J Neurocrit Care.
2023 Jun;16(1):1-9. 10.18700/jnc.230003.
Refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus and evidence for the use of ketamine: a scope review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Intensive Care, Hospital San José FUCS, Hospital El Cruce (Buenos Aires), Clinic Santa Bárbara-CAFAM, Bogotá, Colombia
- 2Department of Intensive Care, Hospital San José FUCS, CIMCA Research Group, Bogotá, Colombia
- 3Department of Neurology, Sleep Section, Fundación Santafé de Bogotá, Bogotá, Colombia
- 4Department of Intensive Care, Hospital San José FUCS, Cobos Medical Center Clinic, GRIBOS Research Group and CIMCA, Coordinator of Intensive Care Clinics CAFAM, Bogotá, Colombia
- KMID: 2543386
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.230003
Abstract
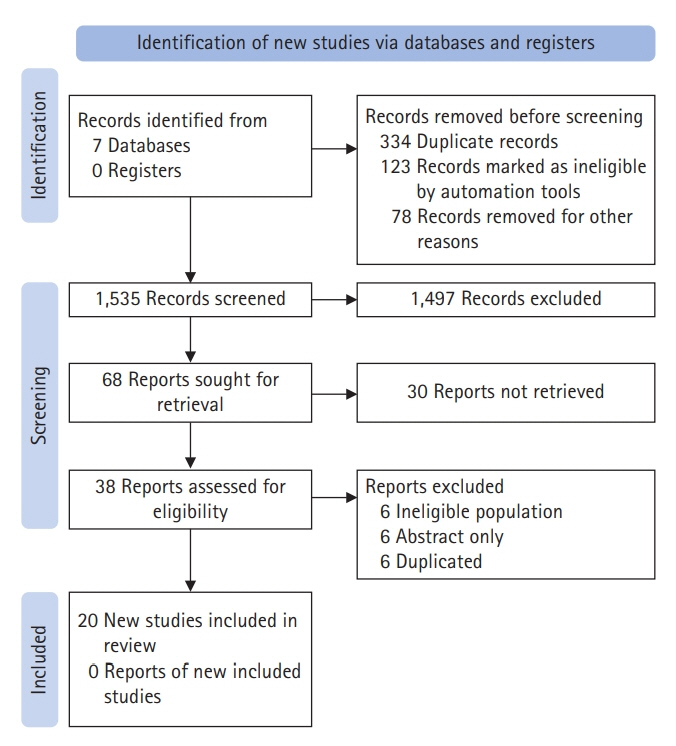
- Status epilepticus (SE) is a neurological emergency with serious consequences for neuronal tissues, therefore, it is considered the most serious manifestation of epilepsy. The response to treatment, its evolution time and duration, and the need to use one or more antiseizure drugs define SE as refractory or super-refractory. Ketamine has been used in SE management since the 90s when an article describing its use in treating SE was published. Since then, at least 24 publications have reported the use of ketamine for the treatment of SE in both adult and pediatric patients. This scoping review seeks to synthesize information on the use of drugs in super-refractory SE, specifically ketamine. Twenty articles were chosen for the final document construction. Few studies have investigated the use of ketamine in refractory status epilepticus (RSE) and super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE). Most of the information comes from retrospective case series studies, mostly with small sample sizes, and although the information is heterogeneous, it points to the efficacy of ketamine as a third-line drug in RES and SRSE, in controlling seizures.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, Rossetti AO, Scheffer IE, Shinnar S, et al. A definition and classification of status epilepticus: report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification of Status Epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2015; 56:1515–23.2. Brophy GM, Bell R, Claassen J, Alldredge B, Bleck TP, Glauser T, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012; 17:3–23.3. Hocker SE, Britton JW, Mandrekar JN, Wijdicks EF, Rabinstein AA. Predictors of outcome in refractory status epilepticus. JAMA Neurol. 2013; 70:72–7.4. Mayer SA, Claassen J, Lokin J, Mendelsohn F, Dennis LJ, Fitzsimmons BF. Refractory status epilepticus: frequency, risk factors, and impact on outcome. Arch Neurol. 2002; 59:205–10.5. Golub D, Yanai A, Darzi K, Papadopoulos J, Kaufman B. Potential consequences of high-dose infusion of ketamine for refractory status epilepticus: case reports and systematic literature review. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2018; 46:516–28.6. Finck AD, Ngai SH. Opiate receptor mediation of ketamine analgesia. Anesthesiology. 1982; 56:291–7.7. Mion G, Villevieille T. Ketamine pharmacology: an update (pharmacodynamics and molecular aspects, recent findings). CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013; 19:370–80.8. Persson J. Ketamine in pain management. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013; 19:396–402.9. Welters ID, Feurer MK, Preiss V, Müller M, Scholz S, Kwapisz M, et al. Continuous S-(+)-ketamine administration during elective coronary artery bypass graft surgery attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine response during and after cardiopulmonary bypass. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 106:172–9.10. Luo AT, Cao ZZ, Xiang Y, Zhang S, Qian CP, Fu C, et al. Ketamine attenuates the Na+-dependent Ca2+ overload in rabbit ventricular myocytes in vitro by inhibiting late Na+ and L-type Ca2+ currents. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015; 36:1327–36.11. Lois F, De Kock M. Something new about ketamine for pediatric anesthesia? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008; 21:340–4.12. Marland S, Ellerton J, Andolfatto G, Strapazzon G, Thomassen O, Brandner B, et al. Ketamine: use in anesthesia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013; 19:381–9.13. Chenge-Said J, Campeñacho-Asencio MÁ, Castellanos-Acuña MJ. New uses for an old friend: ketamine. Rev Mex Anest. 2016; 39(Suppl 1):262–4.14. Walker MC, Howard RS, Smith SJ, Miller DH, Shorvon SD, Hirsch NP. Diagnosis and treatment of status epilepticus on a neurological intensive care unit. QJM. 1996; 89:913–20.15. Höfler J, Trinka E. Intravenous ketamine in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2018; 59 Suppl 2:198–206.16. López-Colomé AM, Somohano F. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the retina: 3-[(+/-)-2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl]-propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP) binding studies. Neuropharmacology. 1992; 31:577–84.17. Ozawa S, Kamiya H, Tsuzuki K. Glutamate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1998; 54:581–618.18. Olney JW. New insights and new issues in developmental neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicology. 2002; 23:659–68.19. Mattson MP, LaFerla FM, Chan SL, Leissring MA, Shepel PN, Geiger JD. Calcium signaling in the ER: its role in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2000; 23:222–9.20. Flores-Soto ME, Chaparro-Huerta V, Escoto-Delgadillo M, Vazquez-Valls E, González-Castañeda RE, Beas-Zarate C. Structure and function of NMDA-type glutamate receptor subunits. Neurologia. 2012; 27:301–10.21. Fountain NB, Lothman EW. Pathophysiology of status epilepticus. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1995; 12:326–42.22. Fujikawa DG. The temporal evolution of neuronal damage from pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1996; 725:11–22.23. Treiman DM, Meyers PD, Walton NY, Collins JF, Colling C, Rowan AJ, et al. A comparison of four treatments for generalized convulsive status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:792–8.24. Arancibia-Cárcamo IL, Kittler JT. Regulation of GABA(A) receptor membrane trafficking and synaptic localization. Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 123:17–31.25. Smith KR, Kittler JT. The cell biology of synaptic inhibition in health and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010; 20:550–6.26. Naylor DE, Liu H, Niquet J, Wasterlain CG. Rapid surface accumulation of NMDA receptors increases glutamatergic excitation during status epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis. 2013; 54:225–38.27. Chen JW, Wasterlain CG. Status epilepticus: pathophysiology and management in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:246–56.28. Kapur J, Macdonald RL. Rapid seizure-induced reduction of benzodiazepine and Zn2+ sensitivity of hippocampal dentate granule cell GABAA receptors. J Neurosci. 1997; 17:7532–40.29. Cock HR, Tong X, Hargreaves IP, Heales SJ, Clark JB, Patsalos PN, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with neuronal death following status epilepticus in rat. Epilepsy Res. 2002; 48:157–68.30. Tan RY, Neligan A, Shorvon SD. The uncommon causes of status epilepticus: a systematic review. Epilepsy Res. 2010; 91:111–22.31. Marchi N, Granata T, Freri E, Ciusani E, Ragona F, Puvenna V, et al. Efficacy of anti-inflammatory therapy in a model of acute seizures and in a population of pediatric drug resistant epileptics. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e18200.32. David Y, Cacheaux LP, Ivens S, Lapilover E, Heinemann U, Kaufer D, et al. Astrocytic dysfunction in epileptogenesis: consequence of altered potassium and glutamate homeostasis? J Neurosci. 2009; 29:10588–99.33. Friedman A, Dingledine R. Molecular cascades that mediate the influence of inflammation on epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2011; 52 Suppl 3:33–9.34. Meldrum BS, Brierley JB. Prolonged epileptic seizures in primates: ischemic cell change and its relation to ictal physiological events. Arch Neurol. 1973; 28:10–7.35. Meldrum B. Excitotoxicity and epileptic brain damage. Epilepsy Res. 1991; 10:55–61.36. Kofke WA, Tempelhoff R, Dasheiff RM. Anesthetic implications of epilepsy, status epilepticus, and epilepsy surgery. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 1997; 9:349–72.37. Ubogu EE, Sagar SM, Lerner AJ, Maddux BN, Suarez JI, Werz MA. Ketamine for refractory status epilepticus: a case of possible ketamine-induced neurotoxicity. Epilepsy Behav. 2003; 4:70–5.38. Robakis TK, Hirsch LJ. Literature review, case report, and expert discussion of prolonged refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2006; 4:35–46.39. Prüss H, Holtkamp M. Ketamine successfully terminates malignant status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2008; 82:219–22.40. Hsieh CY, Sung PS, Tsai JJ, Huang CW. Terminating prolonged refractory status epilepticus using ketamine. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2010; 33:165–7.41. Yeh PS, Shen HN, Chen TY. Oral ketamine controlled refractory nonconvulsive status epilepticus in an elderly patient. Seizure. 2011; 20:723–6.42. Kramer AH. Early ketamine to treat refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012; 16:299–305.43. Synowiec AS, Singh DS, Yenugadhati V, Valeriano JP, Schramke CJ, Kelly KM. Ketamine use in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2013; 105:183–8.44. Zeiler FA, Kaufmann AM, Gillman LM, West M, Silvaggio J. Ketamine for medically refractory status epilepticus after elective aneurysm clipping. Neurocrit Care. 2013; 19:119–24.45. Gaspard N, Foreman B, Judd LM, Brenton JN, Nathan BR, McCoy BM, et al. Intravenous ketamine for the treatment of refractory status epilepticus: a retrospective multicenter study. Epilepsia. 2013; 54:1498–503.46. Zeiler FA, Teitelbaum J, Gillman LM, West M. NMDA antagonists for refractory seizures. Neurocrit Care. 2014; 20:502–13.47. Shrestha GS, Joshi P, Chhetri S, Karn R, Acharya SP. Intravenous ketamine for treatment of super-refractory convulsive status epilepticus with septic shock: a report of two cases. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015; 19:283–5.48. Sabharwal V, Ramsay E, Martinez R, Shumate R, Khan F, Dave H, et al. Propofol-ketamine combination therapy for effective control of super-refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2015; 52(Pt A):264–6.49. Pizzi MA, Kamireddi P, Tatum WO, Shih JJ, Jackson DA, Freeman WD. Transition from intravenous to enteral ketamine for treatment of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. J Intensive Care. 2017; 5:54.50. Alkhachroum A, Der-Nigoghossian CA, Mathews E, Massad N, Letchinger R, Doyle K, et al. Ketamine to treat super-refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 2020; 95:e2286–94.51. Dericioglu N, Arslan D, Arsava EM, Topcuoglu MA. Efficacy and safety of ketamine in refractory/super-refractory nonconvulsive status epilepticus: single-center experience. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2021; 52:345–50.52. Caranzano L, Novy J, Rossetti AO. Ketamine in adult super-refractory status epilepticus: efficacy analysis on a prospective registry. Acta Neurol Scand. 2022; 145:737–42.53. Rosati A, L’Erario M, Ilvento L, Cecchi C, Pisano T, Mirabile L, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine in refractory status epilepticus in children. Neurology. 2012; 79:2355–8.54. Mewasingh LD, Sékhara T, Aeby A, Christiaens FJ, Dan B. Oral ketamine in paediatric non-convulsive status epilepticus. Seizure. 2003; 12:483–9.55. Bell RF. Ketamine for chronic noncancer pain: concerns regarding toxicity. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012; 6:183–7.56. Chernow B, Lake CR, Cruess D, Coyle J, Hughes P, Balestrieri F, et al. Plasma, urine, and CSF catecholamine concentrations during and after ketamine anesthesia. Crit Care Med. 1982; 10:600–3.57. Neder Meyer T, Lázaro Da Silva A. Ketamine reduces mortality of severely burnt rats, when compared to midazolam plus fentanyl. Burns. 2004; 30:425–30.58. Taniguchi T, Takemoto Y, Kanakura H, Kidani Y, Yamamoto K. The dose-related effects of ketamine on mortality and cytokine responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1769–72.59. Hatakeyama N, Yamazaki M, Shibuya N, Yamamura S, Momose Y. Effects of ketamine on voltage-dependent calcium currents and membrane potentials in single bullfrog atrial cells. J Anesth. 2001; 15:149–53.60. Waxman K, Shoemaker WC, Lippmann M. Cardiovascular effects of anesthetic induction with ketamine. Anesth Analg. 1980; 59:355–8.61. Sibley A, Mackenzie M, Bawden J, Anstett D, Villa-Roel C, Rowe BH. A prospective review of the use of ketamine to facilitate endotracheal intubation in the helicopter emergency medical services (HEMS) setting. Emerg Med J. 2011; 28:521–5.62. Hunter G, Young GB. Status epilepticus: a review, with emphasis on refractory cases. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012; 39:157–69.63. Mazarati AM, Baldwin RA, Sankar R, Wasterlain CG. Time-dependent decrease in the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs during the course of self-sustaining status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1998; 814:179–85.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Refractory Status Epilepticus Treated with Ketamine
- Status Epilepticus and Beyond: A Clinical Review of Status Epilepticus and an Update on Current Management Strategies in Super-refractory Status Epilepticus
- Sevoflurane for the Management of Refractory Status Epilepticus : A case report
- Management strategies for refractory status epilepticus
- Anesthetic experience for performing a cesarean section for a woman with refractory status epilepticus: A case report