J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Oct;37(43):e310. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e310.
Real-World Accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Diagnostic Tests in the Republic of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2534824
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e310
Abstract
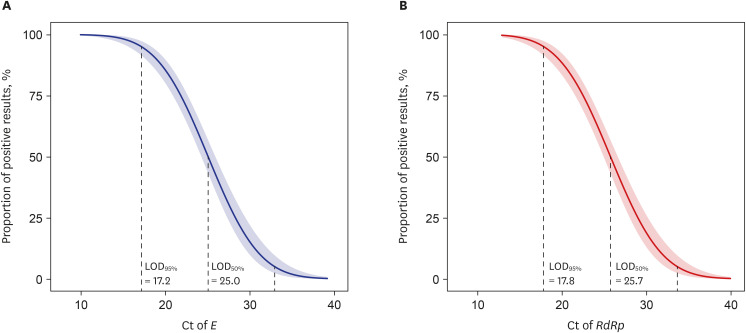
- Antigen rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) became the most important tool for the diagnosis of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), however there have been very few evaluations of the accuracy of the RDTs in actual use. In this study, we investigated the performance accuracy of the RDT, the STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag (STANDARD Q), in the Republic of Korea. We collected a total of 5,792 results that underwent both RDT and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction simultaneously, and overall sensitivity and specificity of the STANDARD Q were 57.6% and 99.9%, respectively. With binomial logistic regression analysis, we estimated that about half of the COVID-19 patients with a cycle threshold value of 25 for E and RdRP were RDT-negative. These results suggest that the clinical sensitivity of RDTs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 is considerably low in a real-world setting, and we recommend that limitations of RDTs should be considered when setting up COVID-19 test strategies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kweon OJ, Lim YK, Kim HR, Choi Y, Kim MC, Choi SH, et al. Evaluation of rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests, AFIAS COVID-19 Ag and ichroma COVID-19 Ag, with serial nasopharyngeal specimens from COVID-19 patients. PLoS One. 2021; 16(4):e0249972. PMID: 33831118.2. Lim YK, Kweon OJ, Kim HR, Kim TH, Lee MK. Field evaluation of seven SARS-COV-2 antigen assays. J Infect Public Health. 2022; 15(2):199–202. PMID: 34991002.3. Lee J, Kim SY, Huh HJ, Kim N, Sung H, Lee H, et al. Clinical performance of the standard Q COVID-19 rapid antigen test and simulation of its real-world application in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2021; 41(6):588–592. PMID: 34108286.4. World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays 2020. Updated 2021. Accessed May 1, 2022. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnosis-of-sars-cov-2infection-using-rapid-immunoassays .5. Rahman MM, Hoque AF, Karim Y, Kawser Z, Siddik AB, Sumiya MK, et al. Clinical evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-based rapid diagnostic test kit for detection of COVID-19 cases in Bangladesh. Heliyon (Lond). 2021; 7(11):e08455.6. Corman VM, Haage VC, Bleicker T, Schmidt ML, Muhlemann B, Zuchowski M, et al. Comparison of seven commercial SARS-CoV-2 rapid point-of-care antigen tests: a single-centre laboratory evaluation study. Lancet Microbe. 2021; 2(7):e311–e319. PMID: 33846704.7. Jegerlehner S, Suter-Riniker F, Jent P, Bittel P, Nagler M. Diagnostic accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test in real-life clinical settings. Int J Infect Dis. 2021; 109:118–122. PMID: 34242764.8. Jeewandara C, Guruge D, Pushpakumara PD, Madhusanka D, Jayadas TT, Chaturanga IP, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of two WHO approved SARS-CoV2 antigen assays in detecting patients with SARS-CoV2 infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2022; 22(1):276. PMID: 35317731.9. Lee J, Kim SY, Huh HJ, Kim N, Sung H, Lee H, et al. Clinical performance of the Standard Q COVID-19 rapid antigen test and simulation of its real-world application in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2021; 41(6):588–592. PMID: 34108286.10. Rhee C, Kanjilal S, Baker M, Klompas M. Duration of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infectivity: when is it safe to discontinue isolation? Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(8):1467–1474. PMID: 33029620.11. Kweon OJ, Lee JH, Choi YS, Kim BS, Lim YK, Lee MK, et al. Positivity of rapid antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2 with serial followed-up nasopharyngeal swabs in hospitalized patients due to COVID-19. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(21):e168. PMID: 35638195.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understandings and Prospects of Laboratory Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2
- Challenges of Scaling Up SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Tests
- Retrospective Validation of Xpert Xpress SARSCoV-2 and Rapid COVID-19 PCR Tests
- Performance of STANDARD™ M10 SARS-CoV-2 Assay for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 from a Nasopharyngeal Swab
- Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea