Acute Crit Care.
2023 May;38(2):238-241. 10.4266/acc.2023.00437.
Septic shock due to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis without conventional risk factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- 2Division of Allergy and Pulmonary medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2543645
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.00437
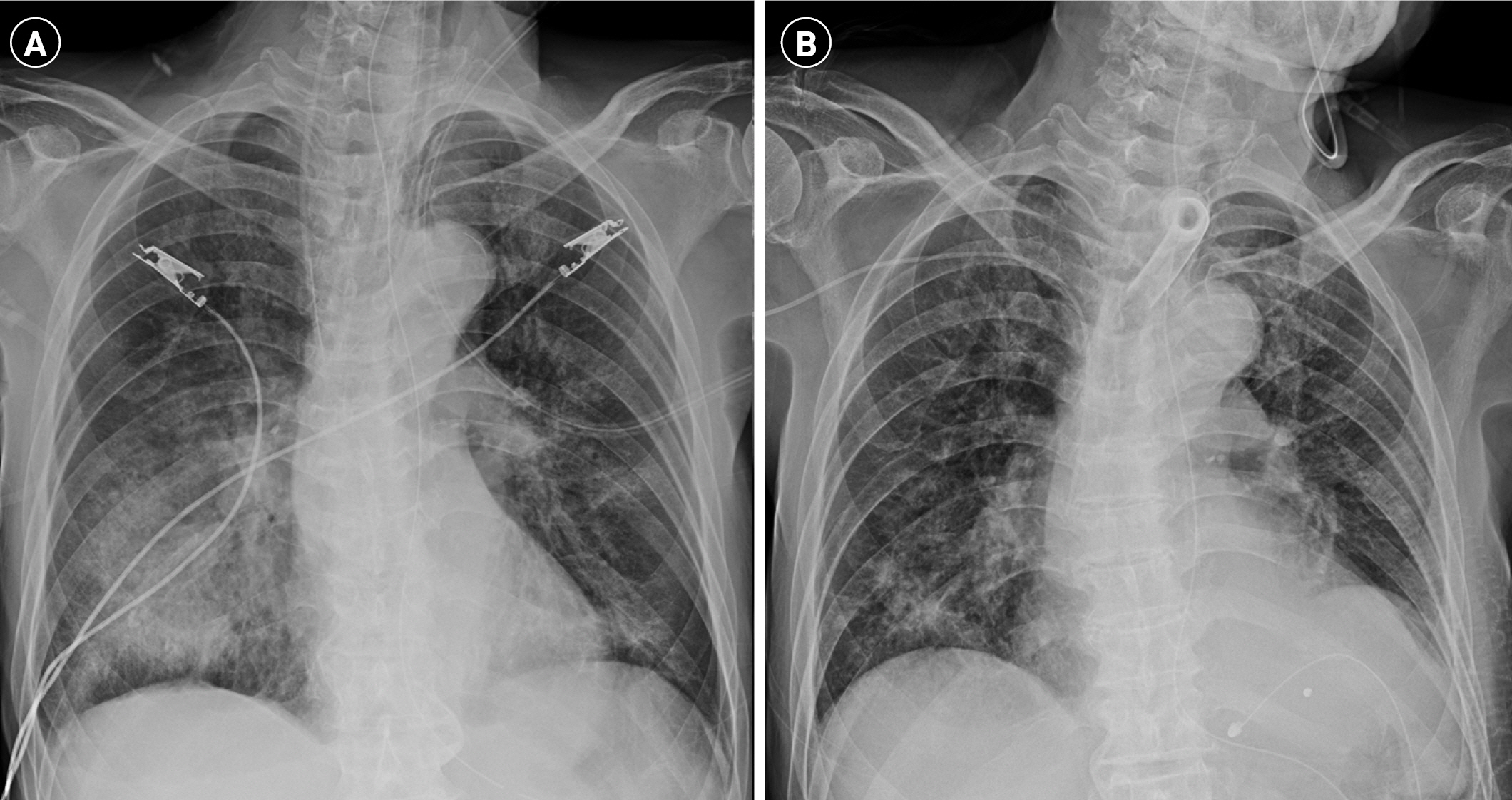
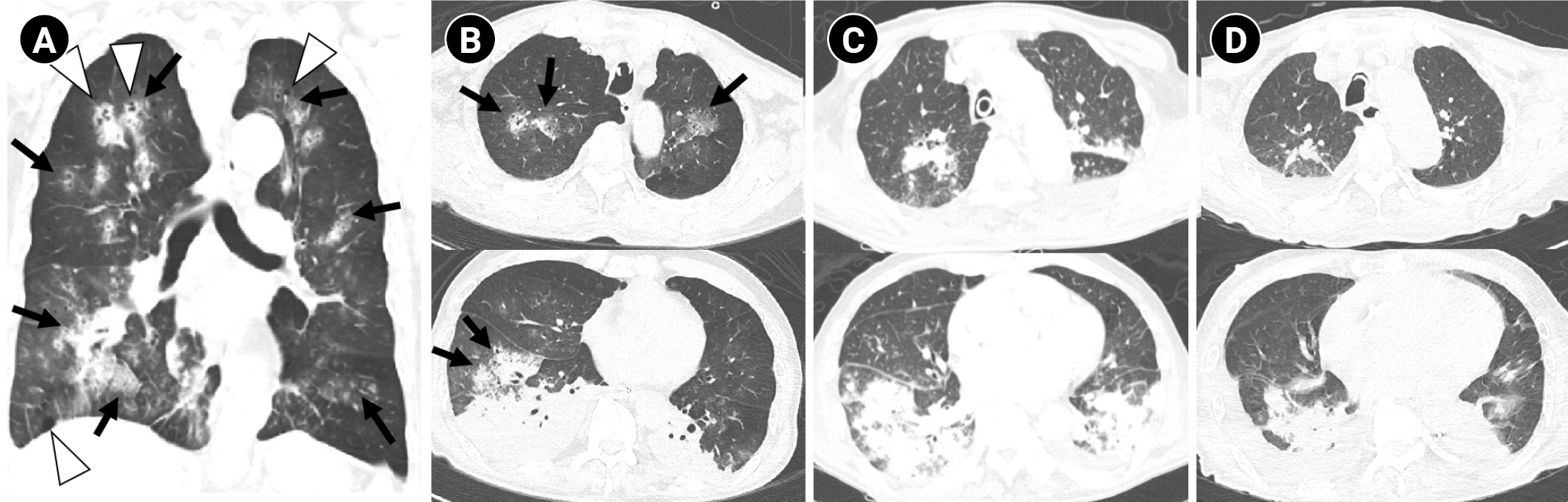
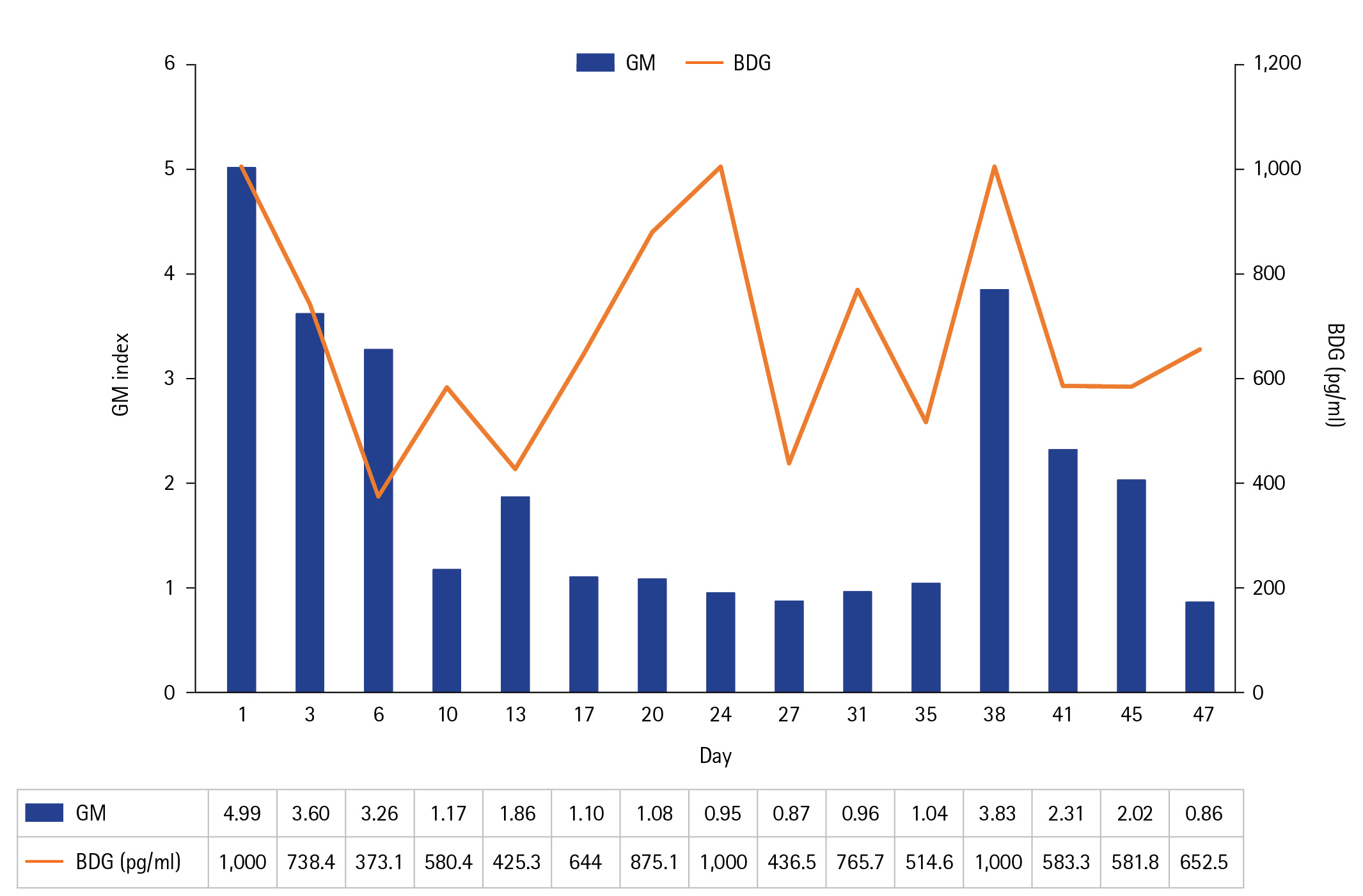
Figure
Reference
-
1. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021; 49:e1063–143.2. Bassetti M, Righi E, De Pascale G, De Gaudio R, Giarratano A, Mazzei T, et al. How to manage aspergillosis in non-neutropenic intensive care unit patients. Crit Care. 2014; 18:458.
Article3. Prohaska S, Henn P, Wenz S, Frauenfeld L, Rosenberger P, Haeberle HA. A case report of fatal disseminated fungal sepsis in a patient with ARDS and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020; 20:107.
Article4. Bassetti M, Azoulay E, Kullberg BJ, Ruhnke M, Shoham S, Vazquez J, et al. EORTC/MSGERC definitions of invasive fungal diseases: summary of activities of the intensive care unit working group. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(Suppl 2):S121–7.
Article5. Acosta J, Catalan M, del Palacio-Pérez-Medel A, Montejo JC, De-La-Cruz-Bértolo J, Moragues MD, et al. Prospective study in critically ill non-neutropenic patients: diagnostic potential of (1,3)-β-D-glucan assay and circulating galactomannan for the diagnosis of invasive fungal disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:721–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Interstitial Pneumonia with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- Primary Invasive Intestinal Aspergillosis in a Non-Severely Immunocompromised Patient
- A Case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis with pulmonary artery aneurysm
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Invaded to Thoracic Vertebra in a Immunocompetent Host: A case report
- Cutaneous Aspergillosis