Acute Crit Care.
2022 Nov;37(4):543-549. 10.4266/acc.2022.00521.
Incidence and risk factors associated with progression to severe pneumonia among adults with non-severe Legionella pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University Gwangmyeong Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Gwangmyeong, Korea
- 3Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2540142
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2022.00521
Abstract
- Background
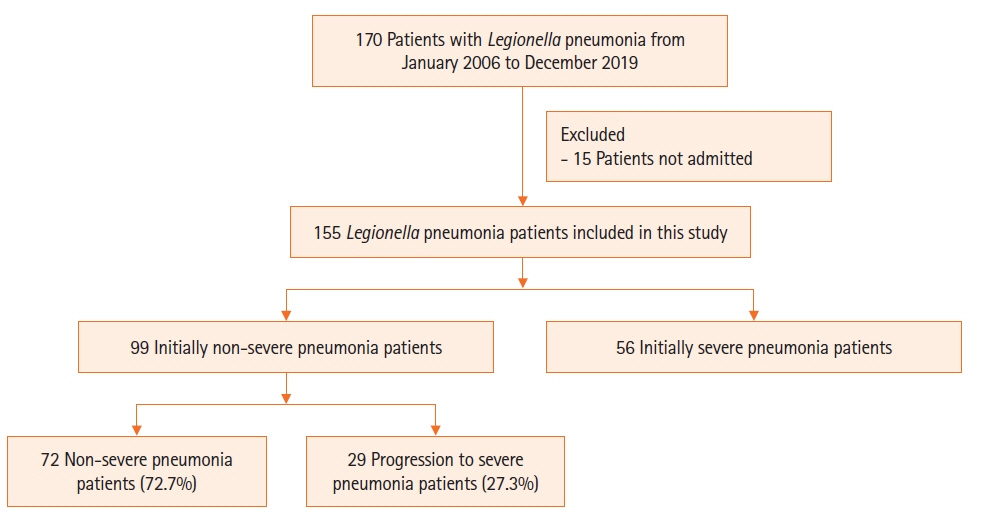
Legionella species are important causative organisms of severe pneumonia. However, data are limited on predictors of progression to severe Legionella pneumonia (LP). Therefore, the risk factors for LP progression from non-severe to the severe form were investigated in the present study. Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study that included adult LP patients admitted to a 2,700-bed referral center between January 2005 and December 2019. Results: A total of 155 patients were identified during the study period; 58 patients (37.4%) initially presented with severe pneumonia and 97 (62.6%) patients with non-severe pneumonia. Among the 97 patients, 28 (28.9%) developed severe pneumonia during hospitalization and 69 patients (71.1%) recovered without progression to severe pneumonia. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed platelet count ≤150,000/mm3 (odds ratio [OR], 2.923; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.100–8.105; P=0.034) and delayed antibiotic treatment >1 day (OR, 3.092; 95% CI, 1.167–8.727; P=0.026) were significant independent factors associated with progression to severe pneumonia. Conclusions: A low platelet count and delayed antibiotic treatment were significantly associated with the progression of non-severe LP to severe LP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diederen BM. Legionella spp. and Legionnaires’ disease. J Infect. 2008; 56:1–12.
Article2. Cunha BA, Burillo A, Bouza E. Legionnaires’ disease. Lancet. 2016; 387:376–85.
Article3. Carratalà J, Garcia-Vidal C. An update on Legionella. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010; 23:152–7.
Article4. Morgan AJ, Glossop AJ. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. BJA Educ. 2016; 16:167–72.
Article5. Chong YP, Jung KS, Lee KH, Kim MN, Moon SM, Park S, et al. The bacterial etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in Korea: a nationwide prospective multicenter study. Infect Chemother. 2010; 42:397–403.
Article6. Sopena N, Sabrià M, Pedro-Botet ML, Manterola JM, Matas L, Domínguez J, et al. Prospective study of community-acquired pneumonia of bacterial etiology in adults. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999; 18:852–8.
Article7. Centers for Disease Control. Notice to readers: final 2014 reports of nationally notifiable infectious diseases. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015; 64:1019.8. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Legionnaires’ disease: annual epidemiological report for 2019. Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; 2019.9. Fukushima S, Hagiya H, Otsuka Y, Koyama T, Otsuka F. Trends in the incidence and mortality of legionellosis in Japan: a nationwide observational study, 1999-2017. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:7246.
Article10. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Legionellosis [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency; 2020 [cited 2022 Sep 1]. Available from: https://www.kdca.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/ist/simple/simplePdStatsMain.do.11. Cassell K, Thomas-Lopez D, Kjelsø C, Uldum S. Provincial trends in Legionnaires’ disease are not explained by population structure in Denmark, 2015 to 2018. Euro Surveill. 2021; 26:2000036.
Article12. Diederen BM, Kluytmans JA, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Peeters MF. Utility of real-time PCR for diagnosis of Legionnaires’ disease in routine clinical practice. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:671–7.
Article13. Han BS, Lee MJ, Kwon YH, Lee WC. A comparative study of the epidemiological aspects of Legionnaires’ disease: outbreaks in Korea and Japan, 2010 - 2014. J Clin Med Res. 2017; 9:67–70.
Article14. Rubin R. Why are Legionnaires disease diagnoses becoming more common in the United States? JAMA. 2018; 319:1753–4.
Article15. Falcó V, Fernández de Sevilla T, Alegre J, Ferrer A, Martínez Vázquez JM. Legionella pneumophila: a cause of severe community-acquired pneumonia. Chest. 1991; 100:1007–11.16. Cargnelli S, Powis J, Tsang JL. Legionella pneumonia in the Niagara region, Ontario, Canada: a case series. J Med Case Rep. 2016; 10:336.
Article17. Chidiac C, Che D, Pires-Cronenberger S, Jarraud S, Campèse C, Bissery A, et al. Factors associated with hospital mortality in community-acquired legionellosis in France. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:963–70.
Article18. Falcone M, Russo A, Tiseo G, Cesaretti M, Guarracino F, Menichetti F. Predictors of intensive care unit admission in patients with Legionella pneumonia: role of the time to appropriate antibiotic therapy. Infection. 2021; 49:321–5.
Article19. Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, Anzueto A, Brozek J, Crothers K, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: an official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019; 200:e45–67.
Article20. Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44(Suppl 2):S27–72.
Article21. Ghoneim AH, Mohammad MA, Elghamrawy MA, Embarak S. Platelet count as a predictor of outcome of hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia at Zagazig University Hospitals, Egypt. Egypt J Bronchol. 2020; 14:11.
Article22. Mirsaeidi M, Peyrani P, Aliberti S, Filardo G, Bordon J, Blasi F, et al. Thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis at time of hospitalization predict mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Chest. 2010; 137:416–20.
Article23. Eriksson O, Mohlin C, Nilsson B, Ekdahl KN. The human platelet as an innate immune cell: interactions between activated platelets and the complement system. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:1590.
Article24. Palm F, Sjöholm K, Malmström J, Shannon O. Complement activation occurs at the surface of platelets activated by Streptococcal M1 protein and this results in phagocytosis of platelets. J Immunol. 2019; 202:503–13.
Article25. Mintz CS, Schultz DR, Arnold PI, Johnson W. Legionella pneumophila lipopolysaccharide activates the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1992; 60:2769–76.
Article26. Larsson A, Nilsson B, Eriksson M. Thrombocytopenia and platelet microvesicle formation caused by Legionella pneumophila infection. Thromb Res. 1999; 96:391–7.
Article27. Chauhan D, Shames SR. Pathogenicity and virulence of Legionella: intracellular replication and host response. Virulence. 2021; 12:1122–44.
Article28. Kao WF, Wang JT, Sheng WH, Chen YC. Community-acquired Legionnaires’ disease at a medical center in northern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019; 52:465–70.
Article29. Zasowski EJ, Bassetti M, Blasi F, Goossens H, Rello J, Sotgiu G, et al. A systematic review of the effect of delayed appropriate antibiotic treatment on the outcomes of patients with severe bacterial infections. Chest. 2020; 158:929–38.
Article