Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Jan;81(1):17-28. 10.4166/kjg.2022.148.
Acute Liver Failure: Current Updates and Management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea
- KMID: 2538684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2022.148
Abstract
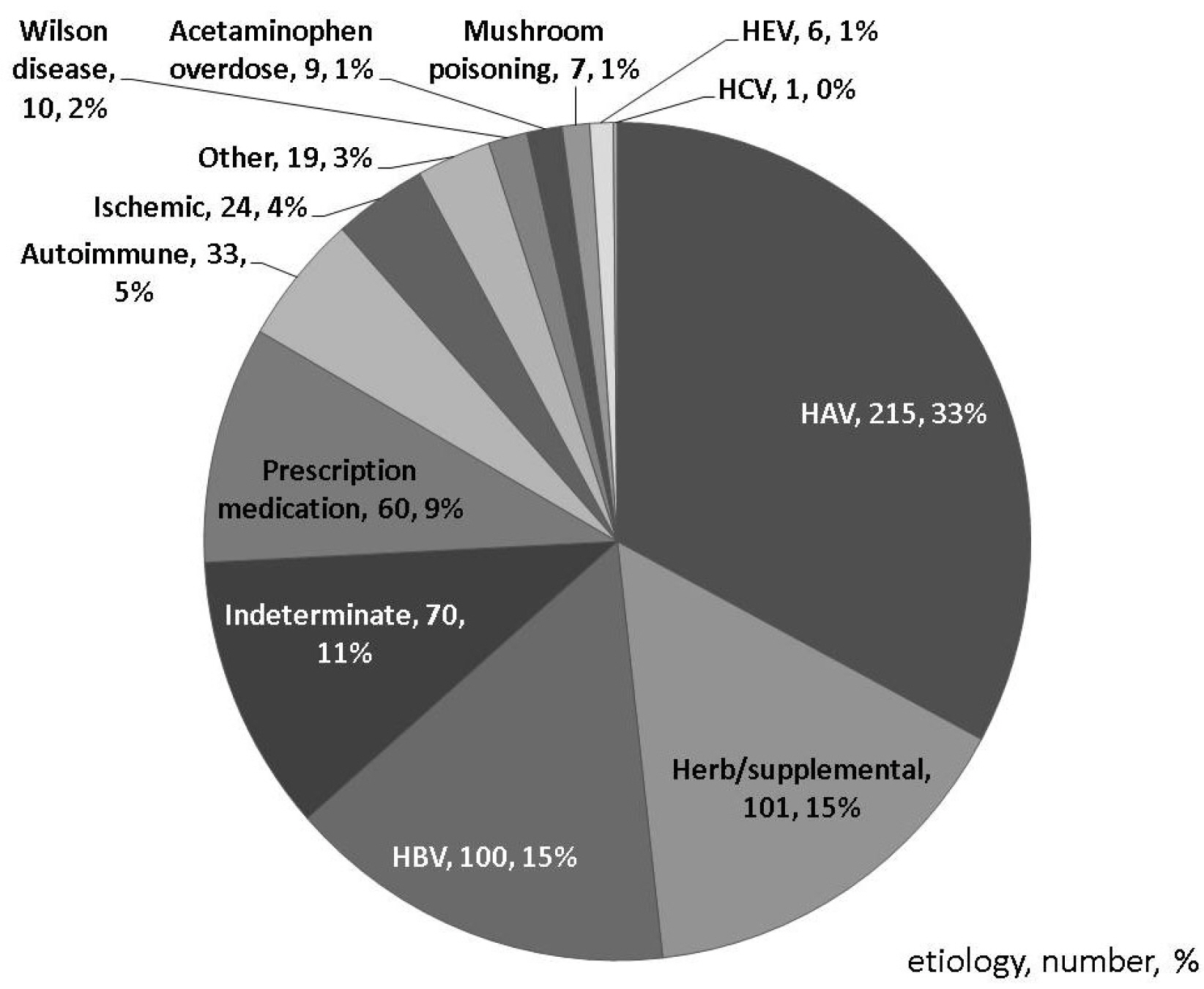
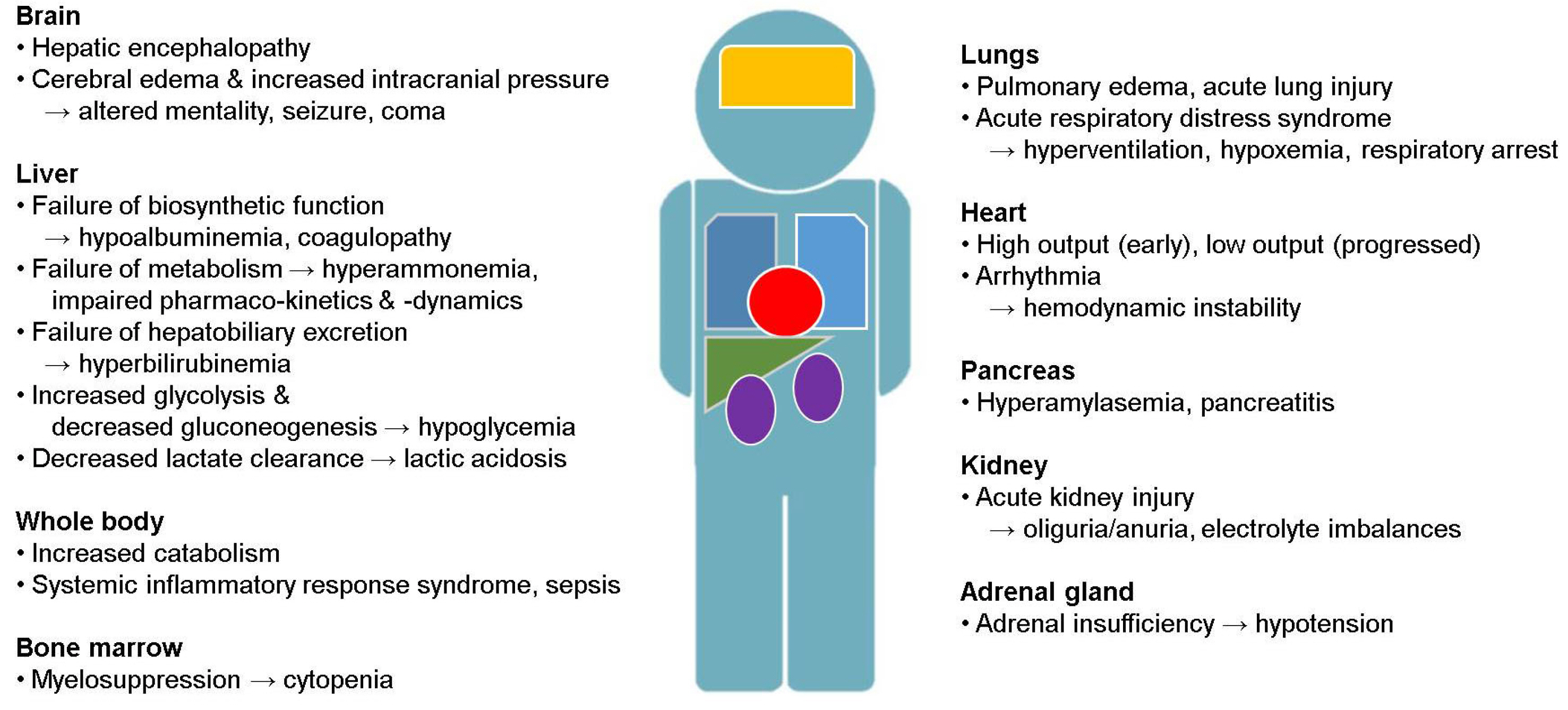
- Acute liver failure (ALF) is a rare disease condition with a dynamic clinical course and catastrophic outcomes. Several etiologies are involved in ALF. Hepatitis A and B infections and indiscriminate use of untested herbs or supplemental agents are the most common causes of ALF in Korea. Noninvasive neurological monitoring tools have been used in patients with ALF in recent times. Ongoing improvements in intensive care, including continuous renal replacement therapy, therapeutic plasma exchange, vasopressor, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, have reduced the mortality rate of patients with ALF. However, liver transplantation is still the most effective treatment for patients with intractable ALF. There is a need for further research in the areas of better prognostication and precise selection of patients for emergency transplantation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. The National Institute of Organ, Tissue and Blood Management. 2020 Annual report of organ transplantation & tissue donation. Seoul: The National Institute of Organ, Tissue and Blood Management;2022.2. Lucke B, Mallory T. 1946; The fulminant form of epidemic hepatitis. Am J Pathol. 22:867–947.3. Trey C, Davidson CS. 1970; The management of fulminant hepatic failure. Prog Liver Dis. 3:282–298.4. O'Grady JG, Schalm SW, Williams R. 1993; Acute liver failure: redefining the syndromes. Lancet. 342:273–275. DOI: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91736-6. PMID: 8101303.5. Lee WM, Stravitz RT, Larson AM. 2012; Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Position Paper on acute liver failure 2011. Hepatology. 55:965–967. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25551. PMID: 22213561. PMCID: PMC3378702.
Article6. O'Grady J, Bernal W. Feldman M, editor. Acute liver failure. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: review and assessment. 11th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier;2021. p. 1499–1508.e2.7. Bernal W, Wendon J. 2013; Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med. 369:2525–2534. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1208937. PMID: 24369077.
Article8. Horvatits T, Drolz A, Trauner M, Fuhrmann V. 2019; liver injury and failure in critical illness. Hepatology. 70:2204–2215. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30824. PMID: 31215660.
Article9. Bernal W, Cross TJ, Auzinger G, et al. 2009; Outcome after wait-listing for emergency liver transplantation in acute liver failure: a single centre experience. J Hepatol. 50:306–313. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.09.012. PMID: 19070386.
Article10. Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiødt FV, et al. U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2002; Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 137:947–954. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-137-12-200212170-00007. PMID: 12484709.
Article11. Gow PJ, Jones RM, Dobson JL, Angus PW. 2004; Etiology and outcome of fulminant hepatic failure managed at an Australian liver transplant unit. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:154–159. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03273.x. PMID: 14731124.
Article12. Khuroo MS, Kamili S. 2003; Aetiology and prognostic factors in acute liver failure in India. J Viral Hepat. 10:224–231. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2003.00415.x. PMID: 12753342.
Article13. Fujiwara K, Mochida S, Matsui A, Nakayama N, Nagoshi S, Toda G. Intractable Liver Diseases Study Group of Japan. 2008; Fulminant hepatitis and late onset hepatic failure in Japan. Hepatol Res. 38:646–657. DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00322.x. PMID: 18328067.
Article14. Tessier G, Villeneuve E, Villeneuve JP. 2002; Etiology and outcome of acute liver failure: experience from a liver transplantation centre in Montreal. Can J Gastroenterol. 16:672–676. DOI: 10.1155/2002/328415. PMID: 12420024.
Article15. Ichai P, Legeai C, Francoz C, et al. French Liver Transplant Teams. 2015; Patients with acute liver failure listed for superurgent liver transplantation in France: reevaluation of the Clichy-Villejuif criteria. Liver Transpl. 21:512–523. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24092. PMID: 25675946.
Article16. Escorsell A, Mas A, de la Mata M. Spanish Group for the Study of Acute Liver Failure. 2007; Acute liver failure in Spain: analysis of 267 cases. Liver Transpl. 13:1389–1395. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21119. PMID: 17370334.
Article17. Heo NY, Lim YS, Kang J, et al. 2006; [Clinical features of fulminant hepatic failure in a tertiary hospital with a liver transplant center in Korea]. Korean J Hepatol. 12:82–92. Korean.18. Park SJ, Lim YS, Hwang S, et al. 2010; Emergency adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure in a hepatitis B virus endemic area. Hepatology. 51:903–911. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23369. PMID: 20041403.
Article19. Kim JD, Cho EJ, Lee D, et al. 2022; Etiology and prognosis of acute liver failure in Korea: a nationwide multicenter study. Hepatol Int. 16(Suppl 1):S92–S93.20. Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J. 2010; Acute liver failure. Lancet. 376:190–201. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60274-7. PMID: 20638564.
Article21. Vaquero J, Chung C, Cahill ME, Blei AT. 2003; Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure. Semin Liver Dis. 23:259–269. DOI: 10.1055/s-2003-42644. PMID: 14523679.
Article22. Karvellas CJ, Stravitz RT. Sanyal A, editor. 2018. Acute liver failure. Zakim and Boyer's hepatology: a textbook of liver disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier;p. 301–323.e4.
Article23. O'Brien CJ, Wise RJ, O'Grady JG, Williams R. 1987; Neurological sequelae in patients recovered from fulminant hepatic failure. Gut. 28:93–95. DOI: 10.1136/gut.28.1.93. PMID: 3817591. PMCID: PMC1432718.24. Baudouin SV, Howdle P, O'Grady JG, Webster NR. 1995; Acute lung injury in fulminant hepatic failure following paracetamol poisoning. Thorax. 50:399–402. DOI: 10.1136/thx.50.4.399. PMID: 7785015. PMCID: PMC474296.
Article25. Trewby PN, Warren R, Contini S, et al. 1978; Incidence and pathophysiology of pulmonary edema in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 74(5 Pt 1):859–865. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(78)90142-7. PMID: 346431.
Article26. Rolando N, Wade J, Davalos M, Wendon J, Philpott-Howard J, Williams R. 2000; The systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 32(4 Pt 1):734–739. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2000.17687. PMID: 11003617.
Article27. Wilkinson SP, Blendis LM, Williams R. 1974; Frequency and type of renal and electrolyte disorders in fulminant hepatic failure. Br Med J. 1:186–189. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.1.5900.186. PMID: 4811848. PMCID: PMC1633021.
Article28. Ring-Larsen H, Palazzo U. 1981; Renal failure in fulminant hepatic failure and terminal cirrhosis: a comparison between incidence, types, and prognosis. Gut. 22:585–591. DOI: 10.1136/gut.22.7.585. PMID: 7262632. PMCID: PMC1419318.
Article29. Rolando N, Harvey F, Brahm J, et al. 1990; Prospective study of bacterial infection in acute liver failure: an analysis of fifty patients. Hepatology. 11:49–53. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840110110. PMID: 2295471.
Article30. Rolando N, Philpott-Howard J, Williams R. 1996; Bacterial and fungal infection in acute liver failure. Semin Liver Dis. 16:389–402. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1007252. PMID: 9027952.
Article31. Schiødt FV, Balko J, Schilsky M, Harrison ME, Thornton A, Lee WM. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2003; Thrombopoietin in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 37:558–561. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50113. PMID: 12601353.
Article32. Lisman T, Stravitz RT. 2015; Rebalanced hemostasis in patients with acute liver failure. Semin Thromb Hemost. 41:468–473. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1550430. PMID: 26049071.
Article33. Harry R, Auzinger G, Wendon J. 2002; The clinical importance of adrenal insufficiency in acute hepatic dysfunction. Hepatology. 36:395–402. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2002.34514. PMID: 12143048.
Article34. Ede RJ, Moore KP, Marshall WJ, Williams R. 1988; Frequency of pancreatitis in fulminant hepatic failure using isoenzyme markers. Gut. 29:778–781. DOI: 10.1136/gut.29.6.778. PMID: 2454877. PMCID: PMC1433740.
Article35. Coté GA, Gottstein JH, Daud A, Blei AT. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2009; The role of etiology in the hyperamylasemia of acute liver failure. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:592–597. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2008.84. PMID: 19223884. PMCID: PMC3641762.
Article36. Wendon J, Cordoba J, Dhawan A, et al. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2017; EASL Clinical Practical Guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J Hepatol. 66:1047–1081. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.12.003. PMID: 28417882.
Article37. Jung DH, Hwang S, Lim YS, et al. Outcome comparison of liver transplantation for hepatitis A-related versus hepatitis B-related acute liver failure in adult recipients. Clin Transplant. 2018; 32:doi: 10.1111/ctr.13140. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13140. PMID: 29044729.
Article38. Koch DG, Speiser JL, Durkalski V, et al. 2017; The natural history of severe acute liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol. 112:1389–1396. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2017.98. PMID: 28440304. PMCID: PMC5587371.
Article39. Kim JD. Clinical handbook of hepatology. Paju: Koonja;2022. p. 78.40. Ganger DR, Rule J, Rakela J, et al. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2018; Acute liver failure of indeterminate etiology: a comprehensive systematic approach by an expert committee to establish causality. Am J Gastroenterol. 113:1319. DOI: 10.1038/s41395-018-0160-2. PMID: 29946176. PMCID: PMC9252260.
Article41. 2012. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury. [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases;Bethesda (MD): Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548225/?report=reader. cited 2022 Nov 21.42. Macdougall BR, Bailey RJ, Williams R. 1977; H2-receptor antagonists and antacids in the prevention of acute gastrointestinal haemorrhage in fulminant hepatic failure. Two controlled trials. Lancet. 1:617–619. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(77)92055-4. PMID: 66425.43. Senzolo M, Sartori MT, Lisman T. 2009; Should we give thromboprophylaxis to patients with liver cirrhosis and coagulopathy? HPB (Oxford). 11:459–464. DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00079.x. PMID: 19816608. PMCID: PMC2756631.
Article44. Muñoz SJ, Robinson M, Northrup B, et al. 1991; Elevated intracranial pressure and computed tomography of the brain in fulminant hepatocellular failure. Hepatology. 13:209–212. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840130202. PMID: 1995433.
Article45. Reynolds AS, Brush B, Schiano TD, Reilly KJ, Dangayach NS. 2019; Neurological monitoring in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 70:1830–1835. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30760. PMID: 31077591.
Article46. Bernal W, Wang Y, Maggs J, et al. 2016; Development and validation of a dynamic outcome prediction model for paracetamol-induced acute liver failure: a cohort study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:217–225. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30007-3. PMID: 28404094.
Article47. Krishnamoorthy V, Beckmann K, Mueller M, Sharma D, Vavilala MS. 2013; Perioperative estimation of the intracranial pressure using the optic nerve sheath diameter during liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 19:246–249. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23591. PMID: 23225529.
Article48. Das MC, ivastava A Sr, Yadav RK, Yachha SK, Poddar U. 2020; Optic nerve sheath diameter in children with acute liver failure: a prospective observational pilot study. Liver Int. 40:428–436. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14259. PMID: 31549476.
Article49. Cardoso FS, Pereira R, Moreno R, Karvellas CJ, Germano N. 2021; Optic nerve sheath diameter in acute liver failure: a prospective cohort study. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 28:170–178. DOI: 10.1159/000511646. PMID: 34056039. PMCID: PMC8138150.
Article50. Kawakami M, Koda M, Murawaki Y. 2010; Cerebral pulsatility index by transcranial Doppler sonography predicts the prognosis of patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Clin Imaging. 34:327–331. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2009.09.006. PMID: 20813293.
Article51. McNett M, Moran C, Janki C, Gianakis A. 2017; Correlations between hourly pupillometer readings and intracranial pressure values. J Neurosci Nurs. 49:229–234. DOI: 10.1097/JNN.0000000000000290. PMID: 28661946.
Article52. Canalese J, Gimson AE, Davis C, Mellon PJ, Davis M, Williams R. 1982; Controlled trial of dexamethasone and mannitol for the cerebral oedema of fulminant hepatic failure. Gut. 23:625–629. DOI: 10.1136/gut.23.7.625. PMID: 6806155. PMCID: PMC1419771.
Article53. Murphy N, Auzinger G, Bernel W, Wendon J. 2004; The effect of hypertonic sodium chloride on intracranial pressure in patients with acute liver failure. Hepatology. 39:464–470. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20056. PMID: 14767999.
Article54. Jalan R, Olde Damink SW, Deutz NE, Hayes PC, Lee A. 2004; Moderate hypothermia in patients with acute liver failure and uncontrolled intracranial hypertension. Gastroenterology. 127:1338–1346. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.08.005. PMID: 15521003.
Article55. Bernal W, Murphy N, Brown S, et al. 2016; A multicentre randomized controlled trial of moderate hypothermia to prevent intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 65:273–279. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.03.003. PMID: 26980000.
Article56. Ribaud J, McLernon S, Auzinger G. 2022; Targeted temperature management in acute liver failure: a systematic review. Nurs Crit Care. 27:784–795. DOI: 10.1111/nicc.12524. PMID: 32602249.
Article57. Stravitz RT, Kramer DJ. 2009; Management of acute liver failure. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:542–553. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.127. PMID: 19652652.
Article58. Laffey JG, Kavanagh BP. 2002; Hypocapnia. N Engl J Med. 347:43–53. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra012457. PMID: 12097540.
Article59. Ellis A, Wendon J. 1996; Circulatory, respiratory, cerebral, and renal derangements in acute liver failure: pathophysiology and management. Semin Liver Dis. 16:379–388. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-1007251. PMID: 9027951.
Article60. Reid TD, Kratzke IM, Dayal D, et al. 2022; The role of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adult liver transplant patients: a qualitative systematic review of literature. Artif Organs. 46:578–596. DOI: 10.1111/aor.14120. PMID: 34816462.
Article61. Plauth M, Cabré E, Riggio O, et al. 2006; ESPEN guidelines on enteral nutrition: liver disease. Clin Nutr. 25:285–294. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2006.01.018. PMID: 16707194.
Article62. Moore JK, Love E, Craig DG, Hayes PC, Simpson KJ. 2013; Acute kidney injury in acute liver failure: a review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:701–712. DOI: 10.1586/17474124.2013.837264. PMID: 24134153.
Article63. Kramer AH, Roberts DJ, Zygun DA. 2012; Optimal glycemic control in neurocritical care patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Crit Care. 16:R203. DOI: 10.1186/cc11812. PMID: 23082798. PMCID: PMC3682305.
Article64. Cardoso FS, Gottfried M, Tujios S, Olson JC, Karvellas CJ. US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2018; Continuous renal replacement therapy is associated with reduced serum ammonia levels and mortality in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 67:711–720. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29488. PMID: 28859230. PMCID: PMC5832542.
Article65. Broussard CN, Aggarwal A, Lacey SR, et al. 2001; Mushroom poisoning--from diarrhea to liver transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol. 96:3195–3198. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9270(01)03845-X. PMID: 11721773.
Article66. Harrison PM, Keays R, Bray GP, Alexander GJ, Williams R. 1990; Improved outcome of paracetamol-induced fulminant hepatic failure by late administration of acetylcysteine. Lancet. 335:1572–1573. DOI: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91388-Q. PMID: 1972496.
Article67. Keays R, Harrison PM, Wendon JA, et al. 1991; Intravenous acetylcysteine in paracetamol induced fulminant hepatic failure: a prospective controlled trial. BMJ. 303:1026–1029. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.303.6809.1026. PMID: 1954453. PMCID: PMC1671790.
Article68. Bunchorntavakul C, Reddy KR. 2018; Acetaminophen (APAP or N-acetyl-p-aminophenol) and acute liver failure. Clin Liver Dis. 22:325–346. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2018.01.007. PMID: 29605069.
Article69. Siu JT, Nguyen T, Turgeon RD. 2020; N-acetylcysteine for non-paracetamol (acetaminophen)-related acute liver failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12:CD012123. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012123.pub2. PMID: 33294991. PMCID: PMC8095024.
Article70. Aljohani W, Chan BPH, Yaghoobi M. 2020; Role of N-Acetylcysteine in the treatment of acute nonacetaminophen, nonalcoholic and nonviral hepatitis: a meta-analysis. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 4:125–130. DOI: 10.1093/jcag/gwaa017. PMID: 34056530. PMCID: PMC8158650.
Article71. Shrestha DB, Budhathoki P, Sedhai YR, et al. 2021; N-acetyl cysteine versus standard of care for non-acetaminophen induced acute liver injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hepatol. 24:100340. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100340. PMID: 33722689.
Article72. Reuben A, Tillman H, Fontana RJ, et al. Outcomes in adults with acute liver failure between 1998 and 2013: an observational cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2016; 164:724–732. DOI: 10.7326/M15-2211. PMID: 27043883. PMCID: PMC5526039.
Article73. O'Grady J. 2014; Timing and benefit of liver transplantation in acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 60:663–670. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.024. PMID: 24211740.74. Olivo R, Guarrera JV, Pyrsopoulos NT. 2018; Liver transplantation for acute liver failure. Clin Liver Dis. 22:409–417. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2018.01.014. PMID: 29605075.
Article75. Pan JJ, Fontana RJ. 2022; CAQ corner: acute liver failure management and liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 28:1664–1673. DOI: 10.1002/lt.26503. PMID: 35574981. PMCID: PMC9796044.
Article76. Joo DJ. 2021; [Current status of deceased donor liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease in Korea in MELD era]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 77:4–11. Korean. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2020.167. PMID: 33495428.
Article77. Fontana RJ, Ellerbe C, Durkalski VE, et al. US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2015; Two-year outcomes in initial survivors with acute liver failure: results from a prospective, multicentre study. Liver Int. 35:370–380. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12632. PMID: 25039930. PMCID: PMC4291312.
Article78. Reddy KR, Ellerbe C, Schilsky M, et al. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2016; Determinants of outcome among patients with acute liver failure listed for liver transplantation in the United States. Liver Transpl. 22:505–515. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24347. PMID: 26421889. PMCID: PMC4809785.
Article79. Acharya SK, Bhatia V, eenivas V Sr, Khanal S, Panda SK. 2009; Efficacy of L-ornithine L-aspartate in acute liver failure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology. 136:2159–2168. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.050. PMID: 19505424.
Article80. Stravitz RT, Gottfried M, Durkalski V, et al. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2018; Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of l-ornithine phenylacetate in patients with acute liver injury/failure and hyperammonemia. Hepatology. 67:1003–1013. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29621. PMID: 29080224. PMCID: PMC5826861.
Article81. Larsen FS, Schmidt LE, Bernsmeier C, et al. 2016; High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: an open randomised controlled trial. J Hepatol. 64:69–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.018. PMID: 26325537.
Article82. Padmanabhan A, Connelly-Smith L, Aqui N, et al. 2019; Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice - evidence-based approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: the eighth special issue. J Clin Apher. 34:171–354. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21705. PMID: 31180581.
Article83. Kim JE, Chun S, Sinn DH, et al. 2021; Initial experience with high-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure. J Clin Apher. 36:379–389. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21873. PMID: 33400840.
Article84. Stahl K, Hadem J, Schneider A, et al. 2019; Therapeutic plasma exchange in acute liver failure. J Clin Apher. 34:589–597. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21737. PMID: 31348553.
Article85. Maiwall R, Bajpai M, Singh A, et al. 2022; Standard-volume plasma exchange improves outcomes in patients with acute liver failure: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:e831–e854. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.036. PMID: 33524593.
Article86. Karvellas CJ, Subramanian RM. 2016; Current evidence for extracorporeal liver support systems in acute liver failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Crit Care Clin. 32:439–451. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2016.03.003. PMID: 27339682.
Article87. Kanjo A, Ocskay K, Gede N, et al. 2021; Efficacy and safety of liver support devices in acute and hyperacute liver failure: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 11:4189. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83292-z. PMID: 33602961. PMCID: PMC7893063.
Article88. MacDonald AJ, Subramanian RM, Olson JC, et al. U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2022; Use of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system in acute liver failure: results of a multicenter propensity score-matched study. Crit Care Med. 50:286–295. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005194. PMID: 34259656.
Article89. Flamm SL, Yang YX, Singh S, Falck-Ytter YT. AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. 2017; American Gastroenterological Association Institute guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute liver failure. Gastroenterology. 152:644–647. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.026. PMID: 28056348.
Article90. Ellis AJ, Hughes RD, Wendon JA, et al. 1996; Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 24:1446–1451. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510240625. PMID: 8938179.
Article91. Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, et al. 2004; Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 239:660–670. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000124298.74199.e5. PMID: 15082970. PMCID: PMC1356274.
Article92. Wong NZ, Reddy KR, Bittermann T. 2022; Acute liver failure etiology is an independent predictor of waitlist outcome but not posttransplantation survival in a national cohort. Liver Transpl. 28:39–50. DOI: 10.1002/lt.26187. PMID: 34081838. PMCID: PMC8639833.
Article93. O'Grady JG, Alexander GJ, Hayllar KM, Williams R. 1989; Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 97:439–445. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90081-4. PMID: 2490426.94. Koch DG, Tillman H, Durkalski V, Lee WM, Reuben A. 2016; Development of a model to predict transplant-free survival of patients with acute liver failure. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:1199–1206.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.03.046. PMID: 27085756. PMCID: PMC6055510.95. Stravitz RT, Ellerbe C, Durkalski V, Reuben A, Lisman T, Lee WM. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2016; Thrombocytopenia is associated with multi-organ system failure in patients with acute liver failure. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:613–620.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.029. PMID: 26453953. PMCID: PMC5733710.
Article96. Leithead JA, Ferguson JW, Bates CM, et al. 2009; The systemic inflammatory response syndrome is predictive of renal dysfunction in patients with non-paracetamol-induced acute liver failure. Gut. 58:443–449. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2008.154120. PMID: 19001057.
Article97. Craig DG, Reid TW, Wright EC, et al. 2012; The sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score is prognostically superior to the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and MELD variants following paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 35:705–713. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.04996.x. PMID: 22260637.
Article98. Bernuau J, Samuel D, Durand F, et al. 1991; Criteria for emergency liver transplantation in patients with acute viral hepatitis and factor V below 50% of normal: a prospective study. Hepatology. 14:49A.99. Bernal W, Donaldson N, Wyncoll D, Wendon J. 2002; Blood lactate as an early predictor of outcome in paracetamol-induced acute liver failure: a cohort study. Lancet. 359:558–563. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07743-7. PMID: 11867109.
Article100. Schmidt LE, Dalhoff K. 2002; Serum phosphate is an early predictor of outcome in severe acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology. 36:659–665. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2002.35069. PMID: 12198658.
Article101. Schiødt FV, Ostapowicz G, Murray N, et al. 2006; Alpha-fetoprotein and prognosis in acute liver failure. Liver Transpl. 12:1776–1781. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20886. PMID: 17133565.
Article102. Wang J, Liu PH, Xu P, et al. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2022; Hypochloremia as a novel adverse prognostic factor in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 42:2781–2790. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15449. PMID: 36203349.
Article103. Karvellas CJ, Speiser JL, Tremblay M, Lee WM, Rose CF. US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2017; Elevated FABP1 serum levels are associated with poorer survival in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Hepatology. 65:938–949. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28945. PMID: 27859489. PMCID: PMC5319885.
Article104. Tavabie OD, Karvellas CJ, Salehi S, et al. United States Acute Liver Failure Study Group. 2021; A novel microRNA-based prognostic model outperforms standard prognostic models in patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 75:424–434. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.013. PMID: 33857547.
Article105. Zabron A, Quaglia A, Fatourou E, et al. 2018; Clinical and prognostic associations of liver volume determined by computed tomography in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 38:1592–1601. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13725. PMID: 29461676.
Article106. Kuroda H, Abe T, Fujiwara Y, et al. 2021; Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography-based hepatic perfusion for early prediction of prognosis in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 73:2455–2467. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31615. PMID: 33151580. PMCID: PMC8252126.
Article107. Dechêne A, Sowa JP, Schlattjan M, et al. 2014; Mini-laparoscopy guided liver biopsy increases diagnostic accuracy in acute liver failure. Digestion. 90:240–247. DOI: 10.1159/000366517. PMID: 25531058.
Article108. Donaldson BW, Gopinath R, Wanless IR, et al. 1993; The role of transjugular liver biopsy in fulminant liver failure: relation to other prognostic indicators. Hepatology. 18:1370–1376. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840180614. PMID: 8244261.
Article109. Schmidt LE, Larsen FS. 2007; MELD score as a predictor of liver failure and death in patients with acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 45:789–796. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21503. PMID: 17326205.
Article110. Liver Advisory Group NHS Blood and Transplant. Liver transplantation: selection criteria and recipient registration. [Internet]. Bristol: Liver Advisory Group NHS Blood and Transplant;2018. cited 2022 Dec 10. Available from: https://nhsbtdbe.blob.core.windows.net/umbraco-assets-corp/9440/pol195_7-liver-selection-policy.pdf.111. Jayalakshmi VT, Bernal W. 2020; Update on the management of acute liver failure. Curr Opin Crit Care. 26:163–170. DOI: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000697. PMID: 32068578.
Article112. Kumar R, Shalimar , Sharma H, et al. 2012; Prospective derivation and validation of early dynamic model for predicting outcome in patients with acute liver failure. Gut. 61:1068–1075. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301762. PMID: 22337947.
Article113. Kim JD, Cho EJ, Ahn C, et al. 2019; A model to predict 1-month risk of transplant or death in hepatitis a-related acute liver failure. Hepatology. 70:621–629. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30262. PMID: 30194739.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corrigendum: Acute Liver Failure: Current Updates and Management
- Acute liver failure in children
- The Difference of the Clinical Patterns between Acute Liver Failure and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
- Indications for Liver Transplantation in Acute Liver Failure
- Understanding Acute Liver Failure: A Basic Overview of Definition and Treatment