Kosin Med J.
2022 Sep;37(3):203-212. 10.7180/kmj.22.003.
Identification of the transcriptome profile of Miamiensis avidus after mebendazole treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Parasitology and Genetics, Institute for Medical Science, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2538799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.22.003
Abstract
- Background
The scuticociliate Miamiensis avidus is a major pathogenic agent that causes significant economic losses in the flounder aquaculture industry. Many different types of drugs are being tested to control this disease, including mebendazole, which is a broad-spectrum antiprotozoal agent. The purpose of this study was to determine whether mebendazole worked in vitro against M. avidus and to explore its mechanism of action.
Methods
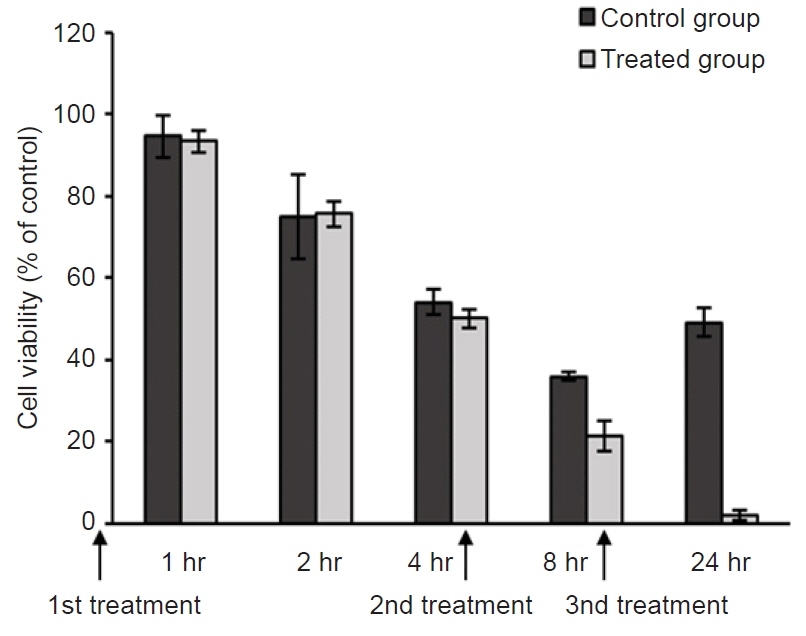
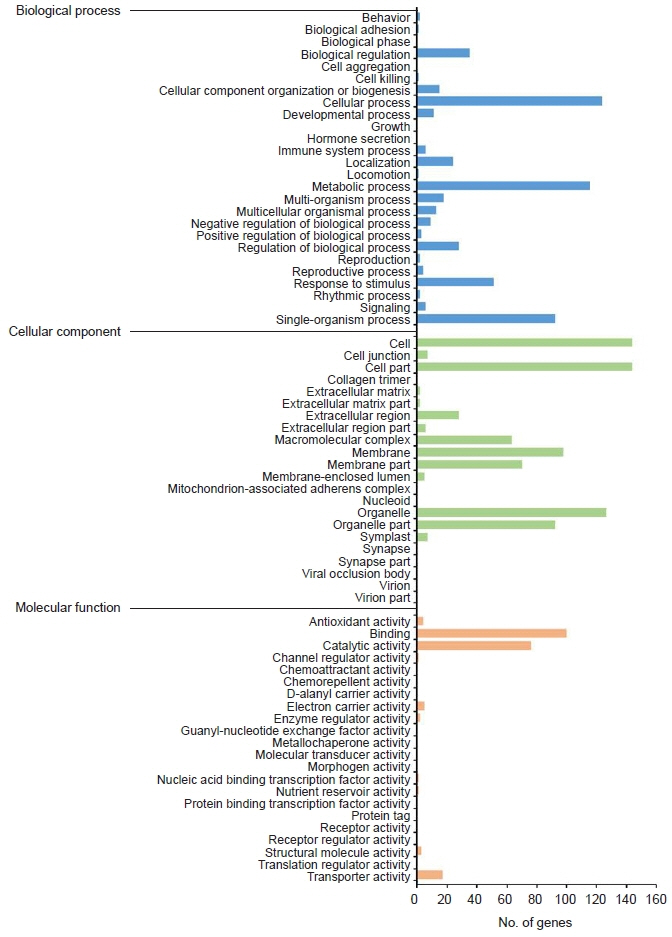
Transcriptome and gene ontology analyses were conducted to investigate the specifically expressed gene profile. We confirmed the cytotoxic effect of mebendazole against M. avidus when it was applied intermittently for a total of three times. We also identified differentially expressed genes using transcriptome analysis.
Results
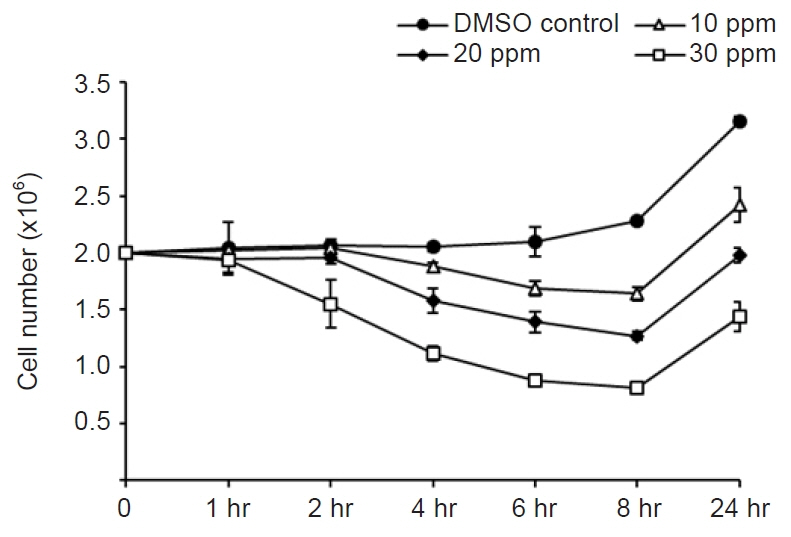
Most of the upregulated genes were membrane transport-related genes, including Na+/K+-ATPase. Most of the downregulated genes were categorized into three groups: tubulin-related, metabolism-related, and transport-related genes. The expression levels of glucose uptake-related genes decreased due to the inhibition of tubulin polymerization, but this was not statistically significant.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that intermittent treatment with mebendazole has a significant cytotoxic effect on M. avidus. Furthermore, mebendazole induces downregulation of the tubulin-alpha chain and metabolism-related genes. It is presumed that this leads to a glucose shortage and the death of M. avidus. Transcriptome analysis will provide useful clues for further studies on mebendazole applications for scutica control.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jee BY, Shin KW, Lee DW, Kim YJ, Lee MK. Monitoring of the mortalities and medications in the inland farms of olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, in South Korea. J Fish Pathol. 2014; 27:77–83.2. Kang BJ, Jang YH, Jhon BK, Park BH, Jin CN. Monitoring of scuticociliatosis of olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) farm in Jeju, Korea from 2007 to 2014. J Fish Pathol. 2015; 28:165–9.3. Retallack H, Okihiro MS, Britton E, Sommeran SV, DeRisi JL. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing reveals Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) in the 2017 epizootic of leopard sharks (Triakis semifasciata) in San Francisco Bay, California, USA. J Wildl Dis. 2019; 55:375–86.4. Jung SJ, Kitamura S, Song JY, Oh MJ. Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida) causes systemic infection of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and is a senior synonym of Philasterides dicentrarchi. Dis Aquat Organ. 2007; 73:227–34.5. Aquaculture Research Department, Aquatic Disease Control Division. Aquatic medicine catalog. Busan: National Institute of Fisheries Science (NIFS);2016. p. 211.6. Mariante RM, Vancini RG, Melo AL, Benchimol M. Giardia lamblia: evaluation of the in vitro effects of nocodazole and colchicine on trophozoites. Exp Parasitol. 2005; 110:62–72.7. van der Werff SD, Vereecken K, van der Laan K, Campos Ponce M, Junco Diaz R, Nunez FA, et al. Impact of periodic selective mebendazole treatment on soil-transmitted helminth infections in Cuban schoolchildren. Trop Med Int Health. 2014; 19:706–18.8. Chai JY, Jung BK, Hong SJ. Albendazole and mebendazole as anti-parasitic and anti-cancer agents: an update. Korean J Parasitol. 2021; 59:189–225.9. Locatelli C, Pedrosa RC, De Bem AF, Creczynski-Pasa TB, Cordova CA, Wilhelm-Filho D. A comparative study of albendazole and mebendazole-induced, time-dependent oxidative stress. Redox Rep. 2004; 9:89–95.10. Kim KH, Park SI, Jee BY. Efficacy of oral administration of praziquantel and mebendazole against Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea) infestation of cultured rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Fish Pathol. 1998; 33:467–71.11. Chagas EC, de Araujo LD, Martins ML, Gomes LC, de Oliveira Malta JC, Varella AB, et al. Mebendazole dietary supplementation controls Monogenoidea (Platyhelminthes: Dactylogyridae) and does not alter the physiology of the freshwater fish Colossoma macropomum (Cuvier, 1818). Aquaculture. 2016; 464:185–9.12. Whang I, Kang HS, Lee J. Identification of scuticociliates (Pseudocohnilembus persalinus, P. longisetus, Uronema marinum and Miamiensis avidus) based on the cox1 sequence. Parasitol Int. 2013; 62:7–13.13. Iglesias R, Parama A, Alvarez MF, Leiro J, Sanmartin ML. Antiprotozoals effective in vitro against the scuticociliate fish pathogen Philasterides dicentrarchi. Dis Aquat Organ. 2002; 49:191–7.14. Barrowman MM, Marriner SE, Bogan JA. The binding and subsequent inhibition of tubulin polymerization in Ascaris suum (in vitro) by benzimidazole anthelmintics. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984; 33:3037–40.15. McKellar QA, Scott EW. The benzimidazole anthelmintic agents: a review. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1990; 13:223–47.16. Andersson CR, Selvin T, Blom K, Rubin J, Berglund M, Jarvius M, et al. Mebendazole is unique among tubulin-active drugs in activating the MEK-ERK pathway. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:13124.17. Cowan AT, Bowman GR, Edwards KF, Emerson JJ, Turkewitz AP. Genetic, genomic, and functional analysis of the granule lattice proteins in Tetrahymena secretory granules. Mol Biol Cell. 2005; 16:4046–60.18. Agrawal A, Bisharyan Y, Papoyan A, Bednenko J, Cardarelli J, Yao M, et al. Fusion to Tetrahymena thermophila granule lattice protein 1 confers solubility to sexual stage malaria antigens in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 2019; 153:7–17.19. Joffe LS, Schneider R, Lopes W, Azevedo R, Staats CC, Kmetzsch L, et al. The anti-helminthic compound mebendazole has multiple antifungal effects against Cryptococcus neoformans. Front Microbiol. 2017; 8:535.20. Schmahl G, Benini J. Treatment of fish parasites. 11. Effects of different benzimidazole derivatives (albendazole, mebendazole, fenbendazole) on Glugea anomala, Moniez, 1887 (Microsporidia): ultrastructural aspects and efficacy studies. Parasitol Res. 1998; 84:41–9.21. Thornalley PJ. Glyoxalase I: structure, function and a critical role in the enzymatic defence against glycation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003; 31(Pt 6):1343–8.22. Reck-Peterson SL, Redwine WB, Vale RD, Carter AP. The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018; 19:382–98.23. Van den Bossche H, De Nollin S. Effects of mebendazole on the absorption of low molecular weight nutrients by Ascaris suum. Int J Parasitol. 1973; 3:401–7.24. Lacey E. Mode of action of benzimidazoles. Parasitol Today. 1990; 6:112–5.25. Medina RA, Owen GI. Glucose transporters: expression, regulation and cancer. Biol Res. 2002; 35:9–26.26. Kitaoka S, Morielli AD, Zhao FQ. FGT-1 is a mammalian GLUT2-like facilitative glucose transporter in Caenorhabditis elegans whose malfunction induces fat accumulation in intestinal cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68475.27. Martin RJ. Modes of action of anthelmintic drugs. Vet J. 1997; 154:11–34.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcriptome analysis of the pathogenic ciliate Miamiensis avidus after hydrogen peroxide treatment
- Efficacy of mebendazole in treatment and control of trichuriasis in Korea
- A Case of Human Gnathostomiasis Successfully Treated with Ivermectin
- Reduced single dose of mebendazole in treatment of Ascaris lumbricoides infection
- Anthelmintic efficacy of methyl-5-benzoylbenzimidazole-2-carbamate(Mebendazole) against multiple helminthic infections