Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Jun;56(2):161-165. 10.5115/acb.22.258.
Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting depressor anguli oris for treating drooping mouth corner
- Affiliations
-
- 1Wonju Public Health Center, Wonju, Korea
- 2Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Human Identification Research Institute, BK21 PLUS Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Anatomy and Acupoint, College of Korean Medicine, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea
- 4Department of Anatomy, Research Institute of Medical Science, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Anatomy, Catholic Institute for Applied Anatomy, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2544076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.258
Abstract
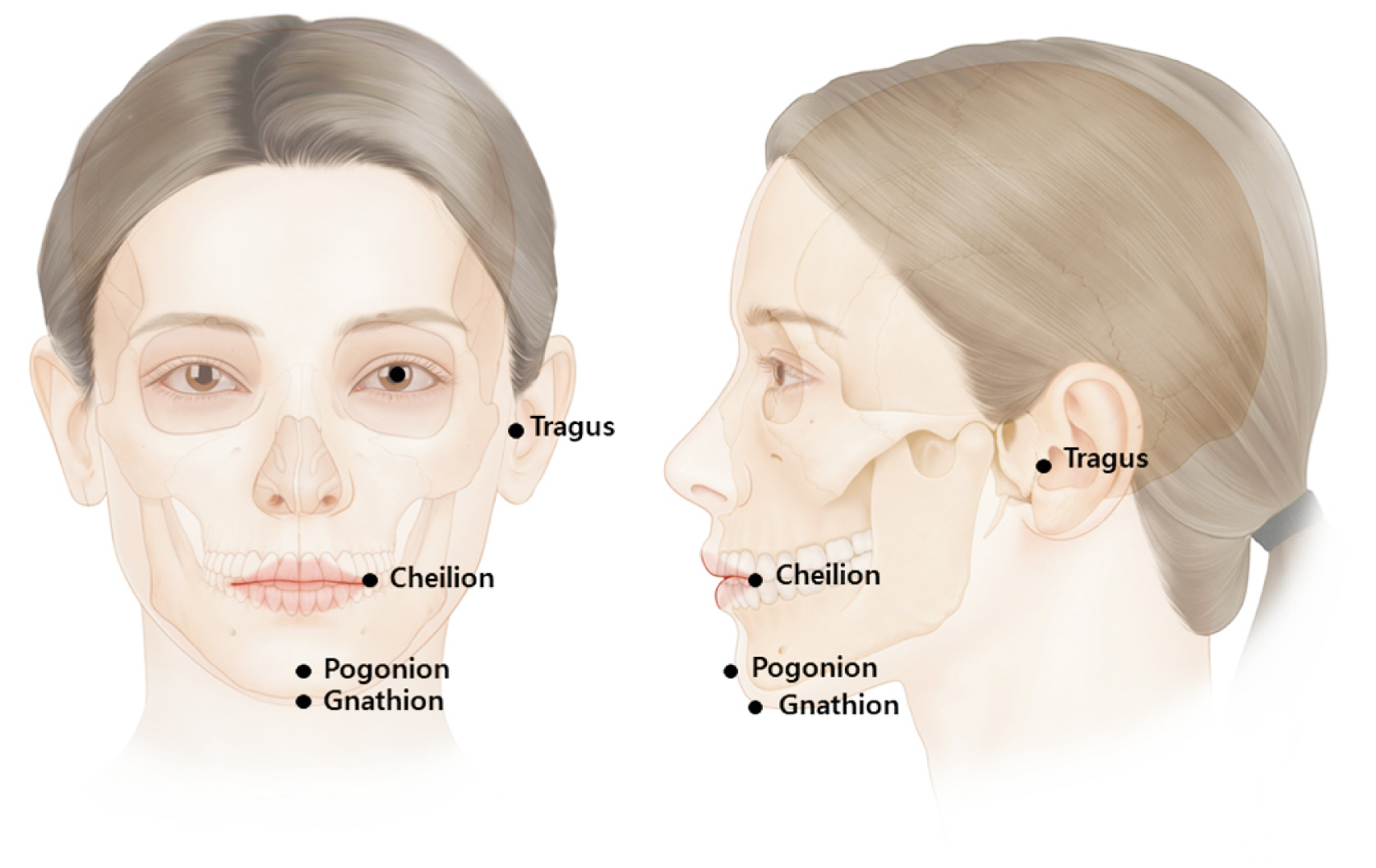
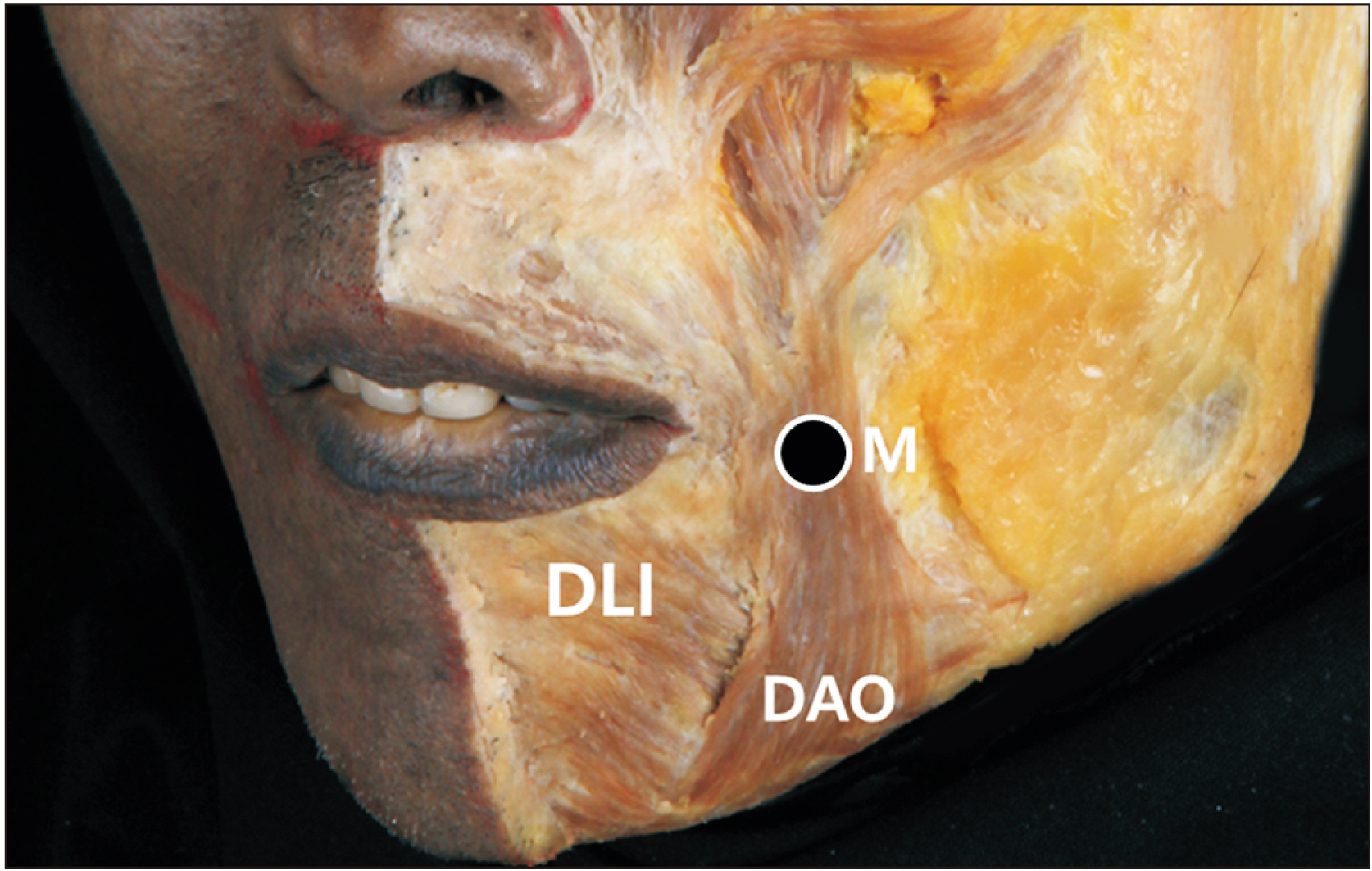
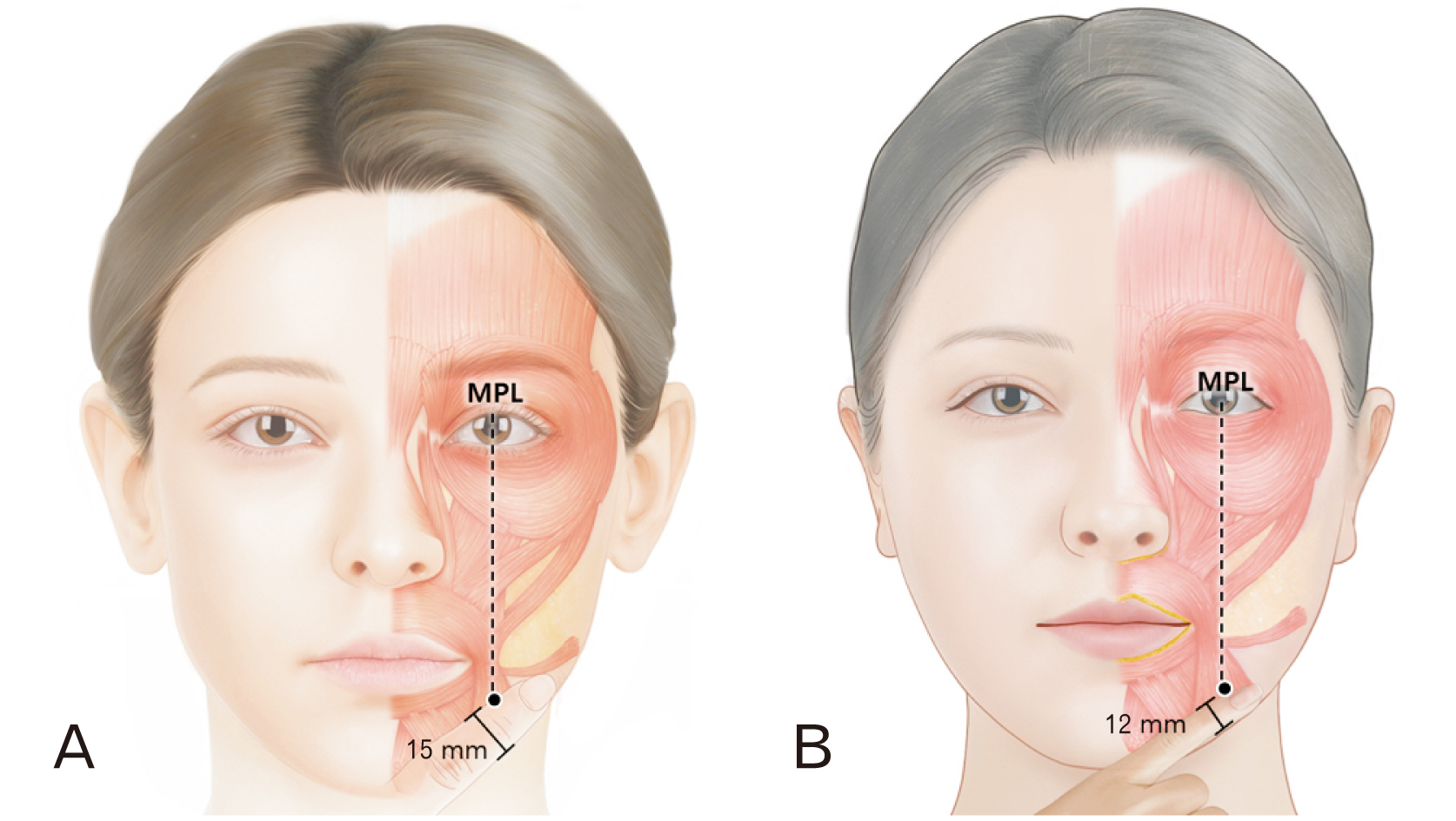
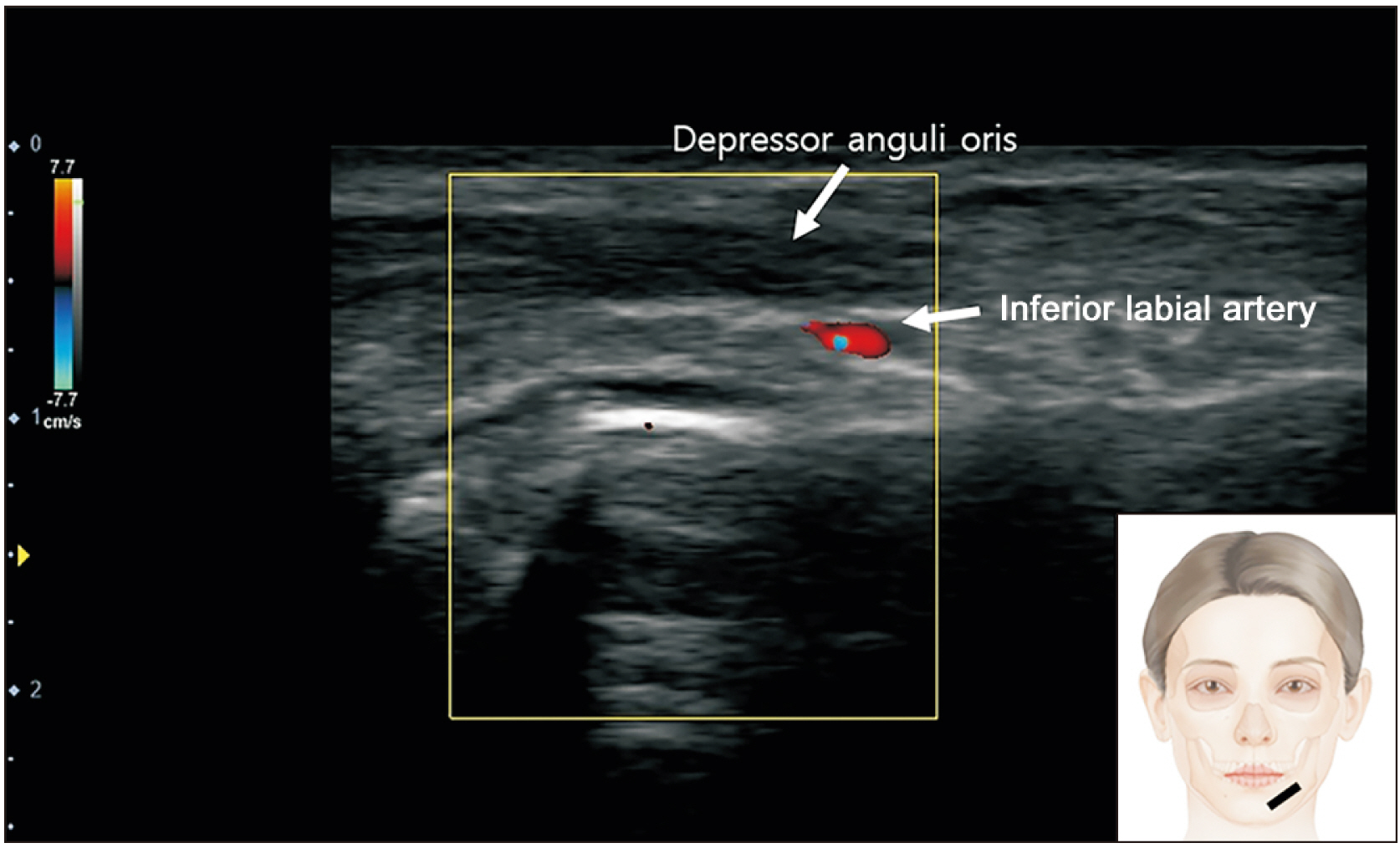
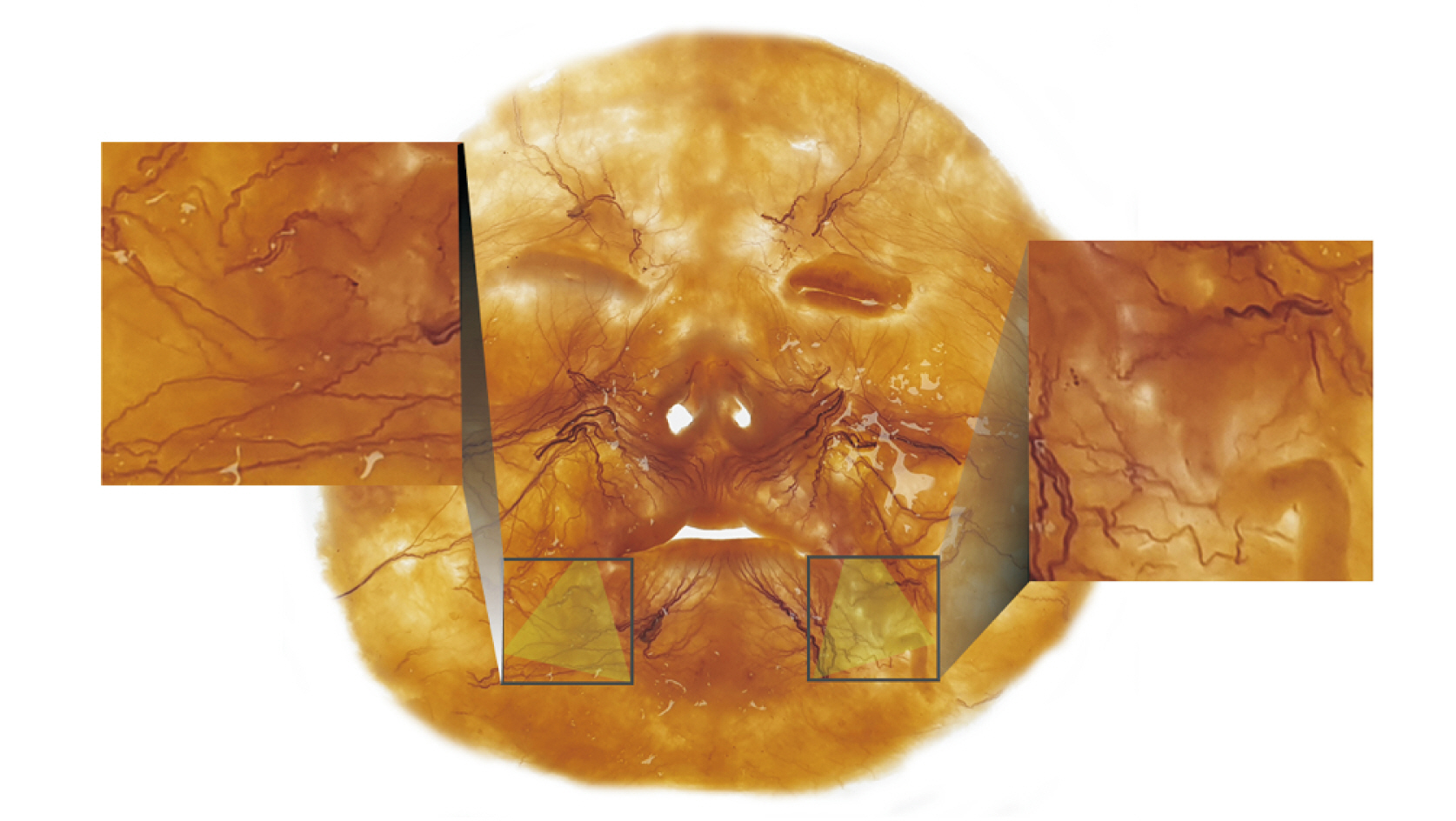
- The depressor anguli oris (DAO) muscle is a thin, superficial muscle located below the corner of the mouth. It is the target for botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injection therapy, aimed at treating drooping mouth corners. Hyperactivity of the DAO muscle can lead to a sad, tired, or angry appearance in some patients. However, it is difficult to inject BoNT into the DAO muscle because its medial border overlaps with the depressor labii inferioris and its lateral border is adjacent to the risorius, zygomaticus major, and platysma muscles. Moreover, a lack of knowledge of the anatomy of the DAO muscle and the properties of BoNT can lead to side effects, such as asymmetrical smiles. Anatomical-based injection sites were provided for the DAO muscle, and the proper injection technique was reviewed. We proposed optimal injection sites based on the external anatomical landmarks of the face. The aim of these guidelines is to standardize the procedure and maximize the effects of BoNT injections while minimizing adverse events, all by reducing the dose unit and injection points.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Intramuscular neural distribution of the teres minor muscle using Sihler’s stain: application to botulinum neurotoxin injection
Kyu-Ho Yi, Soo-Bin Kim, Kangwoo Lee, Hyewon Hu, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hyung-Jin Lee
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(3):322-327. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.087.Botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating plunged nose and post-rhinoplasty: anatomical perspectives of depressor septi nasi, nasalis, leveator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
Kyu-Ho Yi, Ji-Hyun Lee, Seon-Oh Kim, Hyewon Hu, Hyung-Jin Lee, You-Jin Choi, Tae-Hwan Ahn, Hee-Jin Kim
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):409-414. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.054.
Reference
-
References
1. Krag AE, Dumestre D, Hembd A, Glick S, Mohanty AJ, Rozen SM. 2021; Topographic and neural anatomy of the depressor anguli oris muscle and implications for treatment of synkinetic facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 147:268e–78e. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007593. PMID: 33565832.
Article2. Choi YJ, Kim JS, Gil YC, Phetudom T, Kim HJ, Tansatit T, Hu KS. 2014; Anatomical considerations regarding the location and boundary of the depressor anguli oris muscle with reference to botulinum toxin injection. Plast Reconstr Surg. 134:917–21. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000589. PMID: 25347627.
Article3. Hur MS, Hu KS, Cho JY, Kwak HH, Song WC, Koh KS, Lorente M, Kim HJ. 2008; Topography and location of the depressor anguli oris muscle with a reference to the mental foramen. Surg Radiol Anat. 30:403–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-008-0343-4. PMID: 18385924.
Article4. Moradi A, Shirazi A. 2022; A retrospective and anatomical study describing the injection of botulinum neurotoxins in the depressor anguli oris. Plast Reconstr Surg. 149:850–7. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000008967. PMID: 35139057.
Article5. Childers MK. 2004; Targeting the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscles. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 83(10 Suppl):S38–44. DOI: 10.1097/01.PHM.0000141129.23219.42. PMID: 15448576.
Article6. Kaplan SE, Sherris DA, Gassner HG, Friedman O. 2007; The use of botulinum toxin A in perioral rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 15:415–21. v–vi. DOI: 10.1016/j.fsc.2007.07.001. PMID: 18005882.
Article7. Kim HM, Ree YS, Park MS, Kim JS, Ahn JH, Yi KH. 2022; Clinical guideline: deoxycholic acid injection for submental fat reduction. The Aesthetics. 3:7–11. DOI: 10.46738/Aesthetics.2022.3.2.7.
Article8. Lee HJ, Lee JH, Yi KH, Kim HJ. 2020; Nov. 25. Sonoanatomy and an ultrasound scanning protocol of the intramuscular innervation pattern of the infraspinatus muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1136/rapm-2022-103682. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2022-103682. PMID: 36427902.
Article9. Lee HJ, Lee JH, Yi KH, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular innervation of the supraspinatus muscle assessed using Sihler's staining: potential application in myofascial pain syndrome. Toxins (Basel). 14:3. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050310. PMID: 35622557. PMCID: PMC9143847. PMID: 34b169cd96874bde9b8c4748508d0448.
Article10. Rha DW, Yi KH, Park ES, Park C, Kim HJ. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution of the hamstring muscles: application to treating spasticity. Clin Anat. 29:746–51. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22735. PMID: 27213466.
Article11. Yi KH, Cong L, Bae JH, Park ES, Rha DW, Kim HJ. 2017; Neuromuscular structure of the tibialis anterior muscle for functional electrical stimulation. Surg Radiol Anat. 39:77–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-016-1698-6. PMID: 27206542.
Article12. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee JH, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Intramuscular neural distribution of rhomboid muscles: evaluation for botulinum toxin injection using modified Sihler's method. Toxins (Basel). 12:289. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12050289. PMID: 32375284. PMCID: PMC7291336. PMID: 2a43e00b63b34292bd34bcaa4ce50d09.
Article13. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Hur HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection for facial contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 150:562e–71e. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009444. PMID: 35759641.
Article14. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural arborization of the latissimus dorsi muscle: application of botulinum neurotoxin injection in flap reconstruction. Toxins (Basel). 14:107. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14020107. PMID: 35202134. PMCID: PMC8878018. PMID: 0c7534ebd76b4902bff96b4bfe81c6b3.
Article15. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical guidelines on botulinum neurotoxin injection for wrinkles in the nose region. Toxins (Basel). 14:342. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050342. PMID: 35622589. PMCID: PMC9144745. PMID: 95ea3c07c66d4527b5265c5ec719f652.
Article16. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim GY, Yoon SW, Oh W, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting lateral canthal rhytids. Toxins (Basel). 14:462. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070462. PMID: 35878200. PMCID: PMC9316553. PMID: 46755210c7064a99b625f2d6b6dc6e0a.
Article17. Yi KH, Choi YJ, Cong L, Lee KL, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2020; Effective botulinum toxin injection guide for treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 33:192–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23430. PMID: 31301235.
Article18. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Lee K, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical guide for botulinum neurotoxin injection: application to cosmetic shoulder contouring, pain syndromes, and cervical dystonia. Clin Anat. 34:822–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23690. PMID: 32996645.
Article19. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Lee KL, Kim HJ. 2021; Effective botulinum neurotoxin injection in treating iliopsoas spasticity. Clin Anat. 34:431–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23670. PMID: 32805076.
Article20. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Application of botulinum neurotoxin injections in TRAM flap for breast reconstruction: intramuscular neural arborization of the rectus abdominis muscle. Toxins (Basel). 13:269. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13040269. PMID: 33918558. PMCID: PMC8070362. PMID: 15169c322e5c4f158142057c4d95936b.
Article21. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Botulinum neurotoxin injection guidelines regarding flap surgeries in breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 75:503–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjps.2021.09.081. PMID: 34776389.
Article22. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection for glabellar frown lines. Toxins (Basel). 14:268. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040268. PMID: 35448877. PMCID: PMC9032255. PMID: dd131953c6e14366befdc986e94b15dd.
Article23. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural distribution of the serratus anterior muscle: regarding botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome. Toxins (Basel). 14:271. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14040271. PMID: 35448880. PMCID: PMC9033065. PMID: c4ef8fa6e12442a990c0be9185a526e5.
Article24. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HM, Kim HJ. 2022; The botulinum neurotoxin for pain control after breast reconstruction: neural distribution of the pectoralis major muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:322–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102653. PMID: 35039438.
Article25. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee DK, Hu HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Anatomical locations of the motor endplates of sartorius muscle for botulinum toxin injections in treatment of muscle spasticity. Surg Radiol Anat. 43:2025–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-021-02813-7. PMID: 34378107. PMCID: PMC8354843.
Article26. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidance to trigger point injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome: intramuscular neural distribution of the quadratus lumborum. Clin Anat. 35:1100–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23918. PMID: 35655442.
Article27. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Lee K, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2021; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injections in piriformis syndrome. Clin Anat. 34:1028–34. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23711. PMID: 33347678.
Article28. Yi KH, Rha DW, Lee SC, Cong L, Lee HJ, Lee YW, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2016; Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of ankle invertor muscles in human cadaver using sihler stain. Muscle Nerve. 53:742–7. DOI: 10.1002/mus.24939. PMID: 26467315.
Article29. Yi KH, Lee JH, Lee K, Hu HW, Lee HJ, Kim HJ. 2022; Anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting the platysma muscle for treating platysmal band and jawline lifting: a review. Toxins (Basel). 14:868. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14120868. PMID: 36548765. PMCID: PMC9783622. PMID: 1fab78f1f2fb436e8f0adab9755ed1d2.
Article30. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hur HW, Lee HJ, Choi YJ, Kim HJ. 2023; Jan. 6. Distribution of the intramuscular innervation of the triceps brachii: clinical importance in the treatment of spasticity with botulinum neurotoxin. Clin Anat. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.24004. DOI: 10.1002/ca.24004. PMID: 36606364.
Article31. Yi KH, Lee JH, Hu HW, Park HJ, Bae H, Lee K, Kim HJ. 2023; Feb. 17. Novel anatomical guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection in the mentalis muscle: a review. Anat Cell Biol. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.266. DOI: 10.5115/acb.22.266. PMID: 36796830.
Article32. Le Louarn C, Buis J, Buthiau D. 2006; Treatment of depressor anguli oris weakening with the face recurve concept. Aesthet Surg J. 26:603–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.asj.2006.08.001. PMID: 19338950.
Article33. Demiryurek D, Bayramoglu A, Erbil KM, Onderoglu S, Sargon MF, Aldur MM, Korkusuz P, Nazikoglu A. 2003; Three-dimensional structure of the modiolus. A computerized reconstruction study. Saudi Med J. 24:846–9. PMID: 12939669.34. Kim HJ, Seo KK, Lee HK, Kim J. 2016. Clinical anatomy of the face for filler and botulinum toxin injection. Springer;DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-0240-3.35. Borodic GE, Ferrante R, Pearce LB, Smith K. 1994; Histologic assessment of dose-related diffusion and muscle fiber response after therapeutic botulinum A toxin injections. Mov Disord. 9:31–9. DOI: 10.1002/mds.870090106. PMID: 8139603.
Article36. Choi YJ, We YJ, Lee HJ, Lee KW, Gil YC, Hu KS, Tansatit T, Kim HJ. 2021; Three-dimensional evaluation of the depressor anguli oris and depressor labii inferioris for botulinum toxin injections. Aesthet Surg J. 41:NP456–61. DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjaa083. PMID: 32232427.
Article37. Lee HJ, Won SY, O J, Hu KS, Mun SY, Yang HM, Kim HJ. 2018; The facial artery: a comprehensive anatomical review. Clin Anat. 31:99–108. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23007. PMID: 29086435.38. Raspaldo H, Niforos FR, Gassia V, Dallara JM, Bellity P, Baspeyras M, Belhaouari L. 2011; Lower-face and neck antiaging treatment and prevention using onabotulinumtoxin A: the 2010 multidisciplinary French consensus--part 2. J Cosmet Dermatol. 10:131–49. DOI: 10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00560.x. PMID: 21649819.39. Bae JH, Youn KH, Hu KS, Lee JH, Tansatit T, Kim HJ. 2016; Clinical implications of the extension of platysmal fibers on the middle and lower face. Plast Reconstr Surg. 138:365–71. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002346. PMID: 27064219.
Article40. Lee HJ, Kim JS, Youn KH, Lee J, Kim HJ. 2018; Ultrasound-guided botulinum neurotoxin type A injection for correcting asymmetrical smiles. Aesthet Surg J. 38:NP130–4. DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjy128. PMID: 29800051.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correction of Asymmetric Crying Facies with Botulinum Toxin A Injection: A Case Report
- Botulinum neurotoxin injection for treating plunged nose and post-rhinoplasty: anatomical perspectives of depressor septi nasi, nasalis, leveator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
- Location of the Modiolous and the Morphologic Variations of the Risorius and Zygomaticus Major Muscle Related to the Facial Expression in Koreans
- Congenital unilateral hypoplasia of depressor anguli oris muscle in adult
- Two Cases of Asymmetric Crying Facies: Congenital Agenesis of the Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle