Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 Nov;26(4):298-307. 10.14701/ahbps.22-029.
Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy: Update and recommendations on diagnosis and management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
- KMID: 2536378
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.22-029
Abstract
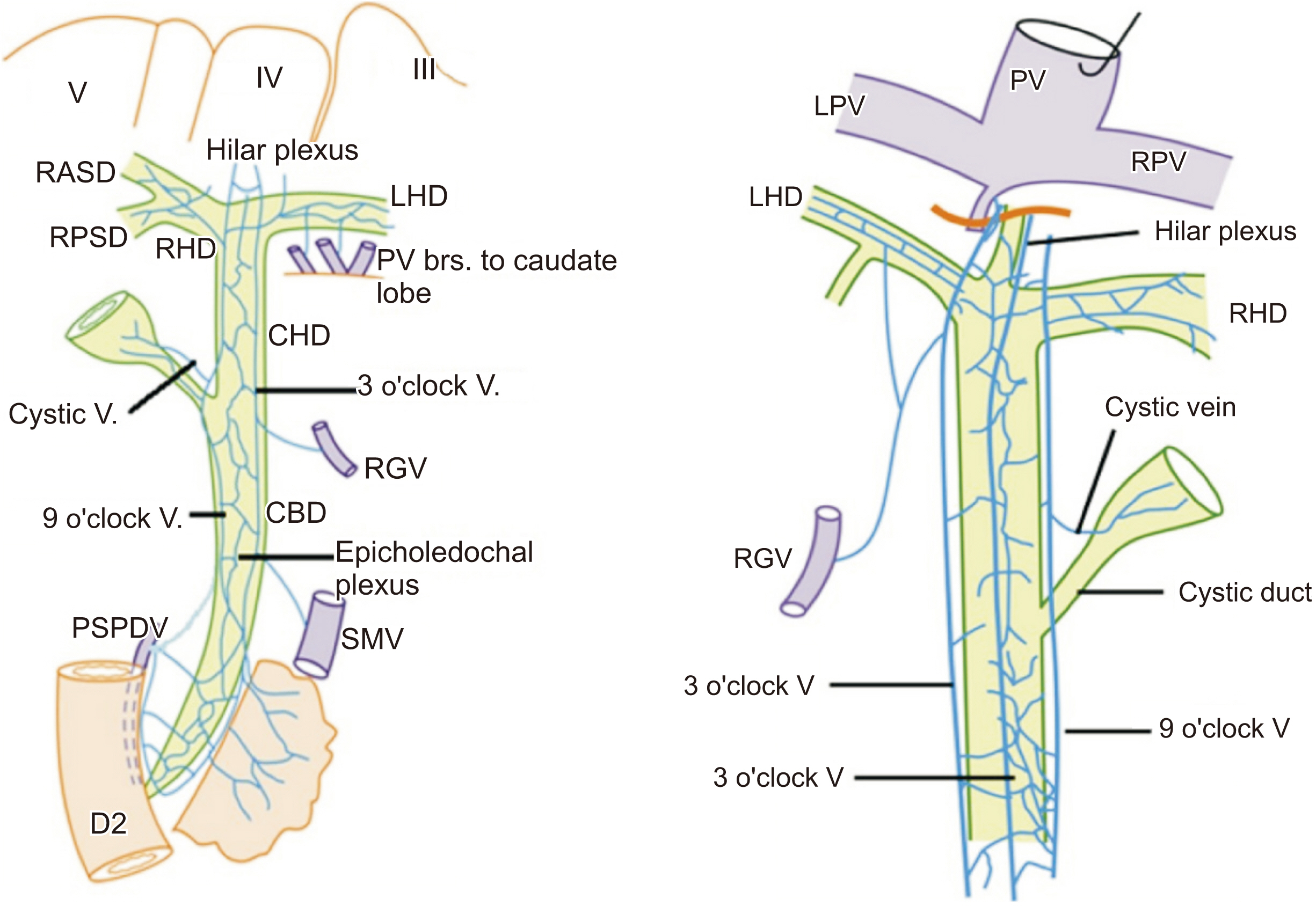
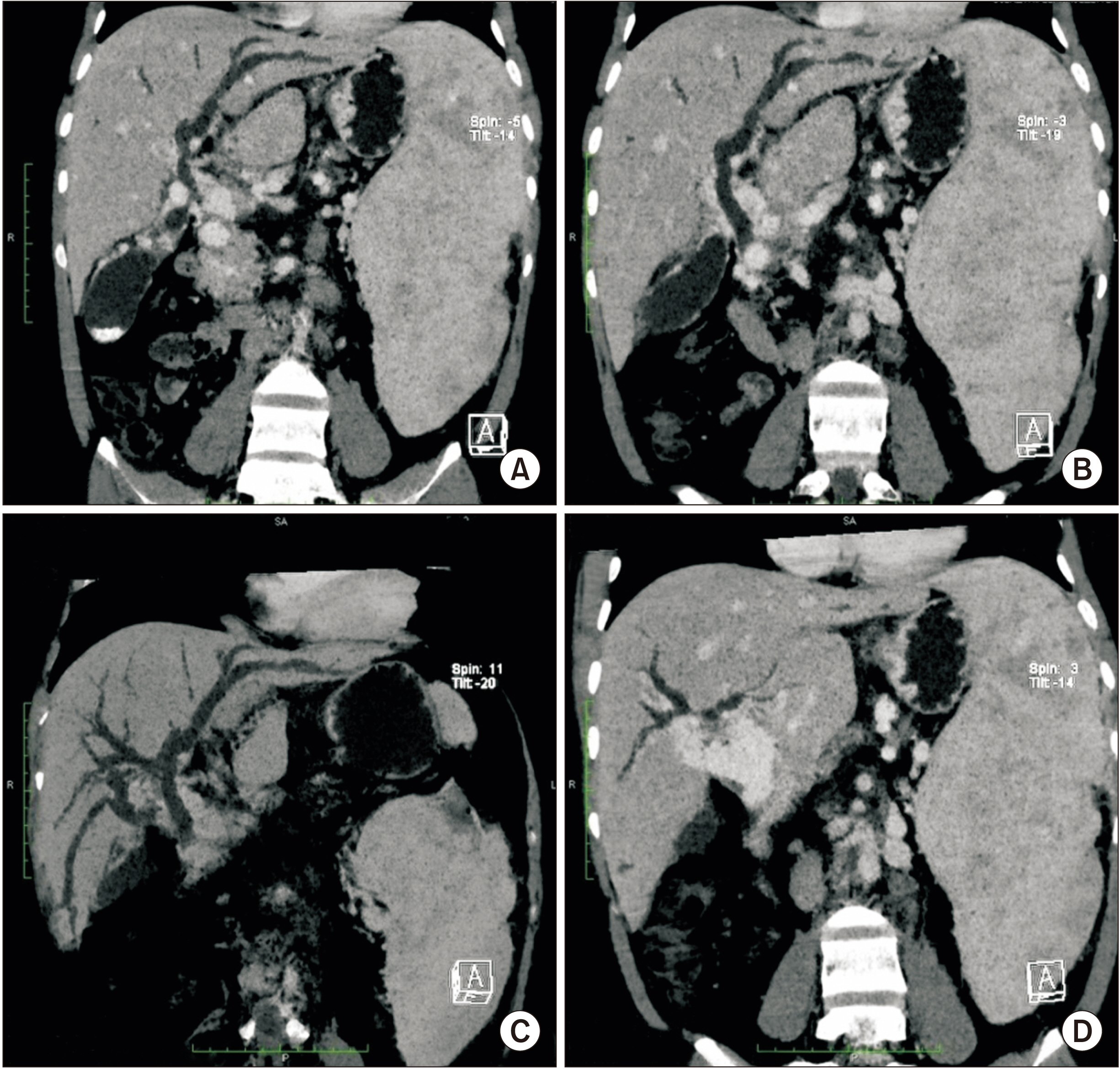
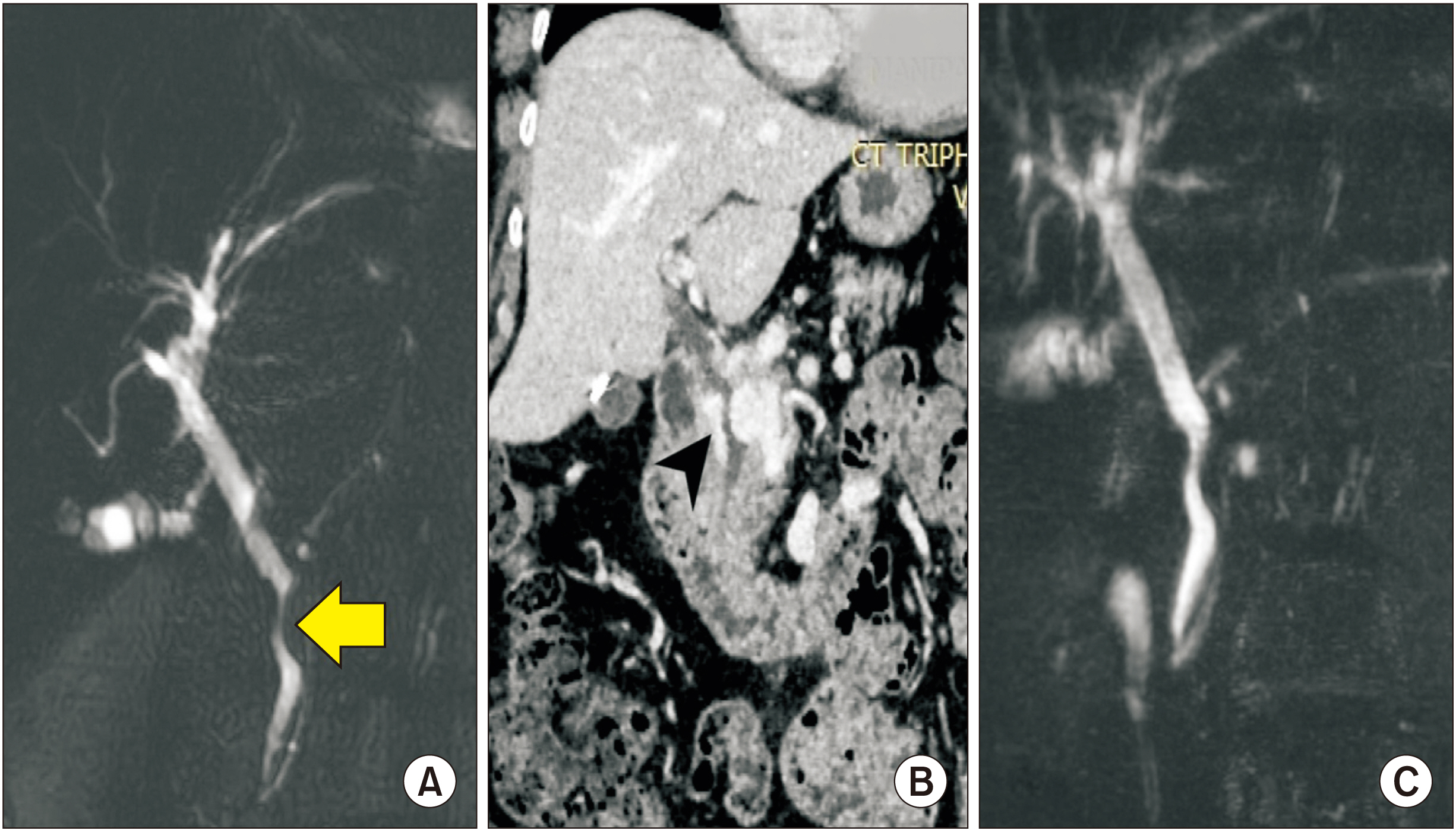
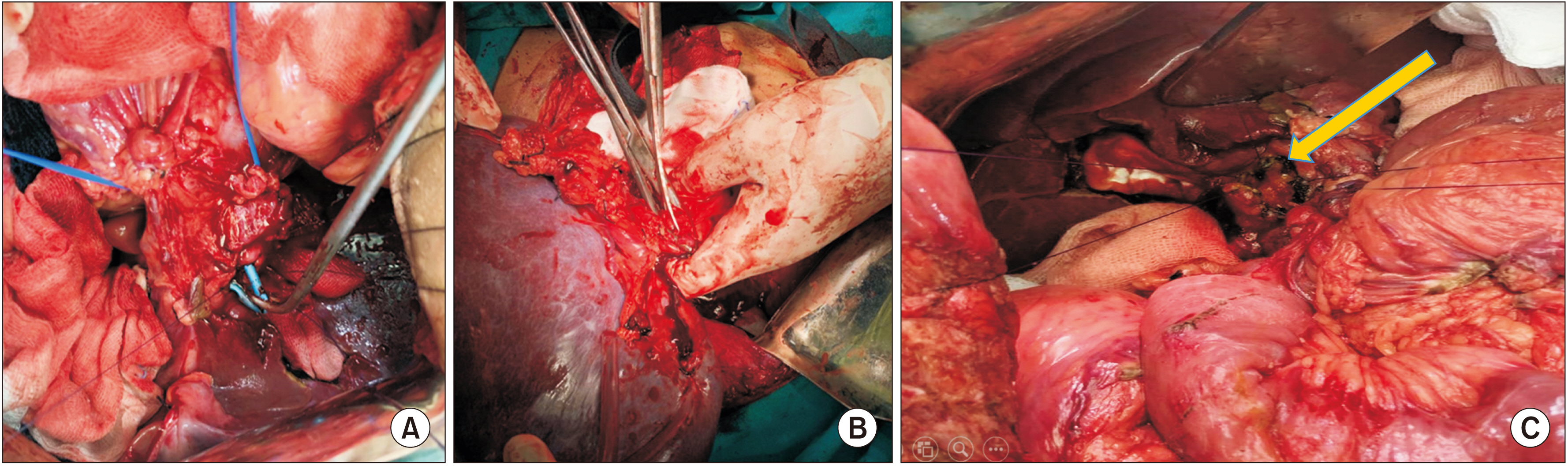
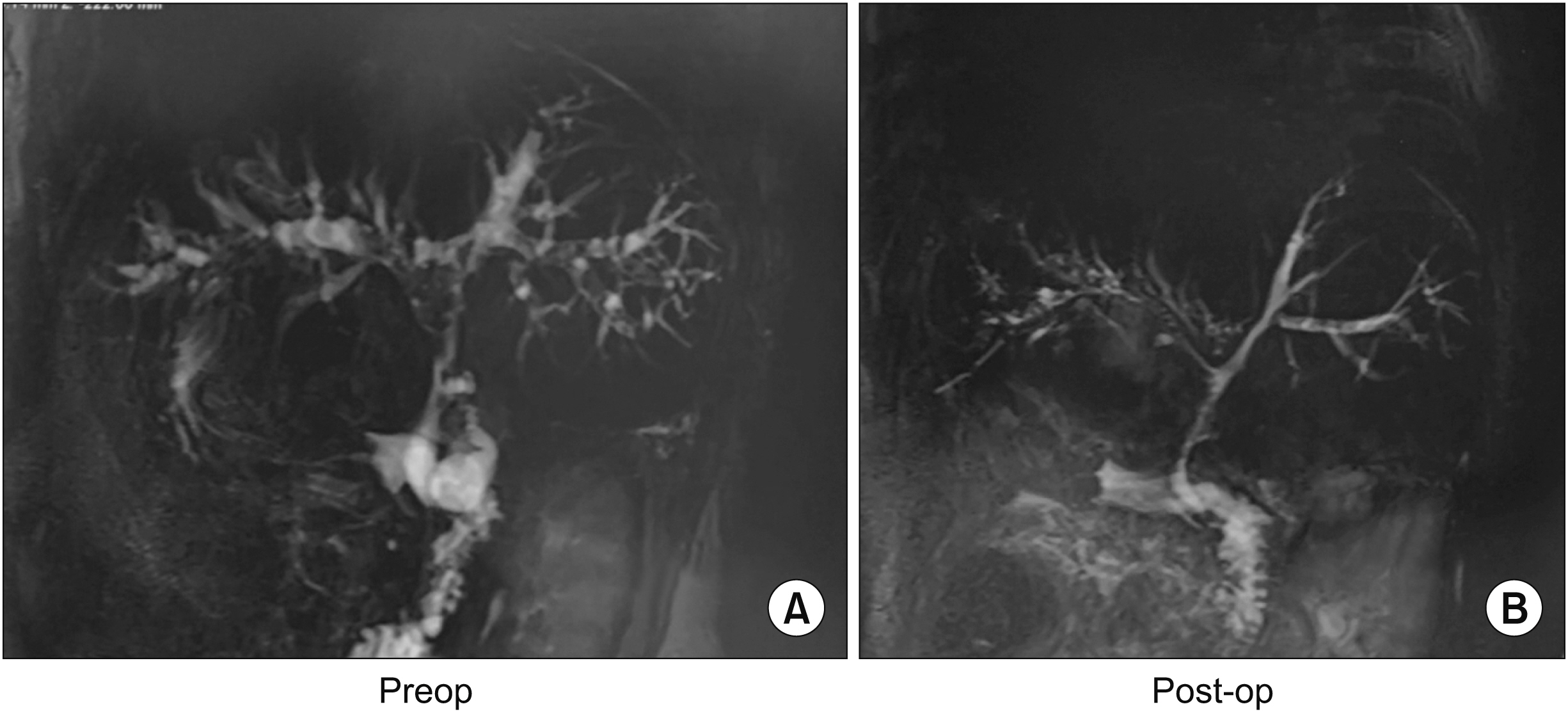
- Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy is defined as an obstruction of the biliary system due to distended veins surrounding bile ducts that mainly occur in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. The periductal venous plexuses encircling the ducts can cause morphological changes which may or may not become symptomatic. Currently, non-invasive techniques such as ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance images are being used to diagnose this disorder. Only a few patients who have symptoms of biliary obstruction require drainage which might be accomplished using endoscopic stenting, decompression of the portal venous system usually via a lienorenal shunt, a difficult direct hepaticojejunostomy, and rarely a liver transplant.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fraser J, Brown AK. 1944; A clinical syndrome associated with a rare anomaly of vena portal system. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 78:520–524.2. Malkan GH, Bhatia SJ, Bashir K, Khemani R, Abraham P, Gandhi MS, et al. 1999; Cholangiopathy associated with portal hypertension: diagnostic evaluation and clinical implications. Gastrointest Endosc. 49(3 Pt 1):344–348. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(99)70011-8. PMID: 10049418.3. Dhiman RK, Chawla Y, Vasishta RK, Kakkar N, Dilawari JB, Trehan MS, et al. 2002; Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis (idiopathic portal hypertension): experience with 151 patients and a review of the literature. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:6–16. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02596.x. PMID: 11895549.4. Chandra R, Kapoor D, Tharakan A, Chaudhary A, Sarin SK. 2001; Portal biliopathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:1086–1092. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2001.02562.x. PMID: 11686833.5. Chawla Y, Agrawal S. 2014; Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy - history, definition and nomenclature. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4(Suppl 1):S15–S17. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.04.001. PMID: 25755589. PMCID: PMC4244831.6. Dhiman RK, Saraswat VA, Valla DC, Chawla Y, Behera A, Varma V, et al. 2014; Portal cavernoma cholangiopathy: consensus statement of a working party of the Indian national association for study of the liver. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4(Suppl 1):S2–S14. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.02.003. PMID: 25755591. PMCID: PMC4274351.7. Ramesh Babu CS, Sharma M. 2014; Biliary tract anatomy and its relationship with venous drainage. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 4(Suppl 1):S18–S26. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2013.05.002. PMID: 25755590. PMCID: PMC4244820.8. Northover J, Terblanche J. 1978; Bile duct blood supply. Its importance in human liver transplantation. Transplantation. 26:67–69. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-197807010-00017. PMID: 97825.9. Furukawa H, Iwata R, Moriyama N, Kosuge T. 1999; Blood supply to the pancreatic head, bile duct, and duodenum: evaluation by computed tomography during arteriography. Arch Surg. 134:1086–1090. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.134.10.1086. PMID: 10522852.10. Saint JH. 1961; The epicholedochal venous plexus and its importance as a means of identifying the common duct during operations on the extrahepatic biliary tract. Br J Surg. 48:489–498. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.18004821104. PMID: 13745435.11. Petren T. 1932; [The veins of the extrahepatic biliary system and their pathologic-anatomic significance]. Verh Anat Ges. 41:139–143. German.12. Dhiman RK, Puri P, Chawla Y, Minz M, Bapuraj JR, Gupta S, et al. 1999; Biliary changes in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction: compression by collaterals or ischemic? Gastrointest Endosc. 50:646–652. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(99)80013-3. PMID: 10536320.13. Bayraktar Y, Balkanci F, Ozenc A, Arslan S, Koseoglu T, Ozdemir A, et al. 1995; The "pseudo-cholangiocarcinoma sign" in patients with cavernous transformation of the portal vein and its effect on the serum alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin levels. Am J Gastroenterol. 90:2015–2019.14. Condat B, Vilgrain V, Asselah T, O'Toole D, Rufat P, Zappa M, et al. 2003; Portal cavernoma-associated cholangiopathy: a clinical and MR cholangiography coupled with MR portography imaging study. Hepatology. 37:1302–1308. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50232. PMID: 12774008.15. Dhiman R, Singh P, Duseja A, Chawla Y, Behera A, Suri S. 2006; Pathogenesis of portal hypertensive biliopathy (PHB): is it compression by collaterals or ischemia? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:A506.16. Dhiman R, Singh P, Behera A, Duseja A, Chawla Y, Suri S. 2006; Diagnosis of portal hypertensive biliopathy (PHB) in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction (EHPVO): endoscopic retrograde cholangiography versus MR cholangiography. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:A507.17. Dhiman RK, Behera A, Chawla YK, Dilawari JB, Suri S. 2007; Portal hypertensive biliopathy. Gut. 56:1001–1008. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.103606. PMID: 17170017. PMCID: PMC1994341.18. Mörk H, Weber P, Schmidt H, Goerig RM, Scheurlen M. 1998; Cavernous transformation of the portal vein associated with common bile duct strictures: report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 47:79–83. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(98)70305-0. PMID: 9468430.19. Chaudhary A, Dhar P, Sarin SK, Sachdev A, Agarwal AK, Vij JC, et al. 1998; Bile duct obstruction due to portal biliopathy in extrahepatic portal hypertension: surgical management. Br J Surg. 85:326–329. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00591.x. PMID: 9529484.20. O'Donnell B, Moloney MA. 1968; Development and course of extrahepatic portal obstruction in children. Lancet. 1:789–791. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(68)92231-9. PMID: 4171132.21. Gibson JB, Johnston GW, Fulton TT, Rodgers HW. 1965; Extrahepatic portal-venous obstruction. Br J Surg. 52:129–139. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800520211. PMID: 14255983.22. Dilawari JB, Chawla YK. 1992; Pseudosclerosing cholangitis in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Gut. 33:272–276. DOI: 10.1136/gut.33.2.272. PMID: 1541425. PMCID: PMC1373944.23. Sarin SK, Bhatia V, Makwana U. 1992; Portal biliopathy in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Indian J Gastroenterol. 11(Suppl 1):A82.24. Khuroo MS, Yattoo GN, Zargar SA, Javid G, Dar MY, Khan BA, et al. 1993; Biliary abnormalities associated with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Hepatology. 17:807–813. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840170510. PMID: 8491448.25. Bayraktar Y, Balkanci F, Kayhan B, Ozenç A, Arslan S, Telatar H. 1992; Bile duct varices or "pseudo-cholangiocarcinoma sign" in portal hypertension due to cavernous transformation of the portal vein. Am J Gastroenterol. 87:1801–1806.26. Nagi B, Kochhar R, Bhasin D, Singh K. 2000; Cholangiopathy in extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Radiological appearances. Acta Radiol. 41:612–615. DOI: 10.1080/028418500127345992. PMID: 11092484.27. Sezgin O, Oğuz D, Altintaş E, Saritaş U, Sahin B. 2003; Endoscopic management of biliary obstruction caused by cavernous transformation of the portal vein. Gastrointest Endosc. 58:602–608. DOI: 10.1067/S0016-5107(03)01975-8. PMID: 14520303.28. Dhiman R, Chawla Y, Duseja A, Chhetri D, Dilawari J. 2006; Portal hypertensive biliopathy (PHB) in patients with extrahepatic portal venous obstruction (EHPVO). J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:A504.29. Llop E, de Juan C, Seijo S, García-Criado A, Abraldes JG, Bosch J, et al. 2011; Portal cholangiopathy: radiological classification and natural history. Gut. 60:853–860. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2010.230201. PMID: 21270119.30. Valla DC, Condat B, Lebrec D. 2002; Spectrum of portal vein thrombosis in the West. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17(Suppl 3):S224–S227. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s3.4.x. PMID: 12472940.31. Webb LJ, Sherlock S. 1979; The aetiology, presentation and natural history of extra-hepatic portal venous obstruction. Q J Med. 48:627–639.32. Vibert E, Azoulay D, Aloia T, Pascal G, Veilhan LA, Adam R, et al. 2007; Therapeutic strategies in symptomatic portal biliopathy. Ann Surg. 246:97–104. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318070cada. PMID: 17592297. PMCID: PMC1899217.33. Aguirre DA, Farhadi FA, Rattansingh A, Jhaveri KS. 2012; Portal biliopathy: imaging manifestations on multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging. 36:126–134. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2011.07.001. PMID: 22370133.34. Gulati G, Pawa S, Chowdhary V, Kumar N, Mittal SK. 2003; Colour Doppler flow imaging findings in portal biliopathy. Trop Gastroenterol. 24:116–119.35. Kessler A, Graif M, Konikoff F, Mercer D, Oren R, Carmiel M, et al. 2007; Vascular and biliary abnormalities mimicking cholangiocarcinoma in patients with cavernous transformation of the portal vein: role of color Doppler sonography. J Ultrasound Med. 26:1089–1095. DOI: 10.7863/jum.2007.26.8.1089. PMID: 17646372.36. Besa C, Cruz JP, Huete A, Cruz F. 2012; Portal biliopathy: a multitechnique imaging approach. Abdom Imaging. 37:83–90. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-011-9765-2. PMID: 21681494.37. Tyagi P, Puri AS, Sharma BC. 2010; Balloon sweep in portal biliopathy. Gastrointest Endosc. 71:885–886. author reply 886DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.08.014. PMID: 20363438.38. Mutignani M, Shah SK, Bruni A, Perri V, Costamagna G. 2002; Endoscopic treatment of extrahepatic bile duct strictures in patients with portal biliopathy carries a high risk of haemobilia: report of 3 cases. Dig Liver Dis. 34:587–591. DOI: 10.1016/S1590-8658(02)80093-7. PMID: 12502216.39. Kim S, Chew FS. 1988; Choledochal varices. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 150:578–580. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.150.3.578. PMID: 3257612.40. Sharma M, Ponnusamy RP. 2009; Is balloon sweeping detrimental in portal biliopathy? A report of 3 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 70:171–173. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.11.002. PMID: 19409559.41. Suhocki PV, Lungren MP, Kapoor B, Kim CY. 2015; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt complications: prevention and management. Semin Intervent Radiol. 32:123–132. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1549376. PMID: 26038620. PMCID: PMC4447874.42. Borg PC, Hollemans M, Van Buuren HR, Vleggaar FP, Groeneweg M, Hop WC, et al. 2004; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term patency and clinical results in a patient cohort observed for 3-9 years. Radiology. 231:537–545. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2312021797. PMID: 15044746.43. Khare R, Sikora SS, ikanth G Sr, Choudhuri G, Saraswat VA, Kumar A, et al. 2005; Extrahepatic portal venous obstruction and obstructive jaundice: approach to management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:56–61. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03528.x. PMID: 15610447.44. Agarwal AK, Sharma D, Singh S, Agarwal S, Girish SP. 2011; Portal biliopathy: a study of 39 surgically treated patients. HPB (Oxford). 13:33–39. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00232.x. PMID: 21159101. PMCID: PMC3019539.45. Chattopadhyay S, Govindasamy M, Singla P, Varma V, Mehta N, Kumaran V, et al. 2012; Portal biliopathy in patients with non-cirrhotic portal hypertension: does the type of surgery affect outcome? HPB (Oxford). 14:441–447. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00473.x. PMID: 22672545. PMCID: PMC3384873.46. Dhiman R, Chhetri D, Behera A, Duseja A, Chawla Y, Singh P, et al. 2006; Management of biliary obstruction in patients with portal hypertensive biliopathy (PHB). J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:A505.47. Kim HB, Pomposelli JJ, Lillehei CW, Jenkins RL, Jonas MM, Krawczuk LE, et al. 2005; Mesogonadal shunts for extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis and variceal hemorrhage. Liver Transpl. 11:1389–1394. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20487. PMID: 16237690.48. Drews JA, Castagna J. 1976; Inferior mesorenal shunt as a second procedure for portal decompression. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 142:84–86.49. Warren WD, Salam A, Smith RB 3rd. 1974; The meso-spleno-renal shunt procedures: a comprehensive approach to portasystemic decompression. Ann Surg. 179:791–798. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-197405000-00035. PMID: 4545091. PMCID: PMC1356077.50. Camerlo A, Fara R, Barbier L, Grégoire E, Le Treut YP. 2010; Which treatment to choose for portal biliopathy with extensive portal thrombosis? Dig Surg. 27:380–383. DOI: 10.1159/000314610. PMID: 20938181.51. Poddar U, Borkar V. 2011; Management of extra hepatic portal venous obstruction (EHPVO): current strategies. Trop Gastroenterol. 32:94–102.52. Filipponi F, Urbani L, Catalano G, Iaria G, Biancofiore G, Cioni R, et al. 2004; Portal biliopathy treated by liver transplantation. Transplantation. 77:326–327. DOI: 10.1097/01.TP.0000101795.29250.10. PMID: 14743009.53. Perakath B, Sitaram V, Mathew G, Khanduri P. 2003; Post-cholecystectomy benign biliary stricture with portal hypertension: is a portosystemic shunt before hepaticojejunostomy necessary? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 85:317–320. DOI: 10.1308/003588403769162422. PMID: 14594535. PMCID: PMC1964328.54. Agarwal AK, Gupta V, Singh S, Agarwal S, Sakhuja P. 2008; Management of patients of postcholecystectomy benign biliary stricture complicated by portal hypertension. Am J Surg. 195:421–426. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.03.013. PMID: 18304509.55. Cellich PP, Crawford M, Kaffes AJ, Sandroussi C. 2015; Portal biliopathy: multidisciplinary management and outcomes of treatment. ANZ J Surg. 85:561–566. DOI: 10.1111/ans.12436. PMID: 24237891.56. Hajdu CH, Murakami T, Diflo T, Taouli B, Laser J, Teperman L, et al. 2007; Intrahepatic portal cavernoma as an indication for liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 13:1312–1316. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21243. PMID: 17763385.57. D'Souza MA, Desai D, Joshi A, Abraham P, Shah SR. 2009; Bile duct stricture due to caused by portal biliopathy: treatment with one-stage portal-systemic shunt and biliary bypass. Indian J Gastroenterol. 28:35–37. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-009-0010-7. PMID: 19529903.58. Gupta V, Chandra A. 2013; Portal biliopathy: is splenectomy with devascularization really effective? HPB (Oxford). 15:559. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00606.x. PMID: 23750497. PMCID: PMC3692027.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Feasibility of laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic gallstone disease with portal cavernoma: Can prior portal vein decompression be avoided?
- Why is my phlegm green? A rare case of bronchobiliary fistula
- The First Case Report of Ketamine-Induced Cholangiopathy in Korea
- Treatment Update on Portal Hypertension and Complications
- Pseudocholangiocarcinoma Sign: Management of Portal Cavernoma Biliopathy with Fully-Covered Self-Expandable Metal Stent