J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2023 Jun;49(3):125-134. 10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.3.125.
Comparative analysis of craniofacial asymmetry in subjects with and without symptoms of temporomandibular joint disorders: a cross-sectional study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bareilly, India
- KMID: 2544314
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.3.125
Abstract
Objectives
The aim of the study was to quantify and compare craniofacial asymmetry in subjects with and without symptoms of temporomandibular joint disorders (TMDs).
Materials and Methods
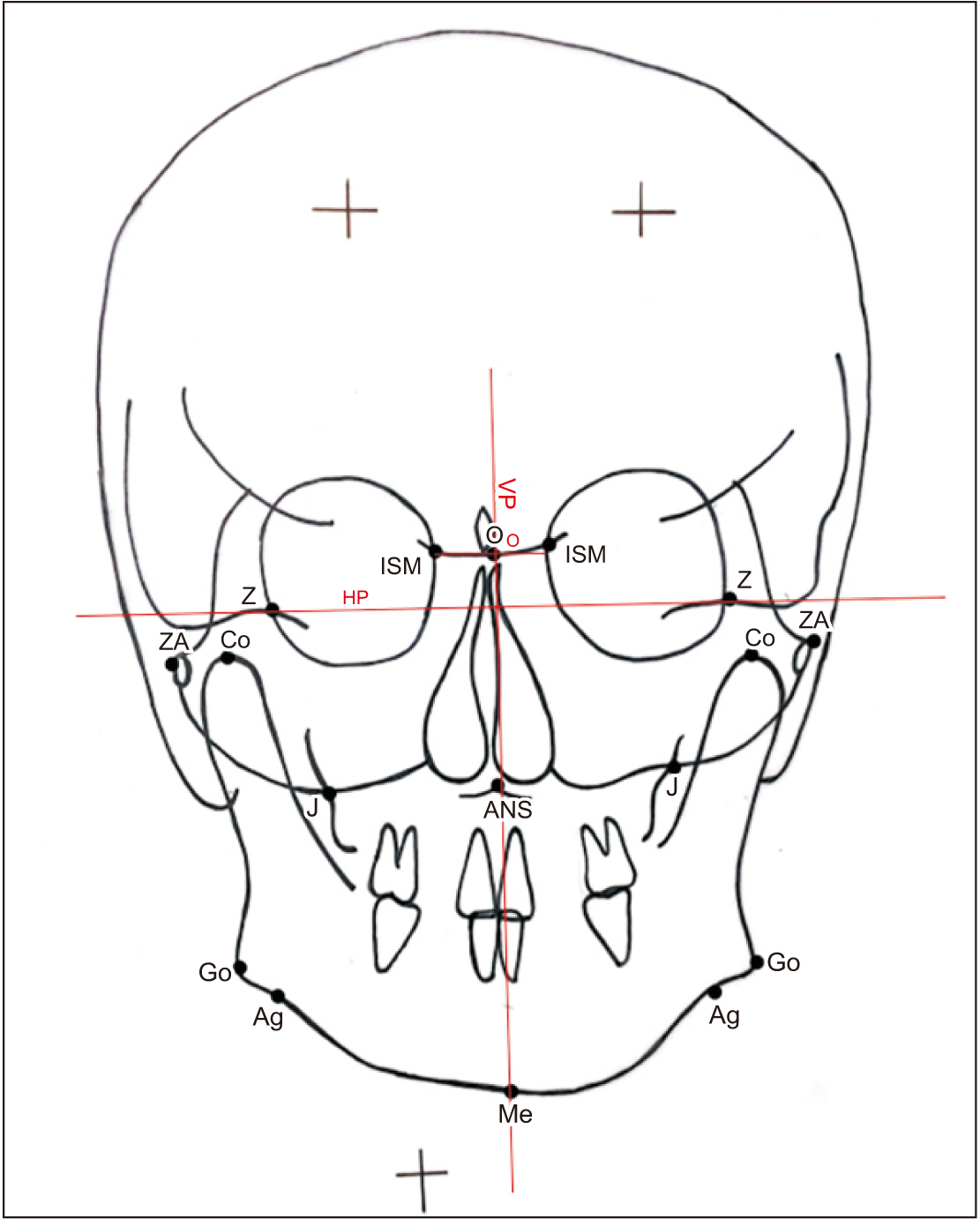
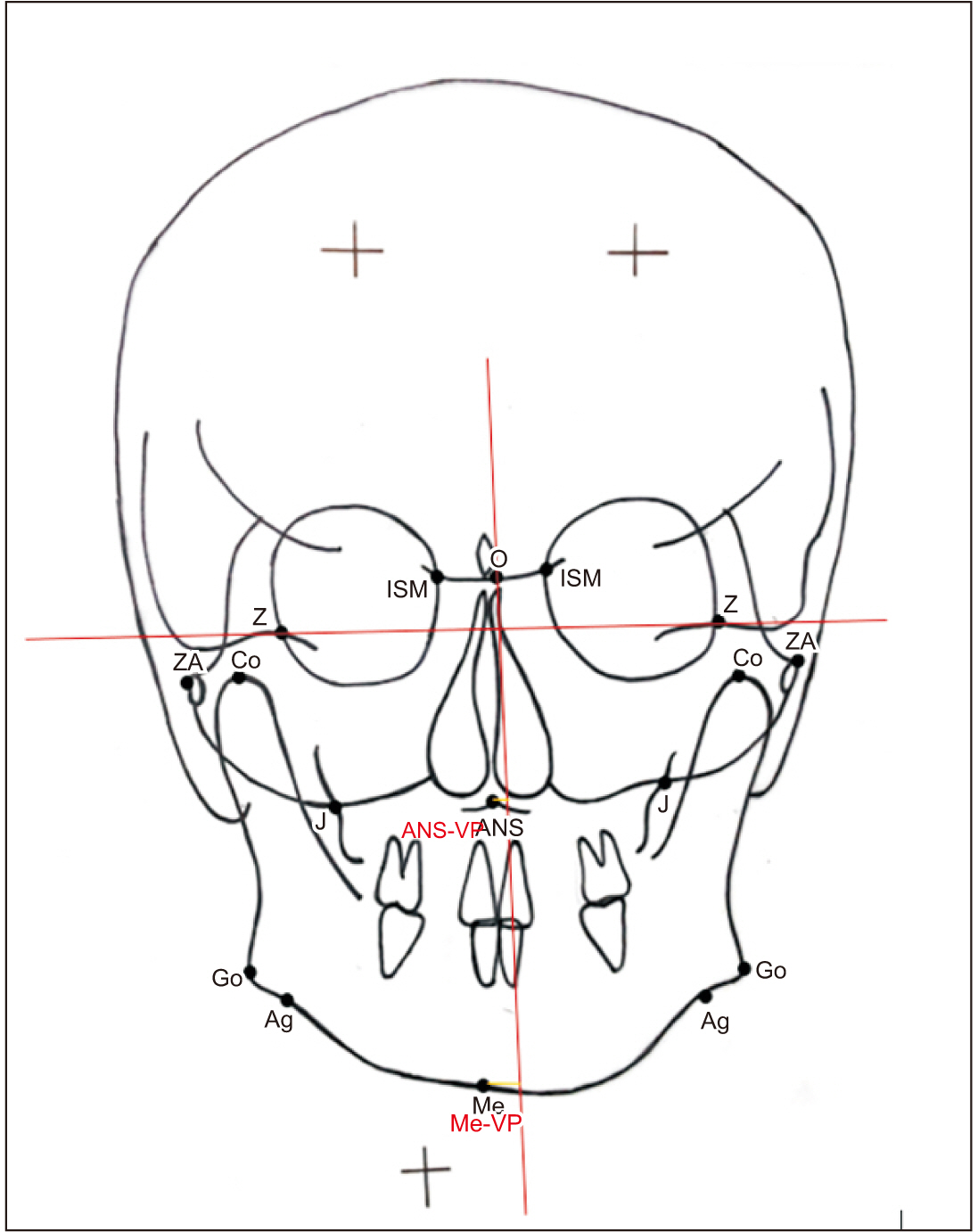
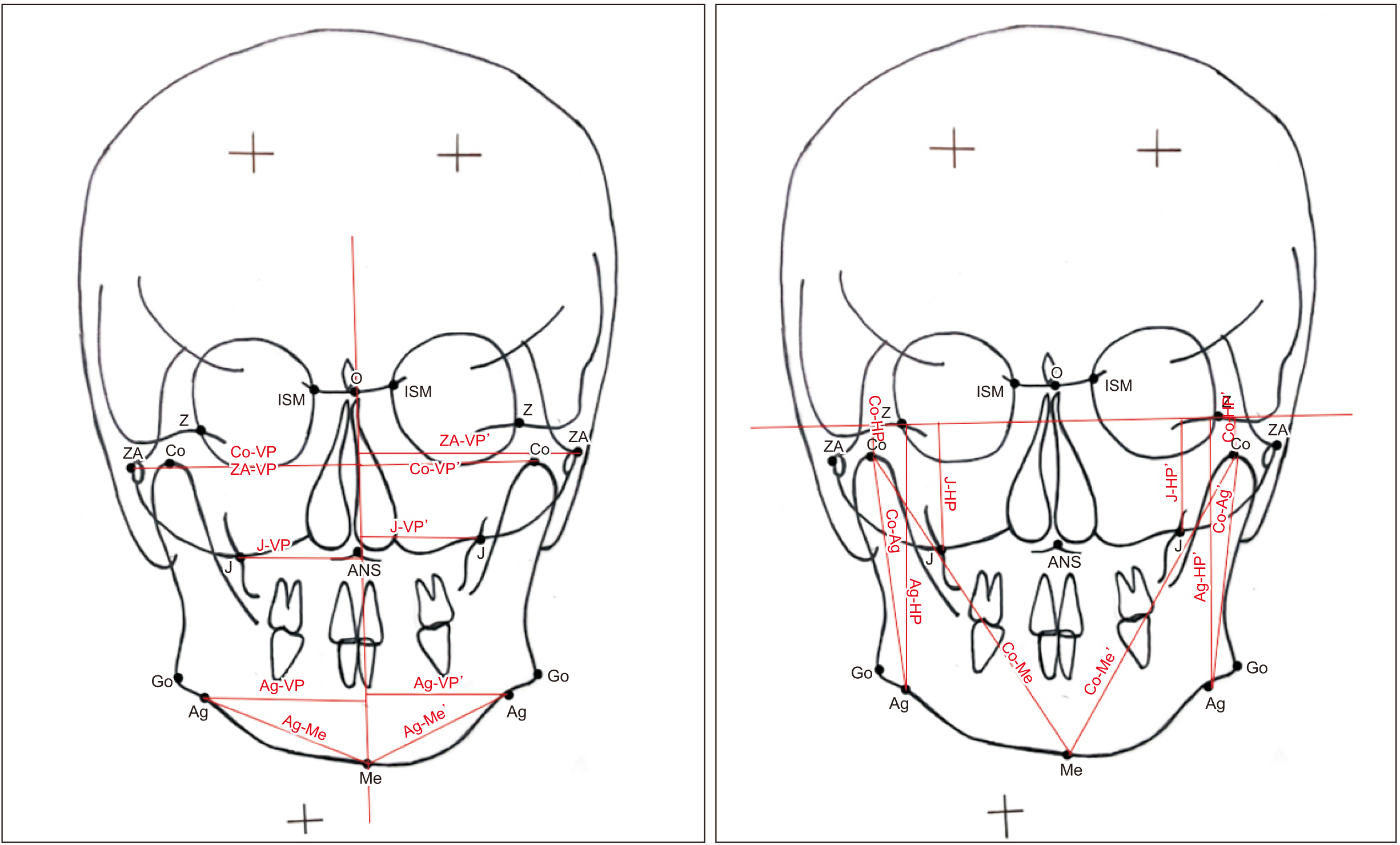
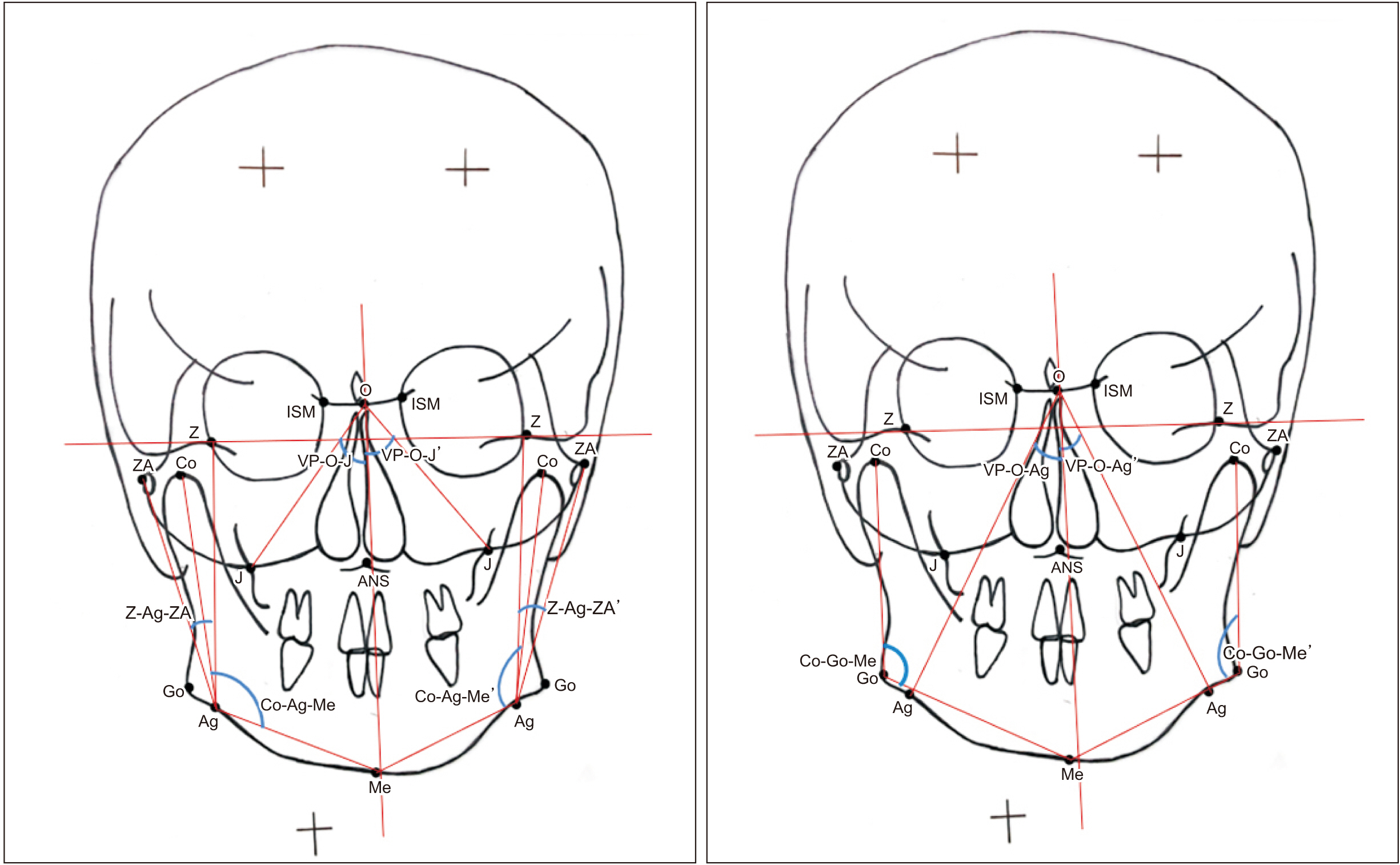
A total of 126 adult subjects were categorized into two groups (63 with a TMDs and 63 without a TMDs), based on detection of symptoms using the Temporomandibular Joint Disorder-Diagnostic Index (TMD-DI) questionnaire. Posteroanterior cephalograms of each subject were traced manually and 17 linear and angular measurements were analyzed. Craniofacial asymmetry was quantified by calculating the asymmetry index (AI) of bilateral parameters for both groups.
Results
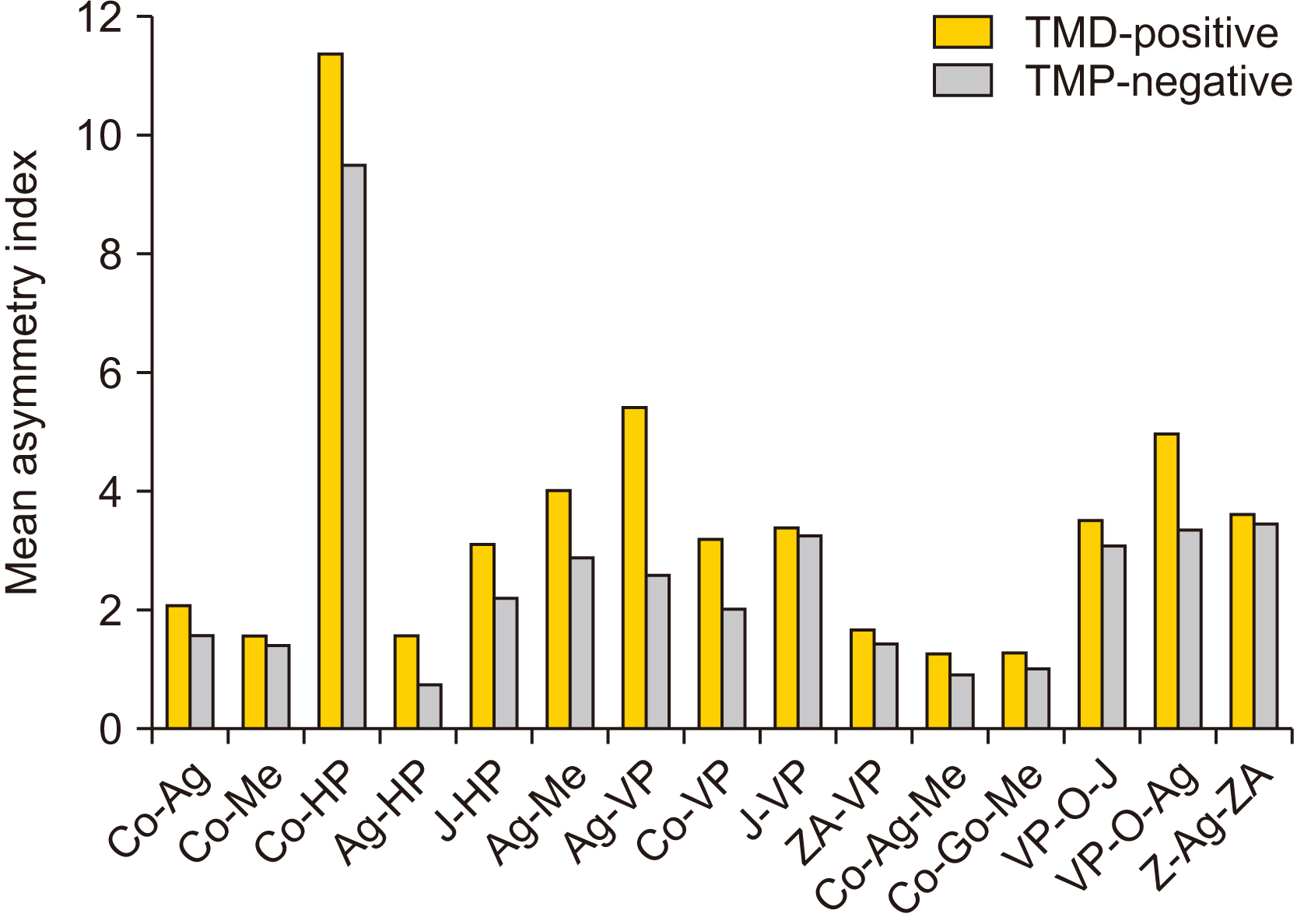
Intra- and intergroup comparisons were analyzed using independent t-test and Mann–Whitney U test, respectively, with a P<0.05 considered statistically significant. An AI for each linear and angular bilateral parameter was calculated; higher asymmetry was found in TMD-positive patients compared with TMD-negative patients. An intergroup comparison of AIs found highly significant differences for the parameters of antegonial notch to horizontal plane distance, jugular point to horizontal plane distance, antegonial notch to menton distance, antegonial notch to vertical plane distance, condylion to vertical plane distance, and angle formed by vertical plane, O point and antegonial notch. Significant deviation of the menton distance from the facial midline was also evident.
Conclusion
Greater facial asymmetry was seen in the TMD-positive group compared with the TMD-negative group. The mandibular region was characterized by asymmetries of greater magnitude compared with the maxilla. Patients with facial asymmetry often require management of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pathology to achieve a stable, functional, and esthetic result. Ignoring the TMJ during treatment or failing to provide proper management of the TMJ and performing only orthognathic surgery may result in worsening of TMJ-associated symptoms (jaw dysfunction and pain) and re-occurrence of asymmetry and malocclusion. Assessments of facial asymmetry should take into account TMJ disorders to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ryu SH, Chang HH. 2005; A study on usefulness of the reference line in diagnosis of the facial asymmetry. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 31:266–73.2. Trpkova B, Major P, Nebbe B, Prasad N. 2000; Craniofacial asymmetry and temporomandibular joint internal derangement in female adolescents: a posteroanterior cephalometric study. Angle Orthod. 70:81–8. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2000)070%3C0081:caatji%3E2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2000)070<0081:CAATJI>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 10730679.
Article3. Rajpara Y, Shyagali TR, Trivedi K, Kambalyal P, Sha T, Jain V. 2014; Evaluation of facial asymmetry in esthetically pleasing faces. J Orthod Res. 2:79–84. https://doi.org/10.4103/2321-3825.131118. DOI: 10.4103/2321-3825.131118.
Article4. Joshi H, Mehta F, Kumar A, Laddha S, Gandhi V. 2017; An assessment of skeletal craniofacial asymmetry in Gujarati population: an autocad study. IP Indian J Orthod Dentofacial Res. 3:148–53.5. Sofyanti E, Boel T, Soegiharto B, Auerkari EI. 2018; TMD symptoms and vertical mandibular symmetry in young adult orthodontic patients in North Sumatra, Indonesia: a cross-sectional study. F1000Res. 7:697. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.14522.2. DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.14522.2. PMID: 29946446. PMCID: PMC5998004.
Article6. Thilander B, Rubio G, Pena L, de Mayorga C. 2002; Prevalence of temporomandibular dysfunction and its association with malocclusion in children and adolescents: an epidemiologic study related to specified stages of dental development. Angle Orthod. 72:146–54. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2002)072%3C0146:potdai%3E2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2002)072<0146:POTDAI>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 11999938.
Article7. Srivastava D, Singh H, Mishra S, Sharma P, Kapoor P, Chandra L. 2018; Facial asymmetry revisited: part I- diagnosis and treatment planning. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 8:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2017.04.010. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2017.04.010. PMID: 29556456. PMCID: PMC5854562.
Article8. Himawan LS, Kusdhany L, Ismail I. 2006; Diagnostic index for temporomandibular disorders in Indonesia. Thai J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 20(2):104–10.9. Ricketts RM, Grummons D. 2003; Frontal cephalometrics: practical applications, part 1. World J Orthod. 4:297–316.10. Grummons DC. Kappeyne van de Coppello MA. 1987; A frontal asymmetry analysis. J Clin Orthod. 21:448–65. PMID: 3476493.11. Reyneke JP. 2010. Essentials of orthognathic surgery. 2nd ed. Quintessence Publishing;Hanover Park (IL):12. Habets LL, Bezuur JN, van Ooij CP, Hansson TL. 1987; The orthopantomogram, an aid in diagnosis of temporomandibular joint problems. I. The factor of vertical magnification. J Oral Rehabil. 14:475–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2842.1987.tb00742.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1987.tb00742.x. PMID: 3478455.
Article13. Habets LL, Bezuur JN, Naeiji M, Hansson TL. 1988; The Orthopantomogram, an aid in diagnosis of temporomandibular joint problems. II. The vertical symmetry. J Oral Rehabil. 15:465–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2842.1988.tb00182.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1988.tb00182.x. PMID: 3244055.
Article14. Tseng YC, Yang YH, Pan CY, Chou ST, Ou KC, Chang HP. 2014; Treatment of adult facial asymmetry with orthodontic therapy or orthognathic surgery: receiver operating characteristic analysis. J Dent Sci. 9:235–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jds.2013.03.007. DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2013.03.007.
Article15. D'Ippolito S, Ursini R, Giuliante L, Deli R. 2014; Correlations between mandibular asymmetries and temporomandibular disorders (TMD). Int Orthod. 12:222–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ortho.2014.03.013. DOI: 10.1016/j.ortho.2014.03.013. PMID: 24820702.16. Almăşan OC, Băciuţ M, Hedeşiu M, Bran S, Almăşan H, Băciuţ G. 2013; Posteroanterior cephalometric changes in subjects with temporomandibular joint disorders. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 42:20120039. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20120039. DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20120039. PMID: 23253565. PMCID: PMC3729188.
Article17. Saglam AA, Sanli G. 2004; Condylar asymmetry measurements in patients with temporomandibular disorders. J Contemp Dent Pract. 5:59–65. DOI: 10.5005/jcdp-5-3-59. PMID: 15318257.
Article18. Kambylafkas P, Kyrkanides S, Tallents RH. 2005; Mandibular asymmetry in adult patients with unilateral degenerative joint disease. Angle Orthod. 75:305–10. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[305:maiapw]2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[305:MAIAPW]2.0.CO;2. PMID: 15898365.
Article19. Singer CP, Mamandras AH, Hunter WS. 1987; The depth of the mandibular antegonial notch as an indicator of mandibular growth potential. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 91:117–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/0889-5406(87)90468-9. DOI: 10.1016/0889-5406(87)90468-9. PMID: 3468794.
Article20. Egermark I, Carlsson GE, Magnusson T. 2005; A prospective long-term study of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in patients who received orthodontic treatment in childhood. Angle Orthod. 75:645–50. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2005)75[645:aplsos]2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1016/s0084-3717(08)70510-5. PMID: 16097235.
Article21. Lee KM, Hwang HS, Cho JH. 2014; Comparison of transverse analysis between posteroanterior cephalogram and cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 84:715–9. https://doi.org/10.2319/072613-555.1. DOI: 10.2319/072613-555.1. PMID: 24325622. PMCID: PMC8650435.
Article22. Tai B, Goonewardene MS, Murray K, Koong B, Islam SM. 2014; The reliability of using postero-anterior cephalometry and cone-beam CT to determine transverse dimensions in clinical practice. Aust Orthod J. 30:132–42. PMID: 25549515.23. Vig PS, Hewitt AB. 1975; Asymmetry of the human facial skeleton. Angle Orthod. 45:125–9. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1975)045%3C0125:aothfs%3E2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(1975)045<0125:AOTHFS>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 1054939.
Article24. Nicot R, Chung K, Vieira AR, Raoul G, Ferri J, Sciote JJ. 2020; Condyle modeling stability, craniofacial asymmetry and ACTN3 genotypes: contribution to TMD prevalence in a cohort of dentofacial deformities. PLoS One. 15:e0236425. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236425. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236425. PMID: 32726330. PMCID: PMC7390436.
Article25. Sunitha S, Mahesh KP, Patil K. 2016; Posteroanterior cephalometric analysis of facial asymmetry in temporomandibular joint disorders. Int J Curr Res. 8:27651–5.26. Legrell PE, Nyquist H, Isberg A. 2000; Validity of identification of gonion and antegonion in frontal cephalograms. Angle Orthod. 70:157–64. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2000)070%3C0157:voioga%3E2.0.co;2. DOI: 10.1043/0003-3219(2000)070<0157:VOIOGA>2.0.CO;2. PMID: 10833005.
Article27. Vig KW, Fields HW. 2000; Facial growth and management of orthodontic problems. Pediatr Clin North Am. 47:1085–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70259-5. DOI: 10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70259-5. PMID: 11059351.
Article28. Boel T, Sofyanti E, Sufarnap E. 2017; Analyzing menton deviation in posteroanterior cephalogram in early detection of temporomandibular disorder. Int J Dent. 2017:5604068. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5604068. DOI: 10.1155/2017/5604068. PMID: 28845159. PMCID: PMC5563424.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Rare Case of Solitary Osteochondroma at the Temporomandibular Joint: A Case Report
- One-stage total reconstruction of temporomandibular joint ankylosis and facial asymmetry
- Considerations in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Temporomandibular Disorders in Children and Adolescents: A Review
- Changes of temporomandiular joint symptoms after orthognathic surgery in the asymmetric prognathism patients
- A study on simultation of the mandibular movement of the patients with temporomandibular joint disorder