J Pathol Transl Med.
2023 Nov;57(6):332-336. 10.4132/jptm.2023.10.30.
Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma: a case report and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
- 4Department of Pathology, Gyeonsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2547931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.30
Abstract
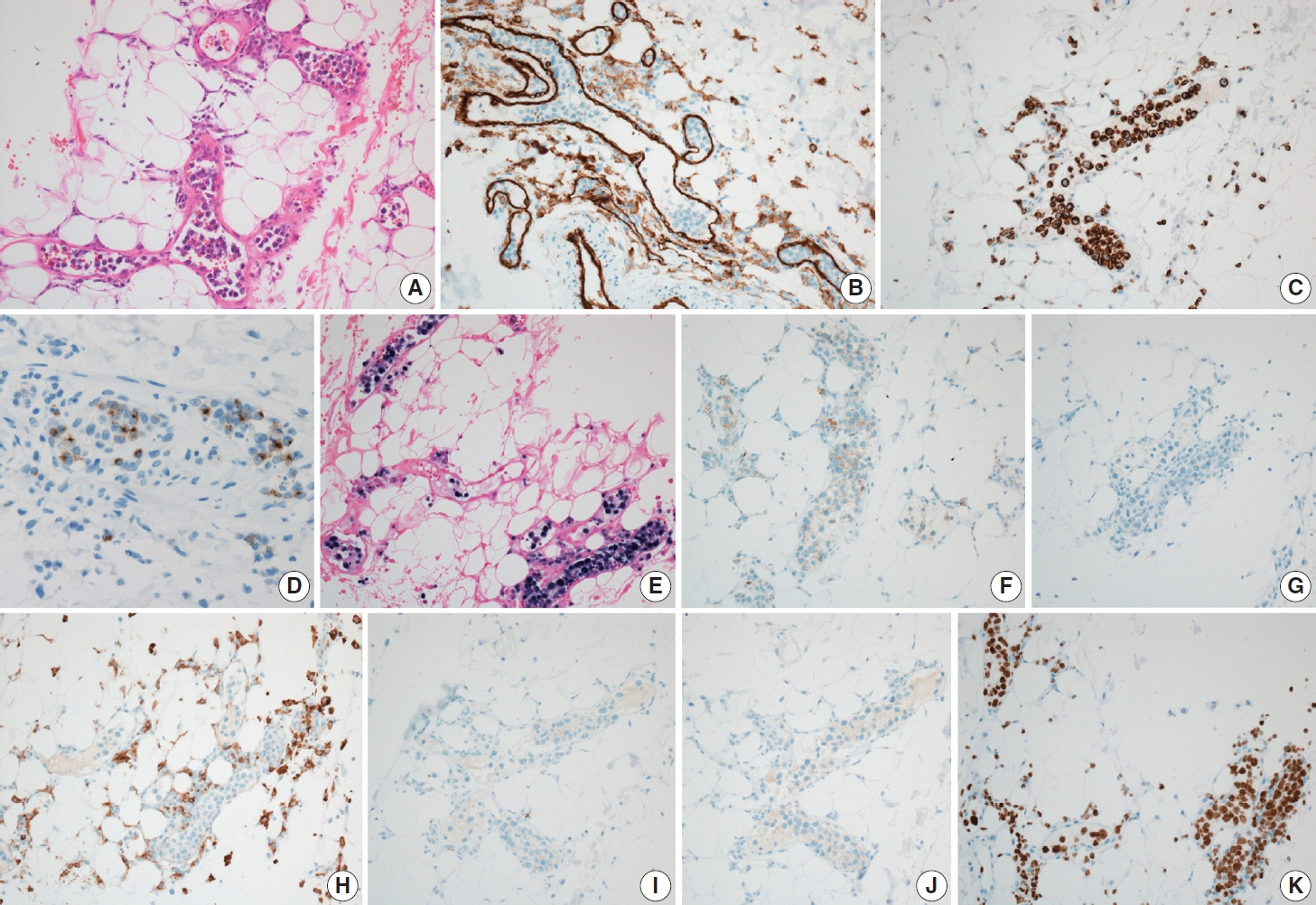
- Intravascular lymphoma is characterized by an exclusively intravascular distribution of tumor cells. Intravascular natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (IVNKTL) is extremely rare, highly aggressive, commonly Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive, and predominantly affects the skin and central nervous system. Here we report a case of IVNKTL diagnosed in a 67-year-old female, presenting with persistent intermittent fever and skin rashes throughout the body. Incisional biopsy of an erythematous lesion on the chest exhibited aggregation of medium to large-sized atypical lymphoid cells confined to the lumen of small vessels that were positive for CD3, granzyme B, and CD56 on immunohistochemistry and EBV-encoded RNA in situ hybridization. EBV DNA was also detected in serum after diagnosis. With a review of 26 cases of IVNKTL to date, we suggest that active biopsy based on EBV DNA detection may facilitate early diagnosis of IVNKTL.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research in Cancer;2017. p. 317–406.2. Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: lymphoid neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022; 36:1720–48.3. Zanelli M, Parente P, Sanguedolce F, et al. Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma: what we know about this diagnostically challenging, aggressive disease. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14:5458.
Article4. Santucci M, Pimpinelli N, Massi D, et al. Cytotoxic/natural killer cell cutaneous lymphomas. Report of EORTC Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force Workshop. Cancer. 2003; 97:610–27.5. Wu H, Said JW, Ames ED, et al. First reported cases of intravascular large cell lymphoma of the NK cell type: clinical, histologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular features. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 123:603–11.
Article6. Kuo TT, Chen MJ, Kuo MC. Cutaneous intravascular NK-cell lymphoma: report of a rare variant associated with Epstein-Barr virus. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:1197–201.
Article7. Song DE, Lee MW, Ryu MH, Kang DW, Kim SJ, Huh J. Intravascular large cell lymphoma of the natural killer cell type. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1279–82.
Article8. Nakamichi N, Fukuhara S, Aozasa K, Morii E. NK-cell intravascular lymphomatosis: a mini-review. Eur J Haematol. 2008; 81:1–7.9. Cerroni L, Massone C, Kutzner H, Mentzel T, Umbert P, Kerl H. Intravascular large T-cell or NK-cell lymphoma: a rare variant of intravascular large cell lymphoma with frequent cytotoxic phenotype and association with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:891–8.10. Gleason BC, Brinster NK, Granter SR, Pinkus GS, Lindeman NI, Miller DM. Intravascular cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58:290–4.
Article11. Liao JB, Hsieh PP, Hwang YC, Lin SL, Wu CS. Cutaneous intravascular natural killer-cell lymphoma: a rare case and review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011; 91:472–3.
Article12. Yanning X, Chen H, Si H, Liu Y, Min Z. Cutaneous intravascular NK-cell lymphoma. Eur J Dermatol. 2013; 23:252–3.
Article13. Gebauer N, Nissen EJ, Driesch P, Feller AC, Merz H. Intravascular natural killer cell lymphoma mimicking mycosis fungoides: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014; 36:e100–4.14. Jang YH, Lee SJ, Choi YH, et al. Intravascular cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma in a young immunocompetent woman. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:496–500.
Article15. Liu Y, Zhang W, An J, Li H, Liu S. Cutaneous intravascular natural killer-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014; 142:243–7.16. Wang L, Chen S, Ma H, et al. Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma: a report of five cases with cutaneous manifestation from China. J Cutan Pathol. 2015; 42:610–7.
Article17. Bi Y, Huo Z, Liang Z, et al. Intravascular NK-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:84.
Article18. Alhumidi A. Cutaneous intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma mimic panniculitis clinically, case report and literature brief review. Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:107.
Article19. Okonkwo L, Jaffe ES. Intravascular large cell lymphoma of NK/Tcell type, EBV positive. Blood. 2017; 130:837.
Article20. Sharma TL, Yeaney GA, Soltanzadeh P, Li Y, Cotta CV. Intravascular T-cell lymphoma: a rare, poorly characterized entity with cytotoxic phenotype. Neuropathology. 2017; 37:365–70.
Article21. Alegria-Landa V, Manzarbeitia F, Salvatierra Calderon MG, Requena L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM. Cutaneous intravascular natural killer/T cell lymphoma with peculiar immunophenotype. Histopathology. 2017; 71:994–1002.
Article22. Zanelli M, Mengoli MC, Del Sordo R, et al. Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma, Epstein-Barr virus positive with multiorgan involvement: a clinical dilemma. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:1115.
Article23. Meissner J, Schmitt M, Andrulis M, et al. Cure of intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022; 57:1451–4.
Article24. Patel PD, Alghareeb R, Hussain A, Maheshwari MV, Khalid N. The association of Epstein-Barr virus with cancer. Cureus. 2022; 14:e26314.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Extranodall NK/T-cell Lymphoma, Nasal type
- A Case of Primary Nasal CD56+ NK/T cell Lymphoma with Cutaneous Involvement
- A Case of Extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma at the Base of Tongue
- Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type that Occurred in Patients with Atrophic Rhinitis
- A Case of Natural Killer T-cell Lymphoma of the Tongue