. Liver Int. 26:512–519. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01269.x. PMID: 16761994.
Article7. Rangari M, Gupta R, Jain M, Malhotra V, Sarin SK. 2003; Hepatic dysfunction in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Liver Int. 23:434–439. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2003.00879.x. PMID: 14986818.
Article8. Yachha SK. 2002; Portal hypertension in children: an Indian perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17 Suppl 3:S228–S231. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s3.5.x. PMID: 12472941.
Article9. Poddar U, Thapa BR, Rao KL, Singh K. 2008; Etiological spectrum of esophageal varices due to portal hypertension in Indian children: is it different from the West? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1354–1357. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05102.x. PMID: 17683492.
Article10. Garcia-Pagán JC, Hernández-Guerra M, Bosch J. 2008; Extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis. Semin Liver Dis. 28:282–292. DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1085096. PMID: 18814081.
Article11. Fagundes ED, Ferreira AR, Roquete ML, Penna FJ, Goulart EM, Figueiredo Filho PP, et al. 2008; Clinical and laboratory predictors of esophageal varices in children and adolescents with portal hypertension syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 46:178–183. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318156ff07. PMID: 18223377.
Article12. Weiss B, Shteyer E, Vivante A, Berkowitz D, Reif S, Weizman Z, et al. 2010; Etiology and long-term outcome of extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4968–4972. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4968. PMID: 20954284. PMCID: PMC2957606.
Article13. Sarin SK, Agarwal SR. 2002; Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Semin Liver Dis. 22:43–58. DOI: 10.1055/s-2002-23206. PMID: 11928078.
Article14. Kumar M, Saraswat VA. 2014; Natural history of portal cavernoma cholangiopathy. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4(Suppl 1):S62–S66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.08.003. PMID: 25755597. PMCID: PMC4244826.
Article15. Mangla V, Pal S, Sahni P. 2016; Surgery for non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: current status. Trop Gastroenterol. 37:152–155. DOI: 10.7869/tg.348.
Article16. Chaudhary N, Mehrotra S, Srivastava M, Nundy S. 2013; Management of bleeding in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Int J Hepatol. 2013:784842. DOI: 10.1155/2013/784842. PMID: 23878740. PMCID: PMC3708426.
Article17. Poddar U, Thapa BR, Singh K. 2005; Band ligation plus sclerotherapy versus sclerotherapy alone in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. J Clin Gastroenterol. 39:626–629. DOI: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000170765.36825.66. PMID: 16000932.
Article18. Poddar U, Bhatnagar S, Yachha SK. 2011; Endoscopic band ligation followed by sclerotherapy: is it superior to sclerotherapy in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:255–259. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06397.x. PMID: 21261713.
Article19. Sharma AK, Rangam HK, Choubey RP. 2000; Splenectomy and lieno-renal shunt for extra hepatic portal venous obstruction. Indian Pediatr. 37:422–425. PMID: 10781238.20. Poddar U, Thapa BR, Singh K. 2004; Frequency of gastropathy and gastric varices in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction treated with sclerotherapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:1253–1256. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03470.x. PMID: 15482531.
Article21. Itha S, Yachha SK. 2006; Endoscopic outcome beyond esophageal variceal eradication in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 42:196–200. DOI: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000189351.55666.45. PMID: 16456415.
Article22. Chaves IJ, Rigsby CK, Schoeneman SE, Kim ST, Superina RA, Ben-Ami T. 2012; Pre- and postoperative imaging and interventions for the meso-Rex bypass in children and young adults. Pediatr Radiol. 42:220–232. quiz 271–272. DOI: 10.1007/s00247-011-2283-0. PMID: 22037931.
Article23. Pal S, Mangla V, Radhakrishna P, Sahni P, Pande GK, Acharya SK, et al. 2013; Surgery as primary prophylaxis from variceal bleeding in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:1010–1014. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12123. PMID: 23301629.
Article24. Anand U, Kumar R, Priyadarshi RN, Parasar K, John AG. 2020; Proximal splenorenal shunt surgery for bleeding gastric varices in non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Cureus. 12:e10464. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10464. PMID: 33083167. PMCID: PMC7566982.
Article25. Zhang DC. 1991; [Hassab's procedure with or without lower esophageal transection in the treatment of portal hypertension. A prospective controlled study]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 29:561–563. 589–560. Chinese.26. Nundy S, Tandon BN. 1980; Emergency operations for bleeding oesophageal varices-a case for doing splenectomy and lienorenal shunts. Trop Gastraenterol. 1:27.27. Lautz TB, Keys LA, Melvin JC, Ito J, Superina RA. 2013; Advantages of the meso-Rex bypass compared with portosystemic shunts in the management of extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children. J Am Coll Surg. 216:83–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.09.013. PMID: 23177370.
Article28. Khamag O, Numanoglu A, Rode H, Millar A, Cox S. 2023; Surgical management of extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children: advantages of MesoRex shunt compared with distal splenorenal shunt. Pediatr Surg Int. 39:128. DOI: 10.1007/s00383-023-05411-3. PMID: 36795156. PMCID: PMC9935711.
Article29. Emre S, Dugan C, Frankenberg T, Hudgins LC, Gagliardi R, Artis AT, et al. 2009; Surgical portosystemic shunts and the Rex bypass in children: a single-centre experience. HPB (Oxford). 11:252–257. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00047.x. PMID: 19590656. PMCID: PMC2697896.
Article30. Prasad AS, Gupta S, Kohli V, Pande GK, Sahni P, Nundy S. 1994; Proximal splenorenal shunts for extrahepatic portal venous obstruction in children. Ann Surg. 219:193–196. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199402000-00011. PMID: 8129490. PMCID: PMC1243121.31. Orloff MJ, Orloff MS, Rambotti M. 1994; Treatment of bleeding esophagogastric varices due to extrahepatic portal hypertension: results of portal-systemic shunts during 35 years. J Pediatr Surg. 29:142–151. discussion 151–154. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3468(94)90309-3. PMID: 8176584.
Article32. Mitra SK, Rao KL, Narasimhan KL, Dilawari JB, Batra YK, Chawla Y, et al. 1993; Side-to-side lienorenal shunt without splenectomy in noncirrhotic portal hypertension in children. J Pediatr Surg. 28:398–401. discussion 401–402. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3468(93)90239-H. PMID: 8468654.33. Rao KL, Goyal A, Menon P, Thapa BR, Narasimhan KL, Chowdhary SK, et al. 2004; Extrahepatic portal hypertension in children: observations on three surgical procedures. Pediatr Surg Int. 20:679–684. DOI: 10.1007/s00383-004-1272-x. PMID: 15351894.34. Superina R, Bambini DA, Lokar J, Rigsby C, Whitington PF. 2006; Correction of extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis by the mesenteric to left portal vein bypass. Ann Surg. 243:515–521. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000205827.73706.97. PMID: 16552203. PMCID: PMC1448975.35. Thomas V, Jose T, Kumar S. 2009; Natural history of bleeding after esophageal variceal eradication in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction; a 20-year follow-up. Indian J Gastroenterol. 28:206–211. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-009-0086-0. PMID: 20425640.
Article36. Bismuth H, Franco D, Alagille D. 1980; Portal diversion for portal hypertension in children. The first ninety patients. Ann Surg. 192:18–24. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-198007000-00003. PMID: 7406558. PMCID: PMC1344799.
Article37. Ohta M, Hashizume M, Ueno K, Tanoue K, Sugimachi K, Hasuo K. 1994; Hemodynamic study of splenic artery aneurysm in portal hypertension. Hepatogastroenterology. 41:181–184. PMID: 8056411.38. Stanley JC, Fry WJ. 1974; Pathogenesis and clinical significance of splenic artery aneurysms. Surgery. 76:898–909. PMID: 4428355.39. Boijsen E, Efsing HO. 1969; Aneurysm of the splenic artery. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 8:29–41. DOI: 10.1177/028418516900800105. PMID: 5800861. PMCID: PMC3788954.
Article40. Mattar SG, Lumsden AB. 1995; The management of splenic artery aneurysms: experience with 23 cases. Am J Surg. 169:580–584. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(99)80225-6. PMID: 7771620.
Article41. McDermott VG, Shlansky-Goldberg R, Cope C. 1994; Endovascular management of splenic artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 17:179–184. DOI: 10.1007/BF00571531. PMID: 7954570.
Article42. de Perrot M, Bühler L, Deléaval J, Borisch B, Mentha G, Morel P. 1998; Management of true aneurysms of the splenic artery. Am J Surg. 175:466–468. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(98)00082-8. PMID: 9645773.
Article43. Qiu JF, Xu L, Wu ZY. 2004; Diagnosis and surgical treatment of giant splenic artery aneurysms with portal hypertension: report of 4 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 3:526–529. PMID: 15567738.44. Puliyath N, Raj N, Sanyal S, Tripathy DK, Gupta R. 2021; Giant splenic artery aneurysm with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction - a rare entity: case report with literature review. J Med Evid. 2:182–184. DOI: 10.4103/JME.JME_59_20.
Article45. Mishra PK, Saluja SS, Sharma AK, Pattnaik P. 2012; Management of splenic artery aneurysm associated with extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 11:330–333. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(12)60170-2. PMID: 22672830.
Article46. Sharma BC, Varakanahalli S, Singh JP, Srivastava S. 2017; Gastric varices in cirrhosis vs. extrahepatic portal venous obstruction and response to endoscopic N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 7:97–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2016.09.002. PMID: 28663672. PMCID: PMC5478943.
Article47. Johns TN, Evans BB. 1962; Collateral pathways in portal hypertension. Ann Surg. 155:838–845. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-196206000-00003. PMID: 14451980. PMCID: PMC1466170.
Article48. Sarin SK, Jain AK, Lamba GS, Gupta R, Chowdhary A. 2003; Isolated gastric varices: prevalence, clinical relevance and natural history. Dig Surg. 20:42–47. DOI: 10.1159/000068865. PMID: 12637804.
Article49. Sarin SK, Lahoti D, Saxena SP, Murthy NS, Makwana UK. 1992; Prevalence, classification and natural history of gastric varices: a long-term follow-up study in 568 portal hypertension patients. Hepatology. 16:1343–1349. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840160607. PMID: 1446890.
Article50. Agarwal AK, Sharma D, Singh S, Agarwal S, Girish SP. 2011; Portal biliopathy: a study of 39 surgically treated patients. HPB (Oxford). 13:33–39. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00232.x. PMID: 21159101. PMCID: PMC3019539.
Article51. Bhatia V. 2014; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in portal cavernoma cholangiopathy - results from different studies and proposal for uniform terminology. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4(Suppl 1):S37–S43. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.05.013. PMID: 25755594. PMCID: PMC4244821.52. George J, Panwar R, Saluja SS, Sahni P. Mishra PK, editor. 2016; Surgery for portal hypertension. Textbook of surgical gastroenterology. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers;1357–1366. DOI: 10.5005/jp/books/12748_125. PMID: 21424236.
Article53. Dutta HK, Baruah M. 2015; Management of extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children: experience in a tertiary care center in Northeast India. J Med Soc. 29:101–105. DOI: 10.4103/0972-4958.163200.
Article54. Mishra PK, Patil NS, Saluja S, Narang P, Solanki N, Varshney V. 2016; High patency of proximal splenorenal shunt: a myth or reality ? - a prospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 27:82–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.12.071. PMID: 26804351.
Article55. Gupta S, Pottakkat B, Kalayarasan R, Senthil G, Nitesh PNB. 2022; Use of caudal pancreatectomy as a novel adjunct procedure to proximal splenorenal shunt in patients with noncirrhotic portal hypertension: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 26:178–183. DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.21-106. PMID: 35193996. PMCID: PMC9136421.
Article56. Orloff MJ, Orloff MS, Girard B, Orloff SL. 2002; Bleeding esophagogastric varices from extrahepatic portal hypertension: 40 years' experience with portal-systemic shunt. J Am Coll Surg. 194:717–728. discussion 728–730. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(02)01170-5. PMID: 12081062.
Article57. Sharma N, Bajpai M, Kumar A, Paul S, Jana M. 2014; Portal hypertension: a critical appraisal of shunt procedures with emphasis on distal splenorenal shunt in children. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 19:80–84. DOI: 10.4103/0971-9261.129599. PMID: 24741210. PMCID: PMC3983772.
Article58. Bismuth H, Franco D, Hepp J. 1974; Portal-systemic shunt in hepatic cirrhosis: does the type of shunt decisively influence the clinical result? Ann Surg. 179:209–218. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-197402000-00019. PMID: 4544047. PMCID: PMC1355781.59. Wani AH, Shah OJ, Zargar SA. 2011; Management of variceal hemorrhage in children with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction-shunt surgery versus endoscopic sclerotherapy. Indian J Surg. 73:409–413. DOI: 10.1007/s12262-011-0345-z. PMID: 23204696. PMCID: PMC3236262.
Article60. Superina R, Shneider B, Emre S, Sarin S, de Ville de Goyet J. 2006; Surgical guidelines for the management of extra-hepatic portal vein obstruction. Pediatr Transplant. 10:908–913. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2006.00598.x. PMID: 17096756.
Article61. Warren WD, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ, Galambos JT, Bryan FC. 1988; Management of variceal bleeding in patients with noncirrhotic portal vein thrombosis. Ann Surg. 207:623–634. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-198805000-00017. PMID: 3259859. PMCID: PMC1493505.
Article62. Sharif K, McKiernan P, de Ville de Goyet J. Mesoportal bypass for extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children: close to a cure for most! J Pediatr Surg. 2010; 45:272–276. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.08.019. PMID: 20105620.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous hepatic arterioportal fistula in extrahepatic portal vein obstruction: Combined endovascular and surgical management
- Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy: Update and recommendations on diagnosis and management
- A Case of Extrahepatic Portal Vein Thrombosis Treated by Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt ( TIPS )
- Gastric salvage after venous congestion during major pancreatic resections: A series of three cases
- Standard or Variant Meso-Rex Shunts for Children with Variceal Bleeding due to Extrahepatic Portal Vein Obstruction: A Report of Two Cases