Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 Mar;27(2):157-165. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.2.157.
The expression of Rab5 and its effect on invasion, migration and exosome secretion in triple negative breast cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, Xinjiang Medical University Affiliated Tumor Hospital, Urumqi, Xinjiang Province 830000, China
- 2Departments of Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University Affiliated Tumor Hospital, Urumqi, Xinjiang Province 830000, China
- KMID: 2539570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.2.157
Abstract
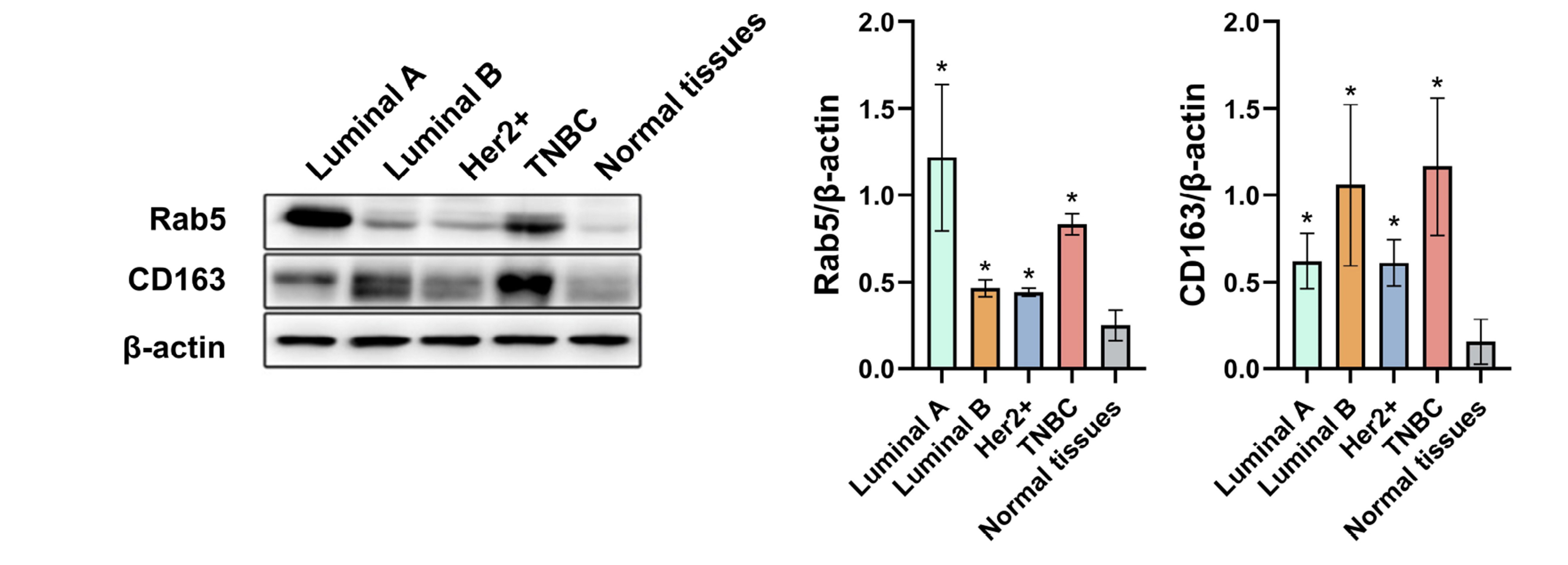
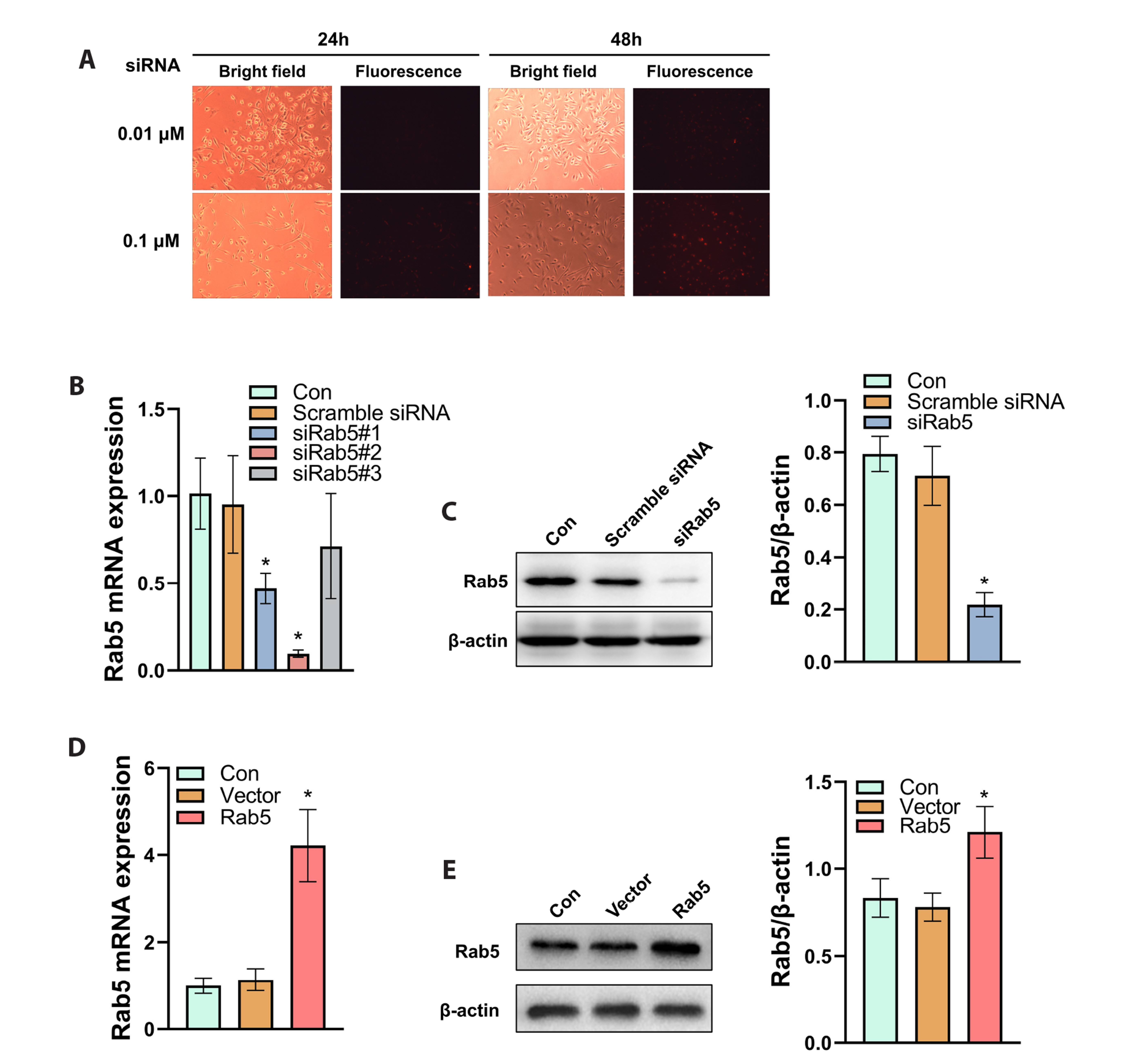
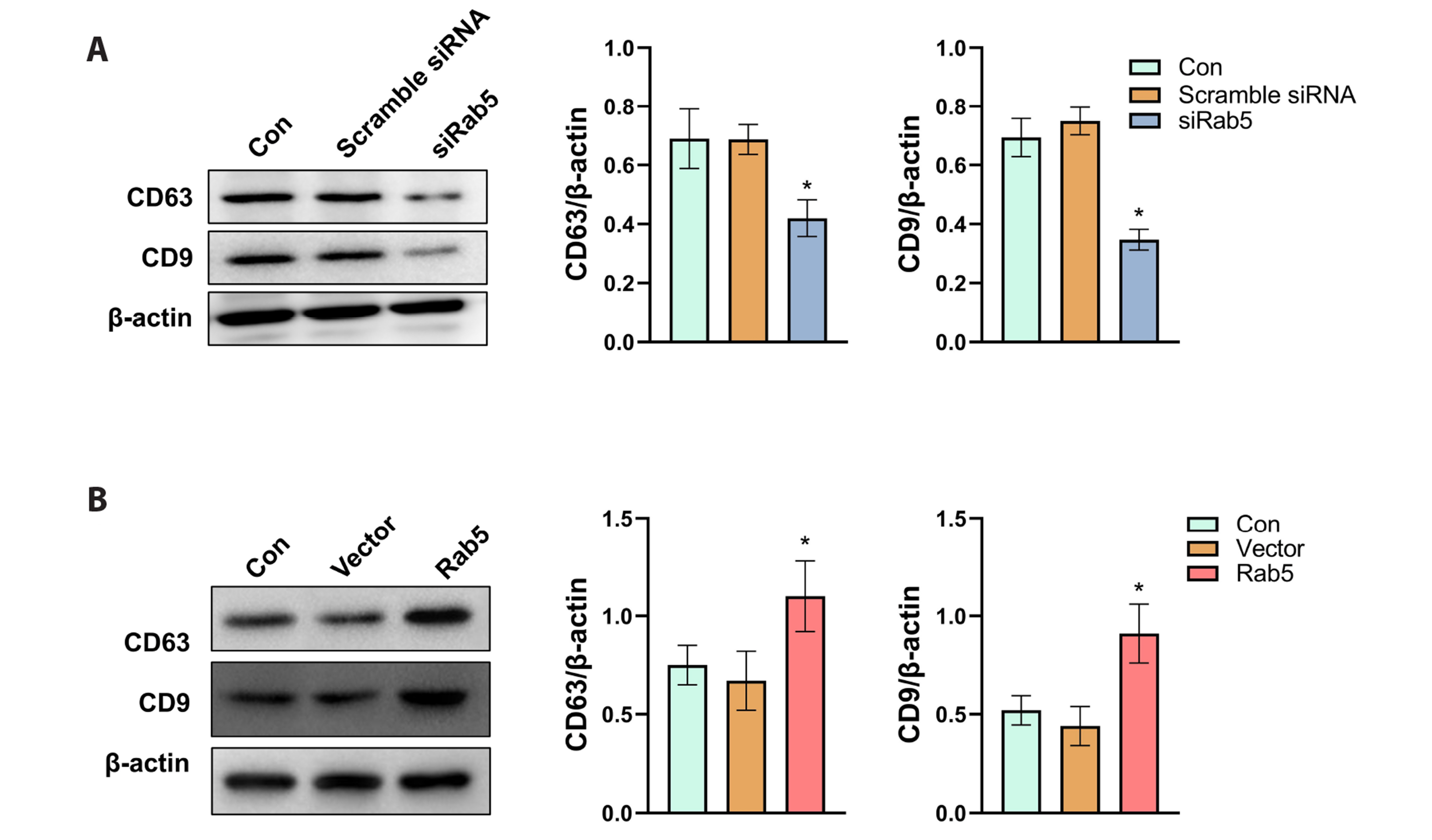
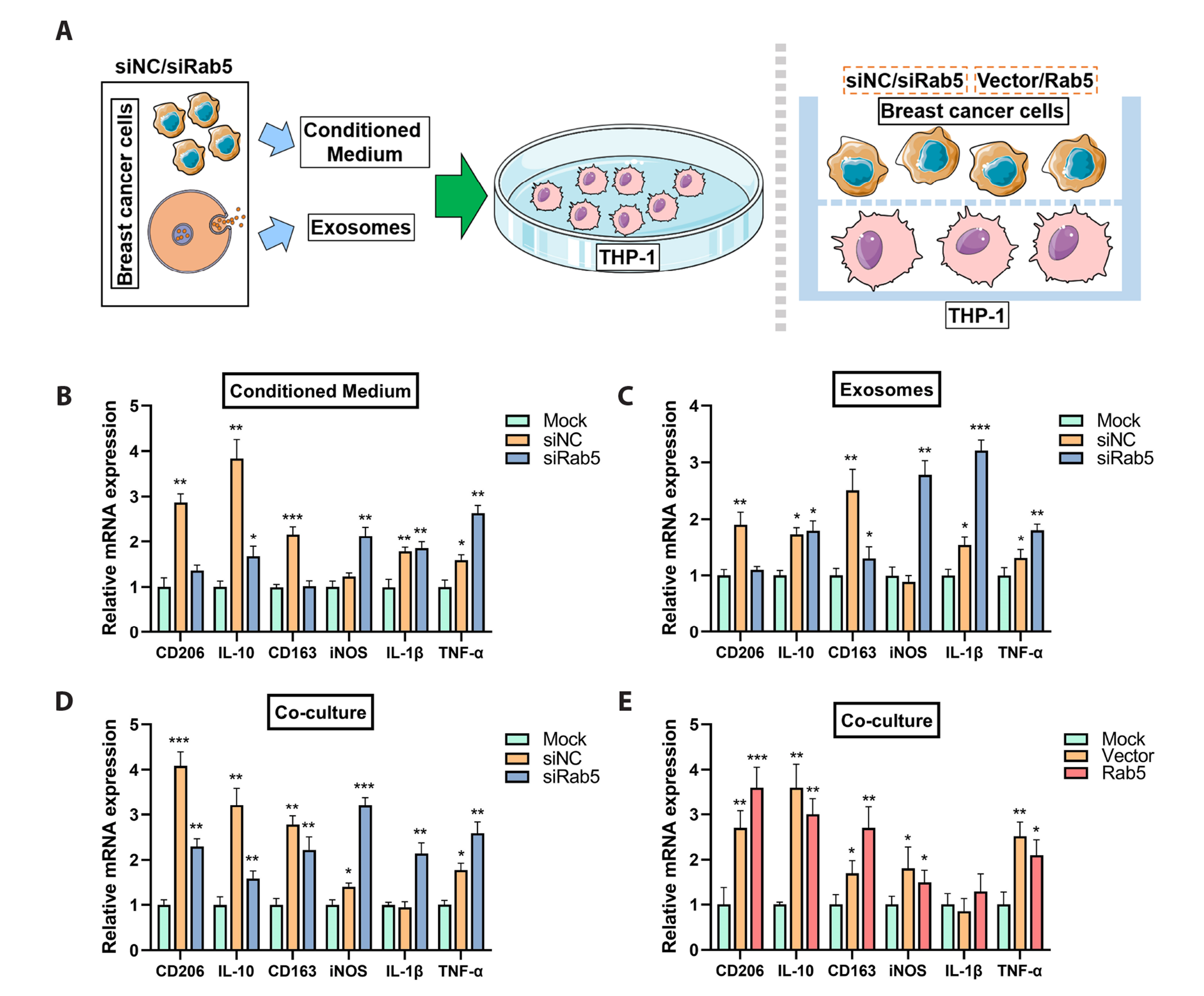
- Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive subtype of breast cancer and current therapeutic strategies are limited in their effectiveness. The expressions of Rab5 and the M2 tumor-associated macrophage marker CD163 in tissues were detected by Western blot. The migration and invasion of cells were determined using a Transwell assay. The expressions of the exosome markers were evaluated by Western blot. The polarization of human macrophages (THP-1) was determined by incubation of THP-1 cells with conditioned medium or exosomes collected from MDA-MB-231 cells with indicated transfections or by a coculture system of THP-1 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The M1 and M2 macrophage markers were evaluated by qRT-PCR. The expression of Rab5 in TNBC was significantly higher than that in normal breast tissue. Rab5 expressions in triple-negative and luminal A breast cancer were higher than those in other molecular subtypes. Higher CD163 expression was observed in triple-negative breast cancer and in triple-negative and luminal B subtypes. Rab5 knockdown suppressed but Rab5 overexpression promoted the migration and invasion capacity of MDA-MB-231 cells. The levels of CD63 and CD9 in the medium of Rab5 knockdown cells were lower than those in control cells, whereas higher levels of CD63 and CD9 were observed in Rab5 overexpression cells. Rab5 knockdown decreased the excretion but did not alter the diameter of the exosomes. Knockdown of Rab5 facilitated the anti-tumor polarization of macrophages, which was partially reversed by Rab5 overexpression. Therefore, Rab5 is expected to be a potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zubor P, Kubatka P, Kajo K, Dankova Z, Polacek H, Bielik T, Kudela E, Samec M, Liskova A, Vlcakova D, Kulkovska T, Stastny I, Holubekova V, Bujnak J, Laucekova Z, Büsselberg D, Adamek M, Kuhn W, Danko J, Golubnitschaja O. 2019; Why the gold standard approach by mammography demands extension by multiomics? Application of liquid biopsy miRNA profiles to breast cancer disease management. Int J Mol Sci. 20:2878. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122878. PMID: 31200461. PMCID: PMC6627787. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85068141313&origin=inward.
Article2. Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. 2010; Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1001389. PMID: 21067385. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=78149483057&origin=inward.
Article3. Tang W, Xia M, Liao Y, Fang Y, Wen G, Zhong J. 2022; Exosomes in triple negative breast cancer: from bench to bedside. Cancer Lett. 527:1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.009. PMID: 34902521. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85121006062&origin=inward.
Article4. Ahmadi M, Rezaie J. 2020; Tumor cells derived-exosomes as angiogenenic agents: possible therapeutic implications. J Transl Med. 18:249. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02426-5. PMID: 32571337. PMCID: PMC7310379. PMID: a888c7c1bef8419eb3b0f370478a74df. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85086947144&origin=inward.
Article5. Baig MS, Roy A, Rajpoot S, Liu D, Savai R, Banerjee S, Kawada M, Faisal SM, Saluja R, Saqib U, Ohishi T, Wary KK. 2020; Tumor-derived exosomes in the regulation of macrophage polarization. Inflamm Res. 69:435–451. DOI: 10.1007/s00011-020-01318-0. PMID: 32162012. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85081932551&origin=inward.
Article6. Tzeng HT, Wang YC. 2016; Rab-mediated vesicle trafficking in cancer. J Biomed Sci. 23:70. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0287-7. PMID: 27716280. PMCID: PMC5053131. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84992036211&origin=inward.
Article7. Kalaidzidis I, Miaczynska M, Brewińska-Olchowik M, Hupalowska A, Ferguson C, Parton RG, Kalaidzidis Y, Zerial M. 2015; APPL endosomes are not obligatory endocytic intermediates but act as stable cargo-sorting compartments. J Cell Biol. 211:123–144. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201311117. PMID: 26459602. PMCID: PMC4602042. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84980327273&origin=inward.
Article8. Zeigerer A, Gilleron J, Bogorad RL, Marsico G, Nonaka H, Seifert S, Epstein-Barash H, Kuchimanchi S, Peng CG, Ruda VM, Del Conte-Zerial P, Hengstler JG, Kalaidzidis Y, Koteliansky V, Zerial M. 2012; Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo. Nature. 485:465–470. DOI: 10.1038/nature11133. PMID: 22622570. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84861423416&origin=inward.
Article9. Zhao Z, Liu XF, Wu HC, Zou SB, Wang JY, Ni PH, Chen XH, Fan QS. 2010; Rab5a overexpression promoting ovarian cancer cell proliferation may be associated with APPL1-related epidermal growth factor signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 101:1454–1462. DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01558.x. PMID: 20412119. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=77954169426&origin=inward.
Article10. Piao HY, Guo S, Wang Y, Zhang J. 2021; Exosome-transmitted lncRNA PCGEM1 promotes invasive and metastasis in gastric cancer by maintaining the stability of SNAI1. Clin Transl Oncol. 23:246–256. DOI: 10.1007/s12094-020-02412-9. PMID: 32519176. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85086172545&origin=inward.
Article11. Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, Moita CF, Schauer K, Hume AN, Freitas RP, Goud B, Benaroch P, Hacohen N, Fukuda M, Desnos C, Seabra MC, Darchen F, Amigorena S, Moita LF, Thery C. 2010; Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 12:19–30. sup pp 1–13. DOI: 10.1038/ncb2000. PMID: 19966785. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=79953136097&origin=inward.
Article12. Frittoli E, Palamidessi A, Marighetti P, Confalonieri S, Bianchi F, Malinverno C, Mazzarol G, Viale G, Martin-Padura I, Garré M, Parazzoli D, Mattei V, Cortellino S, Bertalot G, Di Fiore PP, Scita G. 2014; A RAB5/RAB4 recycling circuitry induces a proteolytic invasive program and promotes tumor dissemination. J Cell Biol. 206:307–328. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201403127. PMID: 25049275. PMCID: PMC4107781. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84904701296&origin=inward.
Article13. Mendoza P, Ortiz R, Díaz J, Quest AF, Leyton L, Stupack D, Torres VA. 2013; Rab5 activation promotes focal adhesion disassembly, migration and invasiveness in tumor cells. J Cell Sci. 126(Pt 17):3835–3847. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.119727. PMID: 23813952. PMCID: PMC4074302. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84883306115&origin=inward.14. Harding CV, Heuser JE, Stahl PD. 2013; Exosomes: looking back three decades and into the future. J Cell Biol. 200:367–371. Erratum in: J Cell Biol. 2013;201:485. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201212113. PMID: 23420870. PMCID: PMC3575527. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84874354368&origin=inward.
Article15. Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. 2013; Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 200:373–383. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201211138. PMID: 23420871. PMCID: PMC3575529. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84874377202&origin=inward.
Article16. Jang JY, Lee JK, Jeon YK, Kim CW. 2013; Exosome derived from epigallocatechin gallate treated breast cancer cells suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and M2 polarization. BMC Cancer. 13:421. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-421. PMID: 24044575. PMCID: PMC3848851. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84883887202&origin=inward.
Article17. Kwon Y, Kim M, Kim Y, Jung HS, Jeoung D. 2020; Exosomal MicroRNAs as mediators of cellular interactions between cancer cells and macrophages. Front Immunol. 11:1167. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01167. PMID: 32595638. PMCID: PMC7300210. PMID: e432839fcb584aab8cbb7750f24e29a0. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85087034958&origin=inward.
Article18. Zhou J, Wang XH, Zhao YX, Chen C, Xu XY, Sun Q, Wu HY, Chen M, Sang JF, Su L, Tang XQ, Shi XB, Zhang Y, Yu Q, Yao YZ, Zhang WJ. 2018; Cancer-associated fibroblasts correlate with tumor-associated macrophages infiltration and lymphatic metastasis in triple negative breast cancer patients. J Cancer. 9:4635–4641. DOI: 10.7150/jca.28583. PMID: 30588247. PMCID: PMC6299377. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85059301446&origin=inward.
Article19. Zhao S, Mi Y, Guan B, Zheng B, Wei P, Gu Y, Zhang Z, Cai S, Xu Y, Li X, He X, Zhong X, Li G, Chen Z, Li D. 2020; Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 13:156. Erratum in: J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:33. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-021-01042-0. PMID: 33618743. PMCID: PMC7901099. PMID: 9031db18aa254d48a7fb7a969f3ec893. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85101278939&origin=inward.
Article20. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. 2018; Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:313. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. PMID: 30207593. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85053395052&origin=inward.
Article21. Brown M, Tsodikov A, Bauer KR, Parise CA, Caggiano V. 2008; The role of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 in the survival of women with estrogen and progesterone receptor-negative, invasive breast cancer: the California Cancer Registry, 1999-2004. Cancer. 112:737–747. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23243. PMID: 18189290. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=39049164069&origin=inward.
Article22. Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P, Narod SA. 2007; Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13(15 Pt 1):4429–4434. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3045. PMID: 17671126. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=34547661993&origin=inward.
Article23. Shabo I, Stål O, Olsson H, Doré S, Svanvik J. 2008; Breast cancer expression of CD163, a macrophage scavenger receptor, is related to early distant recurrence and reduced patient survival. Int J Cancer. 123:780–786. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.23527. PMID: 18506688. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=47049108919&origin=inward.
Article24. Logozzi M, De Milito A, Lugini L, Borghi M, Calabrò L, Spada M, Perdicchio M, Marino ML, Federici C, Iessi E, Brambilla D, Venturi G, Lozupone F, Santinami M, Huber V, Maio M, Rivoltini L, Fais S. 2009; High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS One. 4:e5219. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005219. PMID: 19381331. PMCID: PMC2667632. PMID: 777e9b167fd447db947c5d1cba838ee7. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=65449117971&origin=inward.
Article25. Li Y, Meng X, Feng H, Zhang G, Liu C, Li P. 1999; Over-expression of the RAB5 gene in human lung adenocarcinoma cells with high metastatic potential. Chin Med Sci J. 14:96–101. PMID: 12901617. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0002925345&origin=inward.26. Li Y, Feng H, Chen Y. 1999; RAB5A, a gene possibly related to metastasis of human carcinoma of the lung and stomach. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 21:178–181. Chinese. PMID: 11776829. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=0033004429&origin=inward.27. Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, Speed T, Spellman PT, DeVries S, Lapuk A, Wang NJ, Kuo WL, Stilwell JL, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Waldman FM, et al. 2006; A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 10:515–527. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.008. PMID: 17157791. PMCID: PMC2730521. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=33845209913&origin=inward.
Article28. Condeelis J, Pollard JW. 2006; Macrophages: obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.007. PMID: 16439202. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=31044433663&origin=inward.
Article29. Kanwar SS, Dunlay CJ, Simeone DM, Nagrath S. 2014; Microfluidic device (ExoChip) for on-chip isolation, quantification and characterization of circulating exosomes. Lab Chip. 14:1891–1900. DOI: 10.1039/C4LC00136B. PMID: 24722878. PMCID: PMC4134440. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84899810743&origin=inward.
Article30. Gorji-Bahri G, Moghimi HR, Hashemi A. 2021; RAB5A effect on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line via altering the pro-invasive content of exosomes. Exp Mol Pathol. 120:104632. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104632. PMID: 33831402. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85104090083&origin=inward.
Article31. Gorji-Bahri G, Moghimi HR, Hashemi A. 2021; RAB5A is associated with genes involved in exosome secretion: integration of bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. J Cell Biochem. 122:425–441. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29871. PMID: 33225526. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85096808352&origin=inward.
Article32. Moradi-Chaleshtori M, Hashemi SM, Soudi S, Bandehpour M, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S. 2019; Tumor-derived exosomal microRNAs and proteins as modulators of macrophage function. J Cell Physiol. 234:7970–7982. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27552. PMID: 30378104. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85055652140&origin=inward.
Article33. Han C, Zhang C, Wang H, Zhao L. 2021; Exosome-mediated communication between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages: implications for tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology. 10:1887552. DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1887552. PMID: 33680573. PMCID: PMC7901554. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85101645642&origin=inward.
Article34. Pritchard A, Tousif S, Wang Y, Hough K, Khan S, Strenkowski J, Chacko BK, Darley-Usmar VM, Deshane JS. 2020; Lung tumor cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage polarization. Cells. 9:1303. DOI: 10.3390/cells9051303. PMID: 32456301. PMCID: PMC7290460. PMID: 8fa2e48e22c840c49c89b8fe7810c035. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85085538371&origin=inward.
Article35. Ham S, Lima LG, Chai EPZ, Muller A, Lobb RJ, Krumeich S, Wen SW, Wiegmans AP, Möller A. 2018; Breast cancer-derived exosomes alter macrophage polarization via gp130/STAT3 signaling. Front Immunol. 9:871. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00871. PMID: 29867925. PMCID: PMC5951966. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85046620325&origin=inward.
Article36. Shu Y, Qin M, Song Y, Tang Q, Huang Y, Shen P, Lu Y. 2020; M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages is dependent on integrin β3 via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ up-regulation in breast cancer. Immunology. 160:345–356. DOI: 10.1111/imm.13196. PMID: 32311768. PMCID: PMC7370165. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85084002889&origin=inward.
Article37. Chanmee T, Ontong P, Konno K, Itano N. 2014; Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 6:1670–1690. DOI: 10.3390/cancers6031670. PMID: 25125485. PMCID: PMC4190561. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=84920943285&origin=inward.
Article38. Zhou J, Li X, Wu X, Zhang T, Zhu Q, Wang X, Wang H, Wang K, Lin Y, Wang X. 2018; Exosomes released from tumor-associated macrophages transfer miRNAs that induce a Treg/Th17 cell imbalance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 6:1578–1592. DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0479. PMID: 30396909. PMID: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=85057781557&origin=inward.
Article39. Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Bruno S, Grange C, Fonsato V, Tetta C. 2011; Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am J Cancer Res. 1:98–110. PMID: 21969178. PMCID: PMC3180104.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Noncoding-RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA Processing Endoribonuclease Promotes Carcinogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via the Competing Endogenous RNA Mechanism
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Molecular Classification of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Fear of Cancer Recurrence and Unmet Needs in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Survivors
- Coordinate Regulation of Neurite Outgrowth by LRRK2 and Its Interactor, Rab5