Korean J Pain.
2023 Oct;36(4):465-472. 10.3344/kjp.23186.
New insight into the mandibular nerve at the foramen ovale level for percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Jiujiang University Affiliated Hospital, Jiujiang, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea
- 4Jesaeng-Euise Clinical Anatomy Center, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 5Sarcopenia Total Solution Center, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- KMID: 2546709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.23186
Abstract
- Background
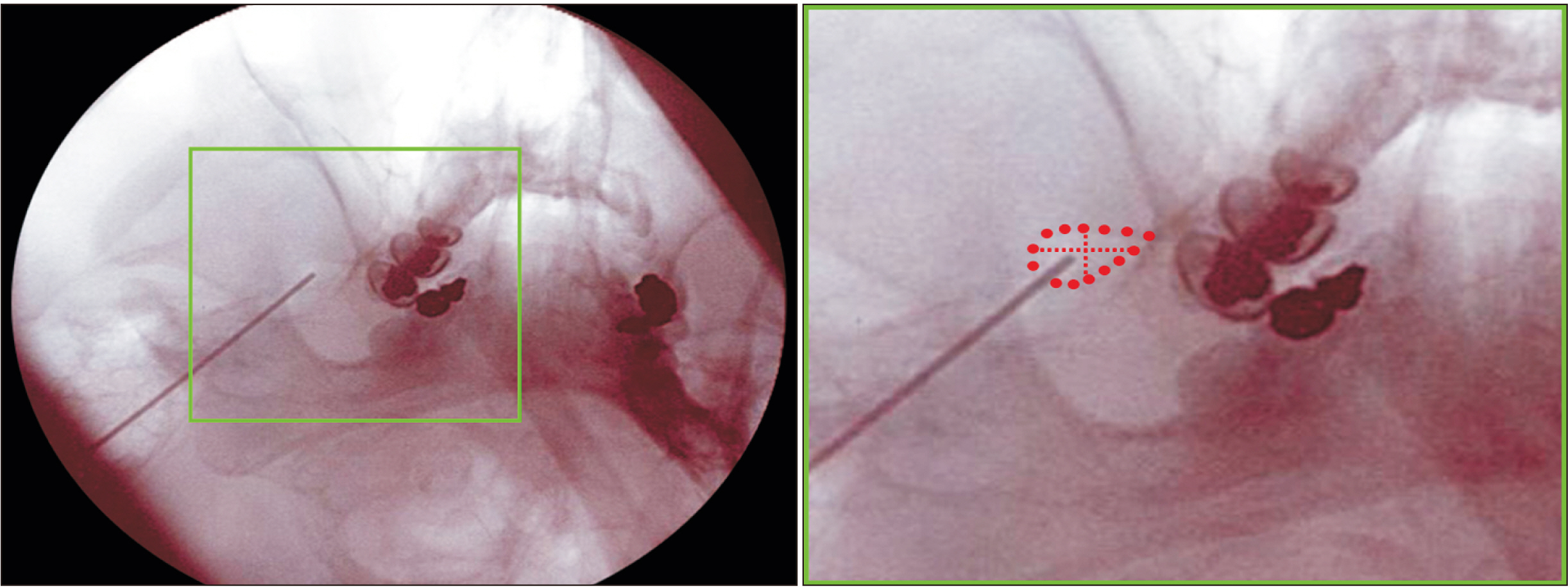
Percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFTC) has been widely utilized in the management of trigeminal neuralgia. Despite using image guidance, accurate needle positioning into the target area still remains a critical element for achieving a successful outcome. This study was performed to precisely clarify the anatomical information required to ensure that the electrode tip is placed on the sensory component of the mandibular nerve (MN) at the foramen ovale (FO) level.
Methods
The study used 50 hemi-half heads from 26 South Korean adult cadavers.
Results
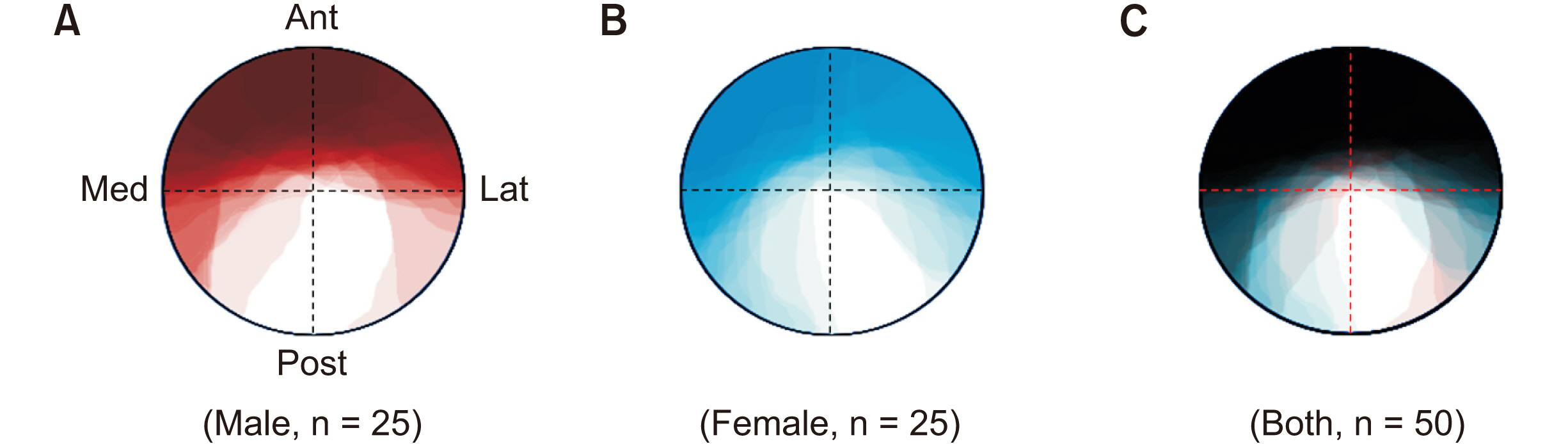
The cross-sectioned anterior and posterior divisions of the MN at the FO level could be distinguished based on an irregular boundary and color difference. The anterior division was clearly brighter than the posterior one. The anterior division of the MN at the FO level was located at the whole anterior (38.0%), anteromedial (6.0%), anterior center (8.0%), and anterolateral (22.0%) parts. The posterior division was often located at the whole posterior or posterolateral parts of the MN at the FO level. The anterior divisions covered the whole MN except for the medial half of the posterolateral part in the overwrapped images of the cross-sectional areas of the MN at the FO level. The cross-sectional areas of the anterior divisions were similar in males and females, whereas those of the posterior divisions were significantly larger in males (P = 0.004).
Conclusions
The obtained anatomical information is expected to help physicians reduce unwanted side effects after percutaneous RFTC within the FO for the MN.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. 2018; The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 38:1–211. DOI: 10.1177/0333102417738202.2. Han KR, Kim C, Kim DW, Cho OG, Cho HW. 2006; Long-term outcome of trigeminal nerve block with alcohol for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Korean J Pain. 19:45–50. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2006.19.1.45.
Article3. Lee CH, Jang HY, Won HS, Kim JS, Kim YD. 2021; Epidemiology of trigeminal neuralgia: an electronic population health data study in Korea. Korean J Pain. 34:332–8. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2021.34.3.332. PMID: 34193639. PMCID: PMC8255158.
Article4. Kim MS, Ryu YJ, Park SY, Kim HY, An S, Kim SW. 2013; Secondary trigeminal neuralgia caused by pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma - A case report -. Korean J Pain. 26:177–80. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.177. PMID: 23614082. PMCID: PMC3629347.
Article5. Neto HS, Camilli JA, Marques MJ. 2005; Trigeminal neuralgia is caused by maxillary and mandibular nerve entrapment: greater incidence of right-sided facial symptoms is due to the foramen rotundum and foramen ovale being narrower on the right side of the cranium. Med Hypotheses. 65:1179–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2005.06.012. PMID: 16084672.
Article6. Cruccu G, Biasiotta A, Galeotti F, Iannetti GD, Innocenti P, Romaniello A, et al. 2006; Diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia: a new appraisal based on clinical and neurophysiological findings. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 58:171–86. DOI: 10.1016/S1567-424X(09)70067-4. PMID: 16623330.7. Bangash TH. 2011; Trigeminal neuralgia: frequency of occurrence in different nerve branches. Anesth Pain Med. 1:70–2. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.2164. PMID: 25729659. PMCID: PMC4335746.
Article8. Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Bekar A, Berk C. 2001; Percutaneous controlled radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: 25-year experience with 1,600 patients. Neurosurgery. 48:524–32. DOI: 10.1097/00006123-200103000-00013. PMID: 11270542.
Article9. Taub E. Lozano AM, Gildenberg PL, Tasker RR, editors. 2009. Radiofrequency rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia. Textbook of stereotactic and functional neurosurgery. Springer;p. 2421–8. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-69960-6_141.10. Gökalp HZ, Kanpolat Y, Tümer B. 1980; Carotid-cavernous fistula following percutaneous trigeminal ganglion approach. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 82:269–72. DOI: 10.1016/0303-8467(80)90019-0. PMID: 6263532.
Article11. Tang YZ, Jin D, Li XY, Lai GH, Li N, Ni JX. 2014; Repeated CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Eur Neurol. 72:54–9. DOI: 10.1159/000357868. PMID: 24853911.
Article12. Huang Q, Liu X, Chen J, Bao C, Liu D, Fang Z, et al. 2016; The effectiveness and safety of thermocoagulation radiofrequency treatment of the ophthalmic division (V1) and/or maxillary (V2) and mandibular (V3) division in idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: an observational study. Pain Physician. 19:E1041–7. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2016.19.E1041.13. Telischak NA, Heit JJ, Campos LW, Choudhri OA, Do HM, Qian X. 2018; Fluoroscopic C-arm and CT-guided selective radiofrequency ablation for trigeminal and glossopharyngeal facial pain syndromes. Pain Med. 19:130–41. DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnx088. PMID: 28472393.
Article14. Huang B, Xie K, Chen Y, Wu J, Yao M. 2019; Bipolar radiofrequency ablation of mandibular branch for refractory V3 trigeminal neuralgia. J Pain Res. 12:1465–74. DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S197967. PMID: 31190956. PMCID: PMC6514122.15. Zeng F, Zhu M, Wan Q, Yan Y, Li C, Zhang Y. 2020; The treatment of V2 + V3 idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia using peripheral nerve radiofrequency thermocoagulation via the foramen rotundum and foramen ovale compared with semilunar ganglion radiofrequency thermocoagulation. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 196:106025. DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106025. PMID: 32590251.16. Berry M, Standring SM, Bannister LH. Williams PL, editor. 1995. Nervous system. Gray's anatomy. 38th ed. Churchill Livingstone;p. 901–1397. DOI: 10.37019/e-anatomy/49576.17. Peris-Celda M, Graziano F, Russo V, Mericle RA, Ulm AJ. 2013; Foramen ovale puncture, lesioning accuracy, and avoiding complications: microsurgical anatomy study with clinical implications. J Neurosurg. 119:1176–93. DOI: 10.3171/2013.1.JNS12743. PMID: 23600929.
Article18. Fillmore EP, Seifert MF. Tubbs RS, Rizk E, Shoja MM, Loukas M, Barbaro N, Spinner R, editors. 2015. Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve. Nerves and nerve injuries. Vol 1: history, embryology, anatomy, imaging, and diagnostics. Academic Press;p. 319–50. DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00023-8.19. Wilson-Pauwels L, Akesson EJ, Stewart PA. 1998. Cranial nerves: anatomy and clinical comments. B.C. Decker;p. 51–69. DOI: 10.37019/e-anatomy/49563.20. Romanes GJ. 1981. Cunningham's textbook of anatomy. 12th ed. Oxford University Press;p. 748–56.21. Woodburne RT, Burkel WE. 1994. Essentials of human anatomy. 9th ed. Oxford University Press;p. 265–8. DOI: 10.5005/jp/books/10278.22. Snell RS. 2000. Clinical anatomy for medical students. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 675.23. Krassioukov AV. Ramachandran VS, editor. 2002. Peripheral nervous system. Encyclopedia of the human brain. 1st ed. Academic Press;p. 817–30. DOI: 10.1016/B0-12-227210-2/00276-4.24. Singh S, Verma R, Kumar M, Rastogi V, Bogra J. 2014; Experience with conventional radiofrequency thermorhizotomy in patients with failed medical management for trigeminal neuralgia. Korean J Pain. 27:260–5. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.260. PMID: 25031812. PMCID: PMC4099239.
Article25. Cheng JS, Lim DA, Chang EF, Barbaro NM. 2014; A review of percutaneous treatments for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 10 Suppl 1:25–33. Erratum in: Neurosurgery 2014; 10 Suppl 2: 372. DOI: 10.1227/NEU.00000000000001687. PMID: 24509496.
Article26. Ding W, Chen S, Wang R, Cai J, Cheng Y, Yu L, et al. 2016; Percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia using neuronavigation-guided puncture from a mandibular angle. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e4940. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004940. PMID: 27749549. PMCID: PMC5059051.
Article27. Toda K. 2008; Operative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: review of current techniques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 106:788–805. 805.e1-6DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.05.033. PMID: 18657454.
Article28. Fraioli MF, Cristino B, Moschettoni L, Cacciotti G, Fraioli C. 2009; Validity of percutaneous controlled radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of isolated third division trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol. 71:180–3. DOI: 10.1016/j.surneu.2007.09.024. PMID: 18291496.
Article29. Cho KH, Shah HA, Schimmoeller T, Machado AG, Papay FA. 2020; An anatomical study of the foramen ovale for neuromodulation of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Neuromodulation. 23:763–9. DOI: 10.1111/ner.13140. PMID: 32243026.
Article30. Zdilla MJ, Hatfield SA, Mangus KR. 2016; Angular relationship between the foramen ovale and the trigeminal impression: percutaneous cannulation trajectories for trigeminal neuralgia. J Craniofac Surg. 27:2177–80. DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000003138. PMID: 28005784. PMCID: PMC5266502.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Lesions
- Unusual Course of the Accessory Meningeal Artery
- Fluoroscopic Landmark to Optimize the View of the Foramen Ovale Using the Neighboring Structure
- Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation Under Fluoroscopic Image-Guidance for Idiopathic Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation in Trigeminal Neuralgia : Analysis of Early and Late Outcomes of 156 Cases and 209 Interventions