J Rhinol.
2023 Jul;30(2):125-128. 10.18787/jr.2023.00022.
Pembrolizumab-Induced Nasal Polyposis: The First Reported Case
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, Dublin, Ireland
- KMID: 2544623
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2023.00022
Abstract
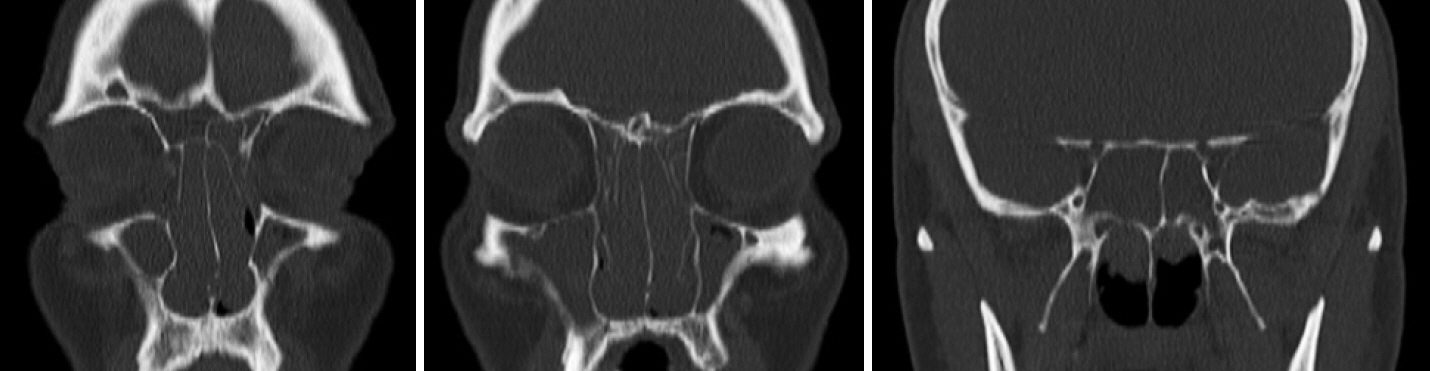
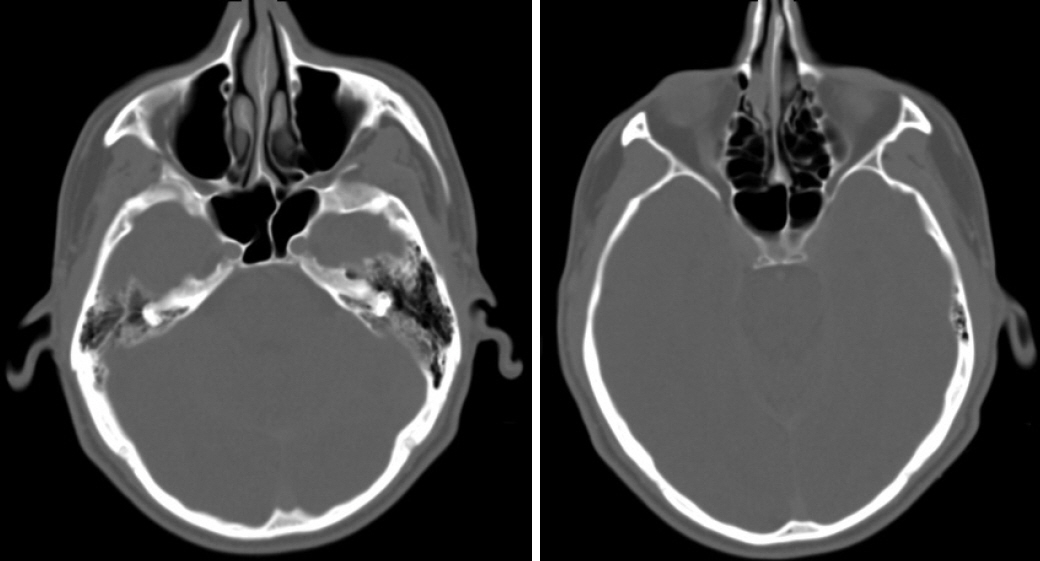
- The last decade has seen the emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of a wide variety of cancer types. While these medications are generally speaking well tolerated, the full long-term side effect profiles of these medications have not been fully elucidated. We describe a case of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis induced treatment with pembrolizumab, the first reported case. We present the case of a 48-year-old man with a background history of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer with bone metastases. He was commenced on pembrolizumab and over the course of the subsequent 5 years he developed significant nasal polyps bilaterally, and was commenced on medical therapy. Sinus CT scan demonstrated bilateral total opacification of all his sinuses and nasal cavity. He subsequently underwent bilateral functional endoscopic sinus surgery. He remains symptom-free and at his last clinical follow-up visit 1 year later. There are limited case reports of nasal polyposis occurring in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, with only one case requiring surgery. We describe the first case of severe nasal polyps due to pembrolizumab and successfully treated with polypectomy. From our review, there were no cases that required a cessation of therapy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Xin Yu J, Hubbard-Lucey VM, Tang J. Immuno-oncology drug development goes global. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019; 18(12):899–900.2. Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N, Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(21):2018–28.3. Friedman CF, Proverbs-Singh TA, Postow MA. Treatment of the immune-related adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2016; 2(10):1346–53.4. Zhou X, Yao Z, Yang H, Liang N, Zhang X, Zhang F. Are immune-related adverse events associated with the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2020; 18(1):87.5. Krane NA, Beswick DM, Sauer D, Detwiller K, Shindo M. Allergic fungal sinusitis imitating an aggressive skull base lesion in the setting of pembrolizumab immunotherapy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2021; 130(1):108–11.6. Kassem F, Rosman Y, Blau I, Nageris B, Zakharov A, Biadsee A. Nivolumab-induced diffuse type 2 rhinosinusitis: a case report. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021; Dec. 26. [Epub]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.12932/AP-240721-1196.7. Dein E, Sharfman W, Kim J, Gellad F, Shah AA, Bingham CO 3rd, et al. Two cases of sinusitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibition. J Immunother. 2017; 40(8):312–4.8. Watanabe H, Asada K, Shirai T, Torii H, Yoshimura K, Kusafuka K. Eosinophilic airway inflammation and eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis during nivolumab and ipilimumab. Respirol Case Rep. 2020; 8(7):e00638.9. Patel GB, Kern RC, Bernstein JA, Hae-Sim P, Peters AT. Current and future treatments of rhinitis and sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020; 8(5):1522–31.10. Jia XH, Geng LY, Jiang PP, Xu H, Nan KJ, Yao Y, et al. The biomarkers related to immune related adverse events caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020; 39(1):284.11. Naidoo J, Wang X, Woo KM, Iyriboz T, Halpenny D, Cunningham J, et al. Pneumonitis in patients treated with anti–programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35(7):709–17.12. Suresh K, Naidoo J, Lin CT, Danoff S. Immune checkpoint immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: benefits and pulmonary toxicities. Chest. 2018; 154(6):1416–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epigenetic Regulation of Nasal Polyp Formation
- A Case of Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome with Nasal Polyposis
- A Case of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyposis Associated with Colonic Hyperplastic Polyposis
- Electrophysiological assessment of the concentration and attention in patient with nasal polyposis
- A Case of Pembrolizumab-Induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis