Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2023 Jul;11(3):219-222. 10.14791/btrt.2023.0019.
A Rare Case of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Abscess Mimicking Brain Tumor in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Neurosurgery, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University, Hwaseong, Korea
- 2Departments of Pathology, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University, Hwaseong, Korea
- KMID: 2545110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2023.0019
Abstract
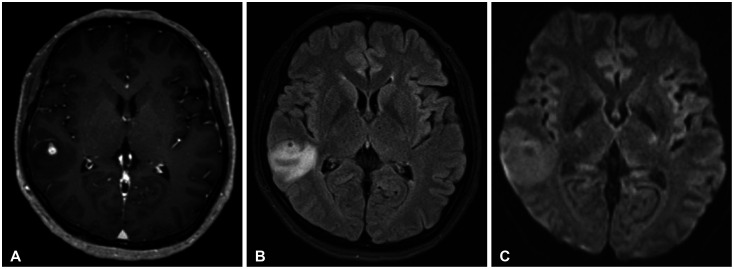
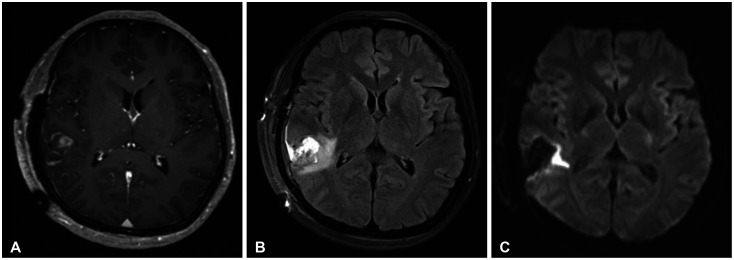
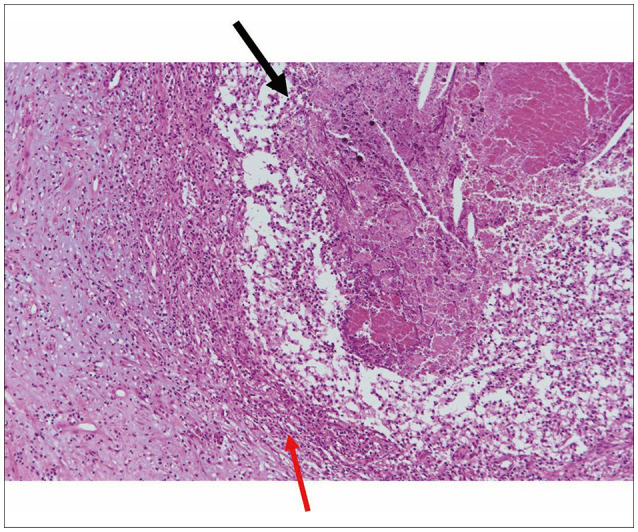
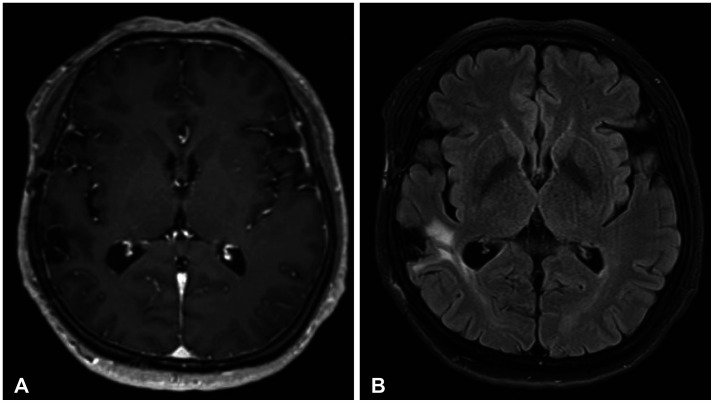
- Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) is a type of bacteria that typically infects the pulmonary system, and NTM–central nervous system (CNS) infection, which occurs in the brain, is a very rare disease. A 64-year-old female patient presented with seizures as the main symptom and was found to have a mass of less than 1 cm in the right temporal lobe with accompanying edema. Although diseases such as tumor metastasis and parasitic cyst were suspected, the patient underwent a surgical resection, and NTM-CNS infection with abscess was diagnosed through biopsy. Antibiotic treatment was initiated after surgery, and the patient has been followed up without any significant symptoms. In this report, we review a rare case of NTM-CNS infection and discuss the understanding and treatment of this disease.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wagner D, Young LS. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections: a clinical review. Infection. 2004; 32:257–270. PMID: 15624889.2. Flor A, Capdevila JA, Martin N, Gavaldà J, Pahissa A. Nontuberculous mycobacterial meningitis: report of two cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 23:1266–1273. PMID: 8953070.3. Cai R, Qi T, Lu H. Central nervous system infection with non-tuberculous mycobacteria: a report of that infection in two patients with AIDS. Drug Discov Ther. 2014; 8:276–279. PMID: 25639308.4. Franco-Paredes C. Infections of the central nervous system caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria. Kon K, Rai M, editors. The microbiology of central nervous system infections. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press;2018. p. 141–147.5. Falkinham JO III. Ecology of nontuberculous mycobacteria. Microorganisms. 2021; 9:2262. PMID: 34835388.6. Shin SH, Jhun BW, Kim SY, Choe J, Jeon K, Huh HJ, et al. Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung diseases caused by mixed infection with Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018; 62:e01105–e01118. PMID: 30104265.7. Lee MR, Cheng A, Lee YC, Yang CY, Lai CC, Huang YT, et al. CNS infections caused by Mycobacterium abscessus complex: clinical features and antimicrobial susceptibilities of isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67:222–225. PMID: 21980068.8. Karne SS, Sangle SA, Kiyawat DS, Dharmashale SN, Kadam DB, Bhardwaj RS. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare brain abscess in HIV-positive patient. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012; 15:54–55. PMID: 22412276.9. Lee KD, Park WB, Jung HS, Kang CI, Kim DM, Kim HB, et al. Mycobacterium avium-intracellularae meningoencephalitis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Infect Chemother. 2003; 35:306–309.10. Talati NJ, Rouphael N, Kuppalli K, Franco-Paredes C. Spectrum of CNS disease caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008; 8:390–398. PMID: 18501854.11. Jarzembowski JA, Young MB. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:1333–1341. PMID: 18684037.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Large Non Healing Ulcer: Non-Tuberculous Mycobacterial Infection of the Laryngopharynx
- Concurrent Nocardia Related Brain Abscess and Semi-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Nocardia Brain Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Recurrent Bilateral Breast Abscess Due to Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection
- Cryptococcal Brainstem Abscess Mimicking Brain Tumors in an Immunocompetent Patient