Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2022 Sep;65(5):468-476. 10.5468/ogs.22001.
Body fat distribution and insulin resistance among Korean middle-aged women: a Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Biostatistics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533820
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.22001
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate menopause-related changes in body fat distribution and their relationship with insulin resistance in middleaged Korean women.
Methods
We analyzed women aged 40-60 years using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2008 to 2011. Body fat was measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Insulin resistance was assessed using the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
Results
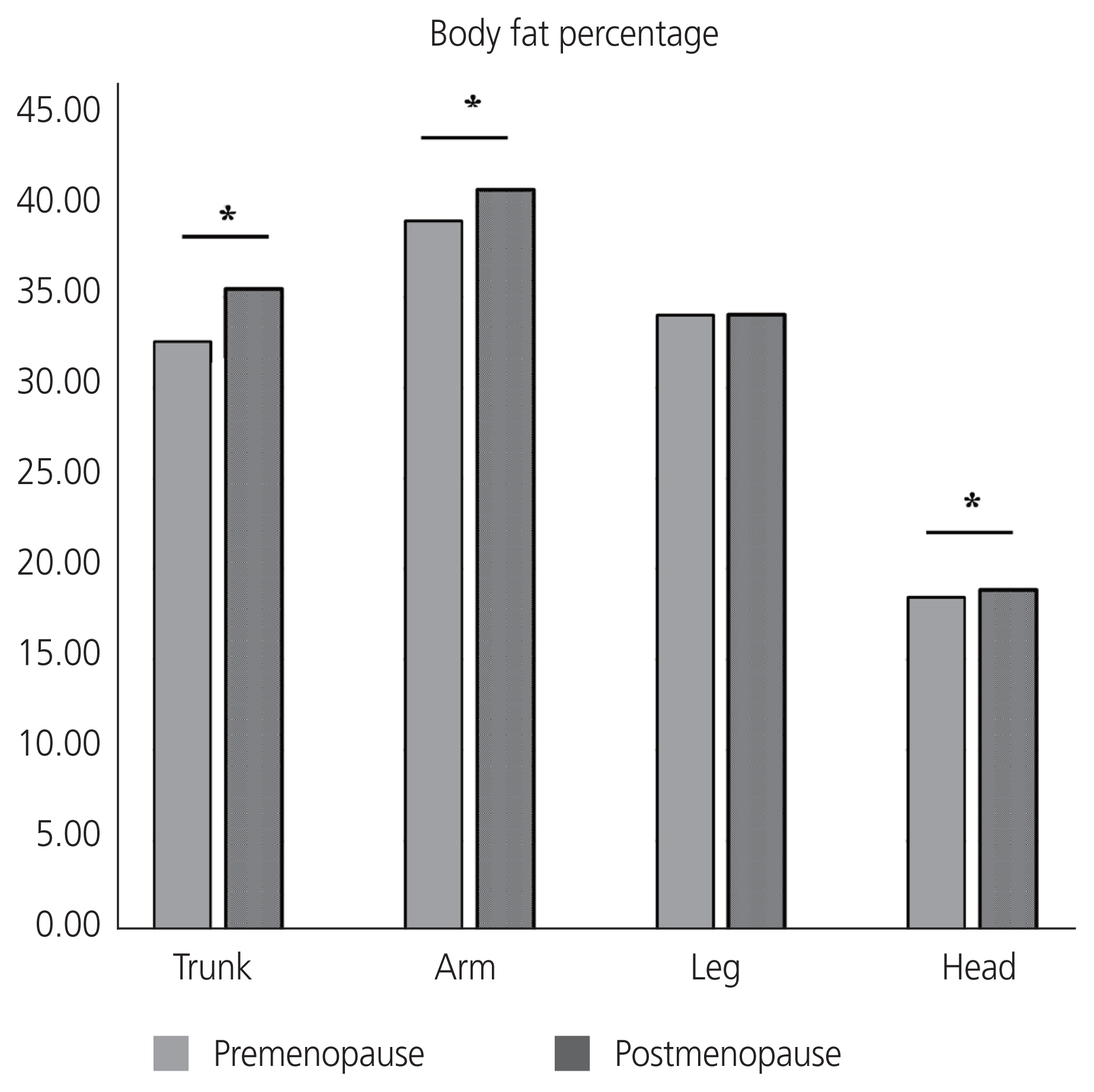
Among 3,468 participants, menopausal women (n=1,489) had a higher body mass index (BMI) and higher trunk, arm, and head fat percentages than premenopausal women (n=1,979). However, no significant difference was found in the leg fat percentage according to menopausal status. Multivariable regression analysis for HOMA-IR showed that trunk fat percentage, BMI, and waist circumference positively correlated with insulin resistance and leg fat percentage negatively correlated after adjusting for several confounding factors, whereas menopausal status was not associated with HOMAIR.
Conclusion
Middle-aged women not only have different body weights and BMI but also have different body fat distributions according to menopausal status. Each fat percentage change in the trunk and leg is differently associated with metabolic health, particularly insulin resistance. To evaluate the metabolic health of middle-aged women, BMI is generally noted; however, body fat distribution, which can be easily assessed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, should also be considered.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Schoenaker DA, Jackson CA, Rowlands JV, Mishra GD. Socioeconomic position, lifestyle factors and age at natural menopause: a systematic review and meta-analyses of studies across six continents. Int J Epidemiol. 2014; 43:1542–62.
Article2. Hong JS, Yi SW, Kang HC, Jee SH, Kang HG, Bayasgalan G, et al. Age at menopause and cause-specific mortality in South Korean women: Kangwha cohort study. Maturitas. 2007; 56:411–9.
Article3. Ku SY, Kang JW, Kim H, Ku PS, Lee SH, Suh CS, et al. Regional differences in age at menopause between Korean-Korean and Korean-Chinese. Menopausea. 2004; 11:569–74.4. Al-Safi ZA, Polotsky AJ. Obesity and menopause. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2015; 29:548–53.
Article5. Matthews KA, Crawford SL, Chae CU, Everson-Rose SA, Sowers MF, Sternfeld B, et al. Are changes in cardiovascular disease risk factors in midlife women due to chronological aging or to the menopausal transition? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54:2366–73.
Article6. Ambikairajah A, Walsh E, Tabatabaei-Jafari H, Cherbuin N. Fat mass changes during menopause: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019; 221:393–409.
Article7. Razmjou S, Abdulnour J, Bastard JP, Fellahi S, Doucet É, Brochu M, et al. Body composition, cardiometabolic risk factors, physical activity, and inflammatory markers in premenopausal women after a 10-year follow-up: a MONET study. Menopause. 2018; 25:89–97.
Article8. Trémollieres FA, Pouilles JM, Ribot CA. Relative influence of age and menopause on total and regional body composition changes in postmenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996; 175:1594–600.
Article9. Park JK, Lim YH, Kim KS, Kim SG, Kim JH, Lim HG, et al. Body fat distribution after menopause and cardiovascular disease risk factors: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2013; 22:587–94.
Article10. Sowers M, Zheng H, Tomey K, Karvonen-Gutierrez C, Jannausch M, Li X, et al. Changes in body composition in women over six years at midlife: ovarian and chronological aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:895–901.
Article11. Hunter GR, Kekes-Szabo T, Treuth MS, Williams MJ, Goran M, Pichon C. Intra-abdominal adipose tissue, physical activity and cardiovascular risk in pre- and postmenopausal women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996; 20:860–5.12. Kannel WB, Cupples LA, Ramaswami R, Stokes J 3rd, Kreger BE, Higgins M. Regional obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease; the Framingham study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991; 44:183–90.
Article13. McFarlane SI, Banerji M, Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:713–8.
Article14. Kapoor E, Collazo-Clavell ML, Faubion SS. Weight gain in women at midlife: a concise review of the pathophysiology and strategies for management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017; 92:1552–8.
Article15. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–9.
Article16. Ley CJ, Lees B, Stevenson JC. Sex- and menopause-associated changes in body-fat distribution. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992; 55:950–4.
Article17. Lovejoy JC, Champagne CM, de Jonge L, Xie H, Smith SR. Increased visceral fat and decreased energy expenditure during the menopausal transition. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:949–58.
Article18. Manolopoulos KN, Karpe F, Frayn KN. Gluteofemoral body fat as a determinant of metabolic health. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010; 34:949–59.
Article19. Snijder MB, Zimmet PZ, Visser M, Dekker JM, Seidell JC, Shaw JE. Independent and opposite associations of waist and hip circumferences with diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia: the Ausdiab study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28:402–9.
Article20. Dowling HJ, Fried SK, Pi-Sunyer FX. Insulin resistance in adipocytes of obese women: effects of body fat distribution and race. Metabolism. 1995; 44:987–95.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum Ferritin Level is an Independent Predictor of Insulin Resistance in Non-diabetic Men Aged Between 30-69 Years: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010
- Adiposity in the Relationship between Serum Vitamin D Level and Insulin Resistance in Middle-Aged and Elderly Korean Adults: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008
- Comparative Study of Serum Leptin and Insulin Resistance Levels Between Korean Postmenopausal Vegetarian and Non-vegetarian Women
- The Association between Type of Work and Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Korean Men: Results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2007~2009)
- Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)