J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2023 Sep;66(5):562-572. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0229.
Effect of Bevacizumab Treatment in Cerebral Radiation Necrosis : Investigation of Response Predictors in a Single-Center Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2545347
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0229
Abstract
Objective
: Bevacizumab is a feasible option for treating cerebral radiation necrosis (RN). We investigated the clinical outcome of RN after treatment with bevacizumab and factors related to the initial response and the sustained effect.
Methods
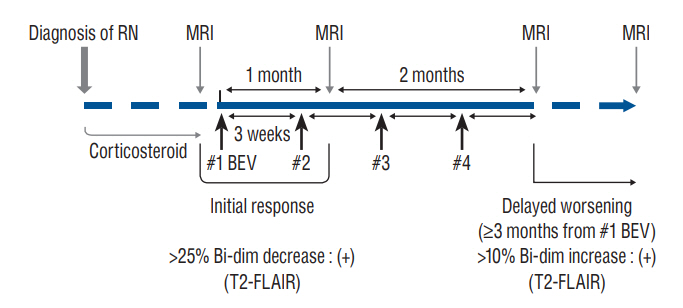
: Clinical data of 45 patients treated for symptomatic RN between September 2019 and February 2021 were retrospectively collected. Bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg) was administered at 3-week intervals with a maximum four-cycle schedule. Changes in the lesions magnetic resonance image (MRI) scans were examined for the response evaluation. The subgroup analysis was performed based on the initial response and the long-term maintenance of the effect.
Results
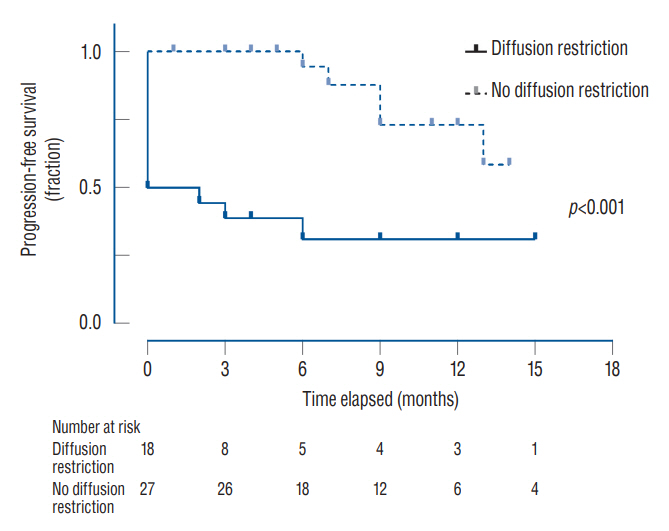
: Of the 45 patients, 36 patients (80.0%) showed an initial response, and eight patients (17.8%) showed delayed worsening of the corresponding lesion. The non-responders showed a significantly higher incidence of diffusion restriction on MRI than the responders (100.0% vs. 25.0%, p<0.001). The delayed worsening group showed a significantly higher proportion of glioma pathology than the maintenance group (87.5% vs. 28.6%, p=0.005). Cumulative survival rates with sustained effect were significantly higher in the groups with non-glioma pathology (p=0.019) and the absence of diffusion restriction (p<0.001). Pathology of glioma and diffusion restriction in MRI were the independent risk factors for non-response or delayed worsening after initial response.
Conclusion
: The initial response of RN to bevacizumab was favorable, with improvement in four-fifths of the patients. However, a certain proportion of patients showed non-responsiveness or delayed exacerbations. Bevacizumab may be more effective in treating RN in patients with non-glioma pathology and without diffusion restriction in the MRI.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Alexiou GA, Tsiouris S, Kyritsis AP, Voulgaris S, Argyropoulou MI, Fotopoulos AD. Glioma recurrence versus radiation necrosis: accuracy of current imaging modalities. J Neurooncol. 95:1–11. 2009.2. Asao C, Korogi Y, Kitajima M, Hirai T, Baba Y, Makino K, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of radiation-induced brain injury for differentiation from tumor recurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 26:1455–1460. 2005.3. Baroni LV, Alderete D, Solano-Paez P, Rugilo C, Freytes C, Laughlin S, et al. Bevacizumab for pediatric radiation necrosis. Neurooncol Pract. 7:409–414. 2020.4. Boothe D, Young R, Yamada Y, Prager A, Chan T, Beal K. Bevacizumab as a treatment for radiation necrosis of brain metastases post stereotactic radiosurgery. Neuro Oncol. 15:1257–1263. 2013.5. Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Spagnolli F, Frezza G, Leonardi M, Calbucci F, et al. Disease progression or pseudoprogression after concomitant radiochemotherapy treatment: pitfalls in neurooncology. Neuro Oncol. 10:361–367. 2008.6. Chan YL, Yeung DK, Leung SF, Chan PN. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in radiation-induced cerebral necrosis. Apparent diffusion coefficient in lesion components. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 27:674–680. 2003.7. Chuba PJ, Aronin P, Bhambhani K, Eichenhorn M, Zamarano L, Cianci P, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radiation-induced brain injury in children. Cancer. 80:2005–2012. 1997.8. Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA. Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol. 12:627–642. 1994.9. Dahl NA, Liu AK, Foreman NK, Widener M, Fenton LZ, Macy ME. Bevacizumab in the treatment of radiation injury for children with central nervous system tumors. Childs Nerv Syst. 35:2043–2046. 2019.10. Giglio P, Gilbert MR. Cerebral radiation necrosis. Neurologist. 9:180–188. 2003.11. Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Friedman AH, Radtke RA, Massey EW, Schold SC Jr. Treatment of radiation-induced nervous system injury with heparin and warfarin. Neurology. 44:2020–2027. 1994.12. Gonzalez J, Kumar AJ, Conrad CA, Levin VA. Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:323–326. 2007.13. Hein PA, Eskey CJ, Dunn JF, Hug EB. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the follow-up of treated high-grade gliomas: tumor recurrence versus radiation injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 25:201–209. 2004.14. Jabeen S, Arbind A, Kumar D, Singh PK, Saini J, Sadashiva N, et al. Combined amino acid PET-MRI for identifying recurrence in post-treatment gliomas: together we grow. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 5:15. 2021.15. Kazda T, Bulik M, Pospisil P, Lakomy R, Smrcka M, Slampa P, et al. Advanced MRI increases the diagnostic accuracy of recurrent glioblastoma: single institution thresholds and validation of MR spectroscopy and diffusion weighted MR imaging. Neuroimage Clin. 11:316–321. 2016.16. Kim JH, Chung YG, Kim CY, Kim HK, Lee HK. Upregulation of VEGF and FGF2 in normal rat brain after experimental intraoperative radiation therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 19:879–886. 2004.17. Kim S, Kim SH, Kim JS. Coexisting cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in Wernicke encephalopathy. Neurol Sci. 35:635–636. 2014.18. Koch S, Rabinstein A, Falcone S, Forteza A. Diffusion-weighted imaging shows cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in eclampsia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:1068–1070. 2001.19. Kotsarini C, Griffiths PD, Wilkinson ID, Hoggard N. A systematic review of the literature on the effects of dexamethasone on the brain from in vivo human-based studies: implications for physiological brain imaging of patients with intracranial tumors. Neurosurgery. 67:1799–1815. discussion 1815. 2010.20. Leber KA, Eder HG, Kovac H, Anegg U, Pendl G. Treatment of cerebral radionecrosis by hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 70 Suppl. 1:229–236. 1998.21. Lee AW, Ng SH, Ho JH, Tse VK, Poon YF, Tse CC, et al. Clinical diagnosis of late temporal lobe necrosis following radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 61:1535–1542. 1988.22. Lee WJ, Choi SH, Park CK, Yi KS, Kim TM, Lee SH, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for the differentiation of true progression from pseudoprogression following concomitant radiotherapy with temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas. Acad Radiol. 19:1353–1361. 2012.23. Letarte N, Bressler LR, Villano JL. Bevacizumab and central nervous system (CNS) hemorrhage. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:1561–1565. 2013.24. Levin VA, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar AJ, Wefel JS, Bekele BN, et al. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:1487–1495. 2011.25. Li YQ, Chen P, Jain V, Reilly RM, Wong CS. Early radiation-induced endothelial cell loss and blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown in the rat spinal cord. Radiat Res. 161:143–152. 2004.26. Liao G, Khan M, Zhao Z, Arooj S, Yan M, Li X. Bevacizumab treatment of radiation-induced brain necrosis: a systematic review. Front Oncol. 11:593449. 2021.27. Liu AK, Macy ME, Foreman NK. Bevacizumab as therapy for radiation necrosis in four children with pontine gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:1148–1154. 2009.28. Lövblad KO, Bassetti C, Schneider J, Ozdoba C, Remonda L, Schroth G. Diffusion-weighted MRI suggests the coexistence of cytotoxic and vasogenic oedema in a case of deep cerebral venous thrombosis. Neuroradiology. 42:728–731. 2000.29. Matuschek C, Bölke E, Nawatny J, Hoffmann TK, Peiper M, Orth K, et al. Bevacizumab as a treatment option for radiation-induced cerebral necrosis. Strahlenther Onkol. 187:135–139. 2011.30. Michinaga S, Koyama Y. Pathogenesis of brain edema and investigation into anti-edema drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 16:9949–9975. 2015.31. Muhsin M, Graham J, Kirkpatrick P. Bevacizumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 3:995–996. 2004.32. Nonoguchi N, Miyatake S, Fukumoto M, Furuse M, Hiramatsu R, Kawabata S, et al. The distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor-producing cells in clinical radiation necrosis of the brain: pathological consideration of their potential roles. J Neurooncol. 105:423–431. 2011.33. Nordal RA, Nagy A, Pintilie M, Wong CS. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 target genes in central nervous system radiation injury: a role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3342–3353. 2004.34. Rahmathulla G, Marko NF, Weil RJ. Cerebral radiation necrosis: a review of the pathobiology, diagnosis and management considerations. J Clin Neurosci. 20:485–502. 2013.35. Raimbault A, Cazals X, Lauvin MA, Destrieux C, Chapet S, Cottier JP. Radionecrosis of malignant glioma and cerebral metastasis: a diagnostic challenge in MRI. Diagn Interv Imaging. 95:985–1000. 2014.36. Rock JP, Scarpace L, Hearshen D, Gutierrez J, Fisher JL, Rosenblum M, et al. Associations among magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficients, and image-guided histopathology with special attention to radiation necrosis. Neurosurgery. 54:1111–1117. discussion 1117-1119. 2004.37. Schaefer PW, Ozsunar Y, He J, Hamberg LM, Hunter GJ, Sorensen AG, et al. Assessing tissue viability with MR diffusion and perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 24:436–443. 2003.38. Shah R, Vattoth S, Jacob R, Manzil FF, O’Malley JP, Borghei P, et al. Radiation necrosis in the brain: imaging features and differentiation from tumor recurrence. Radiographics. 32:1343–1359. 2012.39. Siu A, Wind JJ, Iorgulescu JB, Chan TA, Yamada Y, Sherman JH. Radiation necrosis following treatment of high grade glioma--a review of the literature and current understanding. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 154:191–201. discussion 201. 2012.40. Stadnik TW, Chaskis C, Michotte A, Shabana WM, van Rompaey K, Luypaert R, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral masses: comparison with conventional MR imaging and histologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:969–976. 2001.41. Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Tomiguchi S, Shigematsu Y, Ikushima I, Kira T, et al. Posttherapeutic intraaxial brain tumor: the value of perfusion-sensitive contrast-enhanced MR imaging for differentiating tumor recurrence from nonneoplastic contrast-enhancing tissue. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 21:901–909. 2000.42. Torcuator R, Zuniga R, Mohan YS, Rock J, Doyle T, Anderson J, et al. Initial experience with bevacizumab treatment for biopsy confirmed cerebral radiation necrosis. J Neurooncol. 94:63–68. 2009.43. Wang S, Chen Y, Lal B, Ford E, Tryggestad E, Armour M, et al. Evaluation of radiation necrosis and malignant glioma in rat models using diffusion tensor MR imaging. J Neurooncol. 107:51–60. 2012.44. Xu Y, Rong X, Hu W, Huang X, Li Y, Zheng D, et al. Bevacizumab monotherapy reduces radiation-induced brain necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 101:1087–1095. 2018.45. Yang X, Ren H, Fu J. Treatment of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:4793517. 2021.46. Zakhari N, Taccone MS, Torres C, Chakraborty S, Sinclair J, Woulfe J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of centrally restricted diffusion in the differentiation of treatment-related necrosis from tumor recurrence in high-grade gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 39:260–264. 2018.47. Zhang H, Ma L, Shu C, Wang YB, Dong LQ. Diagnostic accuracy of diffusion MRI with quantitative ADC measurements in differentiating glioma recurrence from radiation necrosis. J Neurol Sci. 351:65–71. 2015.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Experience of Bevacizumab for Radiation Necrosis in Patients with Brain Metastasis
- Excessively Delayed Radiation Changes After Proton Beam Therapy for Brain Tumors: Report of Two Cases
- A Clinical Analysis of Delayed Radiation Necrosis of the Brain
- Management of symptomatic radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery and clinical factors for treatment response
- Expression of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta1 in the Rat Brain After a Single High-Dose Irradiation