Ann Surg Treat Res.
2022 Nov;103(5):280-289. 10.4174/astr.2022.103.5.280.
Comparing efficacies of different treatment regimens in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus using network meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Catholic Kwandong University International St. Mary’s Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2534851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2022.103.5.280
Abstract
- Purpose
Although various treatment regimens have been introduced for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT), comprehensive and direct comparisons between them are limited. Thus, the purpose of this study was to perform a network meta-analysis (NMA) to compare the efficacies of different treatment regimens for HCC accompanied by PVTT.
Methods
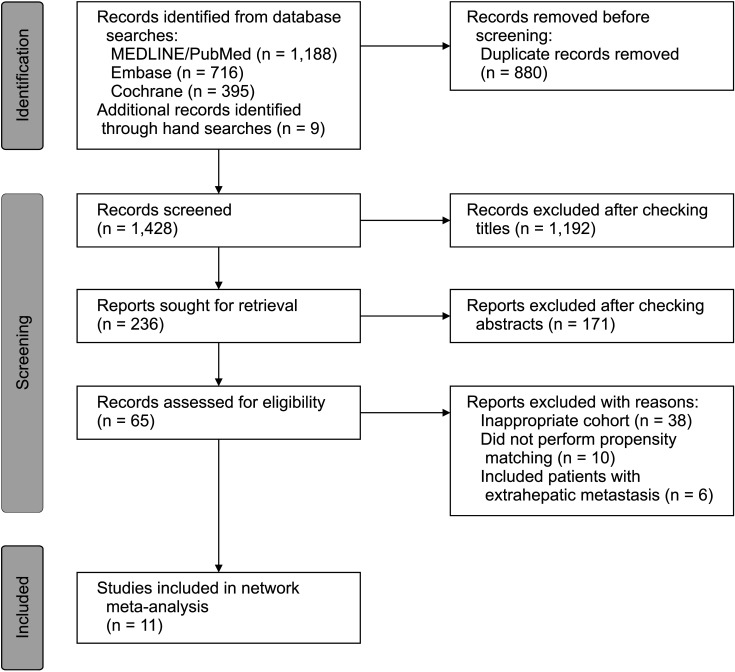
A systematic review was conducted to identify studies comparing 2 or more treatment regimens for HCC accompanied by PVTT without extrahepatic metastasis and reporting each overall survival (OS). Endpoints of this NMA were to hazard ratios with confidential intervals for OS and mean survival time difference of each treatment regimen comparison using a random-effects model. Each treatment regimen was then ranked using the P-score to assess the probability of the superiority of each one.
Results
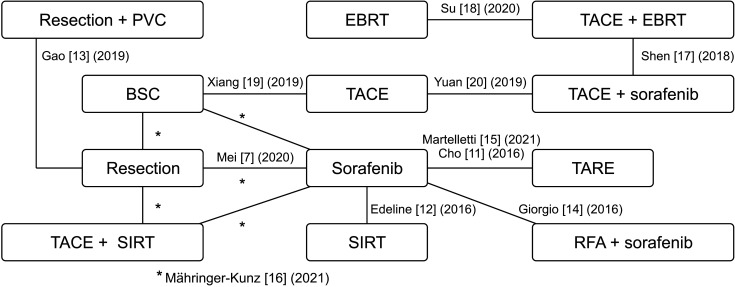
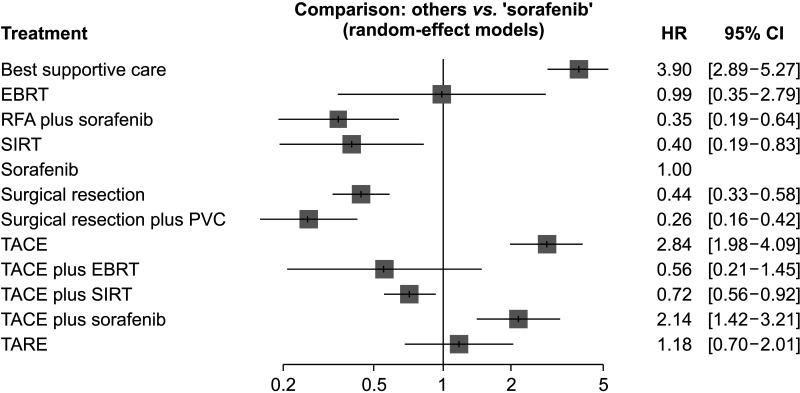
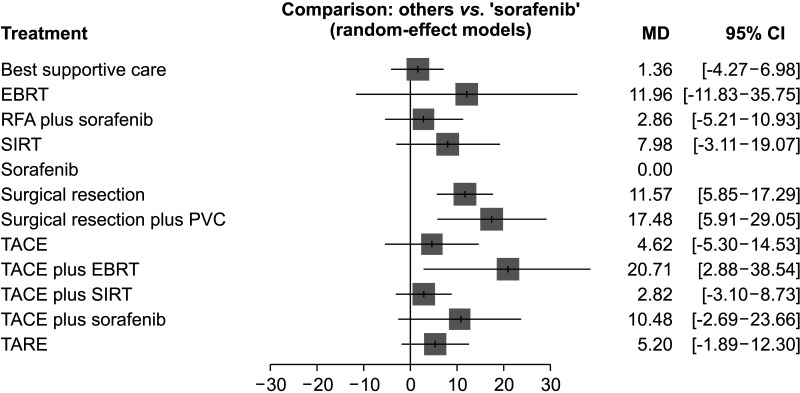
Eleven studies involving 1,623 patients that yielded 16 comparisons were identified and enrolled in this NMA. There were 12 different treatment regimens as comparators, including sorafenib therapy alone (reference treatment). The NMA suggested that the following 4 treatment regimens improved OS compared to sorafenib: surgical resection followed by portal vein chemotherapy (SR plus PVC), SR, radiofrequency ablation plus sorafenib, and transarterial chemoembolization combined with selective internal radiation therapy. SR plus PVC was ranked the best treatment regimen for OS (P-score, 93.9%).
Conclusion
Comparative efficacy based on this NMA may help clinicians select treatment for HCC accompanied by PVTT. If amenable, aggressive locoregional treatment regimens such as SR plus PVC should be considered for HCC accompanied by PVTT.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Prognostic significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression on immune cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Hae Il Jung, Hyein Ahn, Mee-Hye Oh, JongHyuk Yun, Hyunyong Lee, Sang Ho Bae, Yung Kil Kim, Sung Yong Kim, Moo-Jun Baek, Moon-Soo Lee
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2023;105(5):297-309. doi: 10.4174/astr.2023.105.5.297.Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):102-112. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2024.01.31.
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424. PMID: 30207593.
Article2. Hong SK, Lee KW, Lee S, Hong SY, Suh S, Han ES, et al. Impact of tumor size on hepatectomy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide propensity score matching analysis. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022; 102:193–204. PMID: 35475226.
Article3. Kim JM, Rhu J, Ha SY, Choi GS, Kwon CH, Kim G, et al. Realization of improved outcomes following liver resection in hepatocellular carcinoma patients aged 75 years and older. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2021; 101:257–265. PMID: 34796141.
Article4. Costentin CE, Ferrone CR, Arellano RS, Ganguli S, Hong TS, Zhu AX. Hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: defining the optimal treatment strategy. Liver Cancer. 2017; 6:360–374. PMID: 29234639.
Article5. Cerrito L, Annicchiarico BE, Iezzi R, Gasbarrini A, Pompili M, Ponziani FR. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis: beyond the known frontiers. World J Gastroenterol. 2019; 25:4360–4382. PMID: 31496618.
Article6. Qadan M, Kothary N, Sangro B, Palta M. The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2020; 40:1–8.
Article7. Mei J, Li SH, Wang QX, Lu LH, Ling YH, Zou JW, et al. Resection vs. sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: a real world, propensity score matched analytic study. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:573. PMID: 32432036.
Article8. Jang JY, Lee JS, Kim HJ, Shim JJ, Kim JH, Kim BH, et al. The general rules for the study of primary liver cancer. J Liver Cancer. 2017; 17:19–44.
Article9. Guyot P, Ades AE, Ouwens MJ, Welton NJ. Enhanced secondary analysis of survival data: reconstructing the data from published Kaplan-Meier survival curves. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012; 12:9. PMID: 22297116.
Article10. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560. PMID: 12958120.
Article11. Cho YY, Lee M, Kim HC, Chung JW, Kim YH, Gwak GY, et al. Radioembolization is a safe and effective treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: a propensity score analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0154986. PMID: 27149067.
Article12. Edeline J, Crouzet L, Campillo-Gimenez B, Rolland Y, Pracht M, Guillygomarc’h A, et al. Selective internal radiation therapy compared with sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016; 43:635–643. PMID: 26455499.
Article13. Gao Y, Wang PX, Cheng JW, Sun YF, Hu B, Guo W, et al. Chemotherapeutic perfusion of portal vein after tumor thrombectomy and hepatectomy benefits patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score-matched survival analysis. Cancer Med. 2019; 8:6933–6944. PMID: 31566899.
Article14. Giorgio A, Merola MG, Montesarchio L, Merola F, Santoro B, Coppola C, et al. Sorafenib combined with radio-frequency ablation compared with sorafenib alone in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma invading portal vein: a Western randomized controlled trial. Anticancer Res. 2016; 36:6179–6183. PMID: 27793949.
Article15. Martelletti C, Ricotti A, Gesualdo M, Carucci P, Gaia S, Rolle E, et al. Radioembolization vs sorafenib in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a propensity score and Bayesian analysis. J Dig Dis. 2021; 22:496–502. PMID: 34189839.
Article16. Mähringer-Kunz A, Steinle V, Kloeckner R, Schotten S, Hahn F, Schmidtmann I, et al. The impact of portal vein tumor thrombosis on survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with different therapies: a cohort study. PLoS One. 2021; 16:e0249426. PMID: 33961627.
Article17. Shen L, Xi M, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang X, Huang Z, et al. Combination therapy after TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: stereotactic body radiotherapy versus sorafenib. Cancers (Basel). 2018; 10:516.
Article18. Su TS, Li LQ, Meng WW, Wang YD, Chen YT, Li JX, et al. Long-term survival analysis of transarterial chemoembolization plus radiotherapy vs. radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:1205. PMID: 32850352.
Article19. Xiang X, Lau WY, Wu ZY, Zhao C, Ma YL, Xiang BD, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization versus best supportive care for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus : a multicenter study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019; 45:1460–1467. PMID: 31005471.
Article20. Yuan J, Yin X, Tang B, Ma H, Zhang L, Li L, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with sorafenib in t reatment of HBV background hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a propensity score matching study. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:2141859. PMID: 31467872.21. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: the 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022; 76:681–693. PMID: 34801630.
Article22. Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018; 68:723–750. PMID: 29624699.
Article23. Vilgrain V, Pereira H, Assenat E, Guiu B, Ilonca AD, Pageaux GP, et al. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:1624–1636. PMID: 29107679.24. Ye JZ, Wang YY, Bai T, Chen J, Xiang BD, Wu FX, et al. Surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus in the Asia-Pacific region beyond the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer treatment algorithms: a review and update. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:93258–93278. PMID: 29190996.
Article25. Zhang YF, Le Y, Wei W, Zou RH, Wang JH, OuYang HY, et al. Optimal surgical strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a propensity score analysis. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:38845–38856. PMID: 27072577.
Article26. Peng BG, He Q, Li JP, Zhou F. Adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization improves efficacy of hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus. Am J Surg. 2009; 198:313–318. PMID: 19285298.
Article27. Sun J, Yang L, Shi J, Liu C, Zhang X, Chai Z, et al. Postoperative adjuvant IMRT for patients with HCC and portal vein tumor thrombus: an open-label randomized controlled trial. Radiother Oncol. 2019; 140:20–25. PMID: 31176205.
Article28. Zhang X, Wang K, Wang M, Yang G, Ye X, Wu M, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with sorafenib versus TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:29416–29427. PMID: 28177886.
Article29. Nakazawa T, Hidaka H, Shibuya A, Okuwaki Y, Tanaka Y, Takada J, et al. Overall survival in response to sorafenib versus radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein tumor thrombosis: propensity score analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:84. PMID: 24886354.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic Resection in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Accompanied by Portal Vein Thrombus
- 3 Cases of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Cirrhosis Treated with Anticoagulation
- Sonographic features of portal vein thrombosis
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the Portal Vein
- Clinical features of portal vein thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma