Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2023 Oct;11(4):246-253. 10.14791/btrt.2023.0032.
Treatment Outcome of the Brain Metastases in Peri-Rolandic Area: Comparison Between Surgery and Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2547413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2023.0032
Abstract
- Background
Brain metastases of peri-Rolandic area is crucial as it directly impacts the quality of life for cancer patients. Surgery or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is considered for peri-Rolandic brain metastases as for other brain metastases. However, the benefit of each treatment modality on functional outcome has not been clearly defined for this tumor. The purpose of this study is to compare the functional course of each treatment and to suggest an effective treatment for patients’ quality of life.
Methods
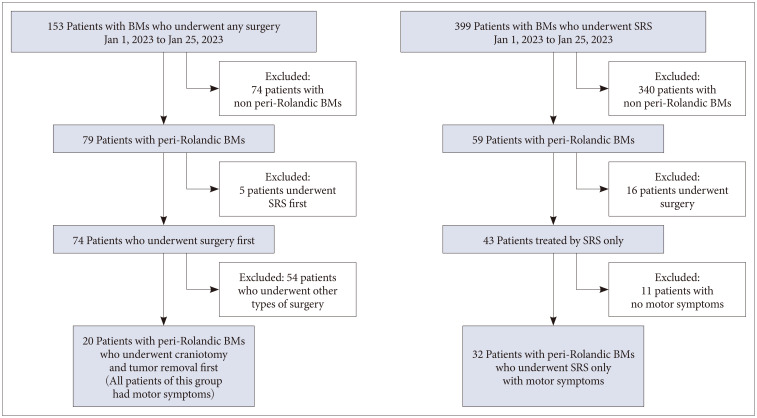
Fifty-two patients who had undergone SRS or surgery for brain metastasis confirmed by enhanced MRI were enrolled retrospectively. Overall survival (OS), progression free survival (PFS), and functional outcomes were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, univariate, multivariate analysis, and Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results
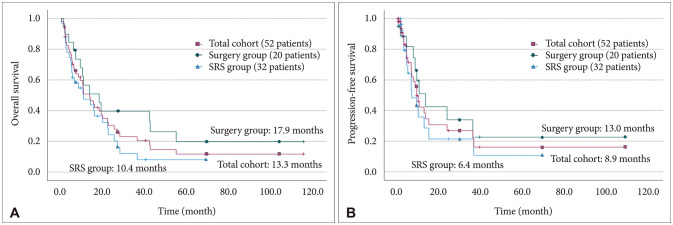
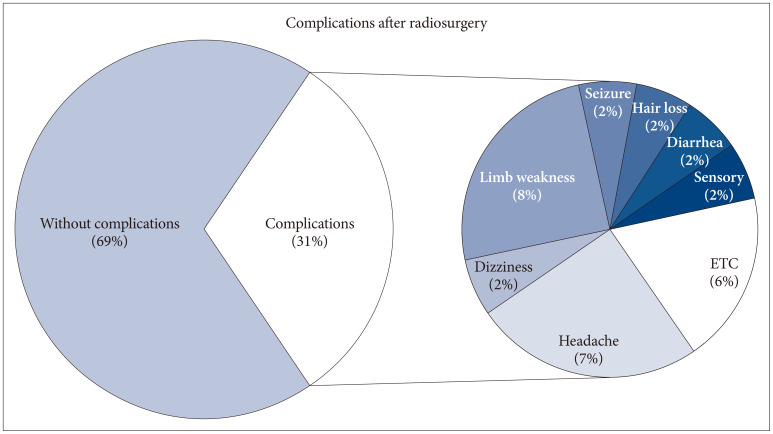
Median OS and PFS were 13.3 months and 8.9 months in our study population. Treatment modalities were not significant factors for OS and PFS. Extracranial systemic cancer progression was significant factor for both parameters (p=0.030 for OS and p=0.040 for PFS). Median symptom improvement (improvement of at least 1 grade after surgery compared to preoperative state) time was significantly shorter in surgery group than in the SRS group (10.5 days vs. 37.5 days, p=0.034).
Conclusion
Surgery for brain metastases can contribute to a positive quality of life for the remain-ing duration of the patient’s life.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sacks P, Rahman M. Epidemiology of brain metastases. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2020; 31:481–488. PMID: 32921345.
Article2. Kim T, Song C, Han JH, Kim IA, Kim YJ, Kim SH, et al. Epidemiology of intracranial metastases in Korea: a national cohort investigation. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:164–174. PMID: 28324921.
Article3. Cagney DN, Martin AM, Catalano PJ, Redig AJ, Lin NU, Lee EQ, et al. Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: a population-based study. Neuro Oncol. 2017; 19:1511–1521. PMID: 28444227.
Article4. Magill ST, Han SJ, Li J, Berger MS. Resection of primary motor cortex tumors: feasibility and surgical outcomes. J Neurosurg. 2018; 129:961–972. PMID: 29219753.
Article5. Hempen C, Weiss E, Hess CF. Dexamethasone treatment in patients with brain metastases and primary brain tumors: do the benefits outweigh the side-effects? Support Care Cancer. 2002; 10:322–328. PMID: 12029432.
Article6. Soffietti R, Cornu P, Delattre JY, Grant R, Graus F, Grisold W, et al. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:674–681. PMID: 16834697.
Article7. Ryken TC, McDermott M, Robinson PD, Ammirati M, Andrews DW, Asher AL, et al. The role of steroids in the management of brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol. 2010; 96:103–114. PMID: 19957014.
Article8. Redmond KJ, De Salles AAF, Fariselli L, Levivier M, Ma L, Paddick I, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for postoperative metastatic surgical cavities: a critical review and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society (ISRS) practice guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021; 111:68–80. PMID: 33891979.
Article9. Fuentes R, Osorio D, Expósito Hernandez J, Simancas-Racines D, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Bonfill Cosp X. Surgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy for people with single or solitary brain metastasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018; 8:CD012086. PMID: 30125049.
Article10. González L, Castro S, Villa E, Zomosa G. Surgical resection versus stereotactic radiosurgery on local recurrence and survival for patients with a single brain metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg. 2021; 35:703–713. PMID: 34431733.
Article11. Naidich TP, Blum JT, Firestone MI. The parasagittal line: an anatomic landmark for axial imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:885–895. PMID: 11337334.12. Wagner M, Jurcoane A, Hattingen E. The U sign: tenth landmark to the central region on brain surface reformatted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:323–326. PMID: 22821920.
Article13. Schiff D, Messersmith H, Brastianos PK, Brown PD, Burri S, Dunn IF, et al. Radiation therapy for brain metastases: ASCO guideline endorsement of ASTRO guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2022; 40:2271–2276. PMID: 35561283.
Article14. Yaeger KA, Nair MN. Surgery for brain metastases. Surg Neurol Int. 2013; 4(Suppl 4):S203–S208. PMID: 23717791.
Article15. Raffa G, Picht T, Scibilia A, Rösler J, Rein J, Conti A, et al. Surgical treatment of meningiomas located in the rolandic area: the role of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for preoperative planning, surgical strategy, and prediction of arachnoidal cleavage and motor outcome. J Neurosurg. 2019; 133:107–118.
Article16. Roos DE, Smith JG, Stephens SW. Radiosurgery versus surgery, both with adjuvant whole brain radiotherapy, for solitary brain metastases: a randomised controlled trial. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011; 23:646–651. PMID: 21592754.
Article17. Krist DT, Naik A, Thompson CM, Kwok SS, Janbahan M, Olivero WC, et al. Management of brain metastasis. Surgical resection versus stereotactic radiotherapy: a meta-analysis. Neurooncol Adv. 2022; 4:vdac033. PMID: 35386568.
Article18. Sahgal A, Ruschin M, Ma L, Verbakel W, Larson D, Brown PD. Stereotactic radiosurgery alone for multiple brain metastases? A review of clinical and technical issues. Neuro Oncol. 2017; 19(suppl 2):ii2–ii15. PMID: 28380635.
Article19. Vadhan JD, Speth RC. The role of the brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). Pharmacol Ther. 2021; 218:107684. PMID: 32956721.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumor
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery after Stereotactic Aspiration for Large Cystic Brain Metastases
- Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Using the Novalis Tx® System
- Introduction to Radiosurgery