Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2023 Oct;25(2):93-102. 10.14253/acn.2023.25.2.93.
Are there network differences between the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres of pain in patients with episodic migraine without aura?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2547401
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2023.25.2.93
Abstract
- Background
We aimed to identif y any differences in the structural covariance network based on structural volume and those in the functional network based on cerebral blood flow between the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres of pain in patients with episodic migraine without aura.
Methods
We prospectively enrolled 27 patients with migraine without aura, all of whom had unilateral migraine pain. We defined the ipsilateral hemisphere as the side of migraine pain. We measured structural volumes on three-dimensional T1-weighted images and cerebral blood flow using arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging. We then analyzed the structural covariance network based on structural volume and the functional network based on cerebral blood flow using graph theory.
Results
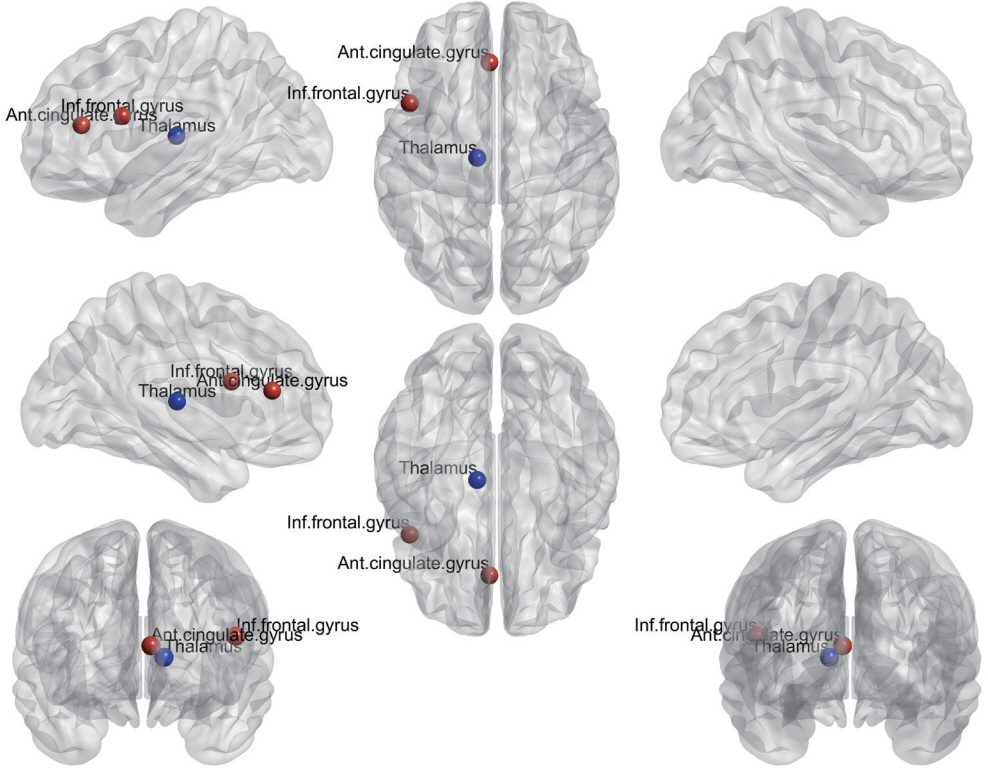
There were no significant differences in structural volume or cerebral blood flow between the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. However, there were significant differences between the hemispheres in the structural covariance network and the functional network. In the structural covariance network, the betweenness centrality of the thalamus was lower in the ipsilateral hemisphere than in the contralateral hemisphere. In the functional network, the betweenness centrality of the anterior cingulate and paracingulate gyrus was lower in the ipsilateral hemisphere than in the contralateral hemisphere, while that of the opercular part of the inferior frontal gyrus was higher in the former hemisphere.
Conclusions
The present findings indicate that there are significant differences in the structural covariance network and the functional network between the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres of pain in patients with episodic migraine without aura.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stewart WF, Wood C, Reed ML, Roy J, Lipton RB. Cumulative lifetime migraine incidence in women and men. Cephalalgia. 2008; 28:1170–1178.
Article2. Leone M, D’Amico D, Frediani F, Torri W, Sjaastad O, Bussone G. Clinical considerations on side-locked unilaterality in long-lasting primary headaches. Headache. 1993; 33:381–384.
Article3. Puledda F, Messina R, Goadsby PJ. An update on migraine: current understanding and future directions. J Neurol. 2017; 264:2031–2039.
Article4. Schwedt TJ, Chiang CC, Chong CD, Dodick DW. Functional MRI of migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2015; 14:81–91.
Article5. Liu J, Zhao L, Li G, Xiong S, Nan J, Li J, et al. Hierarchical alteration of brain structural and functional networks in female migraine sufferers. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e51250.
Article6. de Tommaso M, Trotta G, Vecchio E, Ricci K, Siugzdaite R, Stramaglia S. Brain networking analysis in migraine with and without aura. J Headache Pain. 2017; 18:98.
Article7. Ren J, Xiang J, Chen Y, Li F, Wu T, Shi J. Abnormal functional connectivity under somatosensory stimulation in migraine: a multi-frequency magnetoencephalography study. J Headache Pain. 2019; 20:3.
Article8. Jia Z, Yu S. Grey matter alterations in migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 2017; 14:130–140.
Article9. Chong CD, Aguilar M, Schwedt TJ. Altered hypothalamic region covariance in migraine and cluster headache: a structural MRI study. Headache. 2020; 60:553–563.
Article10. Chen JJ, Jann K, Wang DJ. Characterizing resting-state brain function using arterial spin labeling. Brain Connect. 2015; 5:527–542.
Article11. Detre JA, Rao H, Wang DJ, Chen YF, Wang Z. Applications of arterial spin labeled MRI in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:1026–1037.
Article12. Pollock JM, Deibler AR, Burdette JH, Kraft RA, Tan H, Evans AB, et al. Migraine associated cerebral hyperperfusion with arterial spin-labeled MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1494–1497.
Article13. Fox MD, Raichle ME. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007; 8:700–711.
Article14. Dai W, Varma G, Scheidegger R, Alsop DC. Quantifying fluctuations of resting state networks using arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016; 36:463–473.
Article15. Lee DA, Lee HJ, Kim HC, Park KM. Network differences based on arterial spin labeling related to anti-seizure medication response in focal epilepsy. Neuroradiology. 2022; 64:313–321.
Article16. Boscolo Galazzo I, Storti SF, Barnes A, De Blasi B, De Vita E, Koepp M, et al. Arterial spin labeling reveals disrupted brain networks and functional connectivity in drug-resistant temporal epilepsy. Front Neuroinform. 2019; 12:101.
Article17. Headache classification committee of the international headache society (IHS) the international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018;38:1-211.18. Wang Z, Aguirre GK, Rao H, Wang J, Fernández-Seara MA, Childress AR, et al. Empirical optimization of ASL data analysis using an ASL data processing toolbox: ASLtbx. Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 26:261–269.
Article19. Rolls ET, Joliot M, Tzourio-Mazoyer N. Implementation of a new parcellation of the orbitofrontal cortex in the automated anatomical labeling atlas. Neuroimage. 2015; 122:1–5.
Article20. Mijalkov M, Kakaei E, Pereira JB, Westman E, Volpe G. BRAPH: a graph theory software for the analysis of brain connectivity. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178798.
Article21. Farahani FV, Karwowski W, Lighthall NR. Application of graph theory for identifying connectivity patterns in human brain networks: a systematic review. Front Neurosci. 2019; 13:585.
Article22. May A. Morphing voxels: the hype around structural imaging of headache patients. Brain. 2009; 132:1419–1425.
Article23. Kivimäki I, Lebichot B, Saramäki J, Saerens M. Two betweenness centrality measures based on randomized shortest paths. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:19668.
Article24. Younis S, Hougaard A, Noseda R, Ashina M. Current understanding of thalamic structure and function in migraine. Cephalalgia. 2019; 39:1675–1682.
Article25. Tu Y, Fu Z, Zeng F, Maleki N, Lan L, Li Z, et al. Abnormal thalamocortical network dynamics in migraine. Neurology. 2019; 92:e2706–e2716.
Article26. Coppola G, Di Renzo A, Tinelli E, Lepre C, Di Lorenzo C, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Thalamo-cortical network activity between migraine attacks: insights from MRI-based microstructural and functional resting-state network correlation analysis. J Headache Pain. 2016; 17:100.
Article27. Shin KJ, Lee HJ, Park KM. Alterations of individual thalamic nuclei volumes in patients with migraine. J Headache Pain. 2019; 20:112.
Article28. Russo A, Tessitore A, Esposito F, Marcuccio L, Giordano A, Conforti R, et al. Pain processing in patients with migraine: an event-related fMRI study during trigeminal nociceptive stimulation. J Neurol. 2012; 259:1903–1912.
Article29. Schwedt TJ, Chong CD, Chiang CC, Baxter L, Schlaggar BL, Dodick DW. Enhanced pain-induced activity of pain-processing regions in a case-control study of episodic migraine. Cephalalgia. 2014; 34:947–958.
Article30. Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL. The brain’s default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1124:1–38.31. Tessitore A, Russo A, Giordano A, Conte F, Corbo D, De Stefano M, et al. Disrupted default mode network connectivity in migraine without aura. J Headache Pain. 2013; 14:89.
Article32. Baliki MN, Geha PY, Apkarian AV, Chialvo DR. Beyond feeling: chronic pain hurts the brain, disrupting the default-mode network dynamics. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:1398–1403.
Article33. Xue T, Yuan K, Cheng P, Zhao L, Zhao L, Yu D, et al. Alterations of regional spontaneous neuronal activity and corresponding brain circuit changes during resting state in migraine without aura. NMR Biomed. 2013; 26:1051–1058.
Article34. Apkarian AV, Sosa Y, Sonty S, Levy RM, Harden RN, Parrish TB, et al. Chronic back pain is associated with decreased prefrontal and thalamic gray matter density. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:10410–10415.
Article35. Szabó E, Galambos A, Kocsel N, Édes AE, Pap D, Zsombók T, et al. Association between migraine frequency and neural response to emotional faces: an fMRI study. Neuroimage Clin. 2019; 22:101790.
Article36. Varol U, Úbeda-D’Ocasar E, Cigarán-Méndez M, Arias-Buría JL, Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C, Gallego-Sendarrubias GM, et al. Understanding the psychophysiological and sensitization mechanisms behind fibromyalgia syndrome: a network analysis approach. Pain Med. 2023; 24:275–284.
Article37. Zhang YP, Hong GH, Zhang CY. Brain network changes in lumbar disc herniation induced chronic nerve roots compression syndromes. Neural Plast. 2022; 2022:7912410.
Article38. Zhang JP, Shen J, Xiang YT, Xing XX, Kang BX, Zhao C, et al. Modulation of brain network topological properties in knee osteoarthritis by electroacupuncture in rats. J Pain Res. 2023; 16:1595–1605.
Article39. Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C, Herrero-Montes M, Cancela-Cilleruelo I, Rodríguez-Jiménez J, Parás-Bravo P, Varol U, et al. Understanding sensitization, cognitive and neuropathic associated mechanisms behind post-COVID pain: a network analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12:1538.
Article40. Sui J, Huster R, Yu Q, Segall JM, Calhoun VD. Function-structure associations of the brain: evidence from multimodal connectivity and covariance studies. Neuroimage. 2014; 102 Pt 1:11–23.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics of Migraine with Aura in Korean: a Clinic Based Study
- A study on the therapeutic effects of Topiramate according to the types of migraine
- Migrainous Vertigo
- A Case of Successful Treatment During Migraine Aura Using Isometheptene Compound
- Clinical and Genetic Features of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine