J Korean Med Sci.
2022 Oct;37(40):e296. 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e296.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Biomedical Publications and Their Citation Frequency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Information and Media Services, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2534335
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e296
Abstract
- Background
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has resulted in enormous related publications. However, the citation frequency of these documents and their influence on the journal impact factor (JIF) are not well examined. We aimed to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on biomedical research publications and their citation frequency.
Methods
We searched publications on biomedical research in the Web of Science using the search terms “COVID-19,” “SARS-Cov-2,” “2019 corona*,” “corona virus disease 2019,” “coronavirus disease 2019,” “novel coronavirus infection” and “2019-ncov.” The top 200 journals were defined as those with a higher number of COVID-19 publications than other journals in 2020. The COVID-19 impact ratio was calculated as the ratio of the average number of citations per item in 2021 to the JIF for 2020.
Results
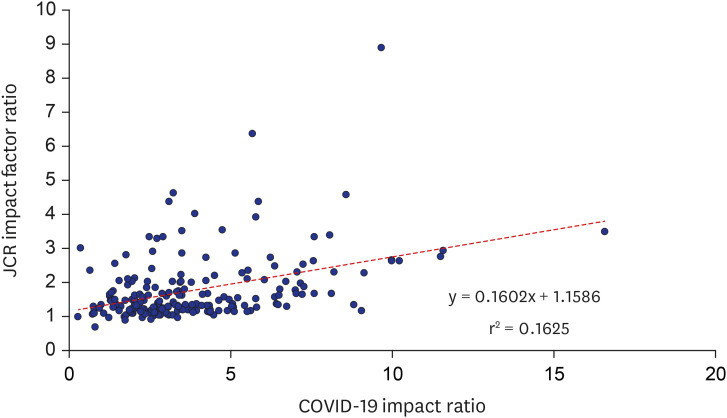
The average number of citations for the top 200 journals in 2021, per item published in 2020, was 25.7 (range, 0–270). The average COVID-19 impact ratio was 3.84 (range, 0.26–16.58) for 197 journals that recorded the JIF for 2020. The average JIF ratio for the top 197 journals including the JIFs for 2020 and 2021 was 1.77 (range, 0.68–8.89). The COVID-19 impact ratio significantly correlated with the JIF ratio (r = 0.403, P = 0.010). Twenty-five Korean journals with a COVID-19 impact ratio > 1.5 demonstrated a higher JIF ratio (1.31 ± 0.39 vs. 1.01 ± 0.18, P < 0.001) than 33 Korean journals with a lower COVID-19 impact ratio.
Conclusion
COVID-19 pandemic infection has significantly impacted the trends in biomedical research and the citation of related publications.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gasparyan AY, Kumar AB, Yessirkepov M, Zimba O, Nurmashev B, Kitas GD. Global health strategies in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic and other unprecedented threats. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(22):e174. PMID: 35668684.
Article2. Yoon SH, Ham SY, Nam BD, Chae KJ, Lee D, Yoo JY, et al. Establishment of a nationwide Korean imaging cohort of coronavirus disease 2019. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(46):e413. PMID: 33258333.
Article3. Yoon YK, Lee J, Kim SI, Peck KR. A systematic narrative review of comprehensive preparedness strategies of healthcare resources for a large resurgence of COVID-19 nationally, with local or regional epidemics: present era and beyond. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(44):e387. PMID: 33200593.
Article4. Gong Y, Ma TC, Xu YY, Yang R, Gao LJ, Wu SH, et al. Early research on COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis. Innovation (Camb). 2020; 1(2):100027. PMID: 32914141.
Article5. Giannos P, Kechagias KS, Katsikas Triantafyllidis K, Falagas ME. Spotlight on early COVID-19 research productivity: a 1-year bibliometric analysis. Front Public Health. 2022; 10:811885. PMID: 35712290.
Article6. Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW. Mapping the situation of research on coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): a preliminary bibliometric analysis during the early stage of the outbreak. BMC Infect Dis. 2020; 20(1):561. PMID: 32738881.
Article7. Älgå A, Eriksson O, Nordberg M. Analysis of scientific publications during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic: topic modeling study. J Med Internet Res. 2020; 22(11):e21559. PMID: 33031049.
Article8. Abd-Alrazaq A, Schneider J, Mifsud B, Alam T, Househ M, Hamdi M, et al. A comprehensive overview of the COVID-19 literature: machine learning-based bibliometric analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021; 23(3):e23703. PMID: 33600346.
Article9. Raynaud M, Goutaudier V, Louis K, Al-Awadhi S, Dubourg Q, Truchot A, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on publication dynamics and non-COVID-19 research production. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2021; 21(1):255. PMID: 34809561.
Article10. Zdravkovic M, Berger-Estilita J, Zdravkovic B, Berger D. Scientific quality of COVID-19 and SARS CoV-2 publications in the highest impact medical journals during the early phase of the pandemic: a case control study. PLoS One. 2020; 15(11):e0241826. PMID: 33152034.
Article11. Shimray SR. Research done wrong: a comprehensive investigation of retracted publications in COVID-19. Account Res. 2022; 1–14.
Article12. Frampton G, Woods L, Scott DA. Inconsistent and incomplete retraction of published research: a cross-sectional study on COVID-19 retractions and recommendations to mitigate risks for research, policy and practice. PLoS One. 2021; 16(10):e0258935. PMID: 34705841.
Article13. Ganesh R, Mahalingam K, Kandaswamy N, Shanmugam C, Vishnu VY, Subbiah A. Top 100 cited articles in one year of COVID-19 research - a bibliometric analysis. Indian J Public Health. 2021; 65(4):375–379. PMID: 34975081.
Article14. Brandt MD, Ghozy SA, Kallmes DF, McDonald RJ, Kadirvel RD. Comparison of citation rates between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 articles across 24 major scientific journals. PLoS One. 2022; 17(7):e0271071. PMID: 35895698.
Article15. Taneja SL, Passi M, Bhattacharya S, Schueler SA, Gurram S, Koh C. Social media and research publication activity during early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic: longitudinal trend analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021; 23(6):e26956. PMID: 33974550.
Article16. Ran N. Association between immediacy of citations and Altmetrics in COVID-19 research by artificial neural networks. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021; 1–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insights and pearls of healthcare systems management of COVID-19 in Asia and its relevance to Asian transplant services
- The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and chronic diseases
- Assessment and Management of Dysphagia during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The COVID-19 pandemic's impact on prostate cancer screening and diagnosis in Korea
- The Management of Thyroid Disease in COVID-19 Pandemic