J Rheum Dis.
2023 Jan;30(1):58-64. 10.4078/jrd.22.0027.
Development of Spondyloarthritis After COVID-19 in HLAB27-Positive Monozygotic Twins: Case Reports With Single Cell Transcriptome Profiling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 3YiPSCELL, Inc., Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2537496
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.22.0027
Abstract
- A subset of spondyloarthritis (SpA) called ‘reactive arthritis’ is triggered by causal pathogens, usually bacteria related to venereal disease or gastrointestinal infection. During the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), there have been case reports about SpA after COVID-19, but the causality is still elusive. We described cases of 23-year-old monozygotic twins both diagnosed with SpA after COVID-19. The probable linkage between SpA and COVID-19 was elaborated with our cases as well as literature reviews. Of note, shared genetic traits by monozygotic twins, particularly HLA-B27 positivity, might have contributed to their susceptibility to COVID-19-induced SpA. Moreover, single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed that the transcriptomic profile of peripheral compartment of SpA after COVID-19 was distinctive from that of typical radiographic axial SpA as shown by differential expression of ribosomal protein S26 (RPS26) and small nucleolar RNA host gene 5 (SNHG5) in nearly all subsets of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
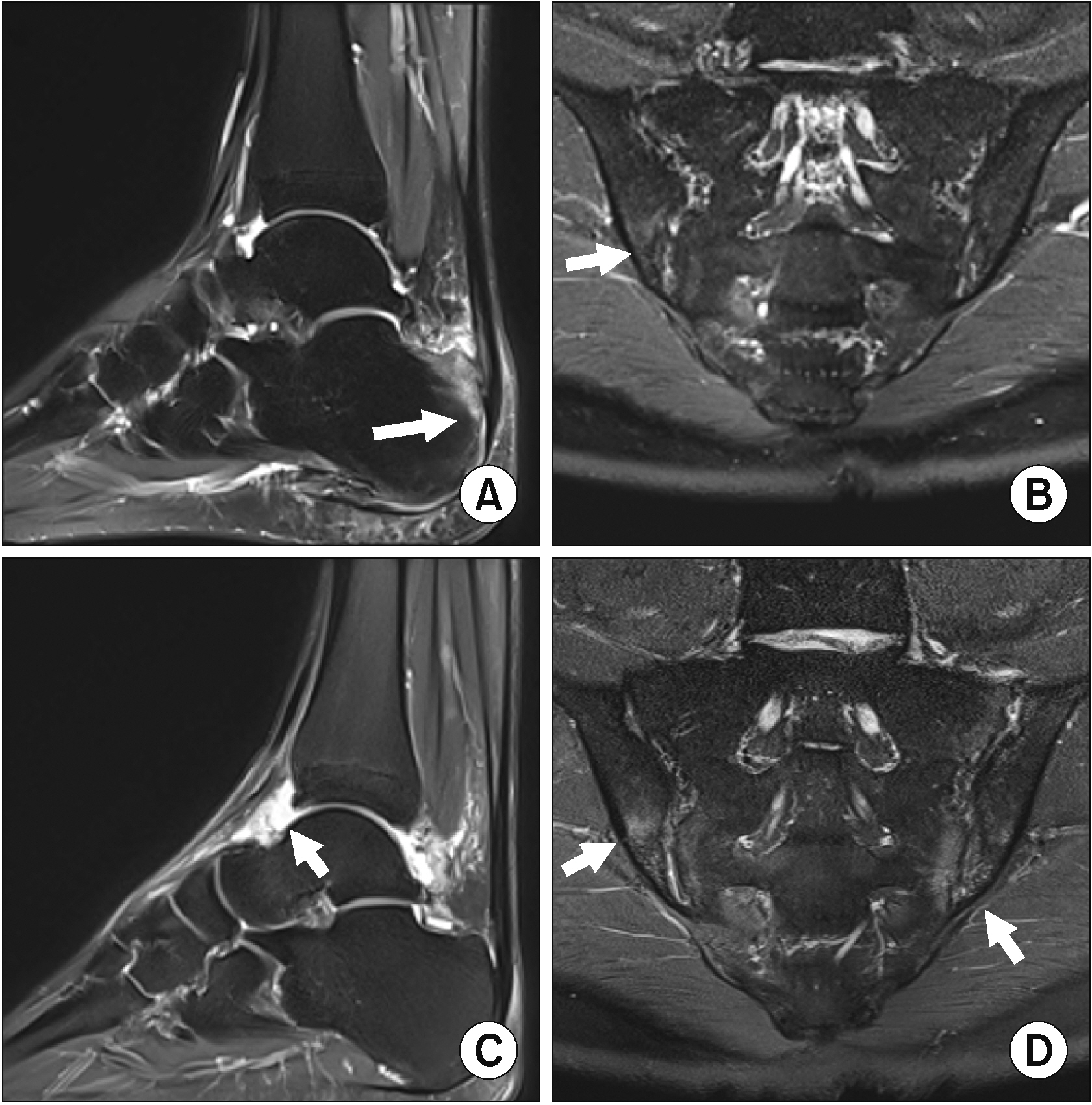
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chams N, Chams S, Badran R, Shams A, Araji A, Raad M, et al. 2020; COVID-19: a multidisciplinary review. Front Public Health. 8:383. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00383. PMID: 32850602. PMCID: PMC7403483.2. Ciaffi J, Meliconi R, Ruscitti P, Berardicurti O, Giacomelli R, Ursini F. 2020; Rheumatic manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Rheumatol. 4:65. DOI: 10.1186/s41927-020-00165-0. PMID: 33123675. PMCID: PMC7591274.3. El Hasbani G, Jawad A, Uthman I. 2021; Axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis triggered by sars-cov-2 infection: a report of two cases. Reumatismo. 73:59–63. DOI: 10.4081/reumatismo.2021.1374. PMID: 33874649.4. Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E, Satija R. 2018; Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol. 36:411–20. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.4096. PMID: 29608179. PMCID: PMC6700744.5. Schenker HM, Hagen M, Simon D, Schett G, Manger B. 2021; Reactive arthritis and cutaneous vasculitis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:479–80. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa689. PMID: 33206974. PMCID: PMC7717428.6. Novelli L, Motta F, Ceribelli A, Guidelli GM, Luciano N, Isailovic N, et al. 2021; A case of psoriatic arthritis triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:e21–3. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa691. PMID: 33206980. PMCID: PMC7717387.7. Coath FL, Mackay J, Gaffney JK. 2021; Axial presentation of reactive arthritis secondary to COVID-19 infection. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:e232–3. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab009. PMID: 33471106. PMCID: PMC7928576.8. Saikali W, Gharib S. 2021; The first non-radiographic axial spondyloarthrits with COVID-19. Immun Inflamm Dis. 9:628–31. DOI: 10.1002/iid3.448. PMID: 33979033. PMCID: PMC8239938.9. Ciaffi J, Mancarella L, Borlandelli E, Facchini G, Meliconi R, Ursini F. 2021; May polyenthesitis follow COVID-19? Joint Bone Spine. 88:105158. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2021.105158. PMID: 33561535. PMCID: PMC8080433.10. De Stefano L, Rossi S, Montecucco C, Bugatti S. 2020; Aug. 4. Transient monoarthritis and psoriatic skin lesions following COVID-19. Ann Rheum Dis. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218520. PMID: 32753423.11. Bentaleb I, Abdelghani KB, Rostom S, Amine B, Laatar A, Bahiri R. 2020; Reactive arthritis: update. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 7:124–32. DOI: 10.1007/s40588-020-00152-6. PMID: 33014690. PMCID: PMC7519381.12. Ferretti MB, Ghalei H, Ward EA, Potts EL, Karbstein K. 2017; Rps26 directs mRNA-specific translation by recognition of Kozak sequence elements. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 24:700–7. DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3442. PMID: 28759050. PMCID: PMC5777333.13. Doherty L, Sheen MR, Vlachos A, Choesmel V, O'Donohue MF, Clinton C, et al. 2010; Ribosomal protein genes RPS10 and RPS26 are commonly mutated in Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Am J Hum Genet. 86:222–8. Erratum. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.12.015. PMID: 20116044. PMCID: PMC2820177.14. Kasela S, Kisand K, Tserel L, Kaleviste E, Remm A, Fischer K, et al. 2017; Pathogenic implications for autoimmune mechanisms derived by comparative eQTL analysis of CD4+ versus CD8+ T cells. PLoS Genet. 13:e1006643. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006643. PMID: 28248954. PMCID: PMC5352142.15. Han W, Shi J, Cao J, Dong B, Guan W. 2020; Latest advances of long non-coding RNA SNHG5 in human cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 13:6393–403. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S252750. PMID: 32753882. PMCID: PMC7342554.