Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Sep;56(3):293-298. 10.5115/acb.22.266.
Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Wonju Public Health Center, Wonju, Korea
- 2Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Human Identification Research Institute, BK21 FOUR Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Anatomy and Acupoint, College of Korean Medicine, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Maylin Anti-Aging Center Apgujeong, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.266
Abstract
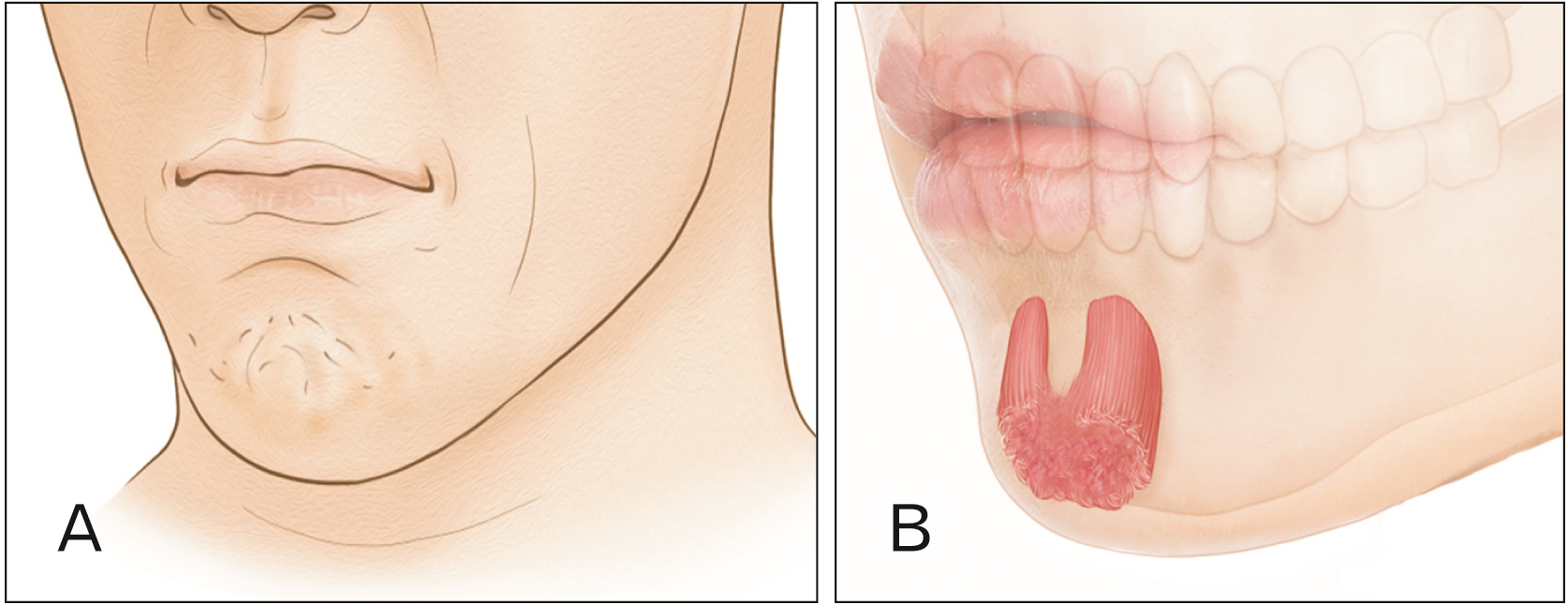
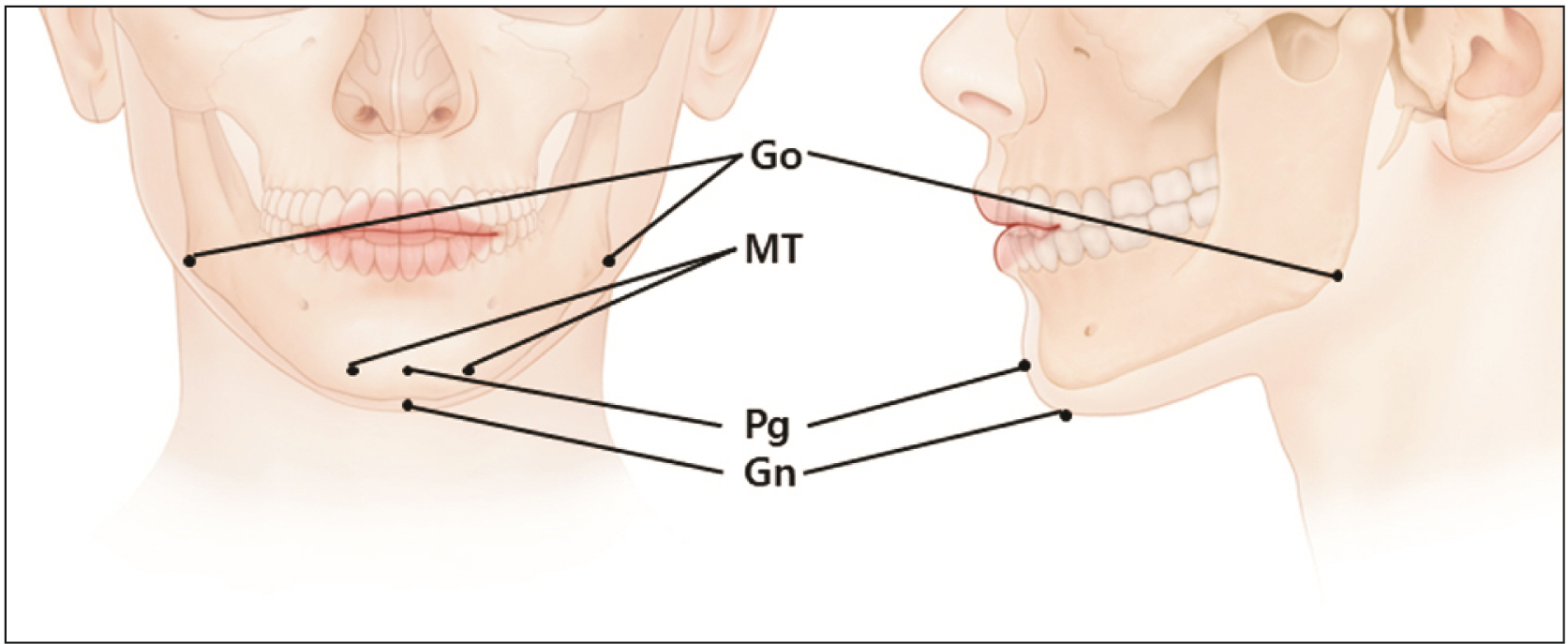
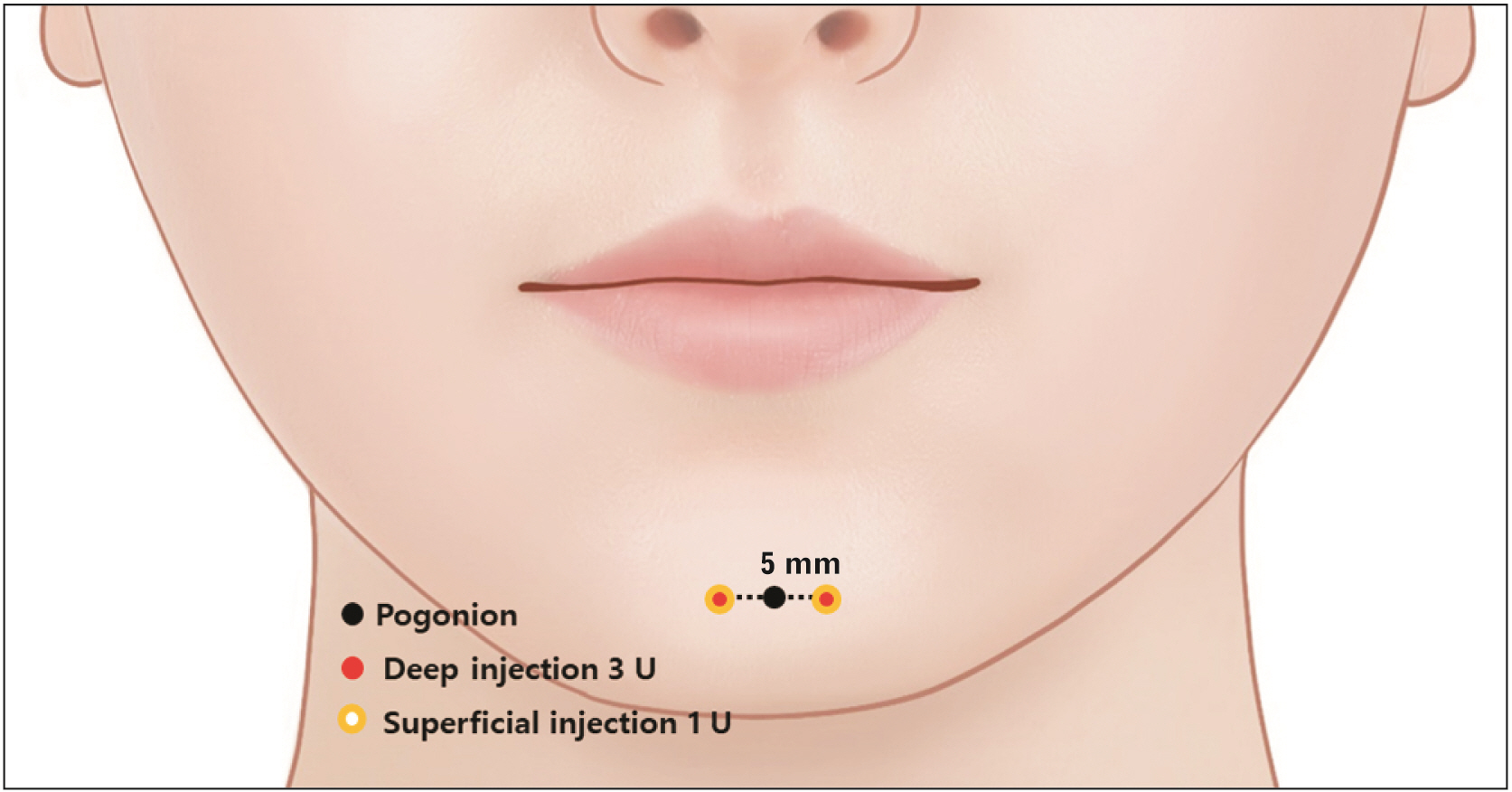
- The mentalis muscle is a paired muscle originating from the alveolar bone of the mandible. This muscle is the main target muscle for botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injection therapy, which aims to treat cobblestone chin caused by mentalis hyperactivity. However, a lack of knowledge on the anatomy of the mentalis muscle and the properties of BoNT can lead to side effects, such as mouth closure insufficiency and smile asymmetry due to ptosis of the lower lip after BoNT injection procedures. Therefore, we have reviewed the anatomical properties associated with BoNT injection into the mentalis muscle. An up-to-date understanding of the localization of the BoNT injection point according to mandibular anatomy leads to better injection localization into the mentalis muscle. Optimal injection sites have been provided for the mentalis muscle and a proper injection technique has been described. We have suggested optimal injection sites based on the external anatomical landmarks of the mandible. The aim of these guidelines is to maximize the effects of BoNT therapy by minimizing the deleterious effects, which can be very useful in clinical settings.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting depressor anguli oris for treating drooping mouth corner
Kyu-Ho Yi, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hye-Won Hu, You-Jin Choi, Kangwoo Lee, Hyung-Jin Lee, Hee-Jin Kim
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(2):161-165. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.258.Botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating plunged nose and post-rhinoplasty: anatomical perspectives of depressor septi nasi, nasalis, leveator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
Kyu-Ho Yi, Ji-Hyun Lee, Seon-Oh Kim, Hyewon Hu, Hyung-Jin Lee, You-Jin Choi, Tae-Hwan Ahn, Hee-Jin Kim
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):409-414. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.054.
Reference
-
References
1. Dessy LA, Mazzocchi M, Rubino C, Mazzarello V, Spissu N, Scuderi N. 2007; An objective assessment of botulinum toxin A effect on superficial skin texture. Ann Plast Surg. 58:469–73. DOI: 10.1097/01.sap.0000244968.16977.1f. PMID: 17452827.
Article2. Childers MK. 2004; Targeting the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscles. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 83(10 Suppl):S38–44. DOI: 10.1097/01.PHM.0000141129.23219.42. PMID: 15448576.
Article3. Choi DY, Bae H, Bae JH, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2021; Effective locations for injecting botulinum toxin into the mentalis muscle; cadaveric and ultrasonographic study. Toxins (Basel). 13:96. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13020096. PMID: 33514053. PMCID: PMC7911364. PMID: 2ffba7fe60e6421aa208765f6742f57e.
Article4. Hsu TS, Dover JS, Arndt KA. 2004; Effect of volume and concentration on the diffusion of botulinum exotoxin A. Arch Dermatol. 140:1351–4. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.140.11.1351. PMID: 15545544.5. Kinnett D. 2004; Botulinum toxin A injections in children: technique and dosing issues. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 83(10 Suppl):S59–64. DOI: 10.1097/01.PHM.0000141131.66648.E9. PMID: 15448579.6. Lepage D, Parratte B, Tatu L, Vuiller F, Monnier G. 2005; Extra- and intramuscular nerve supply of the muscles of the anterior antebrachial compartment: applications for selective neurotomy and for botulinum toxin injection. Surg Radiol Anat. 27:420–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-005-0012-9. PMID: 16308665.
Article7. Pingel J, Nielsen MS, Lauridsen T, Rix K, Bech M, Alkjaer T, Andersen IT, Nielsen JB, Feidenhansl R. 2017; Injection of high dose botulinum-toxin A leads to impaired skeletal muscle function and damage of the fibrilar and non-fibrilar structures. Sci Rep. 7:14746. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14997-3. PMID: 29116170. PMCID: PMC5677119.
Article8. Yi KH, Choi YJ, Cong L, Lee KL, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Effective botulinum toxin injection guide for treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 33:192–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23430. PMID: 31301235.
Article9. Yi KH, Cong L, Bae JH, Park ES, Rha DW, Kim HJ. 2017; Neuromuscular structure of the tibialis anterior muscle for functional electrical stimulation. Surg Radiol Anat. 39:77–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-016-1698-6. PMID: 27206542.
Article10. Yi KH, Rha DW, Lee SC, Cong L, Lee HJ, Lee YW, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of ankle invertor muscles in human cadaver using sihler stain. Muscle Nerve. 53:742–7. DOI: 10.1002/mus.24939. PMID: 26467315.
Article11. Rha DW, Yi KH, Park ES, Park C, Kim HJ. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution of the hamstring muscles: application to treating spasticity. Clin Anat. 29:746–51. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22735. PMID: 27213466.
Article12. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Lee KL, Kim HJ. 2021; Effective botulinum neurotoxin injection in treating iliopsoas spasticity. Clin Anat. 34:431–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23670. PMID: 32805076.
Article13. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee K, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical guide for botulinum neurotoxin injection: application to cosmetic shoulder contouring, pain syndromes, and cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 34:822–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23690. PMID: 32996645.
Article14. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Lee K, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injections in piriformis syndrome. Clin Anat. 34:1028–34. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23711. PMID: 33347678.
Article15. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Application of botulinum neurotoxin injections in TRAM flap for breast reconstruction: intramuscular neural arborization of the rectus abdominis muscle. Toxins (Basel). 13:269. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13040269. PMID: 33918558. PMCID: PMC8070362. PMID: 15169c322e5c4f158142057c4d95936b.
Article16. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee DK, Hu HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical locations of the motor endplates of sartorius muscle for botulinum toxin injections in treatment of muscle spasticity. Surg Radiol Anat. 43:2025–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-021-02813-7. PMID: 34378107. PMCID: PMC8354843.
Article17. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Botulinum neurotoxin injection guidelines regarding flap surgeries in breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 75:503–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2021.09.081. PMID: 34776389.
Article18. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical guidelines on botulinum neurotoxin injection for wrinkles in the nose region. Toxins (Basel). 14:342. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050342. PMID: 35622589. PMCID: PMC9144745. PMID: 95ea3c07c66d4527b5265c5ec719f652.
Article19. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural distribution of the serratus anterior muscle: regarding botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome. Toxins (Basel). 14:271. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040271. PMID: 35448880. PMCID: PMC9033065. PMID: c4ef8fa6e12442a990c0be9185a526e5.
Article20. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection for glabellar frown lines. Toxins (Basel). 14:268. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040268. PMID: 35448877. PMCID: PMC9032255. PMID: dd131953c6e14366befdc986e94b15dd.21. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural arborization of the latissimus dorsi muscle: application of botulinum neurotoxin injection in flap reconstruction. Toxins (Basel). 14:107. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14020107. PMID: 35202134. PMCID: PMC8878018. PMID: 0c7534ebd76b4902bff96b4bfe81c6b3.
Article22. Lee HJ, Lee JH, Yi KH, Kim HJ. 2022; Nov. 25. Sonoanatomy and an ultrasound scanning protocol of the intramuscular innervation pattern of the infraspinatus muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/rapm-2022-103682. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2022-103682. PMID: 36427902.
Article23. Lee HJ, Lee JH, Yi KH, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular innervation of the supraspinatus muscle assessed using Sihler's staining: potential application in myofascial pain syndrome. Toxins (Basel). 14:310. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050310. PMID: 35622557. PMCID: PMC9143847. PMID: 34b169cd96874bde9b8c4748508d0448.
Article24. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee JH, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Intramuscular neural distribution of rhomboid muscles: evaluation for botulinum toxin injection using modified Sihler's method. Toxins (Basel). 12:289. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12050289. PMID: 32375284. PMCID: PMC7291336. PMID: 2a43e00b63b34292bd34bcaa4ce50d09.
Article25. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Hur HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection for facial contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 150:562e–71e. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009444. PMID: 35759641.
Article26. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim GY, Yoon SW, Oh W, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting lateral canthal rhytids. Toxins (Basel). 14:462. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070462. PMID: 35878200. PMCID: PMC9316553. PMID: 46755210c7064a99b625f2d6b6dc6e0a.
Article27. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HM, Kim HJ. 2022; The botulinum neurotoxin for pain control after breast reconstruction: neural distribution of the pectoralis major muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:322–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102653. PMID: 35039438.
Article28. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidance to trigger point injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome: intramuscular neural distribution of the quadratus lumborum. Clin Anat. 35:1100–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23918. PMID: 35655442.
Article29. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee K, Hu HW, Lee HJ, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting the platysma muscle for treating platysmal band and jawline lifting: a review. Toxins (Basel). 14:868. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14120868. PMID: 36548765. PMCID: PMC9783622. PMID: 1fab78f1f2fb436e8f0adab9755ed1d2.
Article30. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hur HW, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Kim HJ. 2023; Jan. 6. Distribution of the intramuscular innervation of the triceps brachii: clinical importance in the treatment of spasticity with botulinum neurotoxin. Clin Anat. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.24004. DOI: 10.1002/ca.24004. PMID: 36606364.31. Zide BM, McCarthy J. 1989; The mentalis muscle: an essential component of chin and lower lip position. Plast Reconstr Surg. 83:413–20. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198903000-00001.
Article32. Hur MS, Kim HJ, Choi BY, Hu KS, Kim HJ, Lee KS. 2013; Morphology of the mentalis muscle and its relationship with the orbicularis oris and incisivus labii inferioris muscles. J Craniofac Surg. 24:602–4. DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318267bcc5. PMID: 23524754.
Article33. Garfein ES, Zide BM. 2008; Chin ptosis: classification, anatomy, and correction. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 1:1–14. DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1098968. PMID: 22110784. PMCID: PMC3052727.
Article34. Seo KK. 2017. Botulinum toxin for Asians. Springer;Singapore: DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-0204-5.35. Le Louarn C. 2001; Botulinum toxin A and facial lines: the variable concentration. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 25:73–84. DOI: 10.1007/s002660010100. PMID: 11349306.
Article36. Klein AW. 2004; Contraindications and complications with the use of botulinum toxin. Clin Dermatol. 22:66–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2003.12.026. PMID: 15158548.
Article37. Yu N, Liu Y, Chen C, Dong R, Yang E, Wang X. 2020; Paradoxical bulging of mentalis after botulinum toxin type A injection. J Cosmet Dermatol. 19:1290–3. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.13437. PMID: 32346978.
Article38. Carruthers J, Carruthers A. 2003; Aesthetic botulinum A toxin in the mid and lower face and neck. Dermatol Surg. 29:468–76. DOI: 10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29115.x. PMID: 12752513.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intramuscular neural distribution of the teres minor muscle using Sihler’s stain: application to botulinum neurotoxin injection
- Intramuscular Neural Distribution of Adductor Pollicis Muscle Spasticity in Cadaver Model Regarding Botulinum Neurotoxin Treatment
- Ultrasonographic study and anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection into the parotid gland
- Botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating plunged nose and post-rhinoplasty: anatomical perspectives of depressor septi nasi, nasalis, leveator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
- Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting depressor anguli oris for treating drooping mouth corner