J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Mar;38(12):e89. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e89.
De Novo Crescentic Glomerulonephritis Following COVID-19 Infection: A Pediatric Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University, College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2541037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e89
Abstract
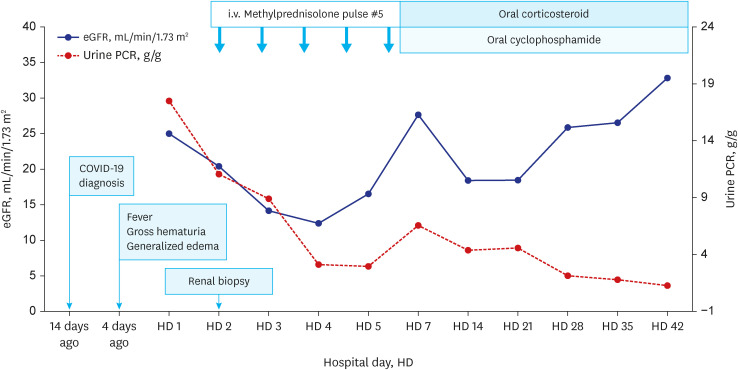
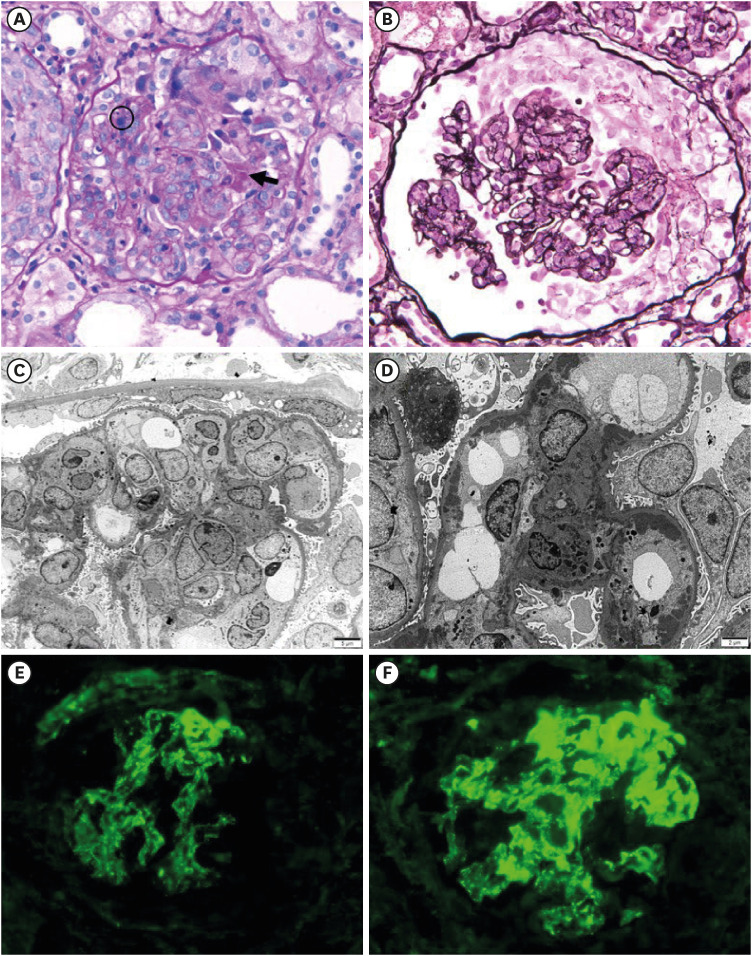
- As the global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to sweep across the globe, reports of kidney involvement in adult patients infected with COVID-19 have been documented, and recently, cases in the pediatric population have also been reported. This report highlights the case of an 11-year-old boy who developed acute kidney injury presenting as gross hematuria, proteinuria, and hypertension immediately after a COVID-19 infection. A renal biopsy allowed us to diagnose the patient with post-COVID-19 infectionassociated de novo crescentic immune-mediated glomerulonephritis. Oral prednisolone and cyclophosphamide treatments were initiated after methylprednisolone pulse therapy administration. Currently, the patient is receiving medical treatment for five weeks, and his renal function is gradually recovering. Previous studies have suggested that, although quite rare, a variety of kidney complications can occur after COVID-19 infection or vaccination, and it is recommended to monitor renal function through evaluation. Herein, we report a pediatric case of post-COVID-19 infection-associated de novo crescentic immune-mediated glomerulonephritis consistent with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cho HY, Chung DL, Kang JH, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y. A clinicopathological study of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in children. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 2004; 8(2):176–185.2. Nomura E, Finn LS, Bauer A, Rozansky D, Iragorri S, Jenkins R, et al. Pathology findings in pediatric patients with COVID-19 and kidney dysfunction. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37(10):2375–2381. PMID: 35166918.3. N V, Singh RKN, Kumari N, Ranjan R, Saini S. A novel association between coronavirus disease 2019 and normocomplementemic rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis-crescentic immunoglobulin A nephropathy: a report of two pediatric cases. Cureus. 2022; 14(2):e22077. PMID: 35308719.4. Lebedev L, Sapojnikov M, Wechsler A, Varadi-Levi R, Zamir D, Tobar A, et al. Minimal change disease following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021; 78(1):142–145. PMID: 33839200.5. Maas RJ, Gianotten S, van der Meijden WAG. An additional case of minimal change disease following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021; 78(2):312.
Article6. D’Agati VD, Kudose S, Bomback AS, Adamidis A, Tartini A. Minimal change disease and acute kidney injury following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021; 100(2):461–463. PMID: 34000278.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- De Novo ANCA-Negative Pauci-Immune Crescentic Glomerulonephritis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination: A Case Report
- Intracranial Hypertension after COVID-19 Infection
- Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A case report
- A Case of de novo MPO-associated Central Nervous System Vasculitis Following Heterogeneous mRNA1273 COVID-19 Booster Vaccination
- A case of Idiopathic Crescentic Glomerulonephritis