Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2023 May;66(3):181-189. 10.5468/ogs.22281.
Verification of selective and individual pulmonary thromboembolism prophylaxes for cesarean delivery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Nara Medical University, Nara, Japan
- KMID: 2542224
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.22281
Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to verify the utility of simple, safe, and effective venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis and implement it with few adverse events during cesarean delivery.
Methods
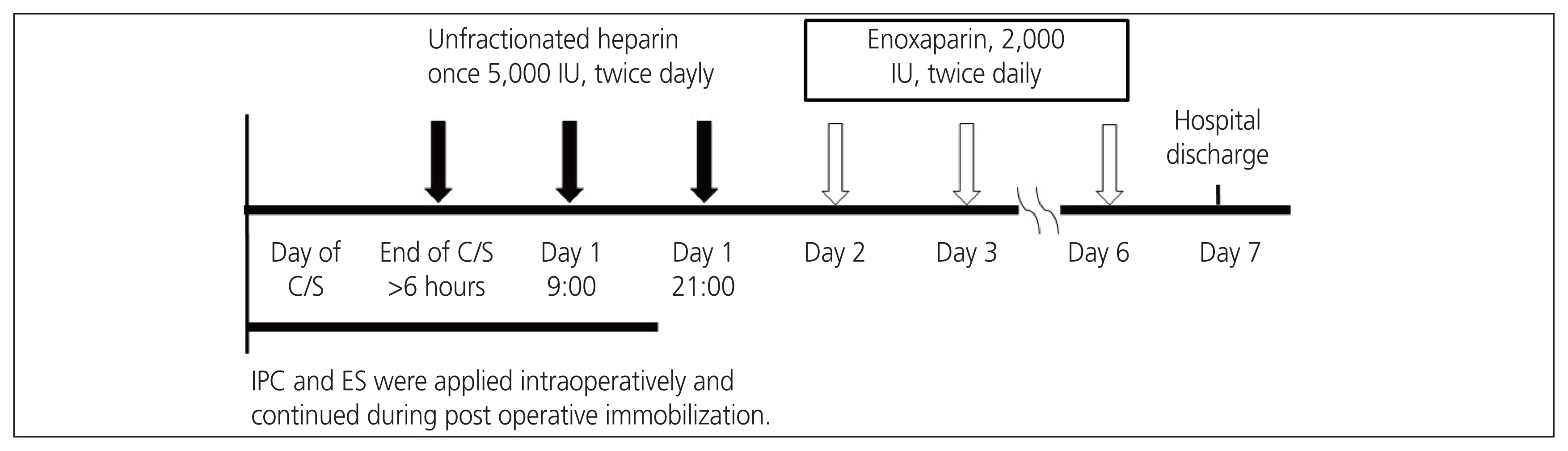
This single-center, prospective study involved pregnant women who underwent cesarean deliveries from August 3, 2020 to March 31, 2022. Patients with VTE risk factors were initially administered unfractionated heparin (5,000 international unit [IU] subcutaneously, twice daily), 6 hours after cesarean delivery. Subsequently, they were administered enoxaparin (2,000 IU subcutaneously, twice daily). They were not administered anticoagulants if one or more of the exclusion criteria were met. The primary efficacy outcome was the incidence of symptomatic VTE. The primary safety outcome was the incidence of major bleeding.
Results
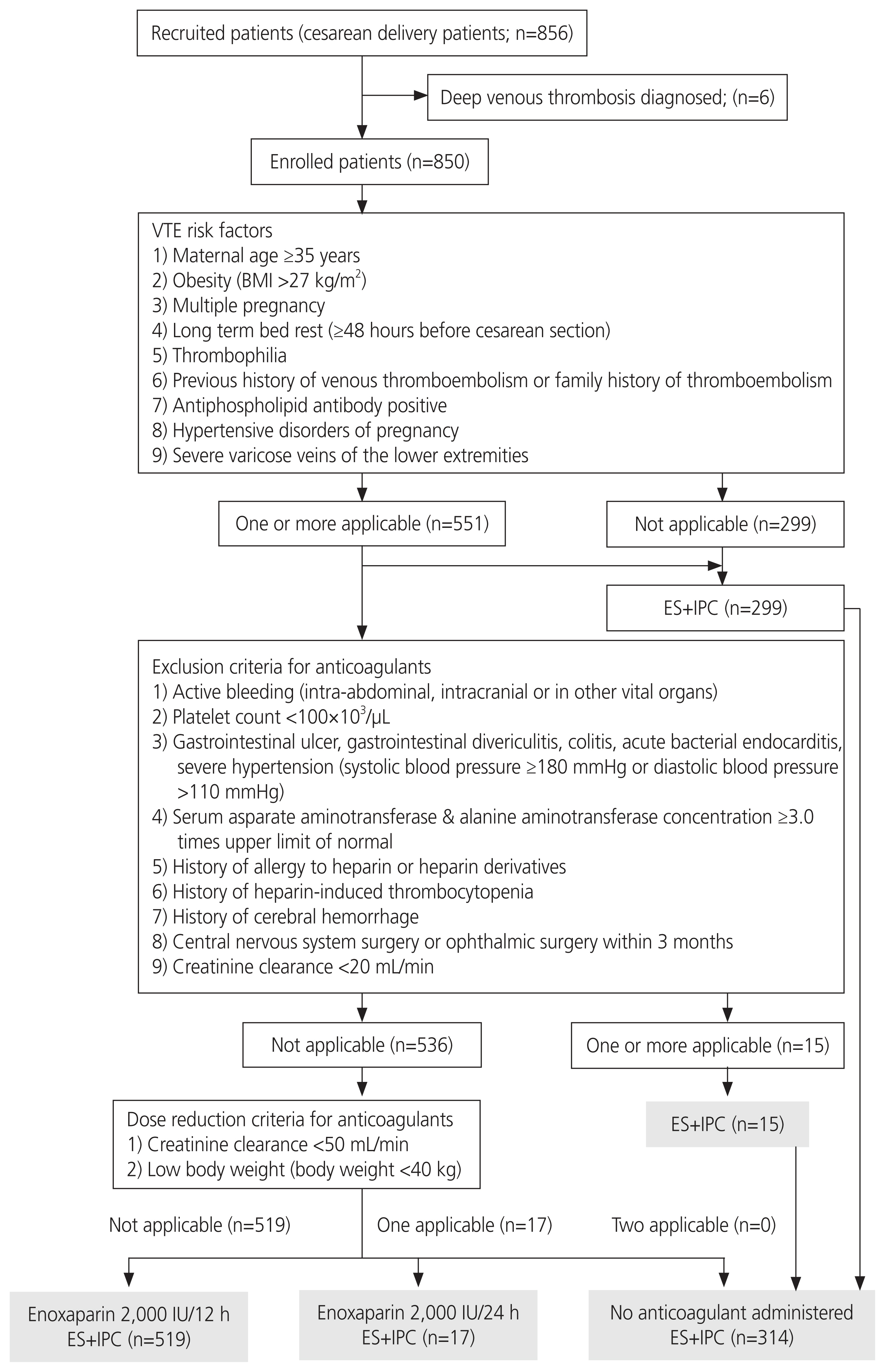
Out of the 850 women eligible for this study, 551 (64.9%) had one or more VTE risk factors and 299 (35.1%) had no risk factors. Of the 551 women with one or more VTE risk factors, 15 met one or more exclusion criteria for enoxaparin administration. A total of 314 women received only perioperative mechanical prophylaxis, including 15 who met the exclusion criteria for anticoagulants and 299 without VTE risk factors. During implementation of the protocol, no woman developed symptomatic VTE after cesarean delivery. Major bleeding occurred in only one woman who received postoperative anticoagulants.
Conclusion
This protocol, which clarified the administration of anticoagulants according to VTE risk factors and dose reduction/discontinuation criteria, may be an effective and safe VTE prophylaxis for cesarean deliveries.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Anderson FA Jr, Spencer FA. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003; 107:I9–16.
Article2. Lidegaard Ø, Edström B, Kreiner S. Oral contraceptives and venous thromboembolism: a five-year national case-control study. Contraception. 2002; 65:187–96.
Article3. Donnelly JC, D’Alton ME. Pulmonary embolus in pregnancy. Semin Perinatol. 2013; 37:225–33.
Article4. Sia WW, Powrie RO, Cooper AB, Larson L, Phipps M, Spencer P, et al. The incidence of deep vein thrombosis in women undergoing cesarean delivery. Thromb Res. 2009; 123:550–5.
Article5. Giannubilo SR, Tranquilli AL. Anticoagulant therapy during pregnancy for maternal and fetal acquired and inherited thrombophilia. Curr Med Chem. 2012; 19:4562–71.
Article6. Haruta S, Kawaguchi R, Hirai T, Kobayashi H. Sequential screening to predict symptomatic pulmonary thromboembolism after gynecologic surgery in Nara, Japan. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016; 132:42–5.
Article7. Bain E, Wilson A, Tooher R, Gates S, Davis LJ, Middleton P. Prophylaxis for venous thromboembolic disease in pregnancy and the early postnatal period. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; (2):CD001689.
Article8. Bates SM, Greer IA, Middeldorp S, Veenstra DL, Prabulos AM, Vandvik PO. VTE, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Ches. 2012; 141:e691S–736S.9. Ahmed I, Majeed A, Powell R. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia: diagnosis and management update. Postgrad Med J. 2007; 83:575–82.
Article10. Jackson E, Curtis KM, Gaffield ME. Risk of venous thromboembolism during the postpartum period: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117:691–703.11. Blondon M, Casini A, Hoppe KK, Boehlen F, Righini M, Smith NL. Risks of venous thromboembolism after cesarean sections: a meta-analysis. Chest. 2016; 150:572–96.
Article12. Ferres MA, Olivarez SA, Trinh V, Davidson C, Sangi-Haghpeykar H, Aagaard-Tillery KM. Rate of wound complications with enoxaparin use among women at high risk for postpartum thrombosis. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117:119–24.
Article13. Bounameaux H. Unfractionated versus low-molecular-weight heparin in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Vasc Med. 1998; 3:41–6.
Article14. Stricker BHC, Spoelstra P. Drug-induced hepatic injury. 2nd. New York: Elsevier;1992. p. 339–40.15. Harrill AH, Roach J, Fier I, Eaddy JS, Kurtz CL, Antoine DJ, et al. The effects of heparins on the liver: application of mechanistic serum biomarkers in a randomized study in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 92:214–20.
Article16. Carlson MK, Gleason PP, Sen S. Elevation of hepatic transaminases after enoxaparin use: case report and review of unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacotherapy. 2001; 21:108–13.
Article17. Arora N, Goldhaber SZ. Anticoagulants and transaminase elevation. Circulation. 2006; 113:e698–702.
Article18. Livertox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases;c2012. [cited 2023 Mar 2]. Abailable from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548009/ .19. Hahn KJ, Morales SJ, Lewis JH. Enoxaparin-induced liver injury: case report and review of the literature and FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS). Drug Saf Case Rep. 2015; 2:17.
Article20. Mehershahi S, Mantri N, Kumar A, Danial S, Harish P. Enoxaparin-induced liver injury. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2020; 14:315–19.
Article21. Martel N, Lee J, Wells PS. Risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis: a meta-analysis. Blood. 2005; 106:2710–5.
Article22. Girolami B, Prandoni P, Stefani PM, Tanduo C, Sabbion P, Eichler P, et al. The incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in hospitalized medical patients treated with subcutaneous unfractionated heparin: a prospective cohort study. Blood. 2003; 101:2955–9.
Article23. Warkentin TE, Sheppard JA, Sigouin CS, Kohlmann T, Eichler P, Greinacher A. Gender imbalance and risk factor interactions in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2006; 108:2937–41.24. Warkentin TE. The paradox of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7:1472–3.
Article25. Warkentin TE, Kelton JG. Delayed-onset heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:502–6.
Article26. Warkentin TE, Levine MN, Hirsh J, Horsewood P, Roberts RS, Gent M, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients treated with low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:1330–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Developed After Cesarean Section
- Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Pulmonary Thromboembolism during Cesarean Delivery: A case report
- Pulmonary Embolism and Uterine Venous Plexus Thrombosis in the Postpartum Period
- A Case of Pulmonary Embolism After Cesarean Delivery
- Efficacy and safety of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis with fondaparinux in women at risk after cesarean section