Blood Res.
2023 Mar;58(1):28-35. 10.5045/br.2023.2022167.
Can the bone marrow harvest volume be reduced safely in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with pediatric sibling donors?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2541062
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2023.2022167
Abstract
- Background
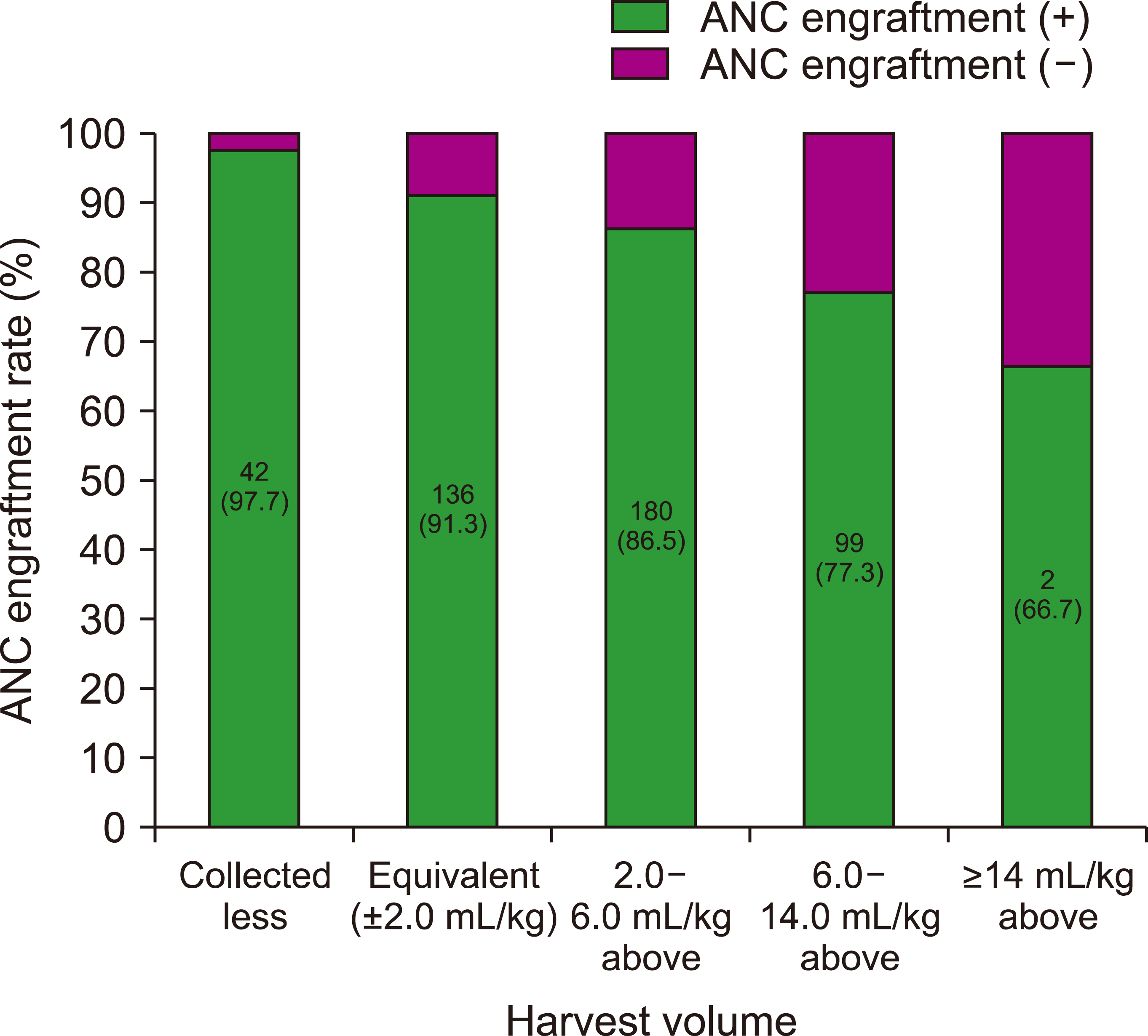
Reduced harvest volumes in pediatric donors appear to have the potential to reduce donor-associated risks while maintaining engraftment in recipients; however, the allowable harvest volume reduction remains undefined.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the data pairs of 553 bone marrow (BM) harvests from pediatric (age at harvest <18 yr) sibling donors and clinical outcomes of 553 pediatric (age at infusion <14 yr) transplant-naïve recipients to assess the optimal BM harvest volume needed from pediatric donors to obtain the desired CD34+ cell count (≥3.0×10 6 cells per kg of recipient weight), and to study its impact on the clinical outcomes of transplantation in pediatric recipients.
Results
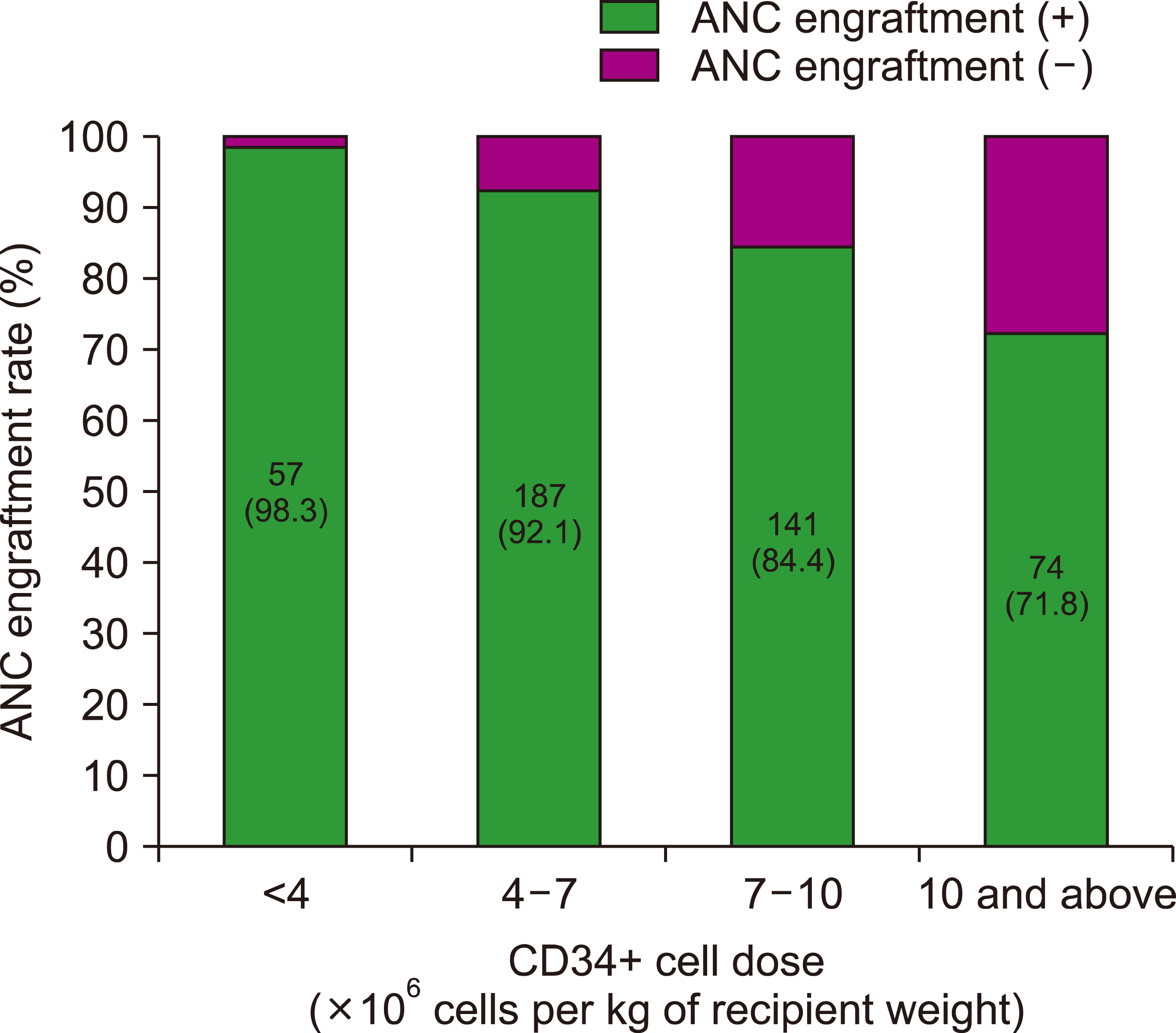
The minimum desired CD34+ cell count of ≥3.0×10 6 per kg of recipient weight was achieved for 506 (95.3%) of donor-recipient pairs. The median CD34+ cell yield was 6.4×10 6 per kg of recipient weight (range, 1.2‒33.8×10 6 ) in donors younger than 5 years old at harvest, 4.7×10 6 (range, 0.3‒28.5×10 6 ) in donors aged 5‒10 years and 2.1×10 6 range, 0.3‒11.3×10 6 ) in donors older than 10 years (P <0.001).
Conclusion
The infused CD34+ cell dose (×10 6 cells/kg of recipient weight) had no impact on GRFS; however, a CD34+ cell dose of >7×10 6 cells/kg of recipient weight did not improve hematopoietic recovery
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Behfar M, Faghihi-Kashani S, Hosseini AS, Ghavamzadeh A, Hamidieh AA. 2018; Long-term safety of short-term administration of filgrastim (rhG-CSF) and leukophresis procedure in healthy children: application of peripheral blood stem cell collection in pediatric donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 24:866–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.12.786. PMID: 29284143.
Article2. Styczynski J, Balduzzi A, Gil L, et al. 2012; Risk of complications during hematopoietic stem cell collection in pediatric sibling donors: a prospective European Group for Blood and Marrow Trans-plantation Pediatric Diseases Working Party study. Blood. 119:2935–42. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-349688. PMID: 22160619.
Article3. Panch SR, Szymanski J, Savani BN, Stroncek DF. 2017; Sources of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and methods to optimize yields for clinical cell therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 23:1241–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.05.003. PMID: 28495640.
Article4. American Academy of Pediatrics. 2010; Committee on Bioethics. Children as hematopoietic stem cell donors. Pediatrics. 125:392–404. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2009-3078. PMID: 20100753. PMCID: PMC3017470.5. Deotare U, Al-Dawsari G, Couban S, Lipton JH. 2015; G-CSF-primed bone marrow as a source of stem cells for allografting: revisiting the concept. Bone Marrow Transplant. 50:1150–6. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2015.80. PMID: 25915812.
Article6. Furey A, Rastogi S, Prince R, et al. 2018; Bone marrow harvest in pediatric sibling donors: role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor priming and CD34+ cell dose. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 24:324–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.10.031. PMID: 29074373.7. Stroncek DF, Holland PV, Bartch G, et al. 1993; Experiences of the first 493 unrelated marrow donors in the National Marrow Donor Program. Blood. 81:1940–6. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V81.7.1940.1940. PMID: 8461478.
Article8. Kuranda K, Vargaftig J, de la Rochere P, et al. 2011; Age-related changes in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Aging Cell. 10:542–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00675.x. PMID: 21418508.
Article9. Yabe M, Morimoto T, Shimizu T, et al. 2014; Feasibility of marrow harvesting from pediatric sibling donors without hematopoietic growth factors and allotransfusion. Bone Marrow Transplant. 49:921–6. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2014.73. PMID: 24777192.
Article10. Bittencourt H, Rocha V, Chevret S, et al. 2002; Association of CD34 cell dose with hematopoietic recovery, infections, and other outcomes after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 99:2726–33. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V99.8.2726. PMID: 11929759.
Article11. Lannert H, Able T, Becker S, et al. 2008; Optimizing BM harvesting from normal adult donors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 42:443–7. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2008.196. PMID: 18622419.
Article12. Lisenko K, Stadtherr P, Bruckner T, et al. 2016; Bone marrow harvesting of allogeneic donors in an outpatient setting: a single-center experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 22:470–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.10.025. PMID: 26551634.
Article13. Frangoul H, Nemecek ER, Billheimer D, et al. 2007; A prospective study of G-CSF primed bone marrow as a stem-cell source for allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in children: a Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Consortium (PBMTC) study. Blood. 110:4584–7. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-101071. PMID: 17827386.14. Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, et al. 1974; Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation. 18:295–304. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-197410000-00001. PMID: 4153799.
Article15. Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, et al. 2015; National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 21:389–401. e1DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.001. PMID: 25529383. PMCID: PMC4329079.
Article16. Holtan SG, DeFor TE, Lazaryan A, et al. 2015; Composite end point of graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 125:1333–8. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-609032. PMID: 25593335. PMCID: PMC4335084.
Article17. Rustia E, Violago L, Jin Z, et al. 2016; Risk factors and utility of a risk-based algorithm for monitoring cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, and adenovirus infections in pediatric recipients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 22:1646–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.05.014. PMID: 27252110. PMCID: PMC5496767.
Article18. Satwani P, Baldinger L, Freedman J, et al. 2009; Incidence of viral and fungal infections following busulfan-based reduced-intensity versus myeloablative conditioning in pediatric allogeneic stem cell transplantation recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 15:1587–95. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.08.006. PMID: 19896083.
Article19. Ince EU, Ileri T, Dogu F, et al. 2015; The impact of donor age and sex on the nucleated cell count and CD34 count in healthy bone marrow donors. Pediatr Transplant. 19:385–90. DOI: 10.1111/petr.12453. PMID: 25761650.
Article20. Kałwak K, Porwolik J, Mielcarek M, et al. 2010; Higher CD34(+) and CD3(+) cell doses in the graft promote long-term survival, and have no impact on the incidence of severe acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease after in vivo T cell-depleted unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 16:1388–401. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.04.001. PMID: 20382248.21. Lee JW, Kim SK, Jang PS, et al. 2015; Impact of CD34+ cell dose in children who receive unrelated PBSCT with in vivo T-cell depletion for hematologic malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 50:68–73. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2014.202. PMID: 25265463.
Article22. Pulsipher MA, Levine JE, Hayashi RJ, et al. 2005; Safety and efficacy of allogeneic PBSC collection in normal pediatric donors: the pediatric blood and marrow transplant consortium experience (PBMTC) 1996-2003. Bone Marrow Transplant. 35:361–7. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1704743. PMID: 15608659.
Article23. Wang TF, Chu SC, Chen SH, et al. 2011; The effect of different harvest strategies on the nucleated cell yields of bone marrow collection. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 17:351–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.05.013. PMID: 20553925.24. Shaughnessy PJ, Kissack B, Bickford DJ, et al. 2000; Correlation of CD34+ cell counts with volume of bone marrow collected for allogeneic bone marrow harvests. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 9:891–4. DOI: 10.1089/152581600750062336. PMID: 11177602.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Aplastic Anemia
- Successful Selective CD34+ Cell Infusion after Late Graft Failure of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Two Cases of Severe Aplastic Anemia
- Evans Syndrome Following Unrelated Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Pediatric Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Korea: April 2000: The Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology
- New therapeutic modalities on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation