J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2023 Nov;40(Suppl):S56-S64. 10.12701/jyms.2023.00689.
Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism after spinal cord disease at a rehabilitation unit: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2548343
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00689
Abstract
- Background
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) are major complications of spinal cord disease. However, studies of their incidence in Korean patients are limited. Thus, this study investigated the incidence and risk factors of DVT and PTE in Korean patients with spinal cord disease.
Methods
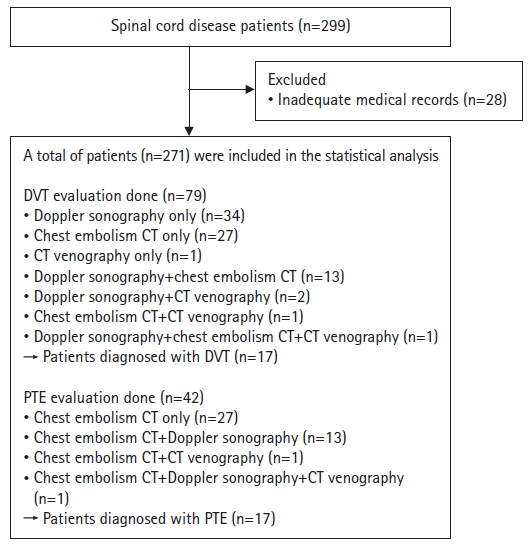
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 271 patients with spinal cord disease who were admitted to a rehabilitation unit within 3 months of disease onset at a tertiary hospital. The presence of DVT and PTE was mainly determined using Doppler ultrasonography and chest embolism computed tomography. Risk factor analysis included variables such as sex, age, obesity, completeness of motor paralysis, neurological level of injury, cause of injury, lower extremity fracture, active cancer, and functional ambulation category (FAC) score.
Results
The incidences of DVT and PTE in the patients with spinal cord disease were both 6.3%. Risk factor analysis revealed that age of ≥65 years (p=0.031) and FAC score of ≤1 (p=0.023) were significantly associated with DVT development. Traumatic cause of injury (p=0.028) and DVT (p<0.001) were significant risk factors of PTE.
Conclusion
Patients with spinal cord disease developed DVT and PTE within 3 months of disease onset with incidence rates of 6.3% and 6.3%, respectively. Age of ≥65 years and an FAC of score ≤1 were risk factors for DVT. Traumatic cause of injury and DVT were risk factors for PTE. However, given the inconsistent results of previous studies, the risk factors for DVT and PTE remain inconclusive. Therefore, early screening for DVT and PTE should be performed in patients with acute-to-subacute spinal cord disease regardless of the presence or absence of these risk factors.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. de Girolami U, Bale TA. Spinal cord. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017; 145:405–25.
Article2. Choi SH, Sung CH, Heo DR, Jeong SY, Kang CN. Incidence of acute spinal cord injury and associated complications of methylprednisolone therapy: a national population-based study in South Korea. Spinal Cord. 2020; 58:232–7.
Article3. Godat LN, Kobayashi L, Chang DC, Coimbra R. Can we ever stop worrying about venous thromboembolism after trauma? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015; 78:475–81.
Article4. Agarwal NK, Mathur N. Deep vein thrombosis in acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2009; 47:769–72.
Article5. Alabed S, Belci M, Van Middendorp JJ, Al Halabi A, Meagher TM. Thromboembolism in the sub-acute phase of spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the literature. Asian Spine J. 2016; 10:972–81.
Article6. Dhall SS, Hadley M, Aarabi B, Gelb DE, Hurlbert RJ, Rozzelle CJ, et al. Deep venous thrombosis and thromboembolism in patients with cervical spinal cord injuries. Neurosurgery. 2013; 72(Suppl 2):244–54.
Article7. Paciaroni M, Ageno W, Agnelli G. Prevention of venous thromboembolism after acute spinal cord injury with low-dose heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin. Thromb Haemost. 2008; 99:978–80.
Article8. Merli GJ, Herbison GJ, Ditunno JF, Weitz HH, Henzes JH, Park CH, et al. Deep vein thrombosis: prophylaxis in acute spinal cord injured patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988; 69:661–4.9. Golan DE, Tashjian AH, Armstrong EJ. Principles of pharmacology: the pathophysiologic basis of drug therapy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2011.10. Furlan JC, Fehlings MG. Role of screening tests for deep venous thrombosis in asymptomatic adults with acute spinal cord injury: an evidence-based analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:1908–16.11. Anderson FA, Spencer FA. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003; 107(23 Suppl 1):I9–16.
Article12. Merli GJ, Crabbe S, Paluzzi RG, Fritz D. Etiology, incidence, and prevention of deep vein thrombosis in acute spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993; 74:1199–205.
Article13. Miranda AR, Hassouna HI. Mechanisms of thrombosis in spinal cord injury. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000; 14:401–16.
Article14. Yao JS. Deep vein thrombosis in spinal cord-injured patients. Evaluation and assessment. Chest. 1992; 102(6 Suppl):645S–648S.
Article15. Jackson AB, Groomes TE. Incidence of respiratory complications following spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994; 75:270–5.
Article16. DeVivo MJ, Kartus PL, Stover SL, Rutt RD, Fine PR. Cause of death for patients with spinal cord injuries. Arch Intern Med. 1989; 149:1761–6.
Article17. Green D, Hartwig D, Chen D, Soltysik RC, Yarnold PR. Spinal cord injury risk assessment for thromboembolism (SPIRATE Study). Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 82:950–6.
Article18. Waring WP, Karunas RS. Acute spinal cord injuries and the incidence of clinically occurring thromboembolic disease. Paraplegia. 1991; 29:8–16.
Article19. Hon B, Botticello A, Kirshblum S. Duplex ultrasound surveillance for deep vein thrombosis after acute traumatic spinal cord injury at rehabilitation admission. J Spinal Cord Med. 2020; 43:298–305.
Article20. Piran S, Schulman S. Incidence and risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with acute spinal cord injury: a retrospective study. Thromb Res. 2016; 147:97–101.
Article21. Mackiewicz-Milewska M, Cisowska-Adamiak M, Pyskir J, Świątkiewicz I. Usefulness of D-dimer and ultrasonography screening for detecting deep vein thrombosis in patients with spinal cord injury undergoing rehabilitation. J Clin Med. 2021; 10:689.
Article22. Sugimoto Y, Ito Y, Tomioka M, Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Nakago K, et al. Deep venous thrombosis in patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury in a Japanese population: assessment with Doppler ultrasonography. J Orthop Sci. 2009; 14:374–6.
Article23. Schulte LM, O'Brien JR, Bean MC, Pierce TP, Yu WD, Meals C. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism after spine surgery: incidence and patient risk factors. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2013; 42:267–70.24. Teasell RW, Hsieh JT, Aubut JA, Eng JJ, Krassioukov A, Tu L, et al. Venous thromboembolism after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 90:232–45.
Article25. Aito S, Pieri A, D'Andrea M, Marcelli F, Cominelli E. Primary prevention of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in acute spinal cord injured patients. Spinal Cord. 2002; 40:300–3.
Article26. Matsumoto S, Suda K, Iimoto S, Yasui K, Komatsu M, Ushiku C, et al. Prospective study of deep vein thrombosis in patients with spinal cord injury not receiving anticoagulant therapy. Spinal Cord. 2015; 53:306–9.
Article27. Do JG, Kim du H, Sung DH. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after spinal cord injury in Korean patients at acute rehabilitation unit. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1382–7.
Article28. Chung SB, Lee SH, Kim ES, Eoh W. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after spinal cord injury: a prospective study in 37 consecutive patients with traumatic or nontraumatic spinal cord injury treated by mechanical prophylaxis. J Trauma. 2011; 71:867–71.
Article29. Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, Forgie M, Kearon C, Dreyer J, et al. Evaluation of D-dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:1227–35.
Article30. Masuda M, Ueta T, Shiba K, Iwamoto Y. D-dimer screening for deep venous thrombosis in traumatic cervical spinal injuries. Spine J. 2015; 15:2338–44.
Article31. Roussi J, Bentolila S, Boudaoud L, Casadevall N, Vallée C, Carlier R, et al. Contribution of D-Dimer determination in the exclusion of deep venous thrombosis in spinal cord injury patients. Spinal Cord. 1999; 37:548–52.
Article32. Goldhaber SZ, Bounameaux H. Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet. 2012; 379:1835–46.
Article33. Chung WS, Lin CL, Chang SN, Chung HA, Sung FC, Kao CH. Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism in patients with spinal cord injury: a nationwide cohort prospective study. Thromb Res. 2014; 133:579–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep Venous Thrombosis and Heterotopic Ossification in the Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury
- Incidence of Deep Vein Thrombosis after Spinal Cord Injury in Korean Patients at Acute Rehabilitation Unit
- Thromboembolism in the Sub-Acute Phase of Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- Incidence of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Spinal Cord Injury
- A Case of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Cellulitis of the Lower Leg