J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2023 Nov;40(Suppl):S47-S55. 10.12701/jyms.2023.00605.
Association between total body muscle percentage and prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults findings from an 18-year follow-up: a prospective cohort study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2548342
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00605
Abstract
- Background
This study aimed to elucidate the association between total lean muscle mass and the incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the adult Korean population.
Methods
Utilizing data derived from the 18-year prospective cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study, NAFLD was diagnosed via the hepatic steatosis index with an established cutoff value of 36. Lean muscle mass was assessed via bioelectrical impedance analysis and subsequently divided into tertiles. A generalized mixed model with a logit link was employed for repeated measures data analysis, accounting for potential confounders.
Results
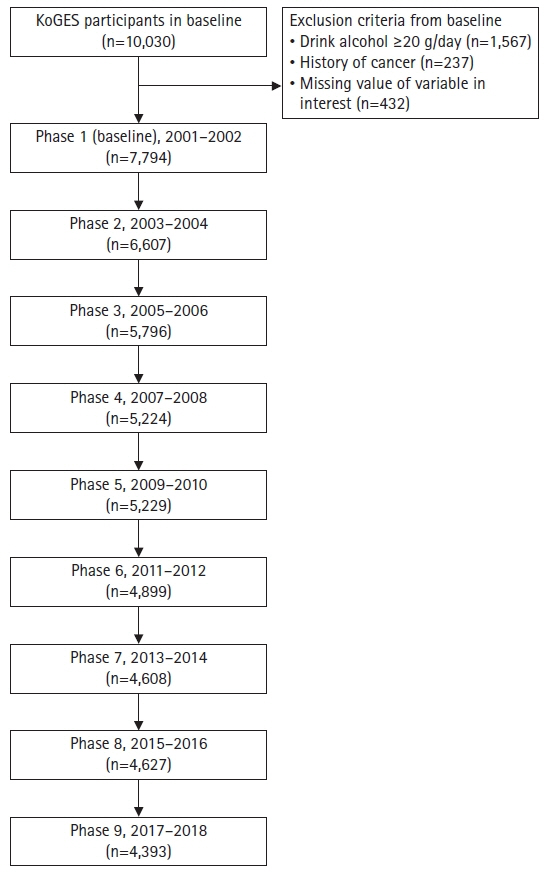
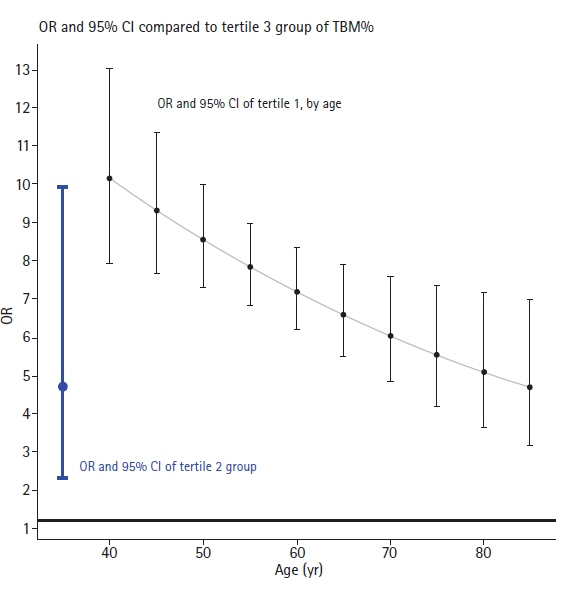
Analysis encompassed 7,794 participants yielding 49,177 measurements. The findings revealed a markedly increased incidence of NAFLD in the lower tertiles of muscle mass, specifically, tertile 1 (odds ratio [OR], 20.65; 95% confidence interval [CI], 9.66–44.11) and tertile 2 (OR, 4.57; 95% CI, 2.11–9.91), in comparison to tertile 3. Age-dependent decreases in the OR were observed within the tertile 1 group, with ORs of 10.12 at age of 40 years and 4.96 at age of 80 years. Moreover, each 1%-point increment in total muscle mass corresponded with an estimated OR of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82–0.93) for NAFLD resolution.
Conclusions
The study demonstrates a significant association between total muscle mass and NAFLD prevalence among Korean adults. Given the potential endocrine role of muscle mass in NAFLD pathogenesis, interventions aimed at enhancing muscle mass might serve as an effective public health strategy for mitigating NAFLD prevalence.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kang SH, Lee HW, Yoo JJ, Cho Y, Kim SU, Lee TH, et al. KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021; 27:363–401.
Article2. Bril F, Sninsky JJ, Baca AM, Superko HR, Portillo Sanchez P, Biernacki D, et al. Hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance, but not steatohepatitis, promote atherogenic dyslipidemia in NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 101:644–52.
Article3. Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G. Meta-analysis: natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann Med. 2011; 43:617–49.
Article4. Lonardo A, Nascimbeni F, Mantovani A, Targher G. Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: cause or consequence? J Hepatol. 2018; 68:335–52.
Article5. Kistner TM, Pedersen BK, Lieberman DE. Interleukin 6 as an energy allocator in muscle tissue. Nat Metab. 2022; 4:170–9.
Article6. Pratesi A, Tarantini F, Di Bari M. Skeletal muscle: an endocrine organ. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2013; 10:11–4.
Article7. Nara H, Watanabe R. Anti-inflammatory effect of muscle-derived interleukin-6 and its involvement in lipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22:9889.
Article8. Cai C, Song X, Chen Y, Chen X, Yu C. Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 2020; 14:115–26.
Article9. Kim Y, Han BG; KoGES group. Cohort profile: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) consortium. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:e20.
Article10. Bugianesi E, Bellentani S, Bedogni G, Tiribelli C; Fatty Liver Italian Network. Clinical update on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis. Ann Hepatol. 2008; 7:157–60.
Article11. Lee YH, Bang H, Park YM, Bae JC, Lee BW, Kang ES, et al. Non-laboratory-based self-assessment screening score for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: development, validation and comparison with other scores. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e107584.
Article12. Tennant PW, Murray EJ, Arnold KF, Berrie L, Fox MP, Gadd SC, et al. Use of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to identify confounders in applied health research: review and recommendations. Int J Epidemiol. 2021; 50:620–32.
Article13. Kim G, Kim JH. Impact of skeletal muscle mass on metabolic health. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:1–6.
Article14. Zhang H, Lin S, Gao T, Zhong F, Cai J, Sun Y, et al. Association between sarcopenia and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and older non-obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2018; 10:364.
Article15. Zuo X, Li X, Tang K, Zhao R, Wu M, Wang Y, et al. Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023; 14:1183–98.
Article16. Chung SM, Moon JS, Chang MC. Prevalence of sarcopenia and its association with diabetes: a meta-analysis of community-dwelling Asian population. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:681232.
Article17. Beaudart C, Zaaria M, Pasleau F, Reginster JY, Bruyère O. Health outcomes of sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0169548.
Article18. Bhanji RA, Narayanan P, Allen AM, Malhi H, Watt KD. Sarcopenia in hiding: the risk and consequence of underestimating muscle dysfunction in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2017; 66:2055–65.
Article19. Wenz T, Rossi SG, Rotundo RL, Spiegelman BM, Moraes CT. Increased muscle PGC-1alpha expression protects from sarcopenia and metabolic disease during aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:20405–10.20. Zhang HJ, Zhang XF, Ma ZM, Pan LL, Chen Z, Han HW, et al. Irisin is inversely associated with intrahepatic triglyceride contents in obese adults. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:557–62.
Article21. Miller AM, Wang H, Bertola A, Park O, Horiguchi N, Ki SH, et al. Inflammation-associated interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation ameliorates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Hepatology. 2011; 54:846–56.
Article22. Zhang J, Xu Y, Lu X, Zhao H. Letter to the editor: NAFLD and sarcopenia: association or causation? Hepatology. 2022; 76:E119–20.
Article23. Chen L, Fan Z, Lv G. Associations of muscle mass and grip strength with severe NAFLD: a prospective study of 333,295 UK Biobank participants. J Hepatol. 2022; 77:1453–4.
Article24. Zhai Y, Xiao Q. The common mechanisms of sarcopenia and NAFLD. Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:6297651.
Article25. Kim G, Lee SE, Lee YB, Jun JE, Ahn J, Bae JC, et al. Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 7-year longitudinal study. Hepatology. 2018; 68:1755–68.
Article26. Lee MJ, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Kim GA, Park SW, Choe J, et al. Age-related decrease in skeletal muscle mass is an independent risk factor for incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 10-year retrospective cohort study. Gut Liver. 2019; 13:67–76.
Article27. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Study Group; Lonardo A, Bellentani S, Argo CK, Ballestri S, Byrne CD, et al. Epidemiological modifiers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: focus on high-risk groups. Dig Liver Dis. 2015; 47:997–1006.
Article28. Guo Z, Li M, Han B, Qi X. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with thyroid function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2018; 50:1153–62.
Article29. Mantovani A, Dalbeni A. NAFLD, MAFLD and DAFLD. Dig Liver Dis. 2020; 52:1519–20.
Article30. Weng G, Dunn W. Effect of alcohol consumption on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 4:70.
Article31. Antonio J, Kenyon M, Ellerbroek A, Carson C, Burgess V, Tyler-Palmer D, et al. Comparison of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) versus a multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance (InBody 770) device for body composition assessment after a 4-week hypoenergetic diet. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2019; 4:23.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- As sociation of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Metabolic Syndrome over 65 Years Elderly
- Association of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetic, Normal Weight Adults
- Association between Muscle Mass Deficits and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Adults with Body Mass Index Less than 23 kg/m2
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Focusing on the Korean Genome Epidemiology Study (KoGES)