Korean J Pain.
2023 Jul;36(3):272-280. 10.3344/kjp.23175.
Coccydynia: anatomic origin and considerations regarding the effectiveness of injections for pain management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 2Jesaeng-Euise Clinical Anatomy Center, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 3Sarcopenia Total Solution Center, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea
- KMID: 2544240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.23175
Abstract
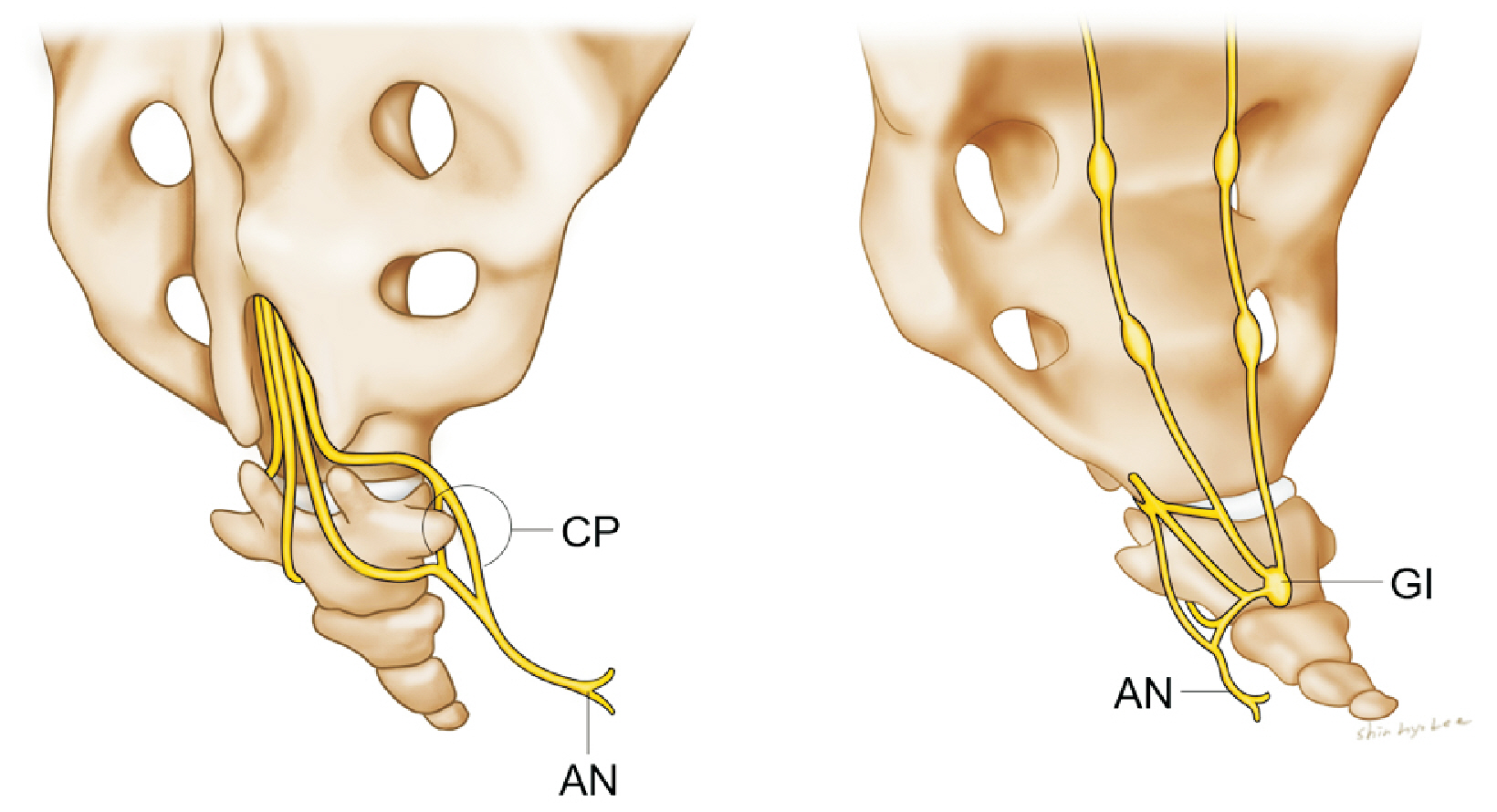
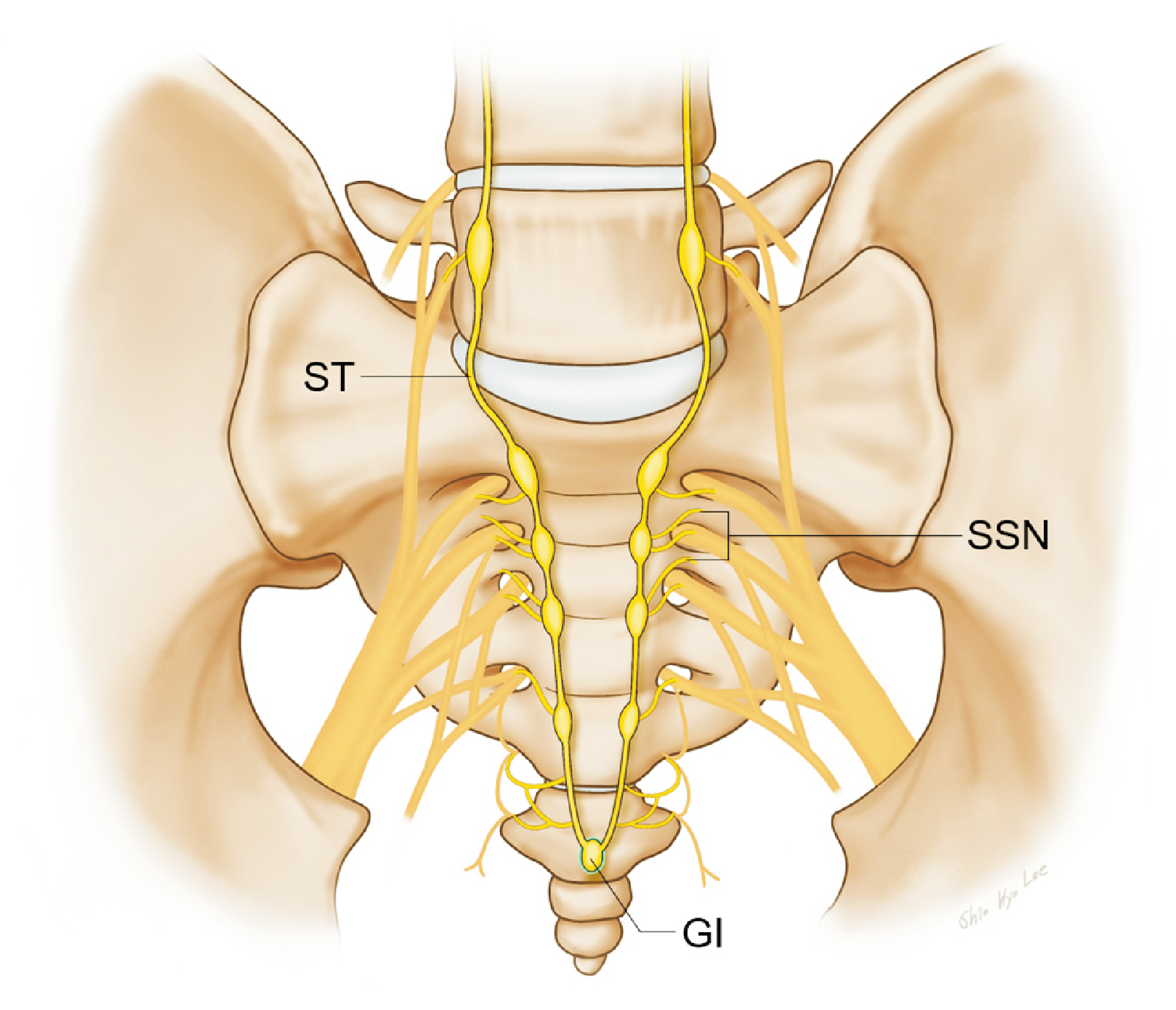
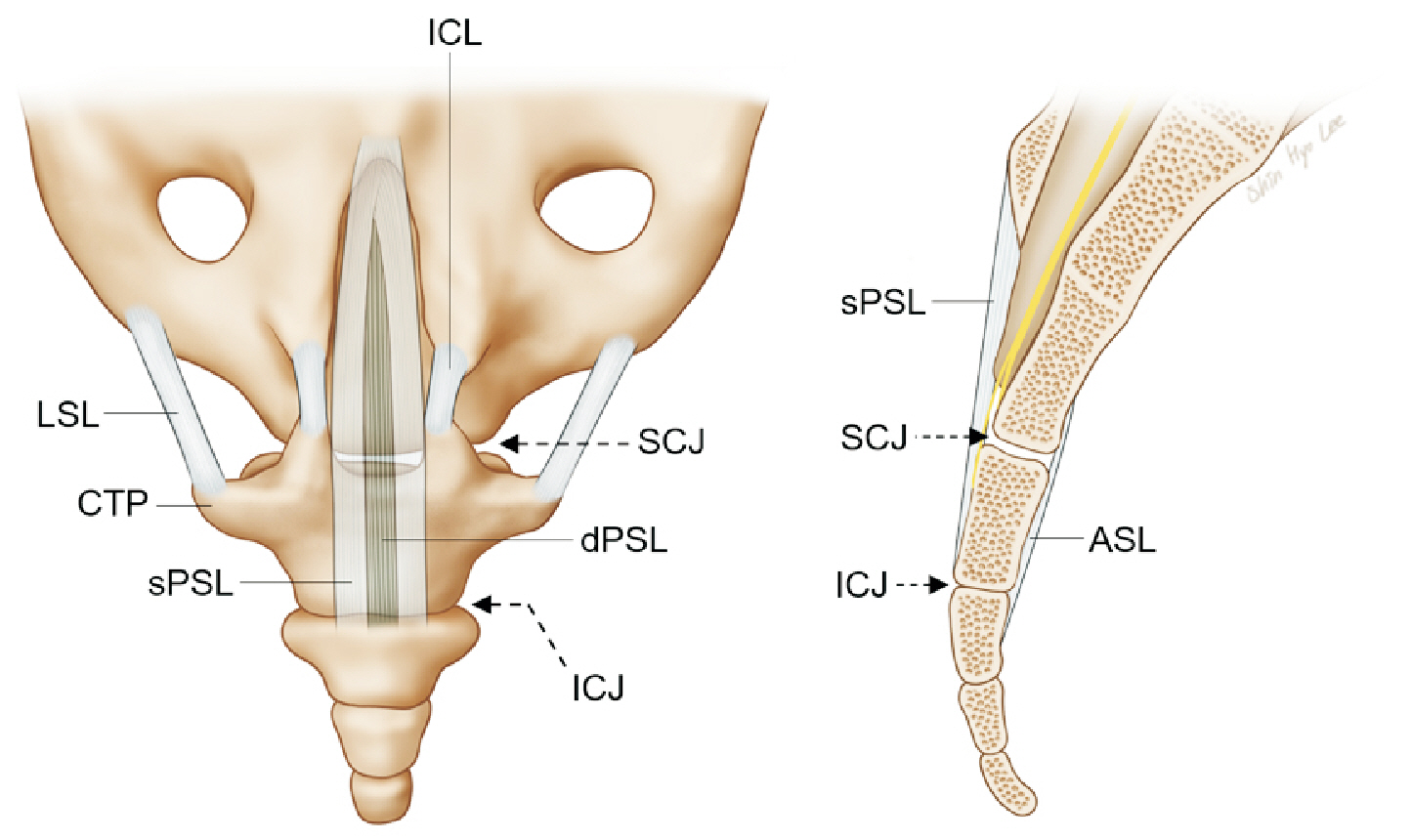
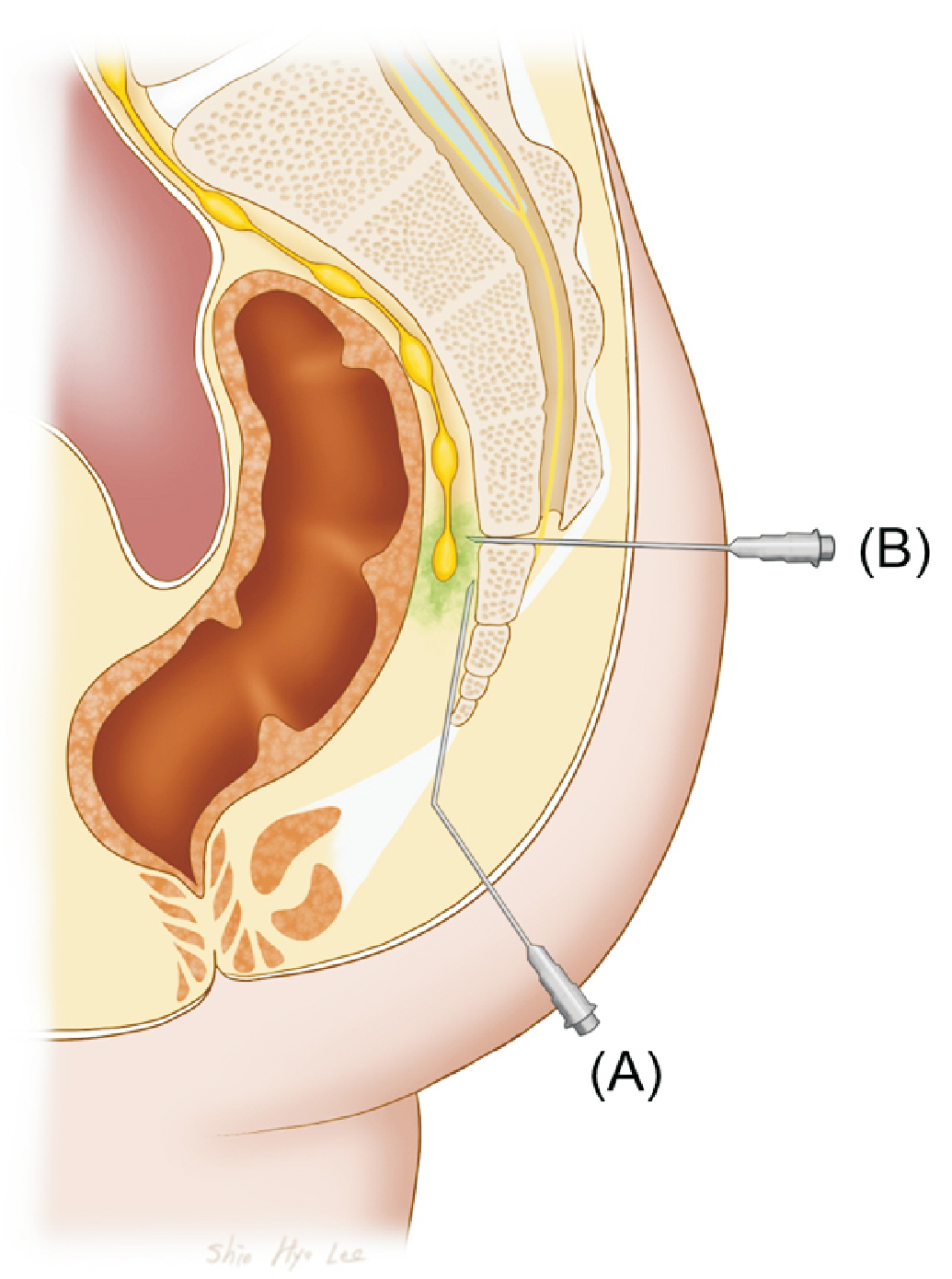
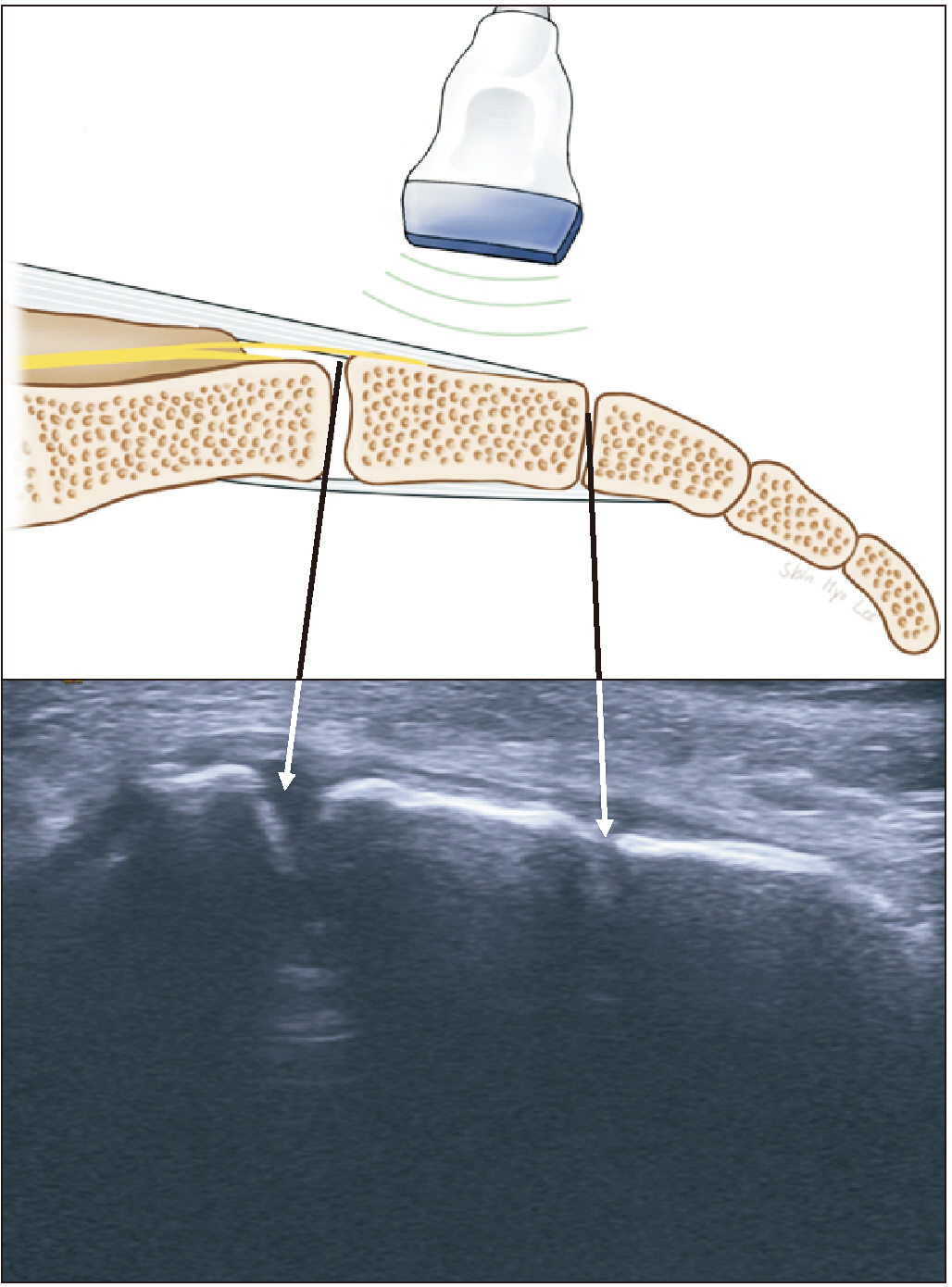
- Coccydynia is a debilitating pain disorder. However, its pathophysiology is not well understood. When approaching coccydynia, the exact underlying cause of pain must be identified to develop an appropriate treatment plan. The specific approach to coccydynia can vary depending on an individual's condition and the underlying cause. Thorough evaluation by a pain physician is essential to determine the most appropriate course of treatment. The purpose of this review is to examine the various causes contributing to coccygeal pain and specifically focus on the exact anatomical neurostructures, such as the anococcygeal nerve, perforating cutaneous nerve, and ganglion impar. We also reviewed the relevant clinical outcomes and suggested recommendations for each anatomical structure.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V, Cohen R, Gallacher D. 2006; Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain. 10:287–333. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.06.009. PMID: 16095934.
Article2. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Datta S, Cohen SP, Hirsch JA. American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians. 2009; Comprehensive review of epidemiology, scope, and impact of spinal pain. Pain Physician. 12:E35–70. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2009/12/E35. PMID: 19668291.3. Carey TS, Garrett J, Jackman A, McLaughlin C, Fryer J, Smucker DR. 1995; The outcomes and costs of care for acute low back pain among patients seen by primary care practitioners, chiropractors, and orthopedic surgeons. The North Carolina Back Pain Project. N Engl J Med. 333:913–7. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199510053331406. PMID: 7666878.
Article4. Kim YD, Moon HS. 2015; Review of medical dispute cases in the pain management in Korea: a medical malpractice liability insurance database study. Korean J Pain. 28:254–64. Erratum in: Korean J Pain 2016; 29: 62. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.4.254. PMID: 26495080. PMCID: PMC4610939.
Article5. Romanes GJ. 1981. Cunningham's textbook of anatomy. 12th ed. Oxford University Press;p. 797–806.6. Berry M, Standring SM, Bannister LH. Williams PL, editor. 1995. Nervous system. Gray's anatomy. 38th ed. Churchill Livingstone;p. 901–1397. DOI: 10.37019/e-anatomy/49576.7. O'Rahilly R, Müller F, Meyer DB. 1990; The human vertebral column at the end of the embryonic period proper. 4. The sacrococcygeal region. J Anat. 168:95–111. PMID: 2182589. PMCID: PMC1256893.8. Pearson AA, Sauter RW, Buckley TF. 1966; Further observations on the cutaneous branches of the dorsal primary rami of the spinal nerves. Am J Anat. 118:891–903. DOI: 10.1002/aja.1001180313. PMID: 4163167.
Article9. Oh CS, Chung IH, Ji HJ, Yoon DM. 2004; Clinical implications of topographic anatomy on the ganglion impar. Anesthesiology. 101:249–50. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200407000-00039. PMID: 15220800.
Article10. Woon JT, Stringer MD. 2012; Clinical anatomy of the coccyx: a systematic review. Clin Anat. 25:158–67. DOI: 10.1002/ca.21216. PMID: 21739475.
Article11. Sugar O. 1995; Coccyx. The bone named for a bird. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:379–83. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199502000-00024. PMID: 7732478.12. Soames RW. Williams PL, editor. 1995. Skeletal system. Gray's anatomy. 38th ed. Churchill Livingstone;p. 425–711. DOI: 10.1308/rcsann.2006.88.4.425a.13. Maigne JY, Guedj S, Straus C. 1994; Idiopathic coccygodynia. Lateral roentgenograms in the sitting position and coccygeal discography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 19:930–4. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199404150-00011. PMID: 8009351.
Article14. Simpson JY. 1859; Clinical lectures on the diseases of women. Lecture XVII: on coccydynia and diseases and deformities of the coccyx. Med Times Gaz. 40:1–7.15. Foye PM. 2010; Stigma against patients with coccyx pain. Pain Med. 11:1872. DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2010.00999.x. PMID: 21134124.
Article16. Ghormley RK. 1958; An etiologic study of back pain. Radiology. 70:649–53. DOI: 10.1148/70.5.649. PMID: 13554831.
Article17. Pennekamp PH, Kraft CN, Stütz A, Wallny T, Schmitt O, Diedrich O. 2005; Coccygectomy for coccygodynia: does pathogenesis matter? J Trauma. 59:1414–9. DOI: 10.1097/01.ta.0000195878.50928.3c. PMID: 16394915.
Article18. Foye PM. 2017; Coccydynia: tailbone pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 28:539–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmr.2017.03.006. PMID: 28676363.19. Przybylski P, Pankowicz M, Boćkowska A, Czekajska-Chehab E, Staśkiewicz G, Korzec M, et al. 2013; Evaluation of coccygeal bone variability, intercoccygeal and lumbo-sacral angles in asymptomatic patients in multislice computed tomography. Anat Sci Int. 88:204–11. DOI: 10.1007/s12565-013-0181-2. PMID: 23700101.
Article20. Postacchini F, Massobrio M. 1983; Idiopathic coccygodynia. Analysis of fifty-one operative cases and a radiographic study of the normal coccyx. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 65:1116–24. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-198365080-00011. PMID: 6226668.
Article21. Woon JT, Maigne JY, Perumal V, Stringer MD. 2013; Magnetic resonance imaging morphology and morphometry of the coccyx in coccydynia. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:E1437–45. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a45e07. PMID: 23917643.
Article22. Doursounian L, Maigne JY, Jacquot F. 2015; Coccygectomy for coccygeal spicule: a study of 33 cases. Eur Spine J. 24:1102–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-014-3753-5. PMID: 25559295.
Article23. Nathan ST, Fisher BE, Roberts CS. 2010; Coccydynia: a review of pathoanatomy, aetiology, treatment and outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 92:1622–7. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.92B12.25486. PMID: 21119164.24. Patijn J, Janssen M, Hayek S, Mekhail N, Van Zundert J, van Kleef M. 2010; 14. Coccygodynia. Pain Pract. 10:554–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2010.00404.x. PMID: 20825565.25. Thiele GH. 1963; Coccygodynia: cause and treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 6:422–36. DOI: 10.1007/BF02633479. PMID: 14082980.26. Lirette LS, Chaiban G, Tolba R, Eissa H. 2014; Coccydynia: an overview of the anatomy, etiology, and treatment of coccyx pain. Ochsner J. 14:84–7. PMID: 24688338. PMCID: PMC3963058.27. De Andres J, Chaves S. 2003; Coccygodynia: a proposal for an algorithm for treatment. J Pain. 4:257–66. DOI: 10.1016/S1526-5900(03)00620-5. PMID: 14622695.
Article28. Won HS, Yang M, Kim YD. 2020; Facet joint injections for management of low back pain: a clinically focused review. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 15:8–18. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.8. PMID: 33329784. PMCID: PMC7713865. PMID: 63f25c93e64244039e30bd124e2632a0.
Article29. Bayne O, Bateman JE, Cameron HU. 1984; The influence of etiology on the results of coccygectomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 190:266–72. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-198411000-00047.
Article30. Perkins R, Schofferman J, Reynolds J. 2003; Coccygectomy for severe refractory sacrococcygeal joint pain. J Spinal Disord Tech. 16:100–3. DOI: 10.1097/00024720-200302000-00016. PMID: 12571492.
Article31. Balain B, Eisenstein SM, Alo GO, Darby AJ, Cassar-Pullicino VN, Roberts SE, et al. 2006; Coccygectomy for coccydynia: case series and review of literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:E414–20. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000219867.07683.7a. PMID: 16741442.
Article32. Trollegaard AM, Aarby NS, Hellberg S. 2010; Coccygectomy: an effective treatment option for chronic coccydynia: retrospective results in 41 consecutive patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 92:242–5. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.92B2.23030. PMID: 20130316.33. Datir A, Connell D. 2010; CT-guided injection for ganglion impar blockade: a radiological approach to the management of coccydynia. Clin Radiol. 65:21–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2009.08.007. PMID: 20103417.
Article34. Foye PM, Buttaci CJ, Stitik TP, Yonclas PP. 2006; Successful injection for coccyx pain. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 85:783–4. DOI: 10.1097/01.phm.0000233174.86070.63. PMID: 16924191.
Article35. Govardhani Y, RamMohan G, Abhijith S, Savithri B. 2021; A comparative retrospective study of the efficacy of caudal epidural with manipulation versus ganglion impar block with manipulation in patients with coccydynia. Indian J Pain. 35:42–5. DOI: 10.4103/ijpn.ijpn_152_20. PMID: 78f2d87aab1945a68dcc81410440728f.
Article36. Sencan S, Yolcu G, Bilim S, Kenis-Coskun O, Gunduz OH. 2022; Comparison of treatment outcomes in chronic coccygodynia patients treated with ganglion impar blockade versus caudal epidural steroid injection: a prospective randomized comparison study. Korean J Pain. 35:106–13. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.1.106. PMID: 34966017. PMCID: PMC8728552.
Article37. Yamada K, Ishihara Y, Saito T. 1994; Relief of intractable perineal pain by coccygeal nerve block in anterior sacrococcygeal ligament after surgery for rectal cancer. J Anesth. 8:52–4. DOI: 10.1007/BF02482755. PMID: 28921200.
Article38. Alimehmeti RH, Schuenke MD, Dellon AL. 2022; Anococcygeal nerve and sitting pain: differential diagnosis and treatment results. Ann Plast Surg. 88:79–83. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002920. PMID: 34670963.39. Lema MJ. 2001; Invasive analgesia techniques for advanced cancer pain. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 10:127–36. DOI: 10.1016/S1055-3207(18)30089-9. PMID: 11406455.
Article40. Toshniwal GR, Dureja GP, Prashanth SM. 2007; Transsacrococcygeal approach to ganglion impar block for management of chronic perineal pain: a prospective observational study. Pain Physician. 10:661–6. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2007/10/661. PMID: 17876362.41. Gunduz OH, Kenis-Coskun O. 2017; Ganglion blocks as a treatment of pain: current perspectives. J Pain Res. 10:2815–26. DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S134775. PMID: 29276402. PMCID: PMC5734237.
Article42. Day M. 2008; Sympathetic blocks: the evidence. Pain Pract. 8:98–109. DOI: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2008.00177.x. PMID: 18366465.
Article43. Munir MA, Zhang J, Ahmad M. 2004; A modified needle-inside-needle technique for the ganglion impar block. Can J Anaesth. 51:915–7. DOI: 10.1007/BF03018890. PMID: 15525617.
Article44. Ho KY, Nagi PA, Gray L, Huh BK. 2006; An alternative approach to ganglion impar neurolysis under computed tomography guidance for recurrent vulva cancer. Anesthesiology. 105:861–2. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200610000-00048. PMID: 17006101.
Article45. Mitra R, Cheung L, Perry P. 2007; Efficacy of fluoroscopically guided steroid injections in the management of coccydynia. Pain Physician. 10:775–8. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2007/10/775. PMID: 17987101.46. Wray CC, Easom S, Hoskinson J. 1991; Coccydynia. Aetiology and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 73:335–8. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.73B2.2005168. PMID: 2005168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulsed Radiofrequency as a Treatment for Coccydynia; A case report
- Orofacial Pain and Nonodotogenic Toothache of Cardiac Origin: Case Report
- Spinal epiduroscopy as an educational tool
- In Response to Risks and Pitfalls of Epidural Injections during Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation: Few Comments
- Are steroids required in the treatment of ganglion impar blockade in chronic coccydynia? a prospective double-blinded clinical trial