J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Jun;38(24):e186. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e186.
Predictive Value of Electromechanical Window for Risk of Fatal Ventricular Arrhythmia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2543975
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e186
Abstract
- Background
As an indicator of electro-mechanical coupling, electromechanical window (EMW) can be used to predict fatal ventricular arrhythmias. We investigated the additive effect of EMW on the prediction of fatal ventricular arrhythmias in high-risk patients.
Methods
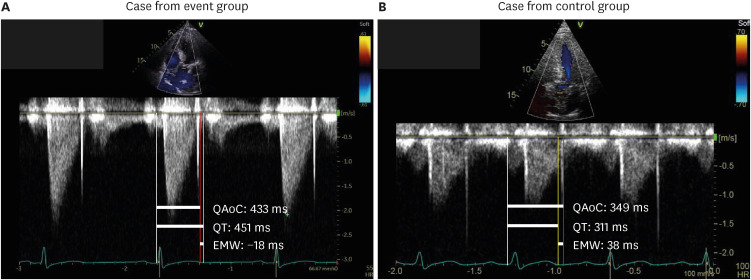
We included patients who had implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) implanted for primary or secondary prevention. The event group was defined as those who received an appropriate ICD therapy. We acquired echocardiograms at ICD implantation and follow-up. The EMW was calculated as the difference between the interval from QRS onset to aortic valve closure and QT interval from the electrocardiogram embedded in the continuous wave doppler image. We evaluated the predictive value of EMW for predicting fatal ventricular arrhythmia.
Results
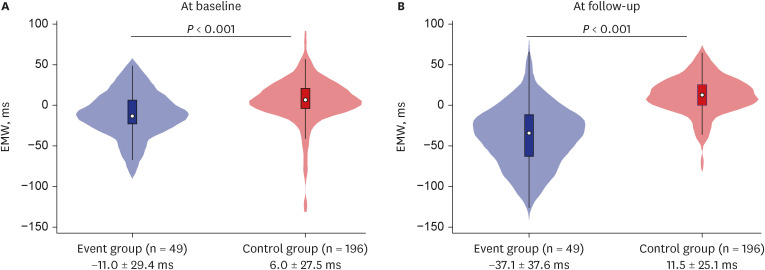
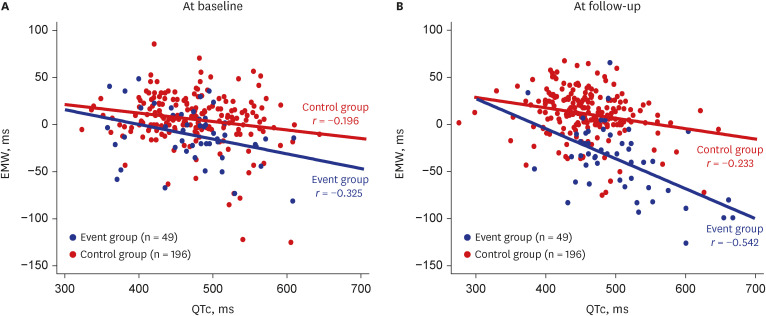
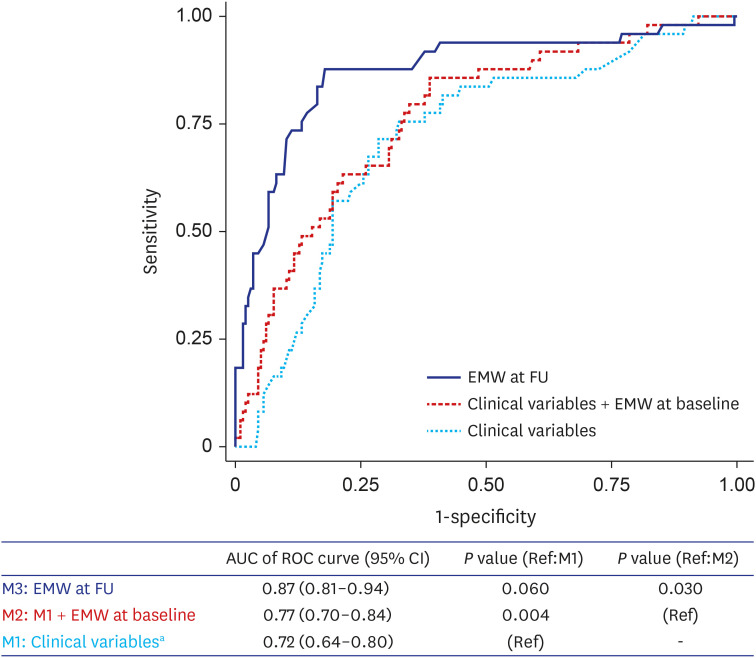
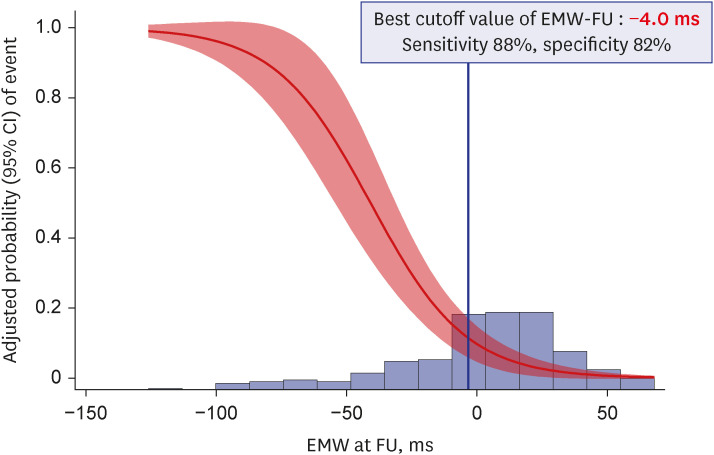
Of 245 patients (67.2 ± 12.8 years, 63.7% men), the event group was 20.0%. EMW at baseline (EMW-Baseline) and follow-up (EMW-FU) was significantly different between event and control groups. After adjustment, both EMW-Baseline (odds ratio [OR]adjust 1.02 [1.01– 1.03], P = 0.004) and EMW-FU (ORadjust 1.06 [1.04–1.07], P < 0.001) remained as significant predictors for fatal arrhythmic events. Adding EMW-Baseline significantly improved the discriminating ability of the multivariable model including clinical variables (area under the curve [AUC] 0.77 [0.70–0.84] vs. AUC 0.72 [0.64–0.80], P = 0.004), while a univariable model using EMW-FU alone showed the best performance among models (AUC 0.87 [0.81– 0.94], P = 0.060 against model with clinical variables; P = 0.030 against model with clinical variables and EMW-Baseline).
Conclusion
The EMW could effectively predict severe ventricular arrhythmia in ICD implanted patients. This finding supports the importance of incorporating the electro-mechanical coupling index into the clinical practice for predicting future fatal arrhythmia events.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sugrue A, van Zyl M, Enger N, Mancl K, Eidem BW, Oh JK, et al. Echocardiography-guided risk stratification for long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 76(24):2834–2843. PMID: 33303072.2. Priori SG, Napolitano C, Schwartz PJ, Grillo M, Bloise R, Ronchetti E, et al. Association of long QT syndrome loci and cardiac events among patients treated with β-blockers. JAMA. 2004; 292(11):1341–1344. PMID: 15367556.3. Hobbs JB, Peterson DR, Moss AJ, McNitt S, Zareba W, Goldenberg I, et al. Risk of aborted cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death during adolescence in the long-QT syndrome. JAMA. 2006; 296(10):1249–1254. PMID: 16968849.4. ter Bekke RM, Haugaa KH, van den Wijngaard A, Bos JM, Ackerman MJ, Edvardsen T, et al. Electromechanical window negativity in genotyped long-QT syndrome patients: relation to arrhythmia risk. Eur Heart J. 2015; 36(3):179–186. PMID: 25205533.5. Song MK, Baek SM, Kim GB, Lee SY, Kwon HW, Lee HJ, et al. Relationship between life-threatening events and electromechanical window in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a novel parameter for risk stratification of sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm. 2022; 19(4):588–594. PMID: 34933113.6. Guns PJ, Johnson DM, Weltens E, Lissens J. Negative electro-mechanical windows are required for drug-induced Torsades de Pointes in the anesthetized guinea pig. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2012; 66(2):125–134. PMID: 22516473.7. Liu X. Classification accuracy and cut point selection. Stat Med. 2012; 31(23):2676–2686. PMID: 22307964.8. Malik M, Batchvarov VN. Measurement, interpretation and clinical potential of QT dispersion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 36(6):1749–1766. PMID: 11092641.9. Haugaa KH, Amlie JP, Berge KE, Leren TP, Smiseth OA, Edvardsen T. Transmural differences in myocardial contraction in long-QT syndrome: mechanical consequences of ion channel dysfunction. Circulation. 2010; 122(14):1355–1363. PMID: 20855658.10. Leren IS, Hasselberg NE, Saberniak J, Håland TF, Kongsgård E, Smiseth OA, et al. Cardiac mechanical alterations and genotype specific differences in subjects with long QT syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 8(5):501–510. PMID: 25890583.11. Haugaa KH, Edvardsen T, Leren TP, Gran JM, Smiseth OA, Amlie JP. Left ventricular mechanical dispersion by tissue Doppler imaging: a novel approach for identifying high-risk individuals with long QT syndrome. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30(3):330–337. PMID: 18940888.12. Boudoulas H, Sohn YH, O’Neill W, Brown R, Weissler AM. The QT greater than QS2 syndrome: a new mortality risk indicator in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1982; 50(6):1229–1235. PMID: 7148696.13. Chambers JB, Ward DE. The QT and QS2 intervals in patients with mitral leaflet prolapse. Am Heart J. 1987; 114(2):355–361. PMID: 3604892.14. Marwick TH. Echocardiography in long QT syndrome: the mechanical face of an electrical disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 76(24):2844–2846. PMID: 33303073.15. ter Bekke RM, Haugaa KH, van den Wijngaard A, Bos JM, Ackerman MJ, Edvardsen T, et al. Electromechanical window negativity in genotyped long-QT syndrome patients: relation to arrhythmia risk. Eur Heart J. 2015; 36(3):179–186. PMID: 25205533.16. ter Bekke RM, Volders PG. Arrhythmogenic mechano-electric heterogeneity in the long-QT syndrome. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012; 110(2-3):347–358. PMID: 22841828.17. ter Bekke RM, Volders PG. Arrhythmogenic mechano-electric heterogeneity in the long-QT syndrome. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012; 110(2-3):347–358. PMID: 22841828.18. Johnson DM, Heijman J, Bode EF, Greensmith DJ, van der Linde H, Abi-Gerges N, et al. Diastolic spontaneous calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum increases beat-to-beat variability of repolarization in canine ventricular myocytes after β-adrenergic stimulation. Circ Res. 2013; 112(2):246–256. PMID: 23149594.19. van der Linde HJ, Van Deuren B, Somers Y, Loenders B, Towart R, Gallacher DJ. The electro-mechanical window: a risk marker for Torsade de Pointes in a canine model of drug induced arrhythmias. Br J Pharmacol. 2010; 161(7):1444–1454. PMID: 21054337.20. Yoon N, Jeong HK, Lee KH, Park HW, Cho JG. Right ventricular longitudinal conduction delay in patients with Brugada syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(11):e75. PMID: 33754508.21. Gallacher DJ, Van de Water A, van der Linde H, Hermans AN, Lu HR, Towart R, et al. In vivo mechanisms precipitating torsades de pointes in a canine model of drug-induced long-QT1 syndrome. Cardiovasc Res. 2007; 76(2):247–256. PMID: 17669388.22. Schneider AE, Bos JM, Ackerman MJ. Effect of left cardiac sympathetic denervation on the electromechanical window in patients with either type 1 or type 2 long QT syndrome: a pilot study. Congenit Heart Dis. 2016; 11(5):437–443. PMID: 26887900.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Postoperative Life-Threatening Recurrent Ventricular Arrhythmia Triggered by the Swan-Ganz Catheter in a Patient Undergoing Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
- Left Stellate Ganglion Block Prior to Induction of Anesthesia for Surgical Sympathectomy in a Patient with Long QT Syndrome
- Cardio-Anesthesia Restoration ; A Case Report (1)
- Non-Compact Cardiomyopathy or Ventricular Non-Compact Syndrome?
- Ventricular Arrhythmia during Tracheal Intubation and Extubation under General Anesthesia Possibly Induced by Amisulpride: A Case Report