J Stroke.
2023 Jan;25(1):126-131. 10.5853/jos.2022.03034.
Practical Nomogram Predicting Apixaban or Rivaroxaban Concentrations from Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Anti-Xa Values: Special Interest in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Service d’hématologie – Hémostase clinique, Hôpital Lariboisière, APHP Nord, Paris, France
- 2EA 3518, Université de Paris Cité, Paris, France
- 3Département de Neurologie, Unité Neuro-vasculaire, Hôpital Lariboisière, APHP Nord, Paris, France
- 4UR 7537 BioSTM (Biostatistics), Faculté de Pharmacie de Paris, Université Paris Cité, Paris, France
- 5INSERM UMRS-1140, Université de Paris Cité, Paris, France
- KMID: 2539065
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2022.03034
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
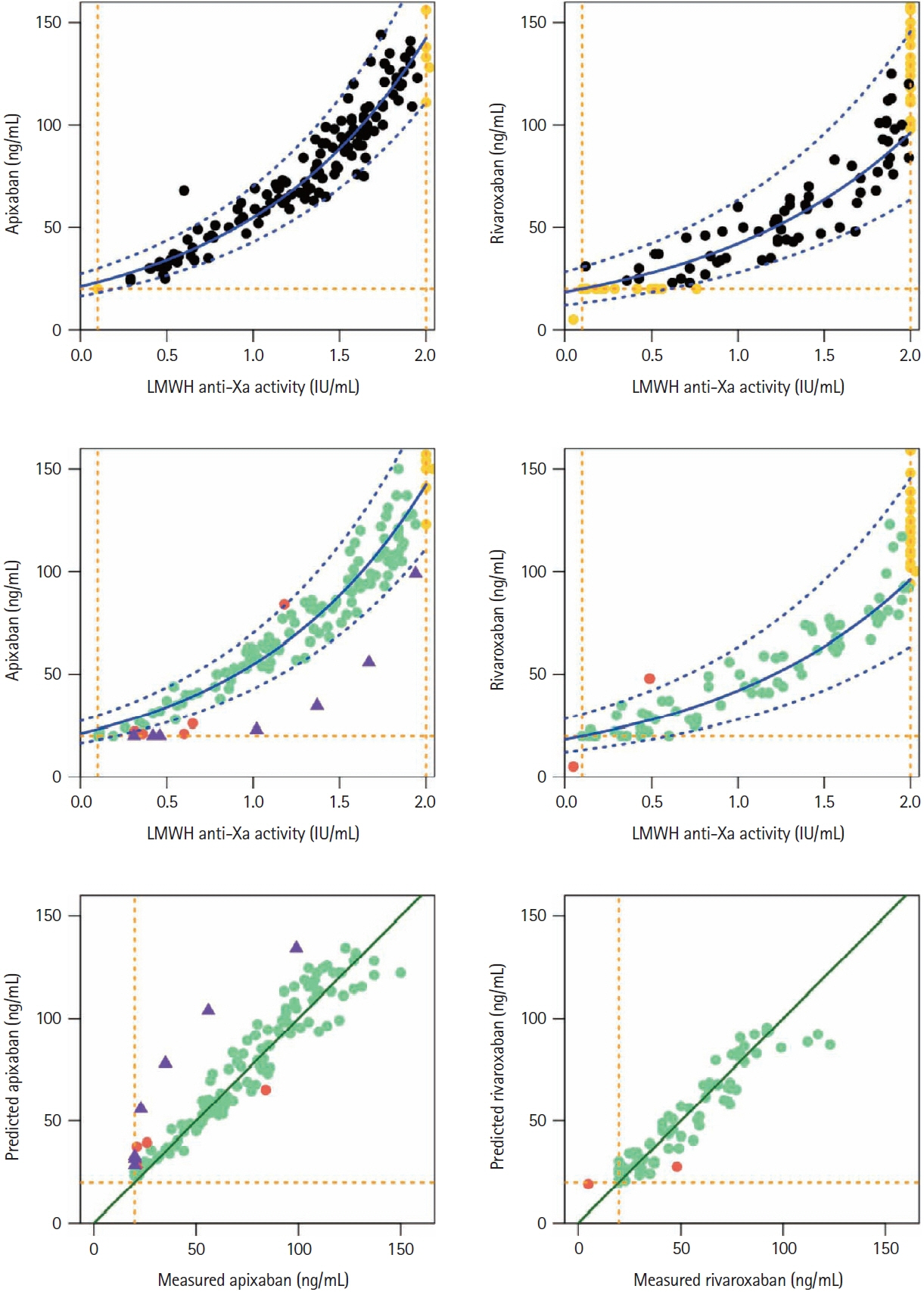
In patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) using a direct oral factor-Xa anticoagulant (DOAC) during the last 48 hours, a fixed plasma heparin-calibrated anti-Xa activity (0.5 IU/mL) was proposed as a threshold below which patients could be eligible for thrombolysis and/or thrombectomy. Besides, specific DOAC-calibrated anti-Xa thresholds up to 50 ng/mL have been proposed. However, specific DOAC assays are not widely available contrarily to low-molecularweight heparin (LMWH) anti-Xa activity. We developed and validated a nomogram for predicting apixaban and rivaroxaban concentrations based on LMWH anti-Xa assay.
Methods
Our prospective study included apixaban (n=325) and rivaroxaban (n=276) patients. On the same sample, we systematically measured specific DOAC concentration and LMWH anti-Xa activity, using STA®-Liquid-Anti-Xa (Stago) and specific DOAC- or LMWH-calibrators, respectively. The nomogram was built using quantifiable values for both assays on the derivation cohorts with a log-linear regression model. Model performances including sensitivity, specificity, and true positive rate for different thresholds were checked on the validation cohorts.
Results
The models built from the derivation cohorts predicted that values <30 ng/mL and <50 ng/ mL DOAC thresholds corresponded to LMWH-anti-Xa values <0.10 IU/mL and <0.64 IU/mL for apixaban; <0.10 IU/mL and <0.71 IU/mL for rivaroxaban. The model accurately predicted apixaban/ rivaroxaban concentrations in the validation cohort.
Conclusions
This easy-to-use nomogram, developed with our reagent, allowed accurately predicting DOAC concentrations based on LMWH-anti-Xa results in emergency situations such as AIS when drug-specific assessments are not rapidly available. Using DOAC <50 ng/mL equivalent threshold, instead of the fixed LMWH <0.5 IU/mL one, would allow proposing thrombolysis to more patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Meinel TR, Branca M, De Marchis GM, Nedeltchev K, Kahles T, Bonati L, et al. Investigators of the Swiss stroke registry. Prior anticoagulation in patients with ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation. Ann Neurol. 2021; 89:42–53.2. Berge E, Whiteley W, Audebert H, De Marchis GM, Fonseca AC, Padiglioni C, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines on intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Eur Stroke J. 2021; 6:I–LXII.3. Touzé E, Gruel Y, Gouin-Thibault I, De Maistre E, Susen S, Sie P, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke in patients on direct oral anticoagulants. Eur J Neurol. 2018; 25:747–e52.4. Seiffge DJ, Traenka C, Polymeris AA, Thilemann S, Wagner B, Hert L, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis in patients with stroke taking rivaroxaban using drug specific plasma levels: experience with a standard operation procedure in clinical practice. J Stroke. 2017; 19:347–355.5. Seiffge DJ, Poli S, Meinel TR, Wu T, Wilson D, Purrucker JC. Intravenous thrombolysis in patients taking direct oral anticoagulants (ESO IVT guidelines comment). Eur Stroke J. 2021; 6:445–446.6. Douxfils J, Adcock DM, Bates SM, Favaloro EJ, Gouin-Thibault I, Guillermo C, et al. 2021 Update of the International Council for Standardization in Haematology Recommendations for laboratory measurement of direct oral anticoagulants. Thromb Haemost. 2021; 121:1008–1020.7. Ebner M, Birschmann I, Peter A, Härtig F, Spencer C, Kuhn J, et al. Limitations of specific coagulation tests for direct oral anticoagulants: a critical analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018; 7:e009807.8. Beyer J, Trujillo T, Fisher S, Ko A, Lind SE, Kiser TH. Evaluation of a heparin-calibrated antifactor Xa assay for measuring the anticoagulant effect of oral direct Xa inhibitors. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016; 22:423–428.9. Maier CL, Asbury WH, Duncan A, Robbins A, Ingle A, Webb A, et al. Using an old test for new tricks: measuring direct oral anti-Xa drug levels by conventional heparin-calibrated antiXa assay. Am J Hematol. 2019; 94:E132–E134.10. Boissier E, Senage T, Babuty A, Gouin-Thibault I, Rozec B, Roussel JC, et al. Heparin anti-Xa activity, a readily available unique test to quantify apixaban, rivaroxaban, fondaparinux, and danaparoid levels. Anesth Analg. 2021; 132:707–716.11. Willekens G, Studt JD, Mendez A, Alberio L, Fontana P, Wuillemin WA, et al. A universal anti-Xa assay for rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban measurements: method validation, diagnostic accuracy and external validation. Br J Haematol. 2021; 193:1203–1212.12. Meihandoest T, Studt JD, Mendez A, Alberio L, Fontana P, Wuillemin WA, et al. Accuracy of a single, heparin-calibrated anti-Xa assay for the measurement of rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban drug concentrations: a prospective cross-sectional study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022; 9:817826.13. Mithoowani S, Moffat KA, Gupta A, Carlino SA, Crowther MA. Low molecular weight heparin anti-Xa assays can identify patients with clinically important apixaban and rivaroxaban drug levels. Thromb Res. 2022; 215:1–4.14. von Horn H, Rasmusson A, Söderblom L, Malmström RE, Antovic J. Using a low-molecular weight heparin-calibrated anti-factor Xa assay to assess the concentration of apixaban and rivaroxaban. Int J Lab Hematol. 2022; 44:163–167.15. Shahjouei S, Tsivgoulis G, Goyal N, Sadighi A, Mowla A, Wang M, et al. Safety of intravenous thrombolysis among patients taking direct oral anticoagulants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2020; 51:533–541.16. Lessire S, Douxfils J, Pochet L, Dincq AS, Larock AS, Gourdin M, et al. Estimation of rivaroxaban plasma concentrations in the perioperative setting in patients with or without heparin bridging. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018; 24:129–138.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent advances in the management of venous thromboembolism
- Rivaroxaban versus Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Venous Thromboembolism in Gastrointestinal and Pancreatobiliary Cancer
- Effect of standard heparin and low molecular weight heparin on fibrinolytic activity
- Recurrent acute portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis treated by rivaroxaban
- Usefulness of a Weighted-based, Patient-Specific Nomogram for Intravenous Heparin Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Patients