Blood Res.
2023 Mar;58(1):20-27. 10.5045/br.2023.2022143.
Abnormal expression of H-Ras induces S-phase arrest and mitotic catastrophe in human T-lymphocyte leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratorio de Biología Molecular, Servicio de Hematología, Hospital General de México, Dr. Eduardo Liceaga, Ciudad de México Molecular Biology Laboratory, Ciudad de México, México.
- 2Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Veracruzana, Veracruz, México.
- 3Servicio de Hematología, Hospital General de México Dr. Eduardo Liceaga, México.
- 4Laboratorio de Inmunología Clínica, Departamento de Inmunología, Escuela Nacional de Ciencias Biológicas, México.
- 5Laboratorio de Inmunología-Genómica y Enfermedades Metabólicas, INMEGEN, Ciudad de México, México.
- KMID: 2541061
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2023.2022143
Abstract
- Background
Leukemia is a neoplasm with high incidence and mortality rates. Mitotic death has been observed in tumor cells treated with chemotherapeutic agents. Ras family proteins participate in the transduction of signals involved in different processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, survival, and paradoxically, initiation of cell death.
Methods
This study investigated the effect of H-Ras expression on human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 cells. Cells were electroporated with either wild-type (Ras wt ) or oncogenic mutant in codon 12 exon 1 (Ras mut ) versions of H-Ras gene and stained for morphological analysis. Cell viability was assessed using trypan blue staining and cell cycle analysis using flow cytometry. H-Ras gene expression was determined using quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The t, ANOVA, and Scheffe tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results
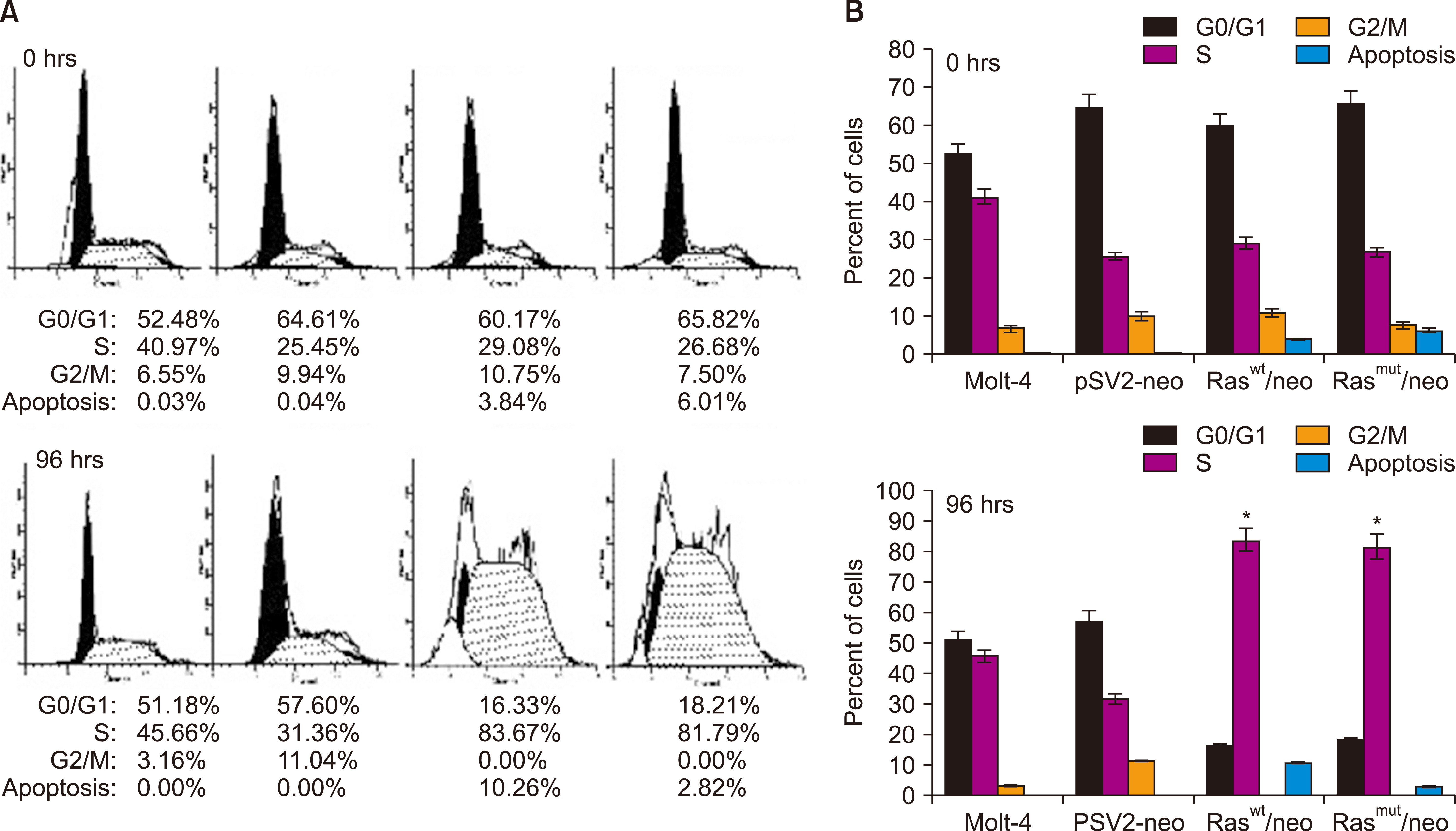
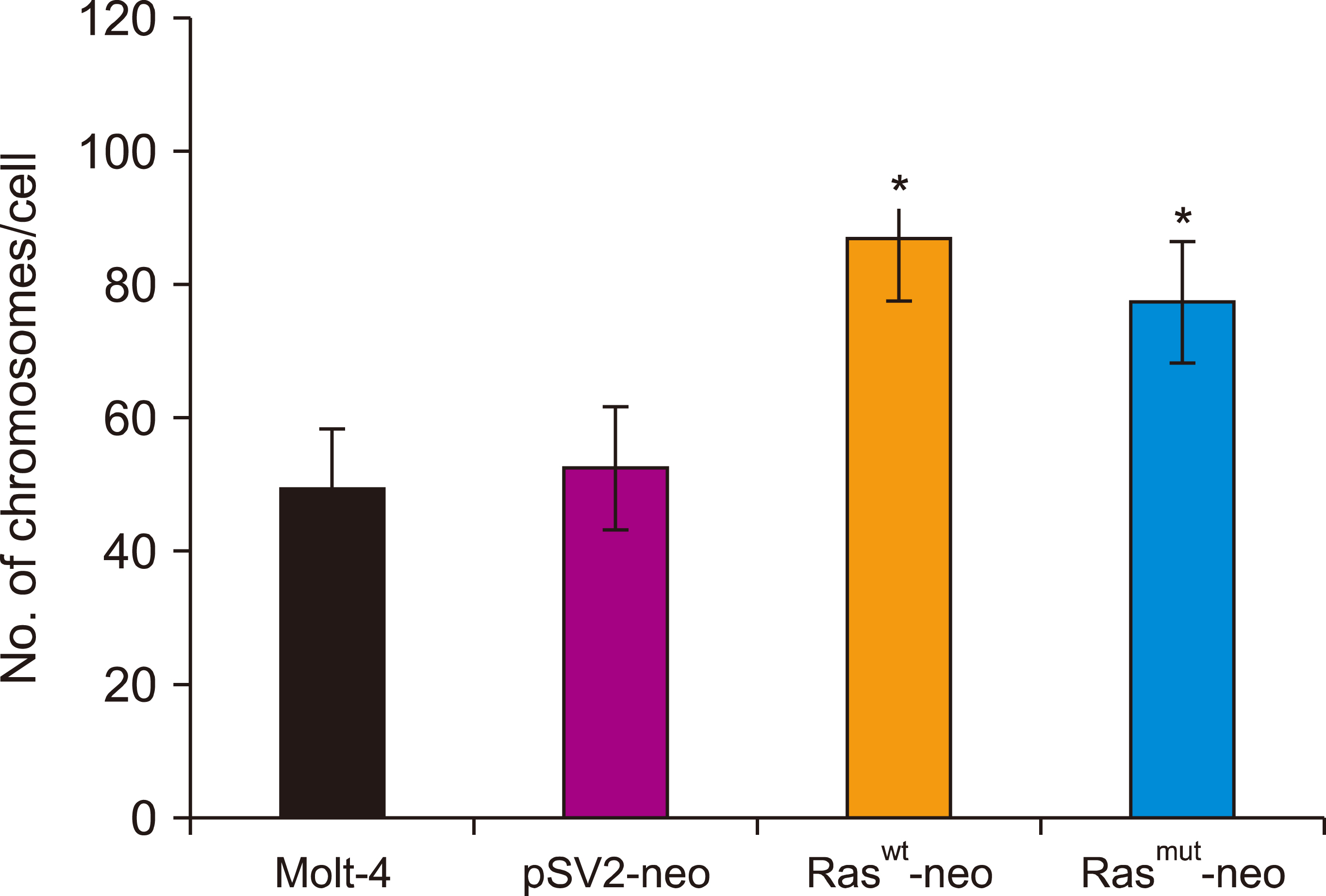
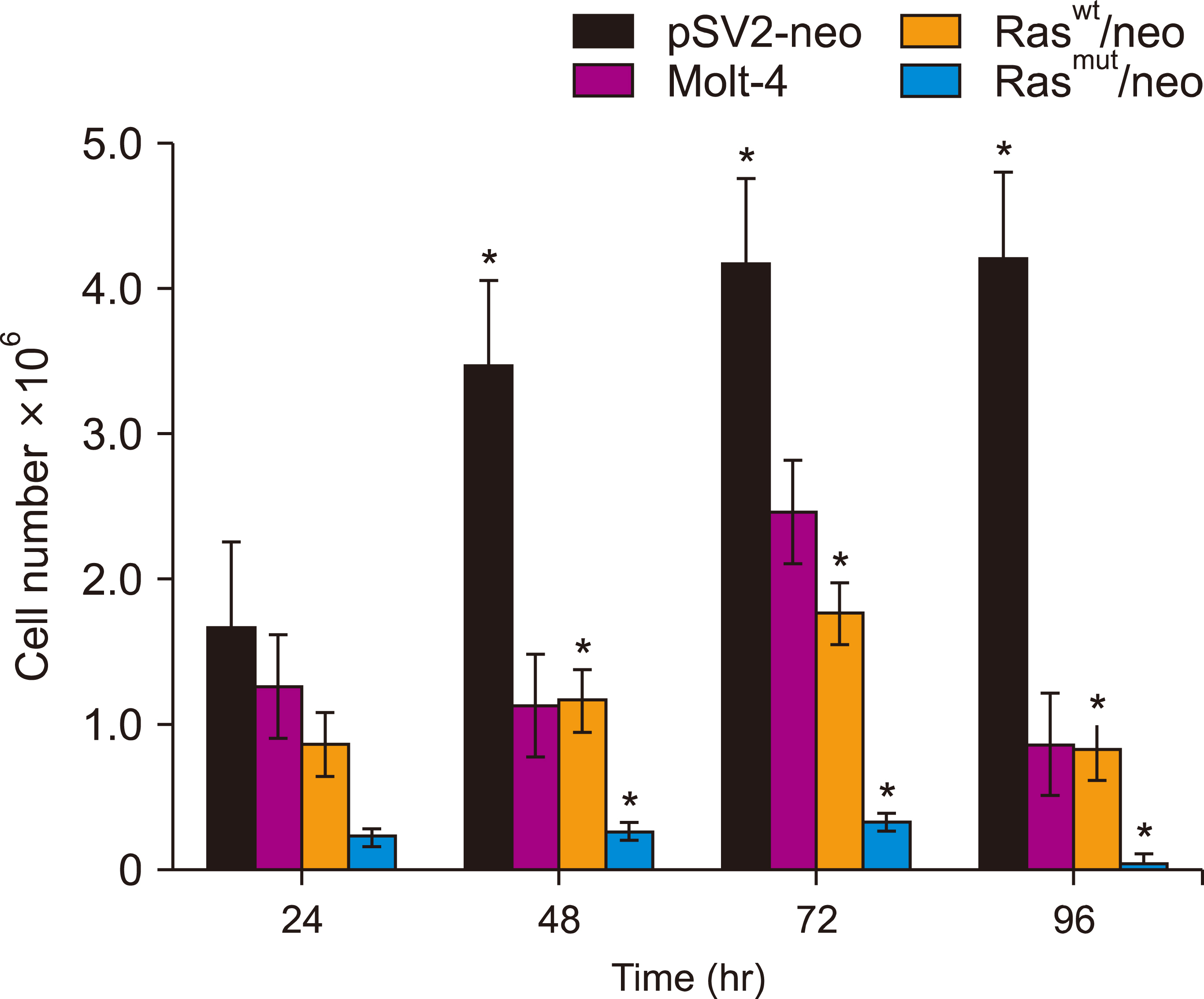
Human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 cells showed nuclear fragmentation and presence of multiple nuclei and micronuclei after transfection with either wt or mutant H-Ras genes. Cell cycle analysis revealed a statistically significant increase in cells in the S phase when transfected with either wt (83.67%, P<0.0005) or mutated (81.79%, P<0.0001) H-Ras genes. Although similar effects for both versions of H-Ras were found, cells transfected with the mutated version died at 120 h of mitotic catastrophe.
Conclusion
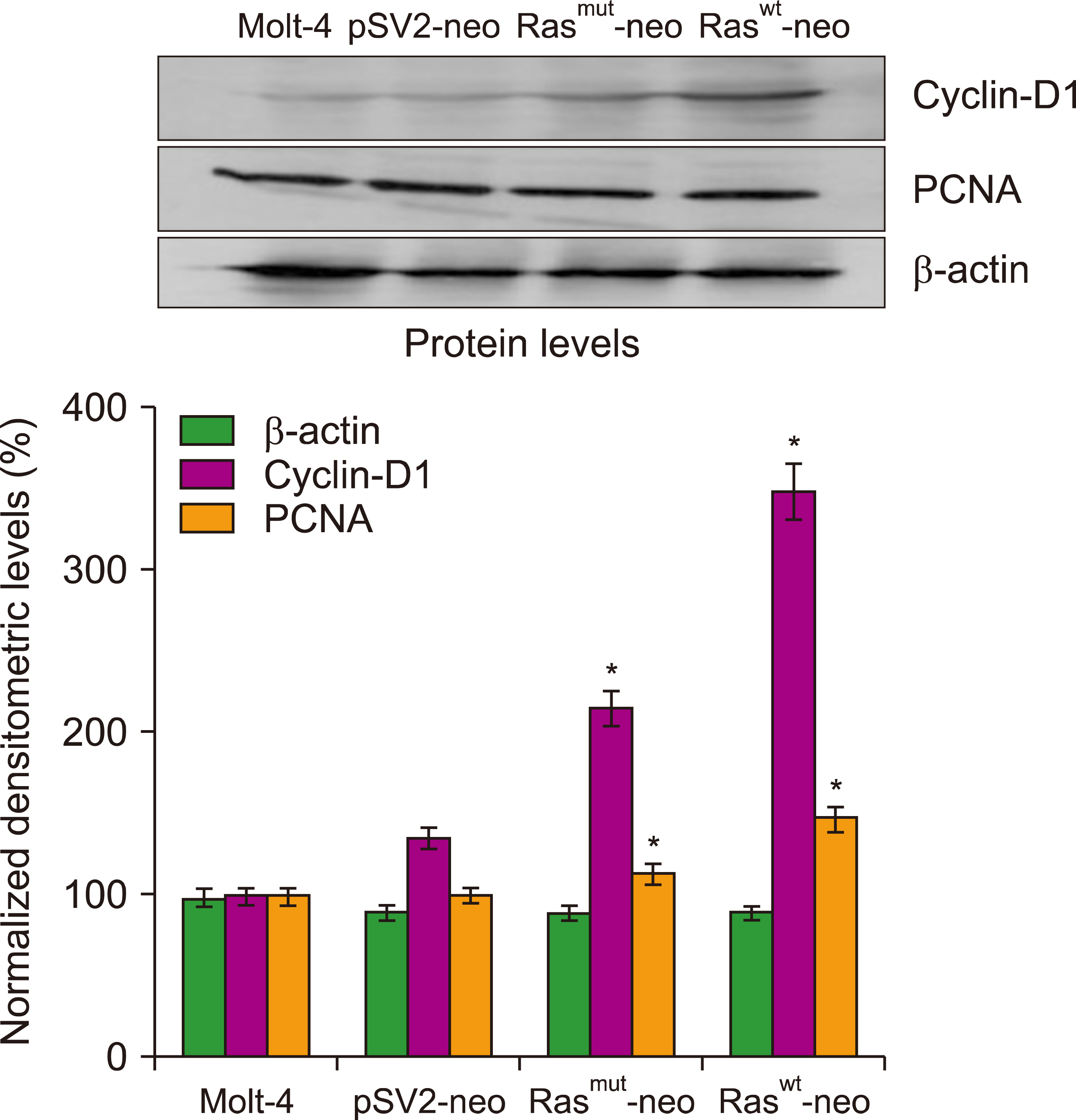
Transfection of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 cells with either normal or mutated H-Ras genes induced alterations in morphology, arrest in the S phase, and death by mitotic catastrophe.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chennamadhavuni A, Lyengar V, Mukkamalla SKR, Shimanovsky A. 2022. Leukemia. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing;Treasure Island, FL: DOI: 10.36255/exon-publications-leukemia-infant-leukemia.2. Pérez-Saldivar ML, Fajardo-Gutiérrez A, Bernáldez-Ríos R, et al. 2011; Childhood acute leukemias are frequent in Mexico City: descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer. 11:355. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-355. PMID: 21846410. PMCID: PMC3171387. PMID: ed1de6d217134566aa6bb2375107ba0d.
Article3. Curran E, Stock W. 2015; How I treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia in older adolescents and young adults. Blood. 125:3702–10. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-11-551481. PMID: 25805810. PMCID: PMC4463735.
Article4. Terwilliger T, Abdul-Hay M. 2017; Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 7:e577. DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2017.53. PMID: 28665419. PMCID: PMC5520400.
Article5. Sterner RC, Sterner RM. 2021; CAR-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 11:69. DOI: 10.1038/s41408-021-00459-7. PMID: 33824268. PMCID: PMC8024391. PMID: 40c1ba0f2ef74dd8953be161f136eb35.
Article6. Sazonova EV, Petrichuk SV, Kopeina GS, Zhivotovsky B. 2021; A link between mitotic defects and mitotic catastrophe: detection and cell fate. Biol Direct. 16:25. DOI: 10.1186/s13062-021-00313-7. PMID: 34886882. PMCID: PMC8656038. PMID: 3a76a226034a4270bb8aa44be03b9aea.
Article7. Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, et al. 2018; Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 25:486–541. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. PMID: 29362479. PMCID: PMC5864239.8. Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Castedo M, Kroemer G. 2011; Mitotic catastrophe: a mechanism for avoiding genomic instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:385–92. DOI: 10.1038/nrm3115. PMID: 21527953.
Article9. Abbas T, Dutta A. 2009; p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:400–14. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2657. PMID: 19440234. PMCID: PMC2722839.
Article10. Fragkos M, Beard P. 2011; Mitotic catastrophe occurs in the absence of apoptosis in p53-null cells with a defective G1 checkpoint. PLoS One. 6:e22946. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022946. PMID: 21853057. PMCID: PMC3154265. PMID: 50ab8a6fae5749c68b7998765a0e5d8e.
Article11. Overmeyer JH, Maltese WA. 2011; Death pathways triggered by activated Ras in cancer cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1693–713. DOI: 10.2741/3814. PMID: 21196257. PMCID: PMC3098755.
Article12. Simanshu DK, Nissley DV, McCormick F. 2017; RAS proteins and their regulators in human disease. Cell. 170:17–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.009. PMID: 28666118. PMCID: PMC5555610.
Article13. Weyandt JD, Lampson BL, Tang S, Mastrodomenico M, Cardona DM, Counter CM. 2015; Wild-type Hras suppresses the earliest stages of tumorigenesis in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 10:e0140253. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140253. PMID: 26452271. PMCID: PMC4599940. PMID: 783c7146ac1a429089962cbbbdc37118.
Article14. Byun JY, Kim MJ, Yoon CH, Cha H, Yoon G, Lee SJ. 2009; Oncogenic Ras signals through activation of both phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Rac1 to induce c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated, caspase-independent cell death. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1534–42. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0542. PMID: 19723872.
Article15. Chen JJ, Bozza WP, Di X, Zhang Y, Hallett W, Zhang B. 2014; H-Ras regulation of TRAIL death receptor mediated apoptosis. Oncotarget. 5:5125–37. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2091. PMID: 25026275. PMCID: PMC4148127.
Article16. Gille H, Downward J. 1999; Multiple Ras effector pathways contribute to G(1) cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem. 274:22033–40. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.31.22033. PMID: 10419529.17. Abramova MV, Pospelova TV, Nikulenkov FP, Hollander CM, Fornace AJ Jr, Pospelov VA. 2006; G1/S arrest induced by histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate in E1A + Ras-transformed cells is mediated through down-regulation of E2F activity and stabilization of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem. 281:21040–51. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M511059200. PMID: 16717102.18. Dikovskaya D, Cole JJ, Mason SM, et al. 2015; Mitotic stress is an integral part of the oncogene-induced senescence program that promotes multinucleation and cell cycle arrest. Cell Rep. 12:1483–96. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.055. PMID: 26299965. PMCID: PMC4562906. PMID: 8190b7e118b64afbb59c9882cf92b89b.
Article19. Shao J, Sheng H, DuBois RN, Beauchamp RD. 2000; Oncogenic Ras- mediated cell growth arrest and apoptosis are associated with increased ubiquitin-dependent cyclin D1 degradation. J Biol Chem. 275:22916–24. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M002235200. PMID: 10781597.20. Cheng G, Lewis AE, Meinkoth JL. 2003; Ras stimulates aberrant cell cycle progression and apoptosis in rat thyroid cells. Mol Endocrinol. 17:450–9. DOI: 10.1210/me.2002-0344. PMID: 12554771.
Article21. Abulaiti A, Fikaris AJ, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL. 2006; Ras induces chromosome instability and abrogation of the DNA damage response. Cancer Res. 66:10505–12. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2351. PMID: 17079472.
Article22. Zhu Q, Hu J, Meng H, Shen Y, Zhou J, Zhu Z. 2014; S-phase cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and molecular mechanisms of aplasia ras homolog member I-induced human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cell lines. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 24:629–34. DOI: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000105. PMID: 24662131. PMCID: PMC4047297.
Article23. Miranda EI, Santana C, Rojas E, Hernández S, Ostrosky-Wegman P, García-Carrancá A. 1996; Induced mitotic death of HeLa cells by abnormal expression of c-H-ras. Mutat Res. 349:173–82. DOI: 10.1016/0027-5107(95)00164-6. PMID: 8600348.
Article24. Gu JJ, Kaufman GP, Mavis C, Czuczman MS, Hernandez- Ilizaliturri FJ. 2017; Mitotic catastrophe and cell cycle arrest are alternative cell death pathways executed by bortezomib in rituximab resistant B-cell lymphoma cells. Oncotarget. 8:12741–53. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14405. PMID: 28055975. PMCID: PMC5355050.
Article25. Zuryń A, Litwiniec A, Gackowska L, Pawlik A, Grzanka AA, Grzanka A. 2012; Expression of cyclin A, B1 and D1 after induction of cell cycle arrest in the Jurkat cell line exposed to doxorubicin. Cell Biol Int. 36:1129–35. DOI: 10.1042/CBI20120274. PMID: 22950819.
Article26. Shen L, Au WY, Wong KY, et al. 2008; Cell death by bortezomib-induced mitotic catastrophe in natural killer lymphoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3807–15. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0641. PMID: 19074855.
Article27. Strauss SJ, Higginbottom K, Jüliger S, et al. 2007; The proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib acts independently of p53 and induces cell death via apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe in B-cell lymphoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 67:2783–90. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3254. PMID: 17363600.
Article28. Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M, Tamm C, Heidari N, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. 2008; DNA damage induces two distinct modes of cell death in ovarian carcinomas. Cell Death Differ. 15:555–66. DOI: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402286. PMID: 18064041.
Article29. Chen M, Guo Y, Zhao R, et al. 2016; Ophiopogonin B induces apoptosis, mitotic catastrophe, and autophagy in A549 cells. Int J Oncol. 49:316–24. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3514. PMID: 27175570.
Article30. Mascaraque M, Delgado-Wicke P, Damian A, Lucena SR, Carrasco E, Juarranz Á. 2019; Mitotic catastrophe induced in HeLa tumor cells by photodynamic therapy with methyl-aminolevulinate. Int J Mol Sci. 20:1229. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051229. PMID: 30862116. PMCID: PMC6429057. PMID: 0d69141616e8435ca359afb15704fb05.
Article31. Filmus J, Robles AI, Shi W, Wong MJ, Colombo LL, Conti CJ. 1994; Induction of cyclin D1 overexpression by activated ras. Oncogene. 9:3627–33. PMID: 7970723.32. Montalto FI, De Amicis F. 2020; Cyclin D1 in cancer: a molecular connection for cell cycle control, adhesion and invasion in tumor and stroma. Cells. 9:2648. DOI: 10.3390/cells9122648. PMID: 33317149. PMCID: PMC7763888. PMID: f8080d020d414e11ba5ca3c32199467e.
Article33. Fukami-Kobayashi J, Mitsui Y. 1999; Cyclin D1 inhibits cell proliferation through binding to PCNA and cdk2. Exp Cell Res. 246:338–47. DOI: 10.1006/excr.1998.4306. PMID: 9925749.
Article34. Han EK, Sgambato A, Jiang W, et al. 1995; Stable overexpression of cyclin D1 in a human mammary epithelial cell line prolongs the S-phase and inhibits growth. Oncogene. 10:953–61.35. Yang K, Guo Y, Stacey WC, et al. 2006; Glycogen synthase kinase 3 has a limited role in cell cycle regulation of cyclin D1 levels. BMC Cell Biol. 7:33. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-7-33. PMID: 16942622. PMCID: PMC1592484. PMID: 6e42ce2f70a64aa6b6ce5fa837030319.
Article36. Olivero OA, Tejera AM, Fernandez JJ, et al. 2005; Zidovudine induces S-phase arrest and cell cycle gene expression changes in human cells. Mutagenesis. 20:139–46. DOI: 10.1093/mutage/gei019. PMID: 15784690.
Article37. Seifrtova M, Havelek R, Chmelarova M, et al. 2011; The effect of ATM and ERK1/2 inhibition on mitoxantrone-induced cell death of leukaemic cells. Folia Biol (Praha). 57:74–81. PMID: 21631964.38. Amanatullah DF, Zafonte BT, Albanese C, et al. 2001; Ras regulation of cyclin D1 promoter. Methods Enzymol. 333:116–27. DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(01)33050-1. PMID: 11400329.
Article39. Liu L, Ling X, Tang H, Chen J, Wen Q, Zou F. 2015; Poly(ADP- ribosyl)ation enhances H-RAS protein stability and causes abnormal cell cycle progression in human TK6 lymphoblastoid cells treated with hydroquinone. Chem Biol Interact. 238:1–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.05.019. PMID: 26047893.
Article40. Murcia L, Clemente-Ruiz M, Pierre-Elies P, Royou A, Milán M. 2019; Selective killing of RAS-malignant tissues by exploiting oncogene-induced DNA damage. Cell Rep. 28:119–31. e4DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.004. PMID: 31269434.
Article41. Kotsantis P, Silva LM, Irmscher S, et al. 2016; Increased global transcription activity as a mechanism of replication stress in cancer. Nat Commun. 7:13087. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13087. PMID: 27725641. PMCID: PMC5062618. PMID: 11549dd2c7d8445a96d11f1f28cfaa77.
Article42. Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A, et al. 2006; Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper- replication. Nature. 444:638–42. DOI: 10.1038/nature05327. PMID: 17136094.
Article43. Chen AY, Chen YC. 2013; A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention. Food Chem. 138:2099–107. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.139. PMID: 23497863. PMCID: PMC3601579.
Article44. Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D, Lowe SW. 1997; Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81902-9. PMID: 9054499.
Article45. Ianzini F, Bertoldo A, Kosmacek EA, Phillips SL, Mackey MA. 2006; Lack of p53 function promotes radiation-induced mitotic catastrophe in mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Cancer Cell Int. 6:11. DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-6-11. PMID: 16640786. PMCID: PMC1479380. PMID: 88ed9c22ae20483185b71d7cac922f22.46. Fischer M, Uxa S, Stanko C, Magin TM, Engeland K. 2017; Human papilloma virus E7 oncoprotein abrogates the p53-p21-DREAM pathway. Sci Rep. 7:2603. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02831-9. PMID: 28572607. PMCID: PMC5453983. PMID: 8835ae107aaf44df83dbe8f3c6cd940b.
Article47. Ikediobi ON, Davies H, Bignell G, et al. 2006; Mutation analysis of 24 known cancer genes in the NCI-60 cell line set. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2606–12. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0433. PMID: 17088437. PMCID: PMC2705832.
Article48. Kechagioglou P, Papi RM, Provatopoulou X, et al. 2014; Tumor suppressor PTEN in breast cancer: heterozygosity, mutations and protein expression. Anticancer Res. 34:1387–400. PMID: 24596386.49. Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP. 2012; The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:283–96. DOI: 10.1038/nrm3330. PMID: 22473468.
Article50. Sherr CJ, Bartek J. 2017; Cell cycle targeted cancer therapies. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 1:41–57. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-040716-075628.51. Huang D, Feng X, Liu Y, et al. 2017; AQP9-induced cell cycle arrest is associated with Ras activation and improves chemotherapy treatment efficacy in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e2894. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.282. PMID: 28640255. PMCID: PMC5520935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mutation of the N-ras Gene in a Patient Suffering from the Blast Phase of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- Molecular Biological Responses of TCDD Transformed Human Keratinocytes Induced by UVB Irradiation
- Down-regulation of Type I Collagen Gene Expression in Human Skin Fibroblasts by G1 Cell Cycle Arrest
- JNK inhibitor SP600125 promotes the formation of polymerized tubulin, leading to G2/M phase arrest, endoreduplication, and delayed apoptosis
- Rap Signaling in Normal Lymphocyte Development and Leukemia Genesis