Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Feb;81(2):66-71. 10.4166/kjg.2023.001.
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2539575
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.001
Abstract
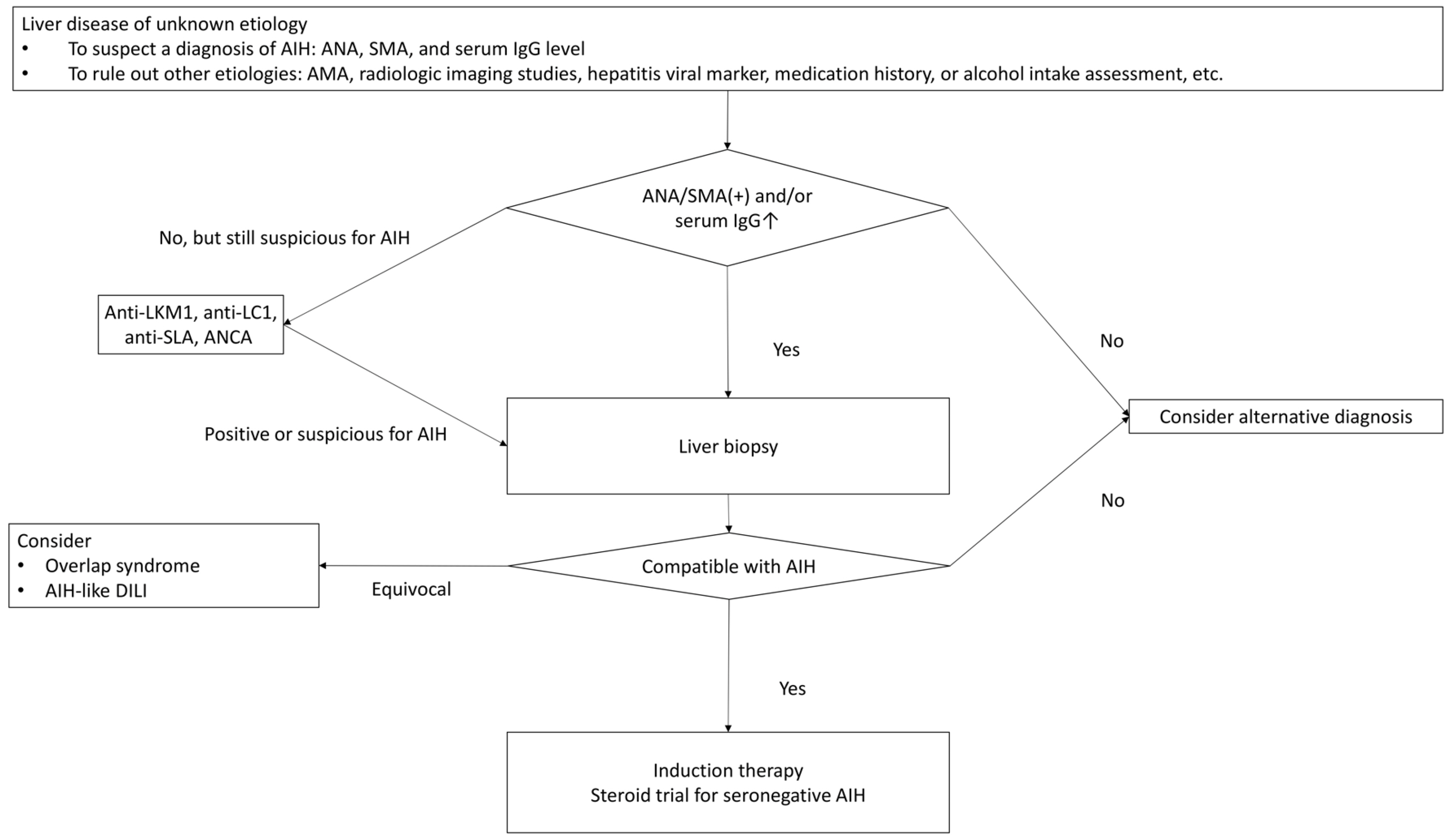
- Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is an immune-mediated inflammatory liver disease with an uncertain cause. The diagnosis of AIH is based on the characteristic clinical and laboratory findings (elevated liver enzyme and hypergammaglobulinemia), the presence of characteristic autoantibodies, and compatible histological abnormalities. AIH lacks a signature diagnostic marker, and the diagnosis requires the exclusion of other diseases (viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, drug-induced liver injury, Wilson’s disease, and hereditary hemochromatosis). Therefore, collaboration between the clinical physician, laboratory medicine experts, and pathologists is important for a diagnosis. In December 2022, the Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL) clinical practice guidelines were established. This review article summarizes the diagnosis part of these guidelines.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mack CL, Adams D, Assis DN, et al. 2020; Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis in adults and children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 72:671–722. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31065. PMID: 31863477.
Article2. Wang G, Tanaka A, Zhao H, et al. 2021; The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidance: the diagnosis and management of patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatol Int. 15:223–257. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10170-1. PMID: 33942203. PMCID: PMC8144150.
Article3. Lim K, Park JG. 2022; Diagnostic approach to autoimmune hepatitis. Korean J Med. 97:33–41. DOI: 10.3904/kjm.2022.97.1.33.
Article4. Tanaka A. 2020; Autoimmune hepatitis: 2019 update. Gut Liver. 14:430–438. DOI: 10.5009/gnl19261. PMID: 32301319. PMCID: PMC7366136.
Article5. Zachou K, Muratori P, Koukoulis GK, et al. 2013; Review article: autoimmune hepatitis -- current management and challenges. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 38:887–913. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12470. PMID: 24010812.
Article6. Hennes EM, Zeniya M, Czaja AJ, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2008; 48:169–176. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22322. PMID: 18537184.
Article7. Fujiwara K, Fukuda Y, Yokosuka O. 2008; Precise histological evaluation of liver biopsy specimen is indispensable for diagnosis and treatment of acute-onset autoimmune hepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 43:951–958. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-008-2254-x. PMID: 19107339.
Article8. Yasui S, Fujiwara K, Yonemitsu Y, Oda S, Nakano M, Yokosuka O. 2011; Clinicopathological features of severe and fulminant forms of autoimmune hepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 46:378–390. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-010-0316-3. PMID: 20821236.
Article9. Laschtowitz A, Zachou K, Lygoura V, et al. 2021; Histological activity despite normal ALT and IgG serum levels in patients with autoimmune hepatitis and cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 3:100321. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100321. PMID: 34381983. PMCID: PMC8333110.
Article10. Joshita S, Yoshizawa K, Umemura T, et al. Japan Autoimmune Hepatitis Study Group (JAIHSG). Clinical features of autoimmune hepatitis with acute presentation: a Japanese nationwide survey. J Gastroenterol. 2018; 53:1079–1088. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-018-1444-4. PMID: 29476251.
Article11. Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. 2022; Autoimmune hepatitis: serum autoantibodies in clinical practice. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 63:124–137. DOI: 10.1007/s12016-021-08888-9. PMID: 34491531. PMCID: PMC9464171.
Article12. Wies I, Brunner S, Henninger J, et al. 2000; Identification of target antigen for SLA/LP autoantibodies in autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 355:1510–1515. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02166-8. PMID: 10801173.
Article13. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2015; EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 63:971–1004. Erratum in: J Hepatol 2015;63:1543-1544. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.09.016.14. Zachou K, Rigopoulou E, Dalekos GN. 2004; Autoantibodies and autoantigens in autoimmune hepatitis: important tools in clinical practice and to study pathogenesis of the disease. J Autoimmune Dis. 1:2. DOI: 10.1186/1740-2557-1-2. PMID: 15679907. PMCID: PMC544946.15. Targan SR, Landers C, Vidrich A, Czaja AJ. 1995; High-titer antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in type-1 autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 108:1159–1166. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90215-5. PMID: 7698584.
Article16. O'Brien C, Joshi S, Feld JJ, Guindi M, Dienes HP, Heathcote EJ. 2008; Long-term follow-up of antimitochondrial antibody-positive autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 48:550–556. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22380. PMID: 18666262.17. Farias AQ, Gonçalves LL, Bittencourt PL, et al. 2006; Applicability of the IAIHG scoring system to the diagnosis of antimitochondrial/anti-M2 seropositive variant form of autoimmune hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:887–893. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04130.x. PMID: 16704541.
Article18. Gassert DJ, Garcia H, Tanaka K, Reinus JF. 2007; Corticosteroid-responsive cryptogenic chronic hepatitis: evidence for seronegative autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 52:2433–2437. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-006-9665-4. PMID: 17429719.
Article19. Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, et al. 1999; International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 31:929–938. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(99)80297-9. PMID: 10580593.
Article20. Balitzer D, Shafizadeh N, Peters MG, Ferrell LD, Alshak N, Kakar S. 2017; Autoimmune hepatitis: review of histologic features included in the simplified criteria proposed by the international autoimmune hepatitis group and proposal for new histologic criteria. Mod Pathol. 30:773–783. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.267. PMID: 28106105.
Article21. Lohse AW, Sebode M, Bhathal PS, et al. 2022; Consensus recommendations for histological criteria of autoimmune hepatitis from the International AIH Pathology Group: Results of a workshop on AIH histology hosted by the European Reference Network on Hepatological Diseases and the European Society of Pathology: Results of a workshop on AIH histology hosted by the European Reference Network on Hepatological Diseases and the European Society of Pathology. Liver Int. 42:1058–1069. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15217. PMID: 35230735.
Article22. Johnson PJ, McFarlane IG. 1993; Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology. 18:998–1005. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840180435. PMID: 8406375.
Article23. Jeong SH. 2018; Current epidemiology and clinical characteristics of autoimmune liver diseases in South Korea. Clin Mol Hepatol. 24:10–19. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2017.0066. PMID: 29307132. PMCID: PMC5875193.
Article24. Czaja AJ. 2008; Performance parameters of the diagnostic scoring systems for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 48:1540–1548. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22513. PMID: 18924244.
Article25. Miyake Y, Iwasaki Y, Kobashi H, et al. 2010; Clinical features of autoimmune hepatitis diagnosed based on simplified criteria of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Dig Liver Dis. 42:210–215. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.06.013. PMID: 19632907.
Article26. Kim BH, Kim YJ, Jeong SH, et al. 2013; Clinical features of autoimmune hepatitis and comparison of two diagnostic criteria in Korea: a nationwide, multicenter study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:128–134. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07292.x. PMID: 23033899.
Article27. Lee YN, Kim YS, Kim SG, et al. 2011; Diagnostic Value and Utility of the Simplified International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group (IAIHG) criteria for autoimmune hepatitis in Korea. Korean J Med. 81:340–350. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2011.26.3.340. PMID: 22016595. PMCID: PMC3192207.28. Kuiper EM, Zondervan PE, van Buuren HR. 2010; Paris criteria are effective in diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:530–534. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.004. PMID: 20304098.
Article29. Chazouillères O, Wendum D, Serfaty L, Montembault S, Rosmorduc O, Poupon R. 1998; Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: clinical features and response to therapy. Hepatology. 28:296–301. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510280203. PMID: 9695990.
Article30. Czaja AJ. 2014; Cholestatic phenotypes of autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:1430–1438. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.08.039. PMID: 24013108.
Article31. Hisamochi A, Kage M, Ide T, et al. 2016; An analysis of drug-induced liver injury, which showed histological findings similar to autoimmune hepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 51:597–607. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-015-1131-7. PMID: 26519284.
Article32. Liu ZX, Kaplowitz N. 2002; Immune-mediated drug-induced liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 6:755–774. DOI: 10.1016/S1089-3261(02)00025-9. PMID: 12362579.
Article33. deLemos AS, Foureau DM, Jacobs C, Ahrens W, Russo MW, Bonkovsky HL. 2014; Drug-induced liver injury with autoimmune features. Semin Liver Dis. 34:194–204. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1375959. PMID: 24879983.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Overlap Syndromebetween Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Cyclosporine Treatment in a Patient with Concurrent Autoimmune Urticaria and Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Recent Korean Trend
- The major diagnostic role of autoantibodies in the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis, a disease of all ages
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Recent Update on Diagnosis and Treatment