Diabetes Metab J.
2022 Sep;46(5):808-812. 10.4093/dmj.2021.0226.
Trends in the Prevalence of Obesity and Its Phenotypes Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2017 in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University Hospital, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Statistics, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533648
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0226
Abstract
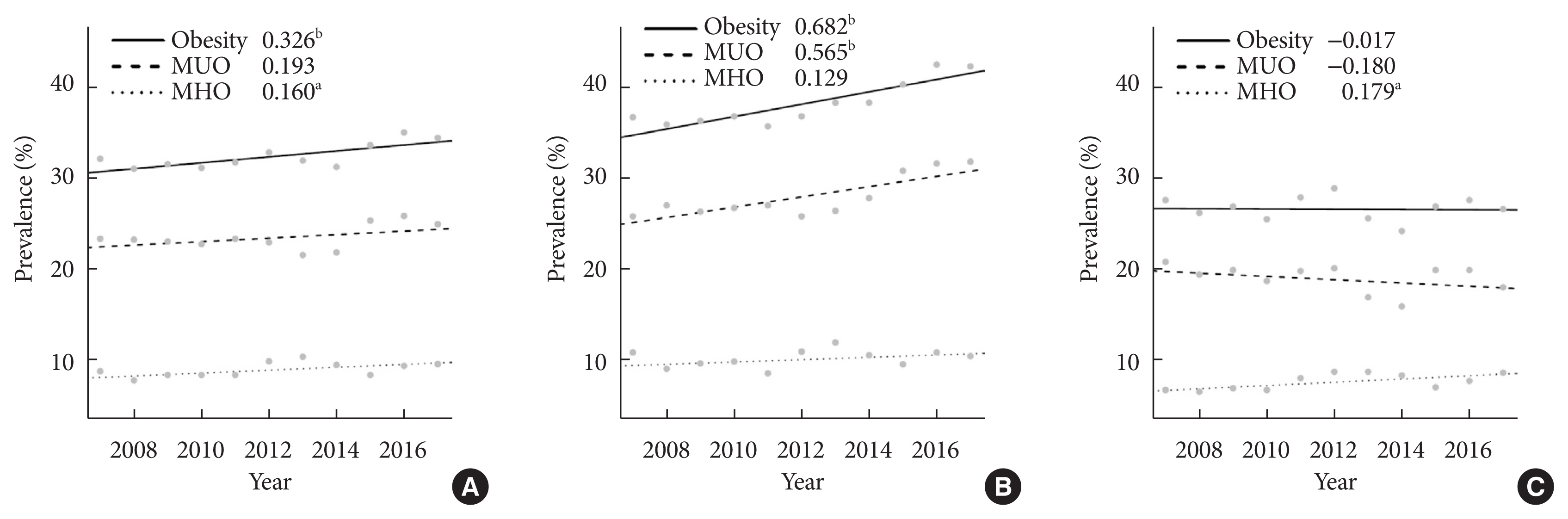
- This study used data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV–VII from 2007 to identify the prevalence of obesity and its phenotypes (metabolically unhealthy obesity [MUO] and metabolically healthy obesity [MHO]) and their secular changes. The prevalence of obesity in Korea increased with significant secular changes observed (β=0.326, P trend <0.01) between 2007 and 2017, and especially in men (β=0.682, P trend <0.001) but not in women. The changes in the prevalence of obesity during the study period were different between men and women (P=0.001). The prevalence of MUO significantly increased only in men (β=0.565, P trend <0.01), while that of MHO increased only in women (β=0.179, P<0.05), especially in the younger age group (β=0.308, P<0.01).
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jaacks LM, Vandevijvere S, Pan A, McGowan CJ, Wallace C, Imamura F, et al. The obesity transition: stages of the global epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:231–40.
Article2. Chin SO, Rhee SY, Chon S, Hwang YC, Jeong IK, Oh S, et al. Sarcopenia is independently associated with cardiovascular disease in older Korean adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) from 2009. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60119.
Article3. Lee YH, Kim SU, Song K, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with significant liver fibrosis independently of obesity and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011). Hepatology. 2016; 63:776–86.
Article4. WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004; 363:157–63.5. Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr, Lenfant C, American Heart Association, et al. Definition of metabolic syndrome: report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. 2004; 109:433–8.6. Hwang YC, Cho IJ, Jeong IK, Ahn KJ, Chung HY. Differential association between sarcopenia and metabolic phenotype in Korean young and older adults with and without obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2017; 25:244–51.
Article7. Guo F, Garvey WT. Cardiometabolic disease risk in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity: stability of metabolic health status in adults. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016; 24:516–25.
Article8. Al-Khalidi B, Kimball SM, Kuk JL, Ardern CI. Metabolically healthy obesity, vitamin D, and all-cause and cardiometabolic mortality risk in NHANES III. Clin Nutr. 2019; 38:820–8.
Article9. Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019; 92:6–10.
Article10. Lin H, Zhang L, Zheng R, Zheng Y. The prevalence, metabolic risk and effects of lifestyle intervention for metabolically healthy obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. A PRISMA-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e8838.11. Slagter SN, Corpeleijn E, van der Klauw MM, Sijtsma A, Swart-Busscher LG, Perenboom C, et al. Dietary patterns and physical activity in the metabolically (un)healthy obese: the Dutch Lifelines cohort study. Nutr J. 2018; 17:18.
Article12. Velho S, Paccaud F, Waeber G, Vollenweider P, Marques-Vidal P. Metabolically healthy obesity: different prevalences using different criteria. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010; 64:1043–51.
Article13. Hinnouho GM, Czernichow S, Dugravot A, Nabi H, Brunner EJ, Kivimaki M, et al. Metabolically healthy obesity and the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes: the Whitehall II cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2015; 36:551–9.
Article14. Phillips CM. Metabolically healthy obesity: definitions, determinants and clinical implications. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013; 14:219–27.
Article15. Prince RL, Kuk JL, Ambler KA, Dhaliwal J, Ball GD. Predictors of metabolically healthy obesity in children. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1462–8.
Article16. Heinzle S, Ball GD, Kuk JL. Variations in the prevalence and predictors of prevalent metabolically healthy obesity in adolescents. Pediatr Obes. 2016; 11:425–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends in Obesity Prevalence by Occupation Based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey From 1998 to 2015
- Secular Trends in Pediatric Overweight and Obesity in Korea
- Temporal trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy overweight and obesity in Korean youth: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2019
- Trends in General and Abdominal Obesity among Korean Adults: Findings from 1998, 2001, 2005, and 2007 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- The prevalence and prevention strategies of pediatric obesity: a narrative review