Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 May;27(3):277-287. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.3.277.
Saturated fatty acid-inducible miR-103-3p impairs the myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells by enhancing cell proliferation through Twinfilin-1/F-actin/YAP1 axis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju 38066, Korea
- 2Channelopathy Research Center (CRC), Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang 10326, Korea
- KMID: 2541639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.3.277
Abstract
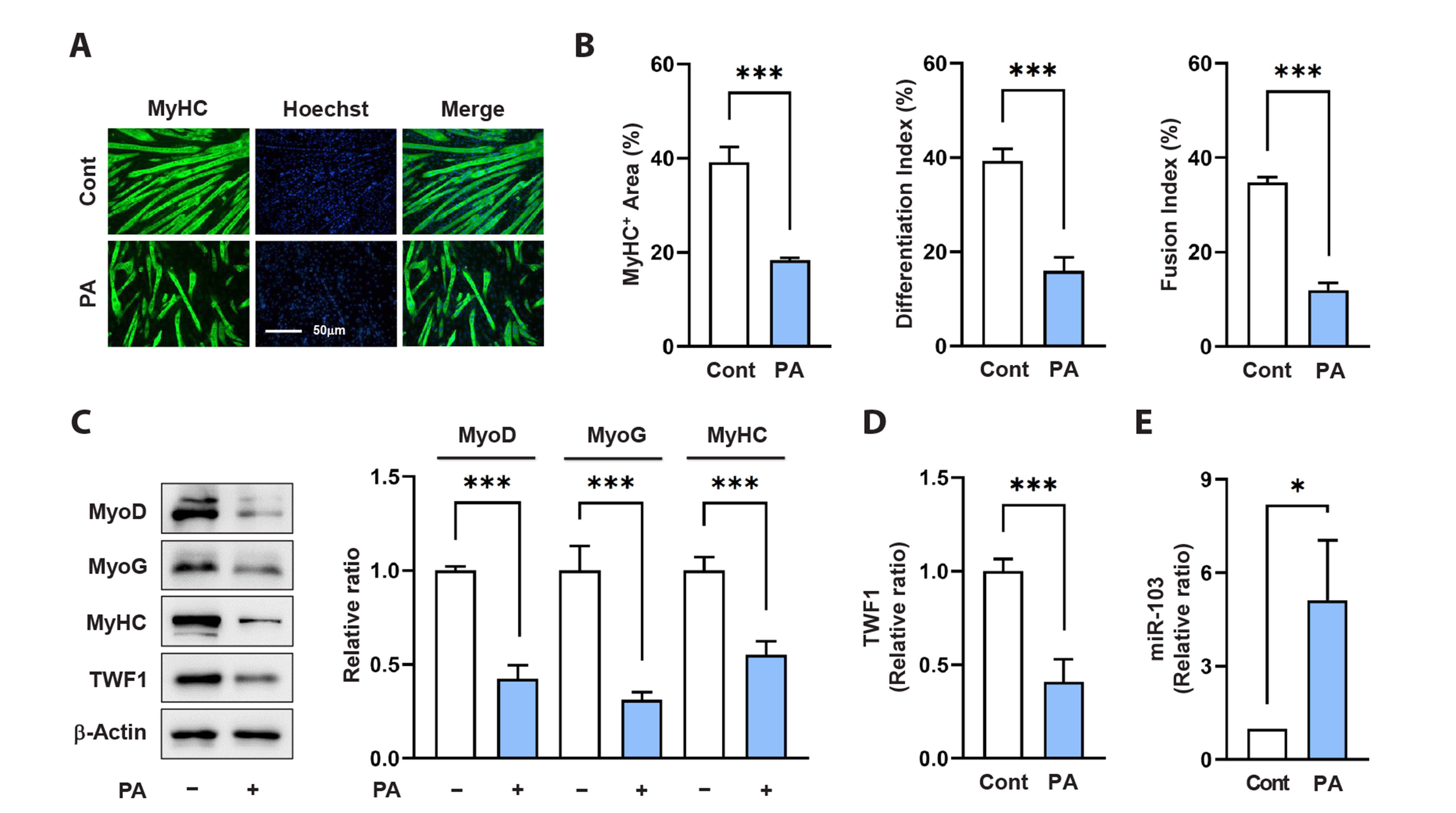
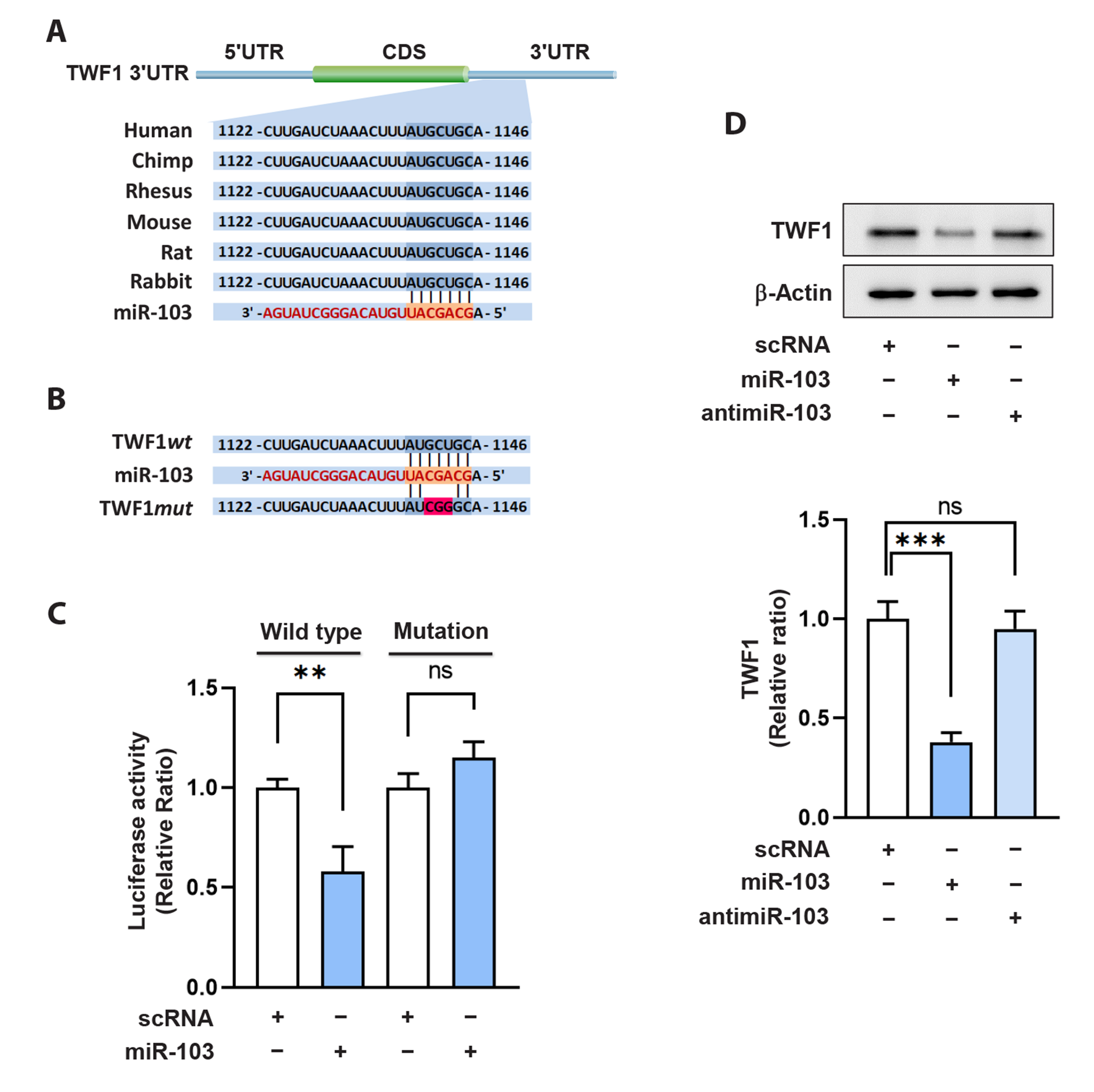
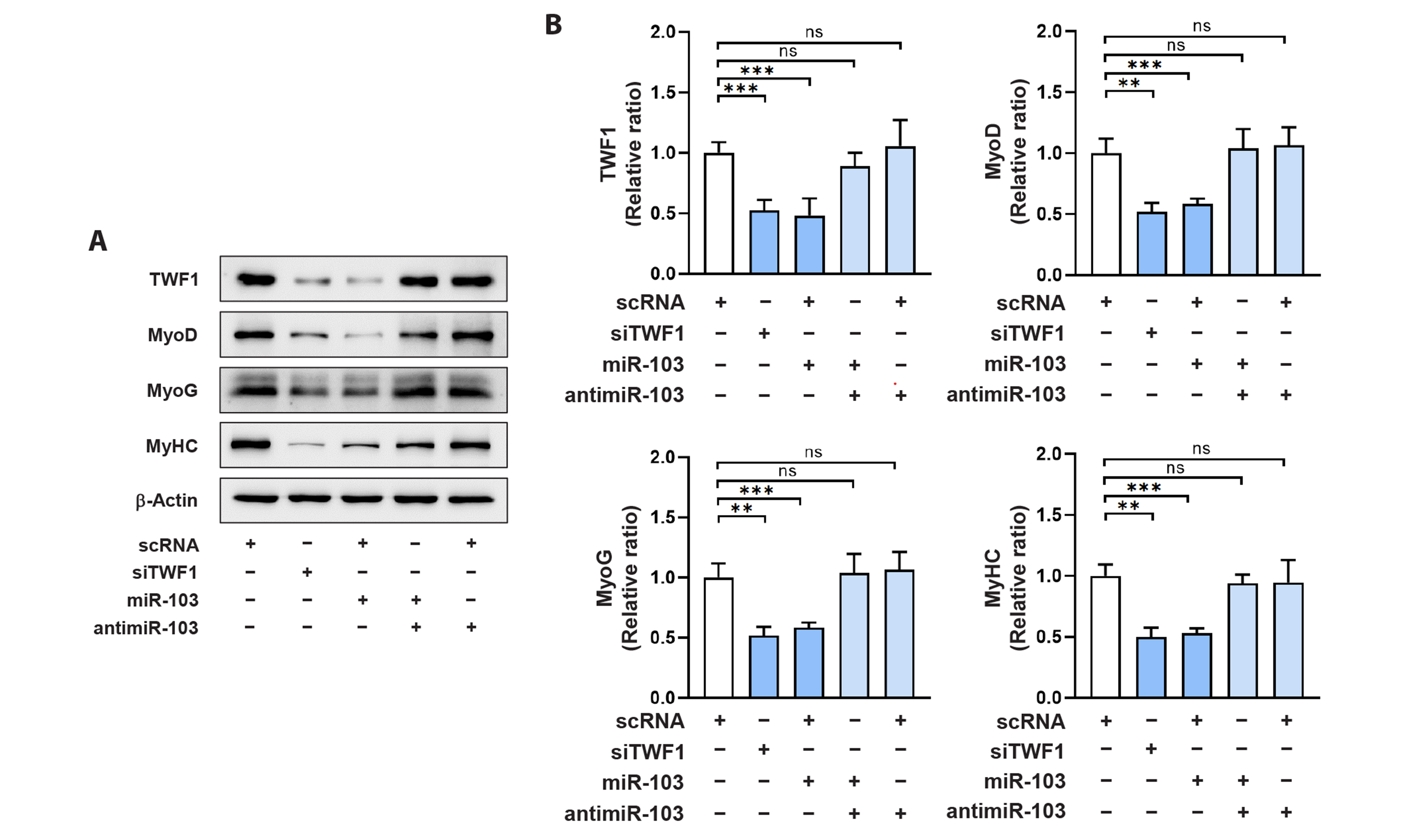
- Actin dynamics play an essential role in myogenesis through multiple mechanisms, such as mechanotransduction, cell proliferation, and myogenic differentiation. Twinfilin-1 (TWF1), an actin-depolymerizing protein, is known to be required for the myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells. However, the mechanisms by which they epigenetically regulate TWF1 by microRNAs under muscle wasting conditions related to obesity are almost unknown. Here, we investigated the role of miR-103-3p in TWF1 expression, actin filament modulation, proliferation, and myogenic differentiation of progenitor cells. Palmitic acid, the most abundant saturated fatty acid (SFA) in the diet, reduced TWF1 expression and impeded myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts, while elevating miR-103-3p levels in myoblasts. Interestingly, miR-103-3p inhibited TWF1 expression by directly targeting its 3’UTR. Furthermore, ectopic expression of miR-103-3p reduced the expression of myogenic factors, i.e., MyoD and MyoG, and subsequently impaired myoblast differentiation. We demonstrated that miR-103-3p induction increased filamentous actin (F-actin) and facilitated the nuclear translocation of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), thereby stimulating cell cycle progression and cell proliferation. Hence, this study suggests that epigenetic suppression of TWF1 by SFA-inducible miR-103-3p impairs myogenesis by enhancing the cell proliferation triggered by F-actin/YAP1.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mukund K, Subramaniam S. 2020; Skeletal muscle: a review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 12:e1462. DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1462. PMID: 31407867. PMCID: PMC6916202.
Article2. Chal J, Pourquié O. 2017; Making muscle: skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development. 144:2104–2122. DOI: 10.1242/dev.151035. PMID: 28634270.3. Sartori R, Romanello V, Sandri M. 2021; Mechanisms of muscle atrophy and hypertrophy: implications in health and disease. Nat Commun. 12:330. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20123-1. PMID: 33436614. PMCID: PMC7803748. PMID: 53db8cc5160a46c3bf9a31a615d5e847.
Article4. Akhmedov D, Berdeaux R. 2013; The effects of obesity on skeletal muscle regeneration. Front Physiol. 4:371. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00371. PMID: 24381559. PMCID: PMC3865699. PMID: bd56e511b6364b308390add5d21b4737.
Article5. Guerin CM, Kramer SG. 2009; Cytoskeletal remodeling during myotube assembly and guidance: coordinating the actin and microtubule networks. Commun Integr Biol. 2:452–457. DOI: 10.4161/cib.2.5.9158. PMID: 19907716. PMCID: PMC2775249.6. Heng YW, Koh CG. 2010; Actin cytoskeleton dynamics and the cell division cycle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1622–1633. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.04.007. PMID: 20412868.
Article7. Watt KI, Goodman CA, Hornberger TA, Gregorevic P. 2018; The Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass and function. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 46:92–96. DOI: 10.1249/JES.0000000000000142. PMID: 29346163. PMCID: PMC6319272.
Article8. Fischer M, Rikeit P, Knaus P, Coirault C. 2016; YAP-mediated mechanotransduction in skeletal muscle. Front Physiol. 7:41. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00041. PMID: 26909043. PMCID: PMC4754448. PMID: 5a6c62c8b18b4f119e329aff69bc2a6e.
Article9. Nguyen NU, Liang VR, Wang HV. 2014; Actin-associated protein palladin is required for migration behavior and differentiation potential of C2C12 myoblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 452:728–733. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.143. PMID: 25194811.
Article10. Li H, Hou L, Zhang Y, Jiang F, Zhu Y, Li QX, Hu CY, Wang C. 2019; PFN2a suppresses C2C12 myogenic development by inhibiting proliferation and promoting apoptosis via the p53 pathway. Cells. 8:959. DOI: 10.3390/cells8090959. PMID: 31450751. PMCID: PMC6770762. PMID: 7a4c017f5f3f4526961f7fd9f6be2d19.
Article11. Nguyen MT, Min KH, Kim D, Park SY, Lee W. 2020; CFL2 is an essential mediator for myogenic differentiation in C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 533:710–716. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.016. PMID: 33187645.
Article12. Dupont S, Morsut L, Aragona M, Enzo E, Giulitti S, Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Le Digabel J, Forcato M, Bicciato S, Elvassore N, Piccolo S. 2011; Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature. 474:179–183. DOI: 10.1038/nature10137. PMID: 21654799.
Article13. Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, Piccolo S. 2013; A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 154:1047–1059. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.042. PMID: 23954413.
Article14. Nguyen MT, Won YH, Kwon TW, Lee W. 2022; Twinfilin-1 is an essential regulator of myogenic differentiation through the modulation of YAP in C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 599:17–23. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.021. PMID: 35168059.
Article15. Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH. 2019; An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 234:5451–5465. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27486. PMID: 30471116.
Article16. Dowling L, Duseja A, Vilaca T, Walsh JS, Goljanek-Whysall K. 2022; MicroRNAs in obesity, sarcopenia, and commonalities for sarcopenic obesity: a systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:68–85. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12878. PMID: 34984856. PMCID: PMC8818592. PMID: 39e3a1acc69341c09daa9bbe73df46d5.
Article17. Zhao Y, Chen M, Lian D, Li Y, Li Y, Wang J, Deng S, Yu K, Lian Z. 2019; Non-coding RNA regulates the myogenesis of skeletal muscle satellite cells, injury repair and diseases. Cells. 8:988. DOI: 10.3390/cells8090988. PMID: 31461973. PMCID: PMC6769629. PMID: c274d319e33148a19d33df3e4507d3d0.
Article18. Sannicandro AJ, Soriano-Arroquia A, Goljanek-Whysall K. 2019; Micro(RNA)-managing muscle wasting. J Appl Physiol (1985). 127:619–632. Erratum in: J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;127:1502. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00961.2018. PMID: 30991011.
Article19. Ji C, Guo X. 2019; The clinical potential of circulating microRNAs in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 15:731–743. DOI: 10.1038/s41574-019-0260-0. PMID: 31611648.
Article20. Xia W, Ni J, Zhuang J, Qian L, Wang P, Wang J. 2016; MiR-103 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth by targeting AKAP12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 71:1–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.017. PMID: 26646106.
Article21. 2017; Correction: miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 77:6788. Erratum for: Cancer Res. 2012;72:3631-3641. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0667. PMID: 22593189.22. Li K, Yuan C. 2020; MicroRNA-103 modulates tumor progression by targeting KLF7 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 46:1013–1028. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4649. PMID: 32582959. PMCID: PMC7387085.
Article23. Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M, Heim MH, Stoffel M. 2011; MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature. 474:649–653. DOI: 10.1038/nature10112. PMID: 21654750.
Article24. Näär AM. 2011; MiRs with a sweet tooth. Cell Metab. 14:149–150. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.07.005. PMID: 21803284. PMCID: PMC3880780.
Article25. Rottiers V, Näär AM. 2012; MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:239–250. Erratum in: Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:1. DOI: 10.1038/nrm3313. PMID: 22436747. PMCID: PMC4021399.
Article26. Cui X, You L, Zhu L, Wang X, Zhou Y, Li Y, Wen J, Xia Y, Wang X, Ji C, Guo X. 2018; Change in circulating microRNA profile of obese children indicates future risk of adult diabetes. Metabolism. 78:95–105. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.09.006. PMID: 28966078.
Article27. Xu Q, Li Y, Shang YF, Wang HL, Yao MX. 2015; miRNA-103: molecular link between insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 21:511–516. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.511. PMID: 25593466. PMCID: PMC4292282.
Article28. Yamamoto H, Morino K, Nishio Y, Ugi S, Yoshizaki T, Kashiwagi A, Maegawa H. 2012; MicroRNA-494 regulates mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle through mitochondrial transcription factor A and Forkhead box j3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 303:E1419–E1427. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00097.2012. PMID: 23047984.
Article29. Pike LS, Smift AL, Croteau NJ, Ferrick DA, Wu M. 2011; Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by etomoxir impairs NADPH production and increases reactive oxygen species resulting in ATP depletion and cell death in human glioblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:726–734. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.10.022. PMID: 21692241.
Article30. Nguyen MT, Min KH, Lee W. 2020; MiR-96-5p induced by palmitic acid suppresses the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by targeting FHL1. Int J Mol Sci. 21:9445. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249445. PMID: 33322515. PMCID: PMC7764195. PMID: 3d4f21be3da14dffb849999903560083.
Article31. Dupont S. 2016; Role of YAP/TAZ in cell-matrix adhesion-mediated signalling and mechanotransduction. Exp Cell Res. 343:42–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.034. PMID: 26524510.
Article32. Whitfield ML, George LK, Grant GD, Perou CM. 2006; Common markers of proliferation. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:99–106. DOI: 10.1038/nrc1802. PMID: 16491069.
Article33. Mok GF, Lozano-Velasco E, Münsterberg A. 2017; microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 72:67–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.10.032. PMID: 29102719.
Article34. Poukkula M, Kremneva E, Serlachius M, Lappalainen P. 2011; Actin-depolymerizing factor homology domain: a conserved fold performing diverse roles in cytoskeletal dynamics. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 68:471–490. DOI: 10.1002/cm.20530. PMID: 21850706.
Article35. Palmgren S, Vartiainen M, Lappalainen P. 2002; Twinfilin, a molecular mailman for actin monomers. J Cell Sci. 115(Pt 5):881–886. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.115.5.881. PMID: 11870207.
Article36. Johnston AB, Collins A, Goode BL. 2015; High-speed depolymerization at actin filament ends jointly catalysed by Twinfilin and Srv2/CAP. Nat Cell Biol. 17:1504–1511. DOI: 10.1038/ncb3252. PMID: 26458246. PMCID: PMC4808055.
Article37. Hakala M, Wioland H, Tolonen M, Kotila T, Jegou A, Romet-Lemonne G, Lappalainen P. 2021; Twinfilin uncaps filament barbed ends to promote turnover of lamellipodial actin networks. Nat Cell Biol. 23:147–159. Erratum in: Nat Cell Biol. 2021;23:437-438. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-020-00629-y. PMID: 33558729.
Article38. Xie H, Lim B, Lodish HF. 2009; MicroRNAs induced during adipogenesis that accelerate fat cell development are downregulated in obesity. Diabetes. 58:1050–1057. DOI: 10.2337/db08-1299. PMID: 19188425. PMCID: PMC2671055.
Article39. Mendez MG, Janmey PA. 2012; Transcription factor regulation by mechanical stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:728–732. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.02.003. PMID: 22387568. PMCID: PMC3445012.
Article40. Pan D. 2010; The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 19:491–505. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011. PMID: 20951342. PMCID: PMC3124840.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MiR-148a-3p Regulates the Invasion and Odontoblastic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells via the Wnt1/β-Catenin Pathway
- MicroRNA-103a-3p controls proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells
- MiR-29a-3p Inhibits Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Targeting FOXO3 and Repressing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis
- MiR-103a-3p Contributes to the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Regulating GREM2 Expression
- DNM3OS Facilitates Ovarian Cancer Progression by Regulating miR-193a-3p/MAP3K3 Axis