Lab Med Online.
2022 Jan;12(1):58-62. 10.47429/lmo.2022.12.1.58.
Identification of a de novo ANK1 Variant in a Patient with Hereditary Spherocytosis on Multi-gene Panel Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Departments of Pediatrics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2538585
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2022.12.1.58
Abstract
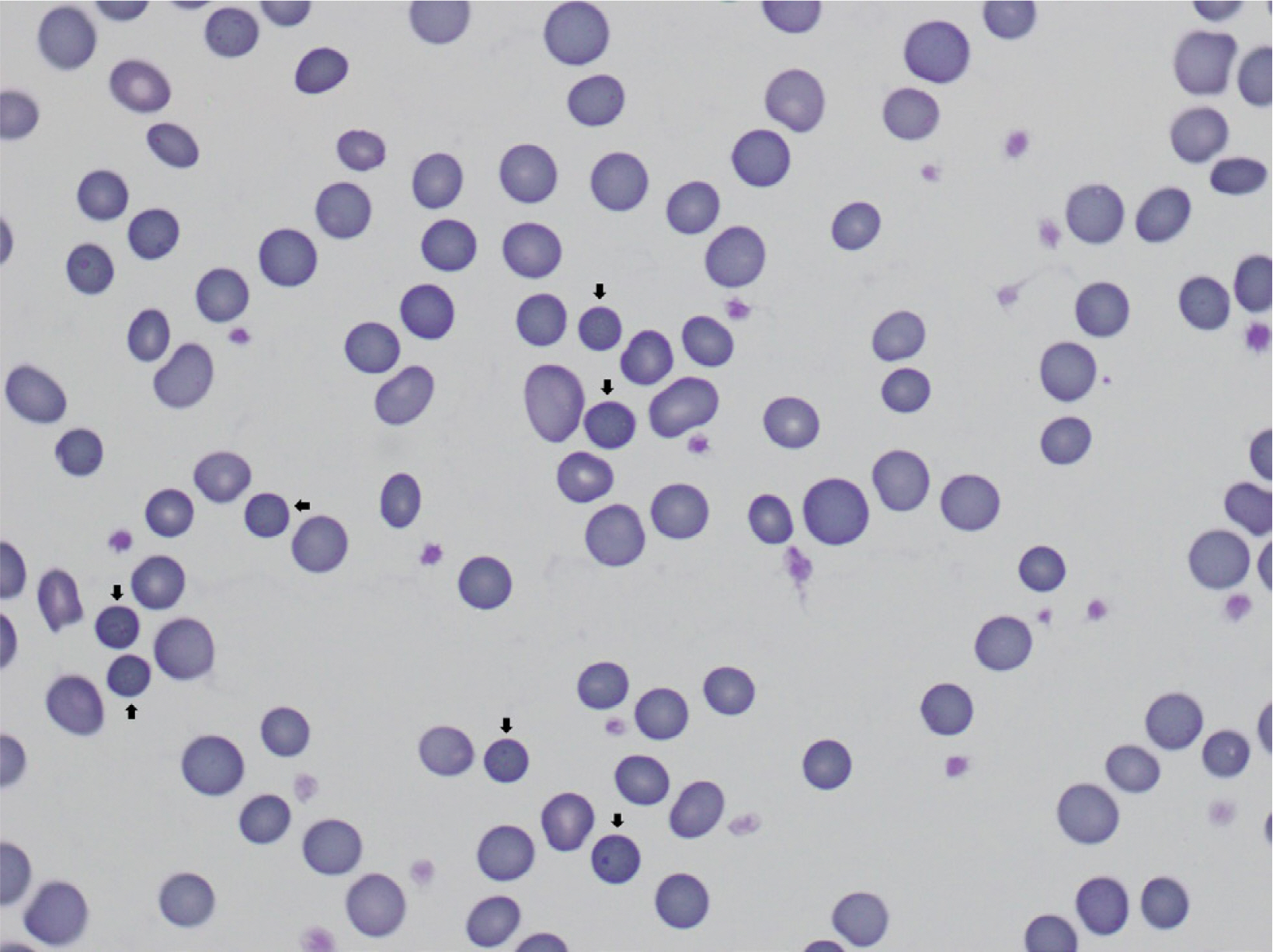
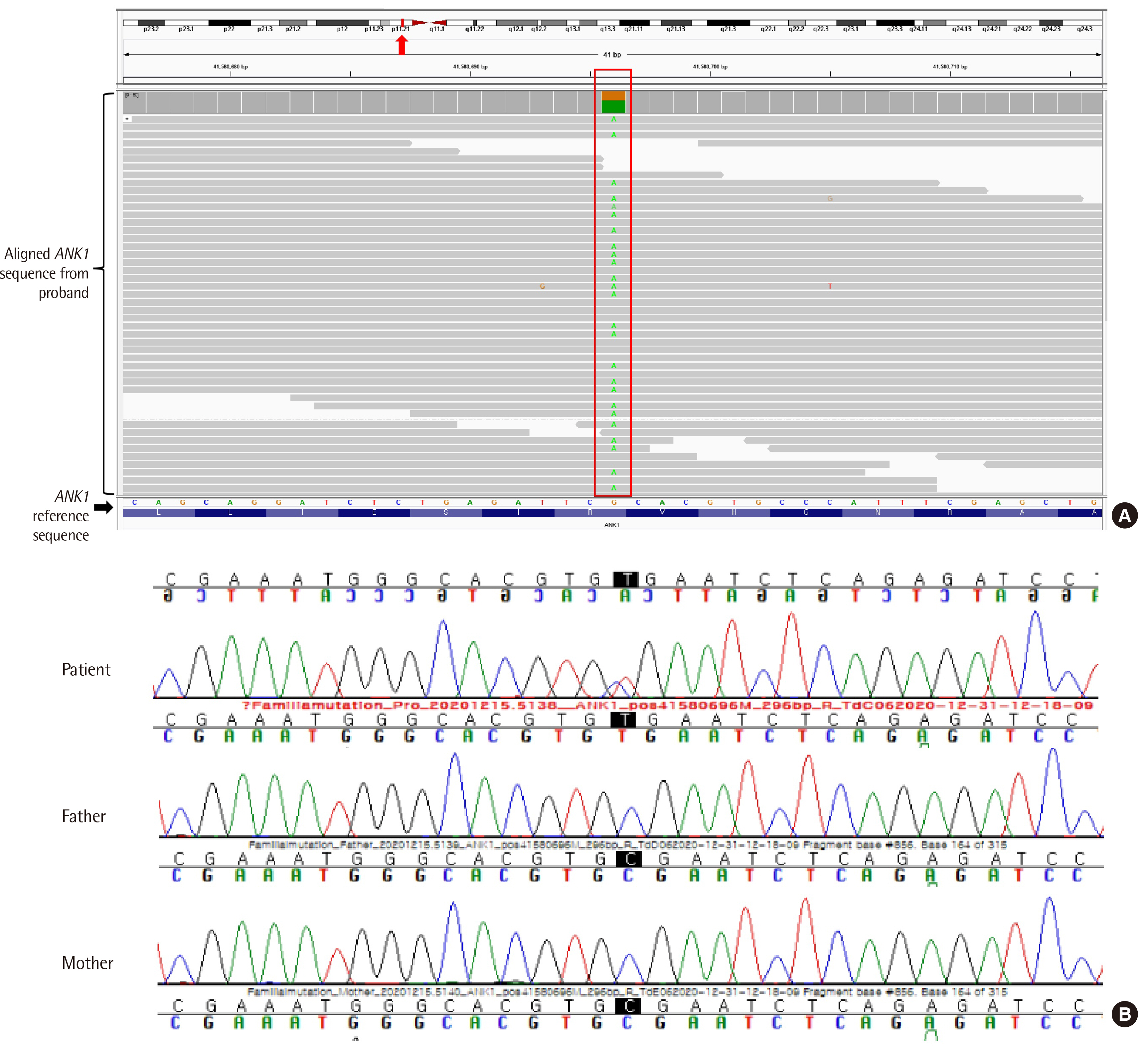
- Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is caused by defects in red blood cell membrane components encoded by SPTA1, SPTB, ANK1, SLC4A1, and EPB42. The low sensitivity and specificity of conventional tests such as peripheral blood smear and osmotic fragility test (OFT) limit the diagnosis of HS, especially in patients with mild phenotypes and no family history of the condition. Mutations in ANK1, which encodes ankyrin-1 protein, are present in more than half of HS cases and is known as the most common cause of HS in Korea. Mutations in ANK1 are mostly inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Here, we report the case of a Korean patient with HS carrying a de novo mutation in ANK1. The patient was suspected of having HS due to neonatal jaundice and clinical manifestations of hemolysis, but the OFT results were unclear. At the age of 20, the patient was definitively diagnosed with HS, caused by a de novo heterozygous ANK1 variant c.856C>T (p.Arg286*), using next-generation sequencing-based multi-gene panel testing and Sanger sequencing analysis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi HS, Choi Q, Kim JA, Im KO, Park SN, Park Y, et al. 2019; Molecular diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis by multi-gene target sequencing in Korea: matching with osmotic fragility test and presence of spherocyte. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 14:114. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1070-0. PMID: 31122244. PMCID: PMC6533652.
Article2. Delaunay J. 2002; Molecular basis of red cell membrane disorders. Acta Haematol. 108:210–8. DOI: 10.1159/000065657. PMID: 12432217.
Article3. Park J, Jeong DC, Yoo J, Jang W, Chae H, Kim J, et al. 2016; Mutational characteristics of ANK1 and SPTB genes in hereditary spherocytosis. Clin Genet. 90:69–78. DOI: 10.1111/cge.12749. PMID: 26830532.4. Tateno Y, Suzuki R, Kitamura Y. 2016; Previously undiagnosed hereditary spherocytosis in a patient with jaundice and pyelonephritis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 10:337. DOI: 10.1186/s13256-016-1144-8. PMID: 27906107. PMCID: PMC5134285.
Article5. Ma S, Deng X, Liao L, Deng Z, Qiu Y, Wei H, et al. 2018; Analysis of the causes of the misdiagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis. Oncol Rep. 40:1451–8. DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6578. PMID: 30015979.
Article6. Bianchi P, Fermo E, Vercellati C, Marcello AP, Porretti L, Cortelezzi A, et al. 2012; Diagnostic power of laboratory tests for hereditary spherocytosis: a comparison study in 150 patients grouped according to molecular and clinical characteristics. Haematologica. 97:516–23. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.052845. PMID: 22058213. PMCID: PMC3347664.
Article7. Kwon JA, Kim Y, Park G, Kim J, Cho YU, Huh J, et al. 2019; Recommendation for the peripheral blood cell morphology report. Lab Med Online. 9:115–25. DOI: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.115.
Article8. McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. 2010; The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 20:1297–303. DOI: 10.1101/gr.107524.110. PMID: 20644199. PMCID: PMC2928508.
Article9. Liu X, Wu C, Li C, Boerwinkle E. 2016; dbNSFP v3.0: A one-stop database of functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Hum Mutat. 37:235–41. DOI: 10.1002/humu.22932. PMID: 26555599. PMCID: PMC4752381.
Article10. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. 2015; Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Gene-tics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–24. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. PMID: 25741868. PMCID: PMC4544753.
Article11. Da Costa L, Galimand J, Fenneteau O, Mohandas N. 2013; Hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis, and other red cell membrane disorders. Blood Rev. 27:167–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.blre.2013.04.003. PMID: 23664421.
Article12. Andolfo I, Russo R, Gambale A, Iolascon A. 2016; New insights on hereditary erythrocyte membrane defects. Haematologica. 101:1284–94. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.142463. PMID: 27756835. PMCID: PMC5394881.
Article13. Steward SC, Chauvenet AR, O'Suoji C. 2014; Hereditary spherocytosis: Consequences of delayed diagnosis. SAGE Open Med. 2:2050312114547093. DOI: 10.1177/2050312114547093. PMID: 26770738. PMCID: PMC4607200.
Article14. Mariani M, Barcellini W, Vercellati C, Marcello AP, Fermo E, Pedotti P, et al. 2008; Clinical and hematologic features of 300 patients affected by hereditary spherocytosis grouped according to the type of the membrane protein defect. Haematologica. 93:1310–7. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.12546. PMID: 18641031.
Article15. Farias MG. 2017; Advances in laboratory diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 55:944–8. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0738. PMID: 27837594.
Article16. Miraglia del Giudice E, Nobili B, Francese M, D'Urso L, Iolascon A, Eber S, et al. 2001; Clinical and molecular evaluation of non-dominant hereditary spherocytosis. Br J Haematol. 112:42–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02501.x. PMID: 11167781.
Article17. Bolton-Maggs PH, Langer JC, Iolascon A, Tittensor P, King MJ. 2012; Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary spherocytosis-2011 update. Br J Haematol. 156:37–49. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08921.x. PMID: 22055020.18. Perrotta S, Gallagher PG, Mohandas N. 2008; Hereditary spherocytosis. Lancet. 372:1411–26. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61588-3. PMID: 18940465.
Article19. van Vuren A, van der Zwaag B, Huisjes R, Lak N, Bierings M, Gerritsen E, et al. 2019; The complexity of genotype-phenotype correlations in hereditary spherocytosis: A cohort of 95 patients: genotype-phenotype correlation in hereditary spherocytosis. Hemasphere. 3:e276. DOI: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000276. PMID: 31723846. PMCID: PMC6745925.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Validity of Next-Generation Sequencing Multi-Gene Panel Testing for Detecting Pathogenic Variants in Patients With Hereditary Breast-Ovarian Cancer Syndrome
- Hereditary Spherocytosis
- Serial CT Findings of Resolving Extramedullary Hematopoiesis as Unilateral Posterior Mediastinal Mass after Splenectomy in Hereditary Spherocytosis: A Case Report
- De novo HCN1 Mutation Identified by Next-Generation Sequencing in a Patient with Early Infantile Epileptic Encephalopathy: Case Report
- Identification of a Novel De Novo Variant in the PAX3 Gene in Waardenburg Syndrome by Diagnostic Exome Sequencing: The First Molecular Diagnosis in Korea