Anesth Pain Med.
2023 Apr;18(2):159-168. 10.17085/apm.22257.
Comparison of the effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam under spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial, single center study in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Nowon Eulji University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2543657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.22257
Abstract
- Background
Cesarean section under spinal anesthesia may cause anxiety and hypotension. Administration of sedative drugs after delivery can diminish these side-effects, but may increase hemodynamic instability. We evaluated the effect of the administration of 0.7 μg/kg dexmedetomidine and compared it with that of 0.03 mg/kg midazolam for usefulness of sedation of the parturient after delivery during cesarean section.
Methods
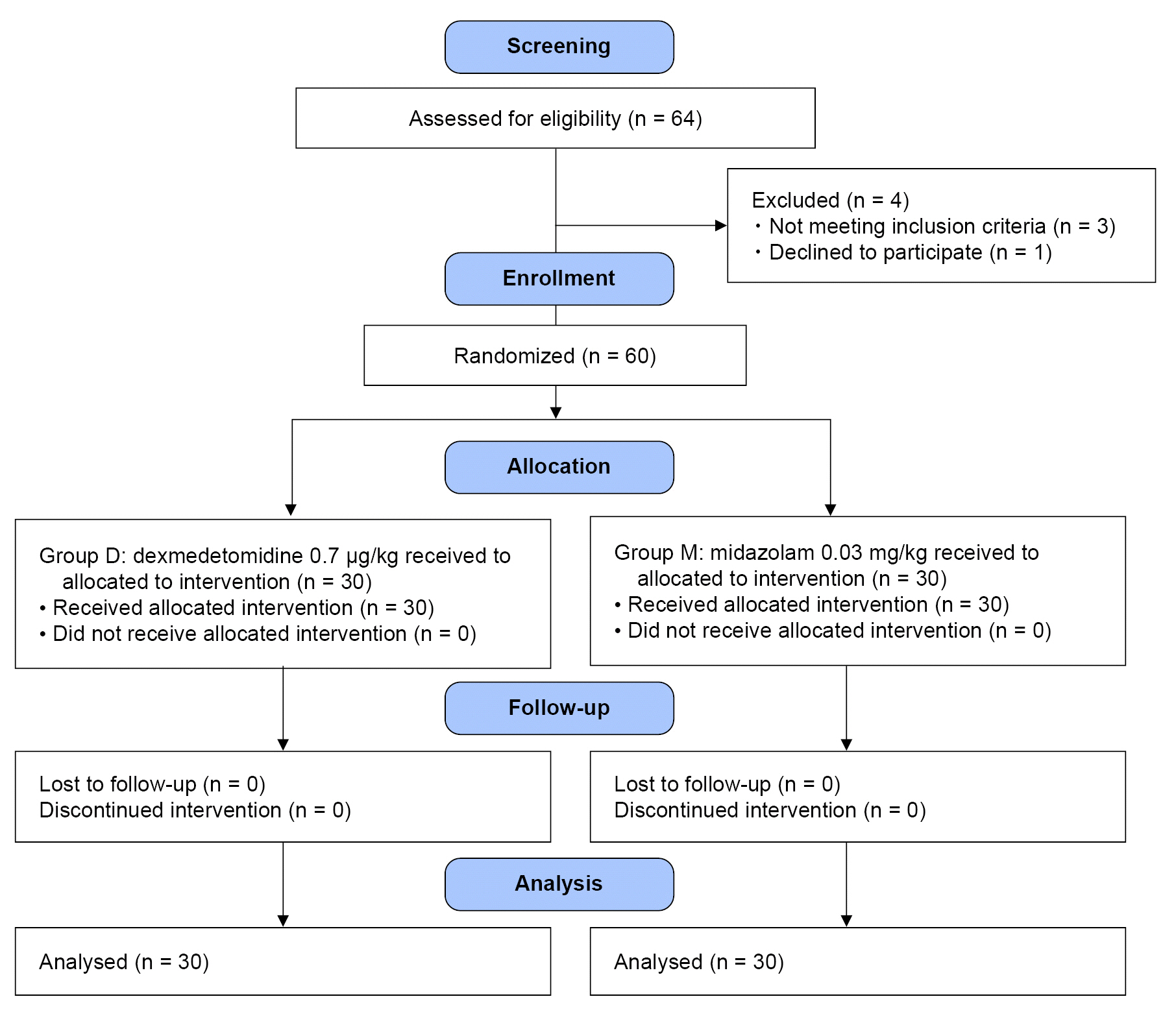
After obtaining written consent and the ethics board approval, 60 parturients aged 20–43 years who underwent elective cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia were recruited. A total of 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine (8–10 mg) and intrathecal fentanyl (10 μg) was given to induce anesthesia. Parturients were then randomly allocated to receive either midazolam (0.03 mg/kg; group M) or dexmedetomidine 0.7 (μg/kg; group D) after delivery. The primary outcome measure was patient satisfaction score. Secondary outcomes included vital signs; vasopressor dosage; incidence of shivering, nausea, and vomiting; incidence of bradycardia; time to sensory and motor recovery; postoperative nausea and vomiting score; and postoperative pain visual analog scale at 6, 24, and 48 h.
Results
Satisfaction scores for sedation were similar between the two groups. The systolic blood pressure, heart rate, oximetry saturation, and tympanic temperature were comparable between the two groups. The predicted mean systolic blood pressure of group D was 106.3 mmHg and that of group M was 107.5 mmHg. Both groups showed comparable adverse intraoperative and postoperative outcomes.
Conclusions
Dexmedetomidine and midazolam showed similar hemodynamic effects and patient satisfaction in parturients under spinal anesthesia.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ng K, Parsons J, Cyna AM, Middleton P. Spinal versus epidural anaesthesia for caesarean section. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; 2004:CD003765.
Article2. Kinsella SM. A prospective audit of regional anaesthesia failure in 5080 caesarean sections. Anaesthesia. 2008; 63:822–32.
Article3. Chima AM, Mahmoud MA, Narayanasamy S. What is the role of dexmedetomidine in modern anesthesia and critical care? Adv Anesth. 2022; 40:111–30.
Article4. Davis PR, Sviggum HP, Delaney DJ, Arendt KW, Jacob AK, Sharpe EE. Intravenous dexmedetomidine as an adjunct to neuraxial anesthesia in cesarean delivery: a retrospective chart review. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2021; 2021:9887825.
Article5. Su Y, Lei X, Yu J. Case report: anesthetic management of cesarean section in a patient with paraplegia. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022; 9:783796.
Article6. Palanisamy A, Klickovich RJ, Ramsay M, Ouyang DW, Tsen LC. Intravenous dexmedetomidine as an adjunct for labor analgesia and cesarean delivery anesthesia in a parturient with a tethered spinal cord. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2009; 18:258–61.
Article7. Kim HJ, Ahn E. Risk factors for dexmedetomidine-associated bradycardia during spinal anesthesia: a retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022; 101:e31306.
Article8. Bao Z, Zhou C, Wang X, Zhu Y. Intravenous dexmedetomidine during spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Int Med Res. 2017; 45:924–32.
Article9. Lamontagne C, Lesage S, Villeneuve E, Lidzborski E, Derstenfeld A, Crochetière C. Intravenous dexmedetomidine for the treatment of shivering during cesarean delivery under neuraxial anesthesia: a randomized-controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2019; 66:762–71.
Article10. Kinsella SM, Carvalho B, Dyer RA, Fernando R, McDonnell N, Mercier FJ, et al. Consensus Statement Collaborators. International consensus statement on the management of hypotension with vasopressors during caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2018; 73:71–92.
Article11. Kwon K, Kim D, Jo H, Park JE, Kim KO. Hemodynamic effects of carbetocin administered as an intravenous bolus or infusion during cesarean delivery. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2020; 15:167–72.
Article12. Perika T, Gupta SL, Elakkumanan LB, Kattimani S. Psychomotor recovery of dexmedetomidine compared with propofol after sedation during spinal anesthesia: a randomized control trial. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2019; 35:236–41.
Article13. Choudhary AK, Prasad MK, Keshri R, Choudhary S. Effects of IV dexmedetomidine as a pre-medication on clinical profile of bupivacaine spinal anaesthesia in lower abdominal surgeries: a randomized clinical study. Pan Afr Med J. 2022; 41:74.
Article14. Lee MH, Ko JH, Kim EM, Cheung MH, Choi YR, Choi EM. The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on spinal anesthesia: comparision of different dose of dexmedetomidine. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 67:252–7.
Article15. Sivachalam SN, Puthenveettil N, Rajan S, Paul J, Kumar L. Comparison of prolongation of spinal anesthesia produced by intravenous dexmedetomidine and midazolam: a randomized control trial. Anesth Essays Res. 2019; 13:330–3.
Article16. Sia AT, Kwek K, Yeo GS. The in vitro effects of clonidine and dexmedetomidine on human myometrium. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2005; 14:104–7.
Article17. Xiong M, Chen B, Hu Z, Gupta S, Li Z, Liu J, et al. Dose comparison of dexmedetomidine sedation following spinal anesthesia: parturient versus nonpregnant women-a randomized trial. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2020; 2020:1059807.
Article18. Hu B, Zhou H, Zou X, Shi J, Li X, Tan L. A comparison of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting caused by hemabate in cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020; 14:2127–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fatal pulmonary aspiration during balanced sedation with dexmedetomidine and midazolam: A case report
- Complete resolution of myoclonus-like involuntary movements under subarachnoid block after midazolam administration in a patient undergoing cesarean section: a case report
- Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness and acceptance of intranasal dexmedetomidine and intranasal midazolam for sedation in children aged 5–8 years using a mucosal atomizer device: a randomized controlled clinical study
- Dexmedetomidine combined with midazolam vs. dexmedetomidine alone for sedation during spinal anesthesia
- The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on spinal anesthesia: comparision of different dose of dexmedetomidine