Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Apr;38(2):226-244. 10.3803/EnM.2022.1604.
Inhibition of Fatty Acid β-Oxidation by Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Induces Ferroptosis in HK2 Cells Under High Glucose Conditions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nephrology, Kidney and Urology Center, The Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, China
- 2Renal Division, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China
- KMID: 2541879
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1604
Abstract
- Background
Ferroptosis, which is caused by an iron-dependent accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides, is a type of cell death linked to diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Previous research has shown that fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) is involved in the regulation of ferroptosis in diabetic retinopathy. The present study was constructed to explore the role of FABP4 in the regulation of ferroptosis in DKD.
Methods
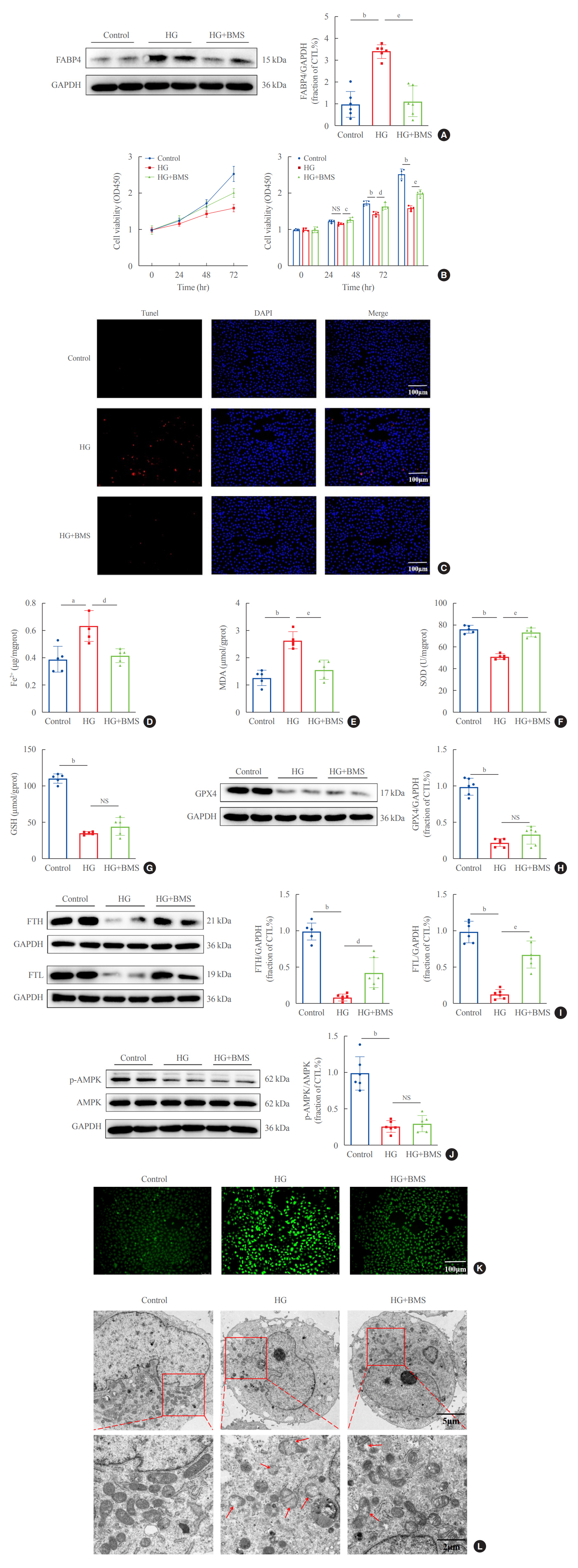
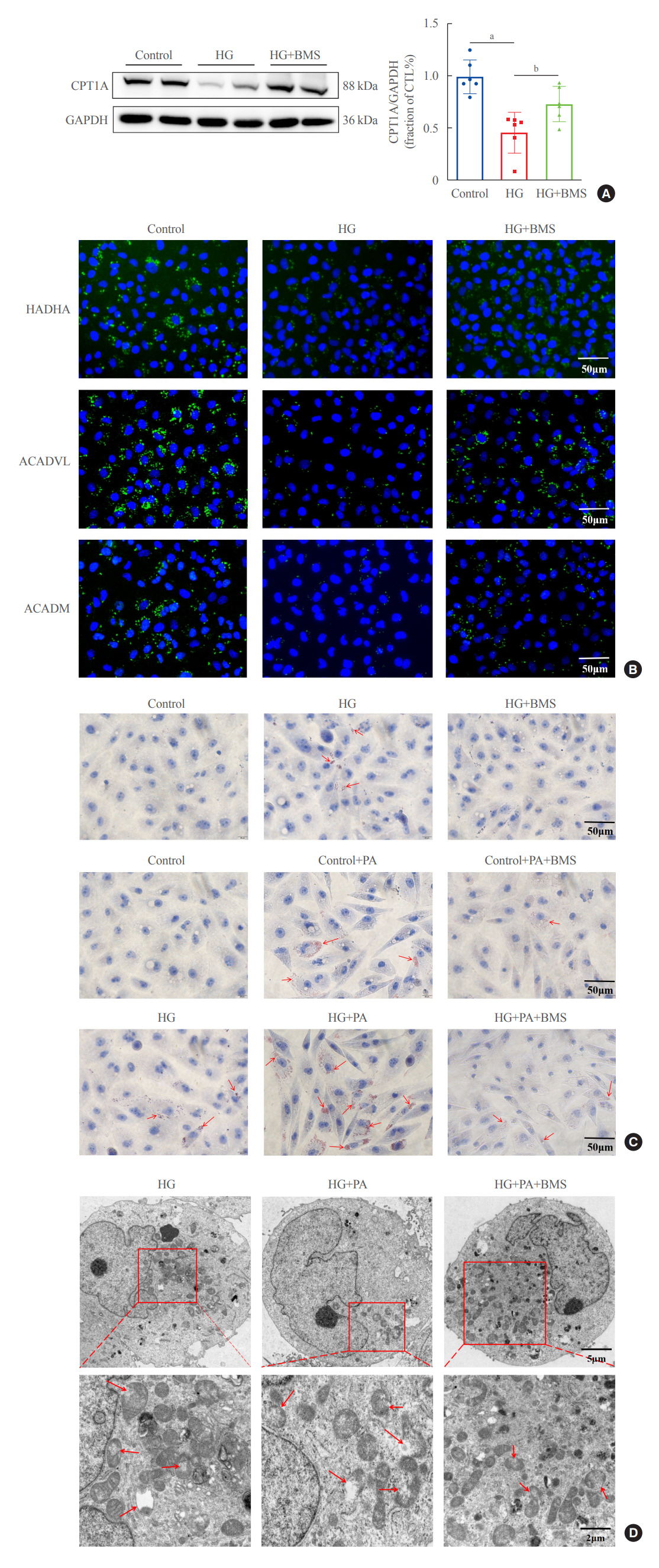
We first detected the expression of FABP4 and proteins related to ferroptosis in renal biopsies of patients with DKD. Then, we used a FABP4 inhibitor and small interfering RNA to investigate the role of FABP4 in ferroptosis induced by high glucose in human renal proximal tubular epithelial (HG-HK2) cells.
Results
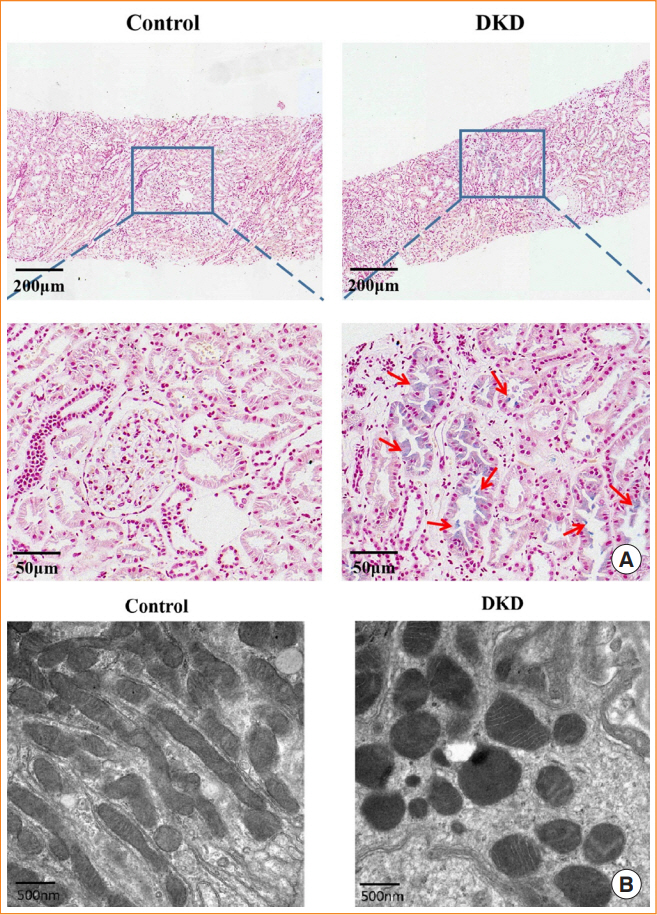
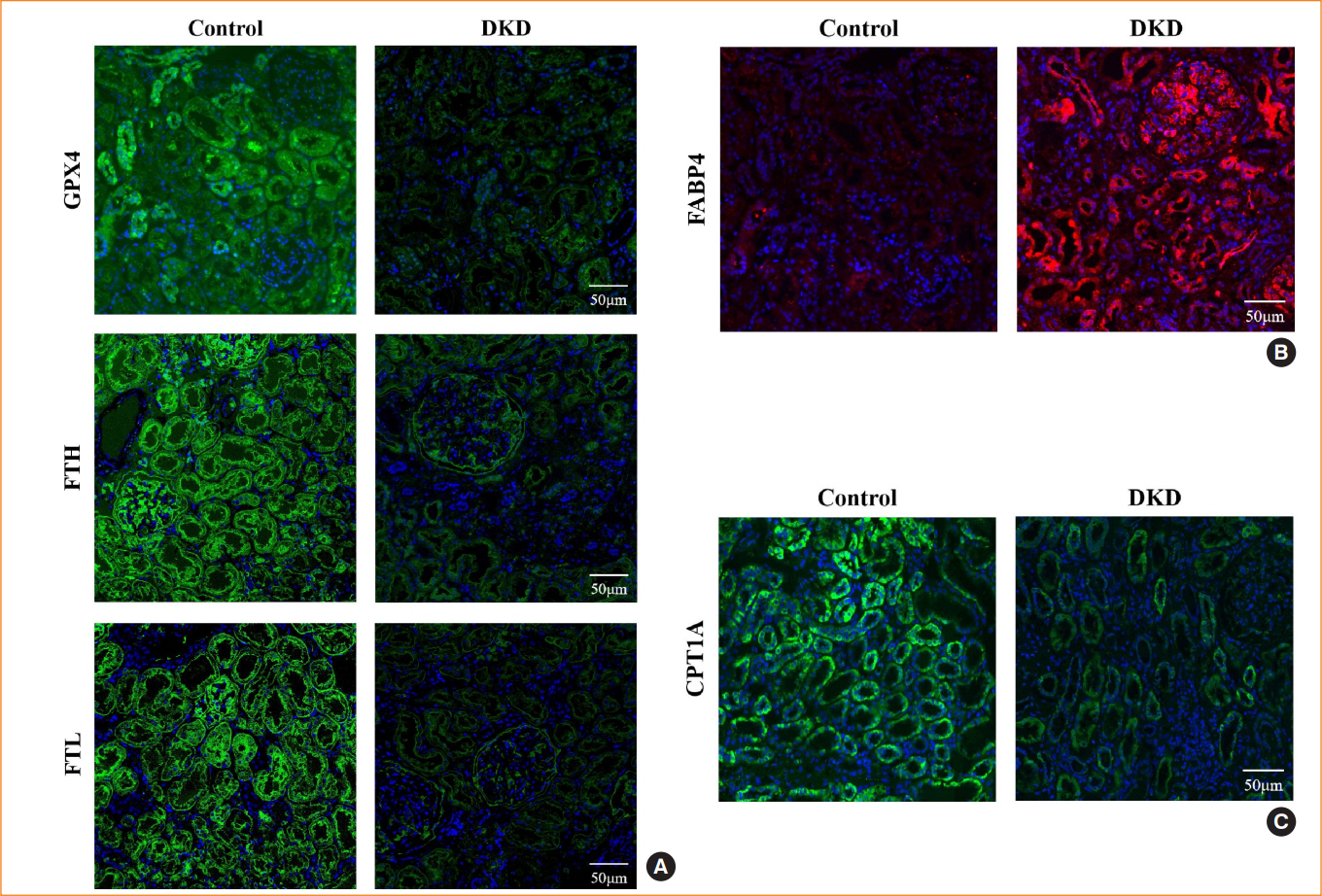
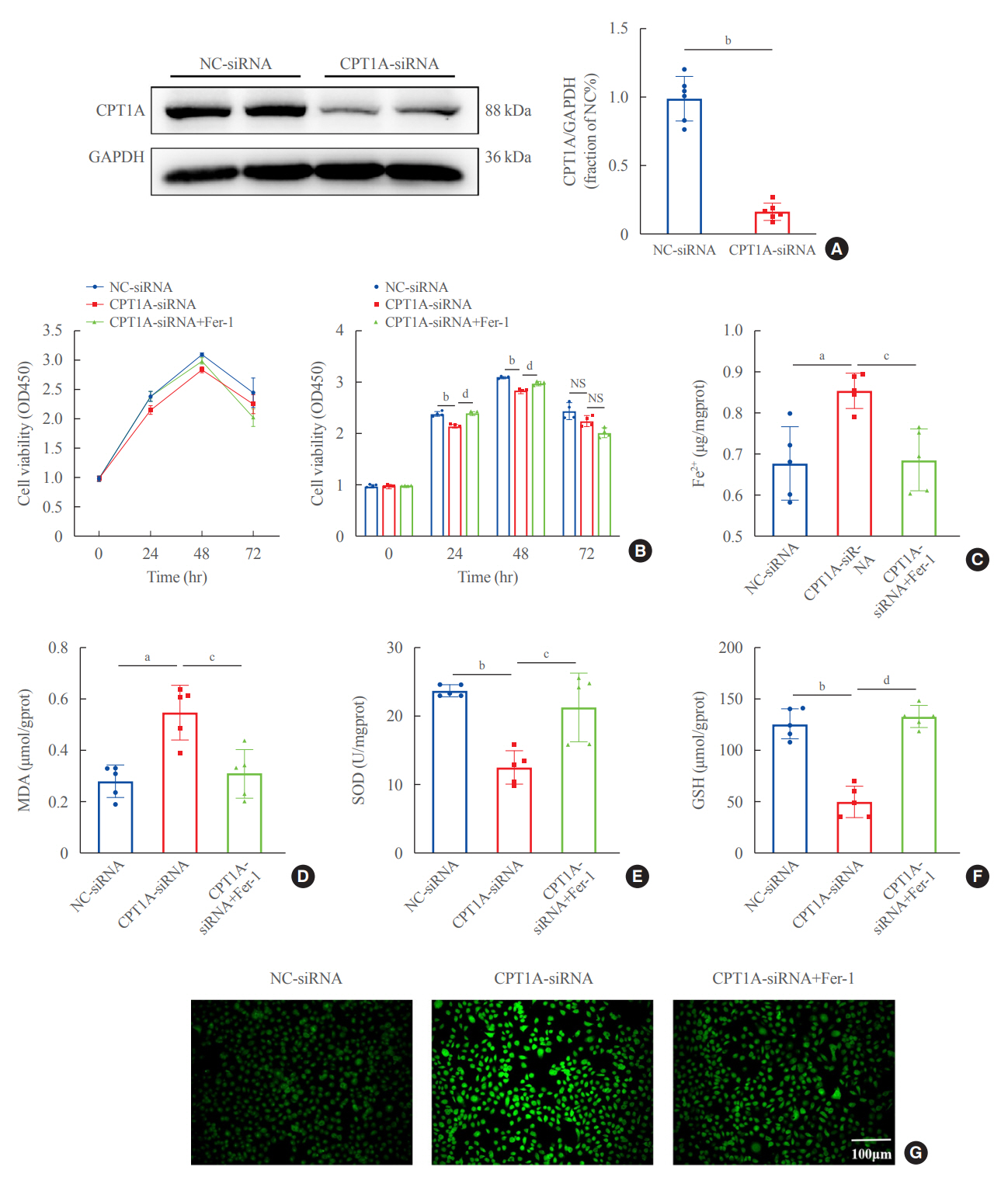
In kidney biopsies of DKD patients, the expression of FABP4 was elevated, whereas carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1A (CP-T1A), glutathione peroxidase 4, ferritin heavy chain, and ferritin light chain showed reduced expression. In HG-HK2 cells, the induction of ferroptosis was accompanied by an increase in FABP4. Inhibition of FABP4 in HG-HK2 cells changed the redox state, sup-pressing the production of reactive oxygen species, ferrous iron (Fe2+), and malondialdehyde, increasing superoxide dismutase, and reversing ferroptosis-associated mitochondrial damage. The inhibition of FABP4 also increased the expression of CPT1A, reversed lipid deposition, and restored impaired fatty acid β-oxidation. In addition, the inhibition of CPT1A could induce ferroptosis in HK2 cells.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that FABP4 mediates ferroptosis in HG-HK2 cells by inhibiting fatty acid β-oxidation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bonner R, Albajrami O, Hudspeth J, Upadhyay A. Diabetic kidney disease. Prim Care. 2020; 47:645–59.
Article2. Cheng HT, Xu X, Lim PS, Hung KY. Worldwide epidemiology of diabetes-related end-stage renal disease, 2000-2015. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44:89–97.
Article3. Levin A, Tonelli M, Bonventre J, Coresh J, Donner JA, Fogo AB, et al. Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet. 2017; 390:1888–917.
Article4. Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019; 12:34.
Article5. Tang S, Xiao X. Ferroptosis and kidney diseases. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020; 52:497–503.
Article6. Weiland A, Wang Y, Wu W, Lan X, Han X, Li Q, et al. Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2019; 56:4880–93.
Article7. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012; 149:1060–72.
Article8. Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11:88.
Article9. Hu W, Liang K, Zhu H, Zhao C, Hu H, Yin S. Ferroptosis and its role in chronic diseases. Cells. 2022; 11:2040.
Article10. Yang WS, Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016; 26:165–76.
Article11. Ayala A, Munoz MF, Arguelles S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014; 2014:360438.
Article12. Ursini F, Maiorino M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020; 152:175–85.
Article13. Wang Y, Qiu S, Wang H, Cui J, Tian X, Miao Y, et al. Transcriptional repression of ferritin light chain increases ferroptosis sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021; 9:719187.
Article14. He J, Li Z, Xia P, Shi A, FuChen X, Zhang J, et al. Ferroptosis and ferritinophagy in diabetes complications. Mol Metab. 2022; 60:101470.
Article15. Thevenod F, Wolff NA. Iron transport in the kidney: implications for physiology and cadmium nephrotoxicity. Metallomics. 2016; 8:17–42.
Article16. Agborbesong E, Li LX, Li L, Li X. Molecular mechanisms of epigenetic regulation, inflammation, and cell death in ADPKD. Front Mol Biosci. 2022; 9:922428.
Article17. Li S, Zheng L, Zhang J, Liu X, Wu Z. Inhibition of ferroptosis by up-regulating Nrf2 delayed the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021; 162:435–49.
Article18. Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22:266–82.
Article19. Zheng J, Conrad M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020; 32:920–37.
Article20. Lee JY, Kim WK, Bae KH, Lee SC, Lee EW. Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis. Biology (Basel). 2021; 10:184.
Article21. Lin Z, Liu J, Kang R, Yang M, Tang D. Lipid metabolism in ferroptosis. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021; 5:e2100396.
Article22. Miess H, Dankworth B, Gouw AM, Rosenfeldt M, Schmitz W, Jiang M, et al. The glutathione redox system is essential to prevent ferroptosis caused by impaired lipid metabolism in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2018; 37:5435–50.
Article23. Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021; 17:2054–81.
Article24. Opazo-Rios L, Mas S, Marin-Royo G, Mezzano S, Gomez-Guerrero C, Moreno JA, et al. Lipotoxicity and diabetic nephropathy: novel mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21:2632.
Article25. Russo GT, De Cosmo S, Viazzi F, Pacilli A, Ceriello A, Genovese S, et al. Plasma triglycerides and HDL-C levels predict the development of diabetic kidney disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes: the AMD Annals Initiative. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:2278–87.
Article26. Herman-Edelstein M, Scherzer P, Tobar A, Levi M, Gafter U. Altered renal lipid metabolism and renal lipid accumulation in human diabetic nephropathy. J Lipid Res. 2014; 55:561–72.
Article27. Saudek CD, Eder HA. Lipid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1979; 66:843–52.
Article28. Li H, Xiao Y, Tang L, Zhong F, Huang G, Xu JM, et al. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein promotes palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in macrophages. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:81.
Article29. Li HL, Wu X, Xu A, Hoo RL. A-FABP in metabolic diseases and the therapeutic implications: an update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22:9386.
Article30. Shi M, Ma L, Fu P. Role of fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) in kidney disease. Curr Med Chem. 2020; 27:3657–64.
Article31. Chen Y, Dai Y, Song K, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhang C, et al. Pre-emptive pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid-binding protein 4 attenuates kidney fibrosis by reprogramming tubular lipid metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12:572.
Article32. Tanaka M, Furuhashi M, Okazaki Y, Mita T, Fuseya T, Ohno K, et al. Ectopic expression of fatty acid-binding protein 4 in the glomerulus is associated with proteinuria and renal dysfunction. Nephron Clin Pract. 2014; 128:345–51.
Article33. Hotamisligil GS, Bernlohr DA. Metabolic functions of FABPs: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11:592–605.
Article34. Ni X, Gu Y, Yu H, Wang S, Chen Y, Wang X, et al. Serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels are independently associated with radioisotope glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetic patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:4578140.
Article35. Lee CH, Cheung CY, Woo YC, Lui DT, Yuen MM, Fong CH, et al. Prospective associations of circulating adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels with risks of renal outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:169–77.
Article36. Fan X, Xu M, Ren Q, Fan Y, Liu B, Chen J, et al. Downregulation of fatty acid binding protein 4 alleviates lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in diabetic retinopathy by regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-mediated ferroptosis. Bioengineered. 2022; 13:10540–51.
Article37. Liu J, Huang R, Li X, Guo F, Li L, Zeng X, et al. Genetic inhibition of FABP4 attenuated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury. Life Sci. 2021; 268:119023.
Article38. Luis G, Godfroid A, Nishiumi S, Cimino J, Blacher S, Maquoi E, et al. Tumor resistance to ferroptosis driven by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) in cancer cells and fatty acid biding protein-4 (FABP4) in tumor microenvironment promote tumor recurrence. Redox Biol. 2021; 43:102006.
Article39. Fang X, Ardehali H, Min J, Wang F. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023; 20:7–23.
Article40. Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021; 18:280–96.
Article41. Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 2022; 185:2401–21.
Article42. Liang D, Minikes AM, Jiang X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol Cell. 2022; 82:2215–27.
Article43. Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113:E4966–75.
Article44. Magtanong L, Ko PJ, To M, Cao JY, Forcina GC, Tarangelo A, et al. Exogenous monounsaturated fatty acids promote a ferroptosis-resistant cell state. Cell Chem Biol. 2019; 26:420–32.
Article45. Lee H, Zandkarimi F, Zhang Y, Meena JK, Kim J, Zhuang L, et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020; 22:225–34.
Article46. Juszczak F, Caron N, Mathew AV, Decleves AE. Critical role for AMPK in metabolic disease-induced chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21:7994.
Article47. Entezari M, Hashemi D, Taheriazam A, Zabolian A, Mohammadi S, Fakhri F, et al. AMPK signaling in diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance and diabetic complications: a pre-clinical and clinical investigation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022; 146:112563.48. Gewin LS. Sugar or fat?: renal tubular metabolism reviewed in health and disease. Nutrients. 2021; 13:1580.
Article49. Thongnak L, Pongchaidecha A, Lungkaphin A. Renal lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity in diabetes. Am J Med Sci. 2020; 359:84–99.
Article50. Stadler K, Goldberg IJ, Susztak K. The evolving understanding of the contribution of lipid metabolism to diabetic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep. 2015; 15:40.
Article51. Miguel V, Tituana J, Herrero JI, Herrero L, Serra D, Cuevas P, et al. Renal tubule Cpt1a overexpression protects from kidney fibrosis by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2021; 131:e140695.
Article52. Shen Y, Chen W, Han L, Bian Q, Fan J, Cao Z, et al. VEGF-B antibody and interleukin-22 fusion protein ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting lipid accumulation and inflammatory responses. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021; 11:127–42.
Article53. Fu Y, Sun Y, Wang M, Hou Y, Huang W, Zhou D, et al. Elevation of JAML promotes diabetic kidney disease by modulating podocyte lipid metabolism. Cell Metab. 2020; 32:1052–62.
Article54. Mori Y, Ajay AK, Chang JH, Mou S, Zhao H, Kishi S, et al. KIM-1 mediates fatty acid uptake by renal tubular cells to promote progressive diabetic kidney disease. Cell Metab. 2021; 33:1042–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Free Fatty Acid on Insulin Secretion in Cultured Rat Pancreatic Islets
- AMPK Activator AICAR Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Fatty Acid Oxidation
- Increase in Fatty Acid Oxidation by AICAR: the Role of p38 MAPK
- Inhibition of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Uptake by Pyruvate and Fatty Acid in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes: Implications for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- Effects of Lovastatin on Free Fatty Acid Oxidation in Cultured L6 Rat Skeletal Muscle Cells