Korean J Pain.
2023 Apr;36(2):184-194. 10.3344/kjp.22289.
Effectiveness of percutaneous epidural neuroplasty using a balloon catheter in patients with chronic spinal stenosis accompanying mild spondylolisthesis: a longitudinal cohort study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Anesthesiology, School of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2541027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.22289
Abstract
- Background
Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis (DLS) is frequently associated with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) and conservative treatments such as epidural steroid injection do not have long-term benefits in LSS patients with DLS. This study evaluated the effectiveness of percutaneous epidural neuroplasty using a balloon catheter in patients with LSS and DLS.
Methods
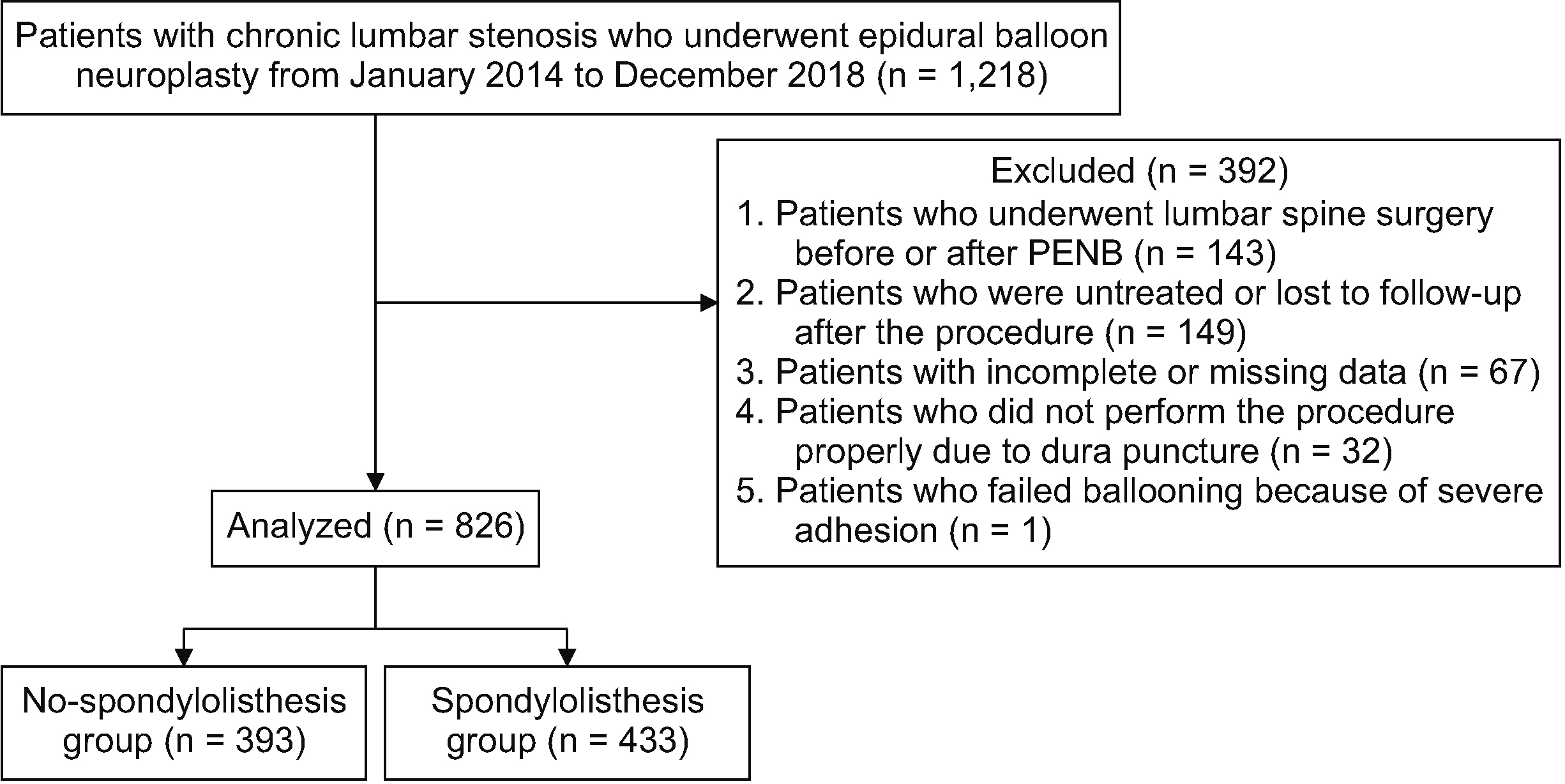
Patients’ sex, age, body mass index, diabetes, hypertension, stenosis grading, pain duration, location, pain intensity, and medications were retrieved from electronic medical records. At 1, 3, and 6 months following the procedure, data on pain severity, medication usage, and physical functional status were analyzed. A generalized estimating equations model was used at the six-month follow-up. Patients were divided into those with DLS (the spondylolisthesis group) and those without DLS (the no spondylolisthesis group) to evaluate whether the effects of percutaneous epidural neuroplasty using a balloon catheter were different.
Results
A total of 826 patients were included (spondylolisthesis: 433 patients, 52.4%; no spondylolisthesis: 393 patients, 47.6%). Age, body mass index, hypertension, pain location, and stenosis grading were statistically different between the two groups. The generalized estimating equations analyses with unadjusted and adjusted estimation revealed a significant improvement in the estimated mean numerical rating scale of pain intensities compared to that at baseline in both groups (P < 0.001). Any adverse events that occurred were minor and temporary.
Conclusions
Percutaneous epidural neuroplasty using a balloon catheter may be an alternative treatment option for patients with chronic LSS, regardless of accompanying DLS, who have had failed conservative management.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Involvement of the spinal γ-aminobutyric acid receptor in the analgesic effects of intrathecally injected hypertonic saline in spinal nerve-ligated rats
Myong-Hwan Karm, Hyun-Jung Kwon, Euiyong Shin, Honggyoon Bae, Young Ki Kim, Seong-Soo Choi
Korean J Pain. 2023;36(4):441-449. doi: 10.3344/kjp.23162.
Reference
-
1. Matz PG, Meagher RJ, Lamer T, Tontz WL Jr, Annaswamy TM, Cassidy RC, et al. 2016; Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 16:439–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.11.055. PMID: 26681351.2. Eismont FJ, Norton RP, Hirsch BP. 2014; Surgical management of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 22:203–13. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-22-04-203. PMID: 24668350.3. Kalichman L, Hunter DJ. 2008; Diagnosis and conservative management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 17:327–35. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-007-0543-3. PMID: 18026865. PMCID: PMC2270383.4. Frymoyer JW. 1994; Degenerative spondylolisthesis: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2:9–15. DOI: 10.5435/00124635-199401000-00002. PMID: 10708989.5. Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Hanscom B, Tosteson AN, Blood EA, et al. 2007; Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med. 356:2257–70. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa070302. PMID: 17538085. PMCID: PMC2553804.6. Sencan S, Ozcan-Eksi EE, Cil H, Tay B, Berven S, Burch S, et al. 2017; The effect of transforaminal epidural steroid injections in patients with spondylolisthesis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 30:841–6. DOI: 10.3233/BMR-160543. PMID: 28372316.7. García-Ramos CL, Valenzuela-González J, Baeza-Álvarez VB, Rosales-Olivarez LM, Alpízar-Aguirre A, Reyes-Sánchez A. 2020; Lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis II: treatment and controversies. Acta Ortop Mex. 34:433–40. DOI: 10.35366/99144. PMID: 34020526.8. Lee F, Jamison DE, Hurley RW, Cohen SP. 2014; Epidural lysis of adhesions. Korean J Pain. 27:3–15. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.3. PMID: 24478895. PMCID: PMC3903797.9. Helm S 2nd, Racz GB, Gerdesmeyer L, Justiz R, Hayek SM, Kaplan ED, et al. 2016; Percutaneous and endoscopic adhesiolysis in managing low back and lower extremity pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 19:E245–82. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2016.19.E245.10. Racz G, Candido K, Helm S. 2018; Neuroplasty is a safe, effective procedure. Anesth Analg. 126:363. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002546. PMID: 29135599.11. Karm MH, Choi SS, Kim DH, Park JY, Lee S, Park JK, et al. 2018; Percutaneous epidural adhesiolysis using inflatable balloon catheter and balloon-less catheter in central lumbar spinal stenosis with neurogenic claudication: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Physician. 21:593–606. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2018.6.593. PMID: 30508987.12. Choi SS, Joo EY, Hwang BS, Lee JH, Lee G, Suh JH, et al. 2014; A novel balloon-inflatable catheter for percutaneous epidural adhesiolysis and decompression. Korean J Pain. 27:178–85. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.2.178. PMID: 24748948. PMCID: PMC3990828.13. Choi SS, Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HK, Lee S, Song KJ, et al. 2016; Effectiveness and factors associated with epidural decompression and adhesiolysis using a balloon-inflatable catheter in chronic lumbar spinal stenosis: 1-year follow-up. Pain Med. 17:476–87. DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnv018. PMID: 26814254.14. Karm MH, Yoon SH, Seo DK, Lee S, Lee Y, Cho SS, et al. 2019; Combined epidural adhesiolysis and balloon decompression can be effective in intractable lumbar spinal stenosis patients unresponsive to previous epidural adhesiolysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e15114. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015114. PMID: 30985668. PMCID: PMC6485831.15. Park JY, Ji GY, Lee SW, Park JK, Ha D, Park Y, et al. 2019; Relationship of success rate for balloon adhesiolysis with clinical outcomes in chronic intractable lumbar radicular pain: a multicenter prospective study. J Clin Med. 8:606. DOI: 10.3390/jcm8050606. PMID: 31058860. PMCID: PMC6572522. PMID: 34f2b46e34144c309c8852977b06c70e.16. Moon DE, Park HJ, Kim YH. 2015; Assessment of clinical outcomes of cervical epidural neuroplasty using a Racz-catheter and predictive factors of efficacy in patients with cervical spinal pain. Pain Physician. 18:E163–70. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2015.18.E163. PMID: 25794215.17. Kim DH, Cho SS, Moon YJ, Kwon K, Lee K, Leem JG, et al. 2017; Factors associated with successful responses to transforaminal balloon adhesiolysis for chronic lumbar foraminal stenosis: retrospective study. Pain Physician. 20:E841–8. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.20.5.E841. PMID: 28934790.18. Schizas C, Theumann N, Burn A, Tansey R, Wardlaw D, Smith FW, et al. 2010; Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:1919–24. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d359bd. PMID: 20671589.19. Lee S, Lee JW, Yeom JS, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Chung SK, et al. 2010; A practical MRI grading system for lumbar foraminal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 194:1095–8. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.09.2772. PMID: 20308517.20. Meyerding HW. 1933; Diagnosis and roentgenologic evidence in spondylolisthesis. Radiology. 20:108–20. DOI: 10.1148/20.2.108.21. Hanson DS, Bridwell KH, Rhee JM, Lenke LG. 2002; Correlation of pelvic incidence with low- and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2026–9. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200209150-00011. PMID: 12634563.22. Gallizzi M, Gagnon C, Harden RN, Stanos S, Khan A. 2008; Medication Quantification Scale Version III: internal validation of detriment weights using a chronic pain population. Pain Pract. 8:1–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2007.00163.x. PMID: 18211588.23. Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L, Guermazi A, Berkin V, Hunter DJ. 2009; Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:199–205. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31818edcfd. PMID: 19139672. PMCID: PMC3793342.24. Bydon M, Alvi MA, Goyal A. 2019; Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: definition, natural history, conservative management, and surgical treatment. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 30:299–304. DOI: 10.1016/j.nec.2019.02.003. PMID: 31078230.25. Faldini C, Pagkrati S, Acri F, Miscione MT, Francesconi D, Giannini S. 2007; Surgical treatment of symptomatic degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis by decompression and instrumented fusion. J Orthop Traumatol. 8:128–33. DOI: 10.1007/s10195-007-0079-7. PMCID: PMC4874964.26. Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Zhao W, Blood EA, Tosteson AN, et al. 2009; Surgical compared with nonoperative treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. four-year results in the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) randomized and observational cohorts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 91:1295–304. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.H.00913. PMID: 19487505. PMCID: PMC2686131.27. Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. 1997; 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:2807–12. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199712150-00003. PMID: 9431616.28. Fischgrund JS. 2004; The argument for instrumented decompressive posterolateral fusion for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:173–4. DOI: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000111142.76601.1A. PMID: 14722410.29. Kaplan NM. 1995; Hypertension in the elderly. Annu Rev Med. 46:27–35. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.med.46.1.27. PMID: 7598464.30. Freedman MK, Hilibrand AS, Blood EA, Zhao W, Albert TJ, Vaccaro AR, et al. 2011; The impact of diabetes on the outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical treatment of patients in the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:290–307. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ef9d8c. PMID: 21270715. PMCID: PMC4005359.31. Kim SH, Choi WJ, Suh JH, Jeon SR, Hwang CJ, Koh WU, et al. 2013; Effects of transforaminal balloon treatment in patients with lumbar foraminal stenosis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Pain Physician. 16:213–24. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2013/16/213. PMID: 23703408.32. Hollmann MW, Durieux ME. 2000; Prolonged actions of short-acting drugs: local anesthetics and chronic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 25:337–9. DOI: 10.1097/00115550-200007000-00001. PMID: 10925925.33. Benzon HT. 1986; Epidural steroid injections for low back pain and lumbosacral radiculopathy. Pain. 24:277–95. DOI: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90115-6. PMID: 3008063.34. Hitchcock E. 1969; Osmolytic neurolysis for intractable facial pain. Lancet. 1:434–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(69)91479-2. PMID: 4179502.35. Breivik H, Borchgrevink PC, Allen SM, Rosseland LA, Romundstad L, Hals EK, et al. 2008; Assessment of pain. Br J Anaesth. 101:17–24. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aen103. PMID: 18487245.36. Kim DY, Lee SH, Lee HY, Lee HJ, Chang SB, Chung SK, et al. 2005; Validation of the Korean version of the Oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:E123–7. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000157172.00635.3a. PMID: 15738775.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous epidural balloon neuroplasty: a narrative review of current evidence
- Ultrasound-guided removal of epidural catheter breakage after percutaneous epidural neuroplasty: A case report
- Acute Motor Weakness of Opposite Lower Extremity after Percutaneous Epidural Neuroplasty
- Percutaneous Epidural Neuroplasty
- Percutaneous Epidural Neuroplasty