J Rheum Dis.
2023 Jul;30(3):151-169. 10.4078/jrd.2023.0025.
Korean treatment recommendations for patients with axial spondyloarthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 5National Health Insurance Service, Wonju, Korea
- 6Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 7Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 8Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- 9Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea
- 10Division of General Internal Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 11Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 12Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Rheumatology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 14Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 15Division of Rheumatology, Daejeon Rheumatoid & Degenerative Arthritis Center, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 16Korea Ankylosing Spondylitis Society, Seoul, Korea
- 17Korea Ankylosing Spondylitis Corporation, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2543942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2023.0025
Abstract
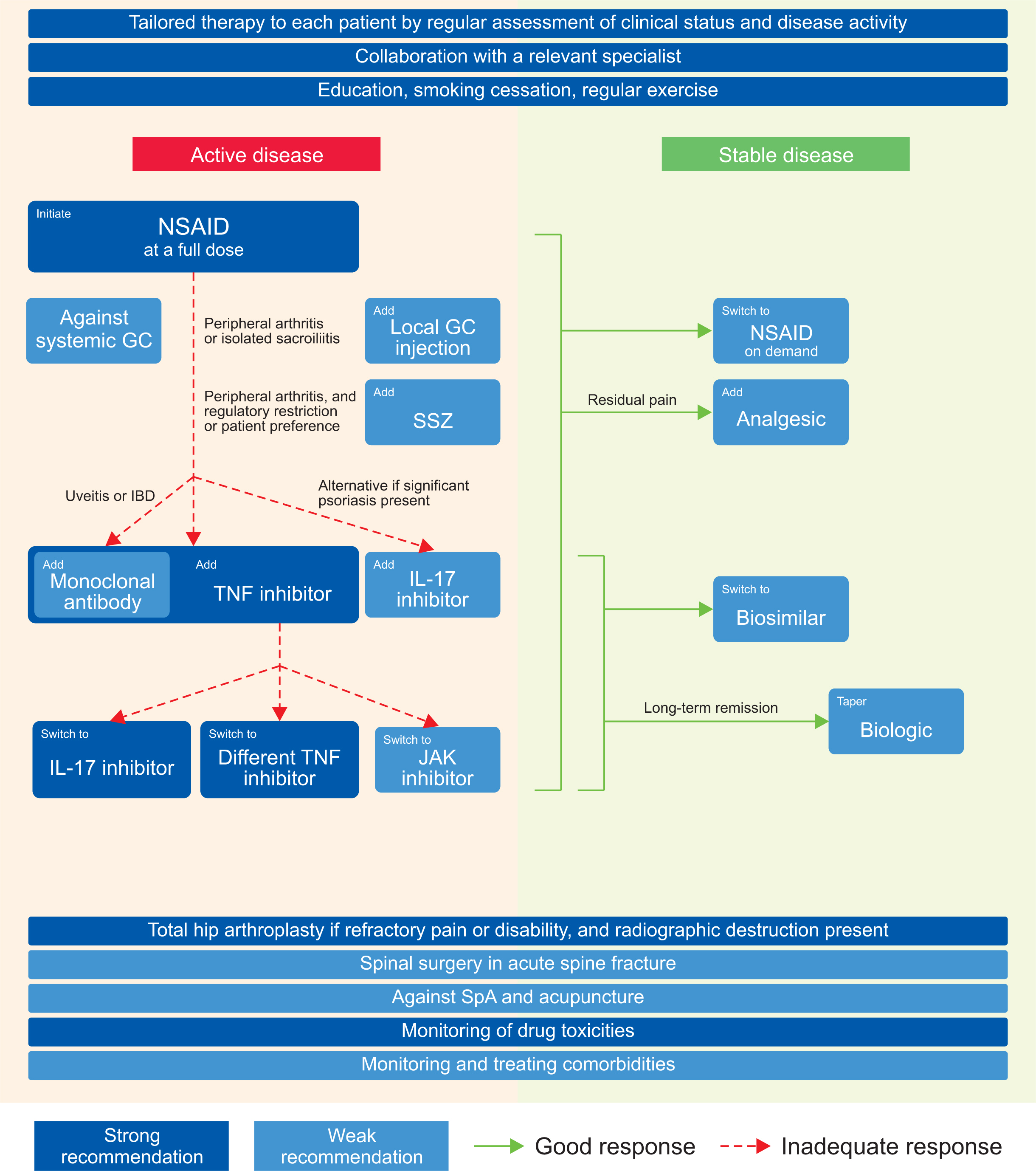
- We aimed to develop evidence-based recommendations for treating axial spondylarthritis (axSpA) in Korea. The development committee was constructed, key clinical questions were determined, and the evidence was searched through online databases including MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, KoreaMed, and KMbase. Systematic literature reviews were conducted, quality of evidence was determined, and draft recommendations were formulated according to the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluations methodology. Recommendations that reached 80% consensus among a voting panel were finalized. Three principles and 21 recommendations were determined. Recommendations 1 and 2 pertain to treatment strategies, regular disease status assessment, and rheumatologist-steered multidisciplinary management. Recommendations 3 and 4 strongly recommend patient education, exercise, and smoking cessation. Recommendations 5~12 address pharmacological treatment of active disease using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids, sulfasalazine, biologics, and Janus kinase inhibitors. Recommendations 13~16 address treatment in stable disease. We suggest against spa and acupuncture as therapies (Recommendation 17). Recommendations 18 and 19 pertain to total hip arthroplasty and spinal surgery. Monitoring of comorbidities and drug toxicities are recommended (Recommendations 20 and 21). Recommendations for axSpA treatment in a Korean context were developed based on comprehensive clinical questions and evidence. These are intended to guide best practice in the treatment of axSpA.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor-α blocker therapy in patients with axial spondyloarthritis who failed conventional treatment: a comparative study focused on improvement in ASAS Health Index
Ah-Ra Choi, Ki-Jeong Park, Ji-Hyoun Kang, Yu Jeong Lee, Hyun Hee Jang, Moon-Ju Kim, Tae-Jong Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2024;31(3):171-177. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0029.
Reference
-
1. Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Märker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, et al. 2009; The early disease stage in axial spondylarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 60:717–27. DOI: 10.1002/art.24483. PMID: 19248087.
Article2. van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Landewé R, Baraliakos X, Van den Bosch F, Sepriano A, et al. 2017; 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:978–91. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210770. PMID: 28087505.3. Ward MM, Deodhar A, Gensler LS, Dubreuil M, Yu D, Khan MA, et al. 2019; 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:1599–613. DOI: 10.1002/art.41042. PMID: 31436036. PMCID: PMC6764882.
Article4. Tam LS, Wei JC, Aggarwal A, Baek HJ, Cheung PP, Chiowchanwisawakit P, et al. 2019; 2018 APLAR axial spondyloarthritis treatment recommendations. Int J Rheum Dis. 22:340–56. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13510. PMID: 30816645.
Article5. Rohekar S, Chan J, Tse SM, Haroon N, Chandran V, Bessette L, et al. 2015; 2014 Update of the Canadian Rheumatology Association/spondyloarthritis research consortium of Canada treatment recommendations for the management of spondyloarthritis. Part I: principles of the management of spondyloarthritis in Canada. J Rheumatol. 42:654–64. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.141000. PMID: 25684770.
Article6. Rohekar S, Chan J, Tse SM, Haroon N, Chandran V, Bessette L, et al. 2015; 2014 Update of the Canadian Rheumatology Association/spondyloarthritis research consortium of Canada treatment recommendations for the management of spondyloarthritis. Part II: specific management recommendations. J Rheumatol. 42:665–81. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.141001. PMID: 25684768.
Article7. Spanish Society of Rheumatology. ESPOGUIA Development Group. c2015. Clinical practice guideline for the treatment of patients with axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis [Internet]. Spanish Society of Rheumatology;Madrid: https://www.ser.es/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/ENGLISH_updated_GPC_Treatment_SpondyloArthritis.pdf. cited 2023 Apr 17.8. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. c2017. Spondyloarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management [Internet]. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence;London: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng65. cited 2023 Apr 17.9. van der Heijde D, Aletaha D, Carmona L, Edwards CJ, Kvien TK, Kouloumas M, et al. 2015; 2014 Update of the EULAR standardised operating procedures for EULAR-endorsed recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:8–13. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206350. PMID: 25261577. PMCID: PMC4283681.
Article10. Kim SY, Choi M, Sheen SS, Ji SM, Park SH, You JH, et al. c2015. Handbook for clinical practice guideline devoloper [Internet]. National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency;Seoul: https://www.neca.re.kr/SKIN_DIR/doc.html?fn=1611820150420175442.pdf&rs=/upload/synap/202304/. cited 2023 Apr 17.11. Ward MM, Deodhar A, Akl EA, Lui A, Ermann J, Gensler LS, et al. 2016; American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network 2015 recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:282–98. DOI: 10.1002/art.39298. PMID: 26401991. PMCID: PMC5123840.
Article12. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. 2019; RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 366:l4898. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l4898. PMID: 31462531.
Article13. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. 2011; GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 64:401–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015. PMID: 21208779.
Article14. Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. 2011; GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. 64:383–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026. PMID: 21195583.
Article15. Andrews J, Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Alderson P, Dahm P, Falck-Ytter Y, et al. 2013; GRADE guidelines: 14. Going from evidence to recommendations: the significance and presentation of recommendations. J Clin Epidemiol. 66:719–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.03.013. PMID: 23312392.
Article16. Navarro-Compán V, Sepriano A, El-Zorkany B, van der Heijde D. 2021; Axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:1511–21. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221035. PMID: 34615639.
Article17. Zink A, Braun J, Listing J, Wollenhaupt J. 2000; Disability and handicap in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis--results from the German rheumatological database. German Collaborative Arthritis Centers. J Rheumatol. 27:613–22.18. Stolwijk C, van Tubergen A, Castillo-Ortiz JD, Boonen A. 2015; Prevalence of extra-articular manifestations in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:65–73. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203582. PMID: 23999006.
Article19. Machado P, Landewé R, Braun J, Hermann KG, Baraliakos X, Baker D, et al. 2011; A stratified model for health outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:1758–64. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2011.150037. PMID: 21791453.
Article20. Hirano F, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen FA, Landewé RBM, Gaujoux-Viala C, Ramiro S. 2021; Determinants of the patient global assessment of well-being in early axial spondyloarthritis: 5-year longitudinal data from the DESIR cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:316–21. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa353. PMID: 32766697. PMCID: PMC7785312.
Article21. Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, van Tubergen A, Stolwijk C, Dougados M, van den Bosch F, et al. 2014; Higher disease activity leads to more structural damage in the spine in ankylosing spondylitis: 12-year longitudinal data from the OASIS cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:1455–61. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205178. PMID: 24812292.
Article22. Landewé R, Dougados M, Mielants H, van der Tempel H, van der Heijde D. 2009; Physical function in ankylosing spondylitis is independently determined by both disease activity and radiographic damage of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:863–7. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.091793. PMID: 18628283.
Article23. van der Heijde D, Joshi A, Pangan AL, Chen N, Betts K, Mittal M, et al. 2016; ASAS40 and ASDAS clinical responses in the ABILITY-1 clinical trial translate to meaningful improvements in physical function, health-related quality of life and work productivity in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 55:80–8. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev267. PMID: 26316575. PMCID: PMC4676905.
Article24. van der Meer R, Arends S, Kruidhof S, Bos R, Bootsma H, Wink F, et al. 2022; Extraskeletal manifestations in axial spondyloarthritis are associated with worse clinical outcomes despite the use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy. J Rheumatol. 49:157–64. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.210308. PMID: 34393101.
Article25. Rueda-Gotor J, Ferraz-Amaro I, Genre F, González Mazón I, Corrales A, Portilla V, et al. 2022; Cardiovascular and disease-related features associated with extra-articular manifestations in axial spondyloarthritis. A multicenter study of 888 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 57:152096. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152096. PMID: 36150319.
Article26. Kelty E, Ognjenovic M, Raymond WD, Inderjeeth CA, Keen HI, Preen DB, et al. 2022; Mortality rates in patients with ankylosing spondylitis with and without extraarticular manifestations and comorbidities: a retrospective cohort study. J Rheumatol. 49:688–93. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.210909. PMID: 35428706.
Article27. Hargraves IG, Montori VM, Brito JP, Kunneman M, Shaw K, LaVecchia C, et al. 2019; Purposeful SDM: a problem-based approach to caring for patients with shared decision making. Patient Educ Couns. 102:1786–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2019.07.020. PMID: 31353170. PMCID: PMC6717012.
Article28. Nikiphorou E, Santos EJF, Marques A, Böhm P, Bijlsma JW, Daien CI, et al. 2021; 2021 EULAR recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:1278–85. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220249. PMID: 33962964. PMCID: PMC8458093.
Article29. Morrison T, Foster E, Dougherty J, Barton J. 2022; Shared decision making in rheumatology: a scoping review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 56:152041. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152041. PMID: 35738040.
Article30. Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Brandt J, Braun J, Sieper J. 2004; Prediction of a major clinical response (BASDAI 50) to tumour necrosis factor alpha blockers in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:665–70. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.016386. PMID: 15037444. PMCID: PMC1755042.31. Xu M, Lin Z, Deng X, Li L, Wei Y, Liao Z, et al. 2011; The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score is a highly discriminatory measure of disease activity and efficacy following tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapies in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthropathies in China. Rheumatology (Oxford). 50:1466–72. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker087. PMID: 21441550.
Article32. van der Heijde D, Lie E, Kvien TK, Sieper J, Van den Bosch F, Listing J, et al. 2009; ASDAS, a highly discriminatory ASAS-endorsed disease activity score in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1811–8. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.100826. PMID: 19060001.
Article33. van der Heijde D, Braun J, Dougados M, Sieper J, Pedersen R, Szumski A, et al. 2012; Sensitivity and discriminatory ability of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score in patients treated with etanercept or sulphasalazine in the ASCEND trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 51:1894–905. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes142. PMID: 22772319.
Article34. Vastesaeger N, van der Heijde D, Inman RD, Wang Y, Deodhar A, Hsu B, et al. 2011; Predicting the outcome of ankylosing spondylitis therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:973–81. Erratum. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.147744. PMID: 21402563. PMCID: PMC3086037.
Article35. Barlow JH, Wright CC, Williams B, Keat A. 2001; Work disability among people with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 45:424–9. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(200110)45:5<424::AID-ART361>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID: 11642641.
Article36. Machado P, Landewé R, Braun J, Hermann KG, Baker D, van der Heijde D. 2010; Both structural damage and inflammation of the spine contribute to impairment of spinal mobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:1465–70. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.124206. PMID: 20498215.
Article37. Poddubnyy D, Haibel H, Listing J, Märker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, et al. 2012; Baseline radiographic damage, elevated acute-phase reactant levels, and cigarette smoking status predict spinal radiographic progression in early axial spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1388–98. DOI: 10.1002/art.33465. PMID: 22127957.
Article38. Braun J, Deodhar A, Landewé R, Baraliakos X, Miceli-Richard C, Sieper J, et al. 2018; Impact of baseline C-reactive protein levels on the response to secukinumab in ankylosing spondylitis: 3-year pooled data from two phase III studies. RMD Open. 4:e000749. DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000749. PMID: 30564451. PMCID: PMC6269637.
Article39. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Xu S, Hsu B. 2016; Serum C-reactive protein levels demonstrate predictive value for radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging outcomes in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis treated with golimumab. J Rheumatol. 43:1704–12. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.160003. PMID: 27422890.
Article40. Benhamou M, Gossec L, Dougados M. 2010; Clinical relevance of C-reactive protein in ankylosing spondylitis and evaluation of the NSAIDs/coxibs' treatment effect on C-reactive protein. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:536–41. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep393. PMID: 20028728.
Article41. Baraliakos X, Szumski A, Koenig AS, Jones H. 2019; The role of C-reactive protein as a predictor of treatment response in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 48:997–1004. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.10.019. PMID: 30473179.
Article42. Song IH, Hermann KG, Haibel H, Althoff CE, Poddubnyy D, Listing J, et al. 2016; Inflammatory and fatty lesions in the spine and sacroiliac joints on whole-body MRI in early axial spondyloarthritis--3-year data of the ESTHER trial. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 45:404–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.08.005. PMID: 26519007.
Article43. Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, Braun J. 2005; Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1216–23. DOI: 10.1002/art.20977. PMID: 15818694.
Article44. Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RG, Conner-Spady B, Maksymowych WP. 2011; Focal fat lesions at vertebral corners on magnetic resonance imaging predict the development of new syndesmophytes in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 63:2215–25. DOI: 10.1002/art.30393. PMID: 21484769.
Article45. Maksymowych WP, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Clare T, Pedersen SJ, Østergaard M, Lambert RG. 2009; Inflammatory lesions of the spine on magnetic resonance imaging predict the development of new syndesmophytes in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence of a relationship between inflammation and new bone formation. Arthritis Rheum. 60:93–102. DOI: 10.1002/art.24132. PMID: 19116919.
Article46. Rudwaleit M, Schwarzlose S, Hilgert ES, Listing J, Braun J, Sieper J. 2008; MRI in predicting a major clinical response to anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:1276–81. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.073098. PMID: 18006539.
Article47. Machado P, Landewé RB, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Hsu B, et al. 2012; MRI inflammation and its relation with measures of clinical disease activity and different treatment responses in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:2002–5. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201999. PMID: 22915615.
Article48. Machado PM, Baraliakos X, van der Heijde D, Braun J, Landewé R. 2016; MRI vertebral corner inflammation followed by fat deposition is the strongest contributor to the development of new bone at the same vertebral corner: a multilevel longitudinal analysis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 75:1486–93. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208011. PMID: 26462728.
Article49. Molto A, López-Medina C, Van den Bosch FE, Boonen A, Webers C, Dernis E, et al. 2021; Efficacy of a tight-control and treat-to-target strategy in axial spondyloarthritis: results of the open-label, pragmatic, cluster-randomised TICOSPA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:1436–44. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219585. PMID: 33958325. PMCID: PMC8522451.
Article50. Rodríguez-Lozano C, Juanola X, Cruz-Martínez J, Peña-Arrébola A, Mulero J, Gratacós J, et al. 2013; Outcome of an education and home-based exercise programme for patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a nationwide randomized study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 31:739–48.51. Ciprian L, Lo Nigro A, Rizzo M, Gava A, Ramonda R, Punzi L, et al. 2013; The effects of combined spa therapy and rehabilitation on patients with ankylosing spondylitis being treated with TNF inhibitors. Rheumatol Int. 33:241–5. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-011-2147-9. PMID: 21947374.
Article52. Altan L, Korkmaz N, Dizdar M, Yurtkuran M. 2012; Effect of Pilates training on people with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 32:2093–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-011-1932-9. PMID: 21499876.
Article53. Sveaas SH, Dagfinrud H, Berg IJ, Provan SA, Johansen MW, Pedersen E, et al. 2020; High-intensity exercise improves fatigue, sleep, and mood in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 100:1323–32. DOI: 10.1093/ptj/pzaa086. PMID: 32367124. PMCID: PMC7439225.
Article54. Sweeney S, Taylor G, Calin A. 2002; The effect of a home based exercise intervention package on outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 29:763–6.55. Kjeken I, Bø I, Rønningen A, Spada C, Mowinckel P, Hagen KB, et al. 2013; A three-week multidisciplinary in-patient rehabilitation programme had positive long-term effects in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: randomized controlled trial. J Rehabil Med. 45:260–7. DOI: 10.2340/16501977-1078. PMID: 23138412.
Article56. Aydın T, Taşpınar Ö, Sarıyıldız MA, Güneşer M, Keskin Y, Canbaz N, et al. 2016; Evaluation of the effectiveness of home based or hospital based calisthenic exercises in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 29:723–30. DOI: 10.3233/BMR-160677. PMID: 26966823.
Article57. Viitanen JV, Heikkilä S. 2001; Functional changes in patients with spondylarthropathy. A controlled trial of the effects of short-term rehabilitation and 3-year follow-up. Rheumatol Int. 20:211–4. DOI: 10.1007/s002960100101. PMID: 11518042.
Article58. Widberg K, Karimi H, Hafström I. 2009; Self- and manual mobilization improves spine mobility in men with ankylosing spondylitis--a randomized study. Clin Rehabil. 23:599–608. DOI: 10.1177/0269215508101748. PMID: 19403551.
Article59. Analay Y, Ozcan E, Karan A, Diracoglu D, Aydin R. 2003; The effectiveness of intensive group exercise on patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rehabil. 17:631–6. DOI: 10.1191/0269215503cr658oa. PMID: 12971708.
Article60. Dundar U, Solak O, Toktas H, Demirdal US, Subasi V, Kavuncu V, et al. 2014; Effect of aquatic exercise on ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 34:1505–11. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-014-2980-8. PMID: 24626605.
Article61. Stasinopoulos D, Papadopoulos K, Lamnisos D, Stergioulas A. 2016; LLLT for the management of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Lasers Med Sci. 31:459–69. DOI: 10.1007/s10103-016-1874-2. PMID: 26796709.
Article62. Stanek A, Cholewka A, Wielkoszyński T, Romuk E, Sieroń A. 2018; Whole-body cryotherapy decreases the levels of inflammatory, oxidative stress, and atherosclerosis plaque markers in male patients with active-phase ankylosing spondylitis in the absence of classical cardiovascular risk factors. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:8592532. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8592532. PMID: 29483842. PMCID: PMC5816841.
Article63. Liao CC, Chen LR. 2007; Anterior and posterior fixation of a cervical fracture induced by chiropractic spinal manipulation in ankylosing spondylitis: a case report. J Trauma. 63:E90–4. DOI: 10.1097/01.ta.0000246957.22573.63. PMID: 18089996.
Article64. Machado P, Landewé R, Lie E, Kvien TK, Braun J, Baker D, et al. 2011; Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS): defining cut-off values for disease activity states and improvement scores. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:47–53. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.138594. PMID: 21068095.
Article65. Barkhuizen A, Steinfeld S, Robbins J, West C, Coombs J, Zwillich S. 2006; Celecoxib is efficacious and well tolerated in treating signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 33:1805–12.66. Dougados M, Béhier JM, Jolchine I, Calin A, van der Heijde D, Olivieri I, et al. 2001; Efficacy of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2-specific inhibitor, in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a six-week controlled study with comparison against placebo and against a conventional nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug. Arthritis Rheum. 44:180–5. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<180::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID: 11212158.
Article67. van der Heijde D, Baraf HS, Ramos-Remus C, Calin A, Weaver AL, Schiff M, et al. 2005; Evaluation of the efficacy of etoricoxib in ankylosing spondylitis: results of a fifty-two-week, randomized, controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1205–15. DOI: 10.1002/art.20985. PMID: 15818702.
Article68. Gao GM, Li YM, Zheng XL, Jiang DB, Zhang LL, Xu PH, et al. 2017; A randomized comparison study of therapy effects of two doses of imrecoxib with celecoxib on axial spondyloarthritis. Lat Am J Pharm. 36:308–13.69. Balazcs E, Sieper J, Bickham K, Mehta A, Frontera N, Stryszak P, et al. 2016; A randomized, clinical trial to assess the relative efficacy and tolerability of two doses of etoricoxib versus naproxen in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 17:426. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1275-5. PMID: 27737664. PMCID: PMC5062857.
Article70. Walker C, Essex MN, Li C, Park PW. 2016; Celecoxib versus diclofenac for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: 12-week randomized study in Norwegian patients. J Int Med Res. 44:483–95. DOI: 10.1177/0300060516628704. PMID: 26980340. PMCID: PMC5536700.
Article71. Sieper J, Klopsch T, Richter M, Kapelle A, Rudwaleit M, Schwank S, et al. 2008; Comparison of two different dosages of celecoxib with diclofenac for the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a 12-week randomised, double-blind, controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:323–9. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.075309. PMID: 17616556.
Article72. Huang F, Gu J, Liu Y, Zhu P, Zheng Y, Fu J, et al. 2014; Efficacy and safety of celecoxib in Chinese patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a 6-week randomized, double-blinded study with 6-week open-label extension treatment. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 76:126–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2014.08.002. PMID: 25516774. PMCID: PMC4266770.
Article73. Batlle-Gualda E, Figueroa M, Ivorra J, Raber A. 1996; The efficacy and tolerability of aceclofenac in the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a multicenter controlled clinical trial. Aceclofenac indomethacin study group. J Rheumatol. 23:1200–6.74. Miao XP, Li JS, Ouyang Q, Hu RW, Zhang Y, Li HY. Tolerability of selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors used for the treatment of rheumatological manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;(10):CD007744. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007744.pub2. PMID: 25340915.
Article75. Moninuola OO, Milligan W, Lochhead P, Khalili H. 2018; Systematic review with meta-analysis: association between acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and risk of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis exacerbation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 47:1428–39. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14606. PMID: 29620794. PMCID: PMC5992031.
Article76. Haibel H, Fendler C, Listing J, Callhoff J, Braun J, Sieper J. 2014; Efficacy of oral prednisolone in active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled short-term trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:243–6. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203055. PMID: 23625982.
Article77. Rodriguez-García SC, Castellanos-Moreira R, Uson J, Naredo E, O'Neill TW, Doherty M, et al. 2021; Efficacy and safety of intra-articular therapies in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: an overview of systematic reviews. RMD Open. 7:e001658. DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001658. PMID: 34103406. PMCID: PMC8186751.
Article78. Maugars Y, Mathis C, Berthelot JM, Charlier C, Prost A. 1996; Assessment of the efficacy of sacroiliac corticosteroid injections in spondylarthropathies: a double-blind study. Br J Rheumatol. 35:767–70. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.8.767. PMID: 8761190.79. Altan L, Bingöl U, Karakoç Y, Aydiner S, Yurtkuran M, Yurtkuran M. 2001; Clinical investigation of methotrexate in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 30:255–9. DOI: 10.1080/03009740410005089.
Article80. van Denderen JC, van der Paardt M, Nurmohamed MT, de Ryck YM, Dijkmans BA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE. 2005; Double blind, randomised, placebo controlled study of leflunomide in the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 64:1761–4. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.036491. PMID: 15901634. PMCID: PMC1755327.
Article81. Gonzalez-Lopez L, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Vazquez-Del-Mercado M, Muñoz-Valle JF, Gamez-Nava JI. 2004; Efficacy of methotrexate in ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 31:1568–74.82. Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Weisman MH, Blackburn WD, Cush JJ, Cannon GW, et al. 1996; Comparison of sulfasalazine and placebo in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. A department of veterans affairs cooperative study. Arthritis Rheum. 39:2004–12. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780391209. PMID: 8961905.
Article83. Khanna Sharma S, Kadiyala V, Naidu G, Dhir V. 2018; A randomized controlled trial to study the efficacy of sulfasalazine for axial disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 21:308–14. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13124. PMID: 28737251.
Article84. Braun J, Zochling J, Baraliakos X, Alten R, Burmester G, Grasedyck K, et al. 2006; Efficacy of sulfasalazine in patients with inflammatory back pain due to undifferentiated spondyloarthritis and early ankylosing spondylitis: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1147–53. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.052878. PMID: 16606646. PMCID: PMC1798286.
Article85. Braun J, Pavelka K, Ramos-Remus C, Dimic A, Vlahos B, Freundlich B, et al. 2012; Clinical efficacy of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis subjects with peripheral joint involvement. J Rheumatol. 39:836–40. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.110885. PMID: 22337244.
Article86. Song IH, Hermann K, Haibel H, Althoff CE, Listing J, Burmester G, et al. 2011; Effects of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in early axial spondyloarthritis on active inflammatory lesions as detected by whole-body MRI (ESTHER): a 48-week randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:590–6. Erratum. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.139667. PMID: 21372193. PMCID: PMC3211465.
Article87. Braun J, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Huang F, Burgos-Vargas R, Vlahos B, Koenig AS, et al. 2011; Clinical efficacy and safety of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, double-blind trial. Arthritis Rheum. 63:1543–51. DOI: 10.1002/art.30223.
Article88. van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Schiff MH, Sieper J, Dijkmans BA, Braun J, et al. 2006; Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 54:2136–46. DOI: 10.1002/art.21913. PMID: 16802350.
Article89. Damjanov N, Shehhi WA, Huang F, Kotak S, Burgos-Vargas R, Shirazy K, et al. 2016; Assessment of clinical efficacy and safety in a randomized double-blind study of etanercept and sulfasalazine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis from Eastern/Central Europe, Latin America, and Asia. Rheumatol Int. 36:643–51. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-016-3452-0. PMID: 26968844.
Article90. Inman RD, Maksymowych WP. 2010; A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of low dose infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 37:1203–10. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.091042. PMID: 20231198.
Article91. Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Maksymowych WP, Scott BB, Boice JA, et al. 2015; A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, sixteen-week study of subcutaneous golimumab in patients with active nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:2702–12. DOI: 10.1002/art.39257. PMID: 26139307. PMCID: PMC4755041.
Article92. Hu Z, Xu M, Li Q, Lin Z, Liao Z, Cao S, et al. 2012; Adalimumab significantly reduces inflammation and serum DKK-1 level but increases fatty deposition in lumbar spine in active ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 15:358–65. DOI: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2012.01734.x. PMID: 22898215.
Article93. Huang F, Gu J, Zhu P, Bao C, Xu J, Xu H, et al. 2014; Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in Chinese adults with active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomised, controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:587–94. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202533. PMID: 23475983.
Article94. Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Mease PJ, Maksymowych WP, Brown MA, et al. 2013; Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1). Ann Rheum Dis. 72:815–22. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201766. PMID: 22772328. PMCID: PMC3664374.
Article95. Inman RD, Davis JC Jr, Heijde D, Diekman L, Sieper J, Kim SI, et al. 2008; Efficacy and safety of golimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3402–12. DOI: 10.1002/art.23969. PMID: 18975305.
Article96. van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, Sieper J, DeWoody K, Williamson P, et al. 2005; Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT). Arthritis Rheum. 52:582–91. DOI: 10.1002/art.20852. PMID: 15692973.
Article97. Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Heldmann F, Wong RL, Kupper H, et al. 2008; Efficacy of adalimumab in the treatment of axial spondylarthritis without radiographically defined sacroiliitis: results of a twelve-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial followed by an open-label extension up to week fifty-two. Arthritis Rheum. 58:1981–91. DOI: 10.1002/art.23606. PMID: 18576337.
Article98. Dougados M, Braun J, Szanto S, Combe B, Elbaz M, Geher P, et al. 2011; Efficacy of etanercept on rheumatic signs and pulmonary function tests in advanced ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study (SPINE). Ann Rheum Dis. 70:799–804. Erratum. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.139261. PMID: 21317434. PMCID: PMC3070274.
Article99. Dougados M, Tsai WC, Saaibi DL, Bonin R, Bukowski J, Pedersen R, et al. 2015; Evaluation of health outcomes with etanercept treatment in patients with early nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol. 42:1835–41. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.141313. PMID: 26276968.
Article100. Davis JC Jr, Revicki D, van der Heijde DM, Rentz AM, Wong RL, Kupper H, et al. 2007; Health-related quality of life outcomes in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis treated with adalimumab: results from a randomized controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 57:1050–7. DOI: 10.1002/art.22887. PMID: 17665483.
Article101. Deodhar A, Reveille JD, Harrison DD, Kim L, Lo KH, Leu JH, et al. 2018; Safety and efficacy of golimumab administered intravenously in adults with ankylosing spondylitis: results through week 28 of the GO-ALIVE study. J Rheumatol. 45:341–8. Erratum. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.170487. PMID: 29247154.
Article102. Dougados M, van der Heijde D, Sieper J, Braun J, Maksymowych WP, Citera G, et al. 2014; Symptomatic efficacy of etanercept and its effects on objective signs of inflammation in early nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:2091–102. DOI: 10.1002/art.38721. PMID: 24891317.
Article103. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A, Alten R, Golder W, et al. 2002; Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 359:1187–93. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08215-6. PMID: 11955536.
Article104. Dougados M, Combe B, Braun J, Landewé R, Sibilia J, Cantagrel A, et al. 2010; A randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of etanercept in adults with refractory heel enthesitis in spondyloarthritis: the HEEL trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:1430–5. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.121533. PMID: 20511606.
Article105. van der Heijde D, Braun J, Deodhar A, Inman RD, Xu S, Mack ME, et al. 2013; Comparison of three enthesitis indices in a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of golimumab in ankylosing spondylitis (GO-RAISE). Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:321–5. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes251. PMID: 23024015.
Article106. Giardina AR, Ferrante A, Ciccia F, Impastato R, Miceli MC, Principato A, et al. 2010; A 2-year comparative open label randomized study of efficacy and safety of etanercept and infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 30:1437–40. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-009-1157-3. PMID: 19851772.
Article107. Ramiro S, Nikiphorou E, Sepriano A, Ortolan A, Webers C, Baraliakos X, et al. 2023; ASAS-EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 82:19–34. DOI: 10.1136/ard-2022-223296. PMID: 36270658.108. Pavelka K, Kivitz A, Dokoupilova E, Blanco R, Maradiaga M, Tahir H, et al. 2017; Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of secukinumab in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, double-blind phase 3 study, MEASURE 3. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:285. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1490-y. PMID: 29273067. PMCID: PMC5741872.
Article109. Sieper J, Deodhar A, Marzo-Ortega H, Aelion JA, Blanco R, Jui-Cheng T, et al. 2017; Secukinumab efficacy in anti-TNF-naive and anti-TNF-experienced subjects with active ankylosing spondylitis: results from the MEASURE 2 Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:571–92. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210023. PMID: 27582421.
Article110. Deodhar A, Poddubnyy D, Pacheco-Tena C, Salvarani C, Lespessailles E, Rahman P, et al. 2019; Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab in the treatment of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: sixteen-week results from a phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with prior inadequate response to or intolerance of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:599–611. DOI: 10.1002/art.40753. PMID: 30343531. PMCID: PMC6593790.
Article111. Park EJ, Kim H, Jung SM, Sung YK, Baek HJ, Lee J. 2020; The use of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for inflammatory arthritis in Korea: results of a Korean Expert Consensus. Korean J Intern Med. 35:41–59. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2019.411. PMID: 31935319. PMCID: PMC6960050.
Article112. Kim M, Won JY, Choi SY, Ju JH, Park YH. 2016; Anti-TNFα treatment for HLA-B27-positive ankylosing spondylitis-related uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 170:32–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2016.07.016. PMID: 27470062.
Article113. Gao X, Wendling D, Botteman MF, Carter JA, Rao S, Cifaldi M. 2012; Clinical and economic burden of extra-articular manifestations in ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. J Med Econ. 15:1054–63. DOI: 10.3111/13696998.2012.692341. PMID: 22563743.
Article114. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Sieper J. 2005; Decreased incidence of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with the anti-tumor necrosis factor agents infliximab and etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 52:2447–51. DOI: 10.1002/art.21197. PMID: 16052578.
Article115. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Davis J, van der Heijde D, Haibel H, et al. 2007; Differences in the incidence of flares or new onset of inflammatory bowel diseases in patients with ankylosing spondylitis exposed to therapy with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents. Arthritis Rheum. 57:639–47. DOI: 10.1002/art.22669. PMID: 17471540.
Article116. Guignard S, Gossec L, Salliot C, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Luc M, Duclos M, et al. 2006; Efficacy of tumour necrosis factor blockers in reducing uveitis flares in patients with spondylarthropathy: a retrospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1631–4. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.052092. PMID: 16901960. PMCID: PMC1798480.
Article117. Koo BS, Hong S, Kim YJ, Lee CK, Yoo B, Kim YG. 2015; The incidence of uveitis in ankylosing spondylitis patients undergoing tumor necrosis factor inhibiting therapy in Korea. J Rheum Dis. 22:288–92. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.5.288.
Article118. Hueber W, Sands BE, Lewitzky S, Vandemeulebroecke M, Reinisch W, Higgins PD, et al. 2012; Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn's disease: unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut. 61:1693–700. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301668. PMID: 22595313. PMCID: PMC4902107.
Article119. Baeten D, Sieper J, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Dougados M, Emery P, et al. 2015; Secukinumab, an interleukin-17A inhibitor, in ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 373:2534–48. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1505066. PMID: 26699169.
Article120. van der Heijde D, Cheng-Chung Wei J, Dougados M, Mease P, Deodhar A, Maksymowych WP, et al. 2018; Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis or radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in patients previously untreated with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (COAST-V): 16 week results of a phase 3 randomised, double-blind, active-controlled and placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 392:2441–51. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31946-9. PMID: 30360964.121. Kivitz AJ, Wagner U, Dokoupilova E, Supronik J, Martin R, Talloczy Z, et al. 2018; Efficacy and safety of secukinumab 150 mg with and without loading regimen in ankylosing spondylitis: 104-week results from MEASURE 4 study. Rheumatol Ther. 5:447–62. DOI: 10.1007/s40744-018-0123-5. PMID: 30121827. PMCID: PMC6251842.
Article122. Huang F, Sun F, Wan WG, Wu LJ, Dong LL, Zhang X, et al. 2020; Secukinumab provided significant and sustained improvement in the signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis: results from the 52-week, Phase III China-centric study, MEASURE 5. Chin Med J (Engl). 133:2521–31. DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001099. PMID: 32925287. PMCID: PMC7722578.
Article123. Deodhar A, van der Heijde D, Gensler LS, Kim TH, Maksymowych WP, Østergaard M, et al. 2020; Ixekizumab for patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-X): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 395:53–64. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32971-X. PMID: 31813637.124. Deodhar A, Blanco R, Dokoupilová E, Hall S, Kameda H, Kivitz AJ, et al. 2021; Improvement of signs and symptoms of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in patients treated with secukinumab: primary results of a randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 73:110–20. DOI: 10.1002/art.41477. PMID: 32770640. PMCID: PMC7839589.
Article125. Baraliakos X, Gossec L, Pournara E, Jeka S, Mera-Varela A, D'Angelo S, et al. 2021; Secukinumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis and axial manifestations: results from the double-blind, randomised, phase 3 MAXIMISE trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:582–90. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218808. PMID: 33334727. PMCID: PMC8053347.
Article126. Ten Bergen LL, Petrovic A, Krogh Aarebrot A, Appel S. 2020; The TNF/IL-23/IL-17 axis-Head-to-head trials comparing different biologics in psoriasis treatment. Scand J Immunol. 92:e12946. DOI: 10.1111/sji.12946.
Article127. Gossec L, Baraliakos X, Kerschbaumer A, de Wit M, McInnes I, Dougados M, et al. 2020; EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:700–12. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217159. PMID: 32434812.128. Ciurea A, Exer P, Weber U, Tamborrini G, Steininger B, Kissling RO, et al. 2016; Does the reason for discontinuation of a first TNF inhibitor influence the effectiveness of a second TNF inhibitor in axial spondyloarthritis? Results from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management Cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:71. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0969-2. PMID: 27000865. PMCID: PMC4802885.
Article129. Rudwaleit M, Van den Bosch F, Kron M, Kary S, Kupper H. 2010; Effectiveness and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis and history of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R117. DOI: 10.1186/ar3054. PMID: 20553600. PMCID: PMC2911911.
Article130. Lie E, van der Heijde D, Uhlig T, Mikkelsen K, Rødevand E, Koldingsnes W, et al. 2011; Effectiveness of switching between TNF inhibitors in ankylosing spondylitis: data from the NOR-DMARD register. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:157–63. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.131797. PMID: 21062852.
Article131. Manica SR, Sepriano A, Pimentel-Santos F, Gouveia N, Barcelos A, Branco JC, et al. 2020; Effectiveness of switching between TNF inhibitors in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: is the reason to switch relevant? Arthritis Res Ther. 22:195. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02288-8. PMID: 32825839. PMCID: PMC7441644.
Article132. Paccou J, Solau-Gervais E, Houvenagel E, Salleron J, Luraschi H, Philippe P, et al. 2011; Efficacy in current practice of switching between anti-tumour necrosis factor- α agents in spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 50:714–20. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq377. PMID: 21131271.133. Deodhar A, Yu D. 2017; Switching tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in the treatment of axial spondyloarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 47:343–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.04.005. PMID: 28551170.
Article134. Deodhar A, Sliwinska-Stanczyk P, Xu H, Baraliakos X, Gensler LS, Fleishaker D, et al. 2021; Tofacitinib for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a phase III, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:1004–13. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219601. PMID: 33906853. PMCID: PMC8292568.
Article135. van der Heijde D, Song IH, Pangan AL, Deodhar A, van den Bosch F, Maksymowych WP, et al. 2019; Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (SELECT-AXIS 1): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 394:2108–17. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32534-6. PMID: 31732180.
Article136. van der Heijde D, Deodhar A, Wei JC, Drescher E, Fleishaker D, Hendrikx T, et al. 2017; Tofacitinib in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a phase II, 16-week, randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:1340–7. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210322. PMID: 28130206. PMCID: PMC5738601.
Article137. Sieper J, Listing J, Poddubnyy D, Song IH, Hermann KG, Callhoff J, et al. 2016; Effect of continuous versus on-demand treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with diclofenac over 2 years on radiographic progression of the spine: results from a randomised multicentre trial (ENRADAS). Ann Rheum Dis. 75:1438–43. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207897. PMID: 26242443.
Article138. Wanders A, Landewé R, Béhier JM, Calin A, Olivieri I, et al. Heijde Dv. 2005; Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs reduce radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1756–65. DOI: 10.1002/art.21054. PMID: 15934081.
Article139. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. c2014. Guideline on similar biological medicinal products [Internet]. European Medicines Agency;London: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-similar-biological-medicinal-products-rev1_en.pdf. cited 2023 Apr 18.140. US Food and Drug Administration. c2015. Scientific considerations in demonstrating biosimilarity to a reference product: guidance for industry [Internet]. US Food and Drug Administration;Silver Spring (MD): https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/scientific-considerations-demonstrating-biosimilarity-reference-product. cited 2023 Apr 18.141. Smolen JS, Goncalves J, Quinn M, Benedetti F, Lee JY. 2019; Era of biosimilars in rheumatology: reshaping the healthcare environment. RMD Open. 5:e000900. DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2019-000900. PMID: 31245050. PMCID: PMC6560670.
Article142. Su J, Li M, He L, Zhao D, Wan W, Liu Y, et al. 2020; Comparison of the efficacy and safety of adalimumab (Humira) and the adalimumab biosimilar candidate (HS016) in Chinese patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel, phase III clinical trial. BioDrugs. 34:381–93. DOI: 10.1007/s40259-020-00408-z. PMID: 32078145. PMCID: PMC7211209.
Article143. Xu H, Li Z, Wu J, Xing Q, Shi G, Li J, et al. 2019; IBI303, a biosimilar to adalimumab, for the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis in China: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 equivalence trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 1:e35–43. DOI: 10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30013-X.
Article144. Park W, Yoo DH, Jaworski J, Brzezicki J, Gnylorybov A, Kadinov V, et al. 2016; Comparable long-term efficacy, as assessed by patient-reported outcomes, safety and pharmacokinetics, of CT-P13 and reference infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: 54-week results from the randomized, parallel-group PLANETAS study. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:25. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0930-4. PMID: 26795209. PMCID: PMC4721187.
Article145. Landewé RB, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Baraliakos X, Van den Bosch FE, Gaffney K, et al. 2020; Maintenance of clinical remission in early axial spondyloarthritis following certolizumab pegol dose reduction. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:920–8. Erratum. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216839. PMID: 32381562. PMCID: PMC7307216.
Article146. Landewé R, Sieper J, Mease P, Inman RD, Lambert RG, Deodhar A, et al. 2018; Efficacy and safety of continuing versus withdrawing adalimumab therapy in maintaining remission in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (ABILITY-3): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind study. Lancet. 392:134–44. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31362-X. PMID: 29961640.
Article147. Gratacós J, Pontes C, Juanola X, Sanz J, Torres F, Avendaño C, et al. 2019; Non-inferiority of dose reduction versus standard dosing of TNF-inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:11. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1772-z. PMID: 30621746. PMCID: PMC6323809.
Article148. Cantini F, Niccoli L, Cassarà E, Kaloudi O, Nannini C. 2013; Duration of remission after halving of the etanercept dose in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, prospective, long-term, follow-up study. Biologics. 7:1–6. DOI: 10.2147/BTT.S31474. PMID: 23319853. PMCID: PMC3540908.
Article149. Fernández-Carballido C, Collantes-Estévez E, Gratacós J, Juanola X, Zarco P. 2021; Remission in axial spondyloarthritis: developing a consensus definition. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 17:380–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.reuma.2020.01.003. PMID: 34301380.
Article150. Chang JK, Yu CT, Lee MY, Yeo K, Chang IC, Tsou HK, et al. 2013; Tramadol/acetaminophen combination as add-on therapy in the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 32:341–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-012-2125-y. PMID: 23192419.
Article151. Gurcay E, Yuzer S, Eksioglu E, Bal A, Cakci A. 2008; Stanger bath therapy for ankylosing spondylitis: illusion or reality? Clin Rheumatol. 27:913–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-008-0873-5. PMID: 18357500.
Article152. van Tubergen A, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Hidding A, Wolter N, Asscher M, et al. 2001; Combined spa-exercise therapy is effective in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 45:430–8. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(200110)45:5<430::AID-ART362>3.0.CO;2-F. PMID: 11642642.
Article153. Jo JH, Kweon JJ, Song YK, Lim HH, Beak HJ. 2012; Acupuncture's efficacy and safety in axial spondyloarthritis within 4 weeks session: a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial. J Orient Rehabil Med. 22:23–36.154. Vander Cruyssen B, Muñoz-Gomariz E, Font P, Mulero J, de Vlam K, Boonen A, et al. 2010; Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: epidemiology and risk factors associated with hip replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:73–81. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep174. PMID: 19605374.
Article155. Jeong H, Eun YH, Kim IY, Kim H, Lee J, Koh EM, et al. 2017; Characteristics of hip involvement in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 32:158–64. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.229. PMID: 27017388. PMCID: PMC5214726.
Article156. Yoo MC, Chung DW, Kim JJ, Lee HK. 1994; Total hip replacement in the ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 1:23–32.157. Joshi AB, Markovic L, Hardinge K, Murphy JC. 2002; Total hip arthroplasty in ankylosing spondylitis: an analysis of 181 hips. J Arthroplasty. 17:427–33. DOI: 10.1054/arth.2002.32170. PMID: 12066271.
Article158. Li J, Xu W, Xu L, Liang Z. 2009; Hip resurfacing arthroplasty for ankylosing spondylitis. J Arthroplasty. 24:1285–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2009.07.003. PMID: 19682837.
Article159. Lee SH, Lee GW, Seol YJ, Park KS, Yoon TR. 2017; Comparison of outcomes of total hip arthroplasty between patients with ankylosing spondylitis and avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Surg. 9:263–9. DOI: 10.4055/cios.2017.9.3.263. PMID: 28861192. PMCID: PMC5567020.
Article160. Lin D, Charalambous A, Hanna SA. 2019; Bilateral total hip arthroplasty in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 4:476–81. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180047. PMID: 31423331. PMCID: PMC6667978.
Article161. Sambrook PN, Geusens P. 2012; The epidemiology of osteoporosis and fractures in ankylosing spondylitis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 4:287–92. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X12441276. PMID: 22859927. PMCID: PMC3403252.
Article162. Vosse D, Lems WF, Geusens PP. 2013; Spinal fractures in ankylosing spondylitis: prevalence, prevention and management. Int J Clin Rheumatol. 8:597–608. DOI: 10.2217/ijr.13.37.
Article163. Ognjenovic M, Raymond WD, Inderjeeth CA, Keen HI, Preen DB, Nossent JC. 2020; The risk and consequences of vertebral fracture in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a population-based data linkage study. J Rheumatol. 47:1629–36. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.190675. PMID: 32062601.
Article164. Westerveld LA, Verlaan JJ, Oner FC. 2009; Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. Eur Spine J. 18:145–56. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-008-0764-0. PMID: 18791749. PMCID: PMC2899332.
Article165. Tu PH, Liu ZH, Yeap MC, Liu YT, Li YC, Huang YC, et al. 2022; Spinal cord injury and spinal fracture in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. BMC Emerg Med. 22:73. DOI: 10.1186/s12873-022-00635-3. PMID: 35501709. PMCID: PMC9063196.
Article166. Kandregula S, Birk HS, Savardekar A, Newman WC, Beyl R, Trosclair K, et al. 2021; Spinal fractures in ankylosing spondylitis: patterns, management, and complications in the United States - analysis of latest Nationwide Inpatient Sample data. Neurospine. 18:786–97. DOI: 10.14245/ns.2142712.356. PMID: 35000333. PMCID: PMC8752689.
Article167. Werner BC, Samartzis D, Shen FH. 2016; Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: etiology, diagnosis, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 24:241–9. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00149. PMID: 26890162.168. Reinhold M, Knop C, Kneitz C, Disch A. 2018; Spine fractures in ankylosing diseases: recommendations of the Spine Section of the German Society for Orthopaedics and Trauma (DGOU). Global Spine J. 8(2 Suppl):56S–68S. DOI: 10.1177/2192568217736268. PMID: 30210963. PMCID: PMC6130102.
Article169. Rustagi T, Drazin D, Oner C, York J, Schroeder GD, Vaccaro AR, et al. 2017; Fractures in spinal ankylosing disorders: a narrative review of disease and injury types, treatment techniques, and outcomes. J Orthop Trauma. 31 Suppl 4:S57–74. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000953. PMID: 28816877.
Article170. Lauper K, Courvoisier DS, Chevallier P, Finckh A, Gabay C. 2018; Incidence and prevalence of major adverse cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 70:1756–63. DOI: 10.1002/acr.23567. PMID: 29609199.
Article171. Zhao SS, Robertson S, Reich T, Harrison NL, Moots RJ, Goodson NJ. 2020; Prevalence and impact of comorbidities in axial spondyloarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 59(Suppl4):iv47–57. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa246. PMID: 33053193. PMCID: PMC7566561.
Article172. Wang JK, Park US, Lee HS, Uhm WS, Kim TH, Bae SC, et al. 2004; The clinical significance of bone mineral density measurement in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 11:342–8.173. Toussirot E, Michel F, Wendling D. 2001; Bone density, ultrasound measurements and body composition in early ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 40:882–8. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.8.882. PMID: 11511757.
Article174. Magrey MN, Lewis S, Asim Khan M. 2016; Utility of DXA scanning and risk factors for osteoporosis in ankylosing spondylitis-a prospective study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 46:88–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.03.003. PMID: 27162010.
Article175. Karberg K, Zochling J, Sieper J, Felsenberg D, Braun J. 2005; Bone loss is detected more frequently in patients with ankylosing spondylitis with syndesmophytes. J Rheumatol. 32:1290–8.176. Guidelines for monitoring drug therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. 1996; American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Clinical Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 39:723–31. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780390503.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Piriformis syndrome as an overlooked cause of pain in a patient with axial spondyloarthritis: a case report
- MRI Features of Axial Spondyloarthritis and Differential Diagnosis: Focusing on the Spine and Sacroiliac Joint
- Simultaneous Presentation of Ocular Sarcoidosis and Early Axial Spondyloarthritis in a Young Woman
- Literature review of non-pharmacological treatment for patients with axial spondyloarthritis
- Assessments of Functioning in Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis