J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2024 Jul;41(3):141-149. 10.12701/jyms.2024.00346.
The prevalence and prevention strategies of pediatric obesity: a narrative review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Korea
- KMID: 2558138
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2024.00346
Abstract
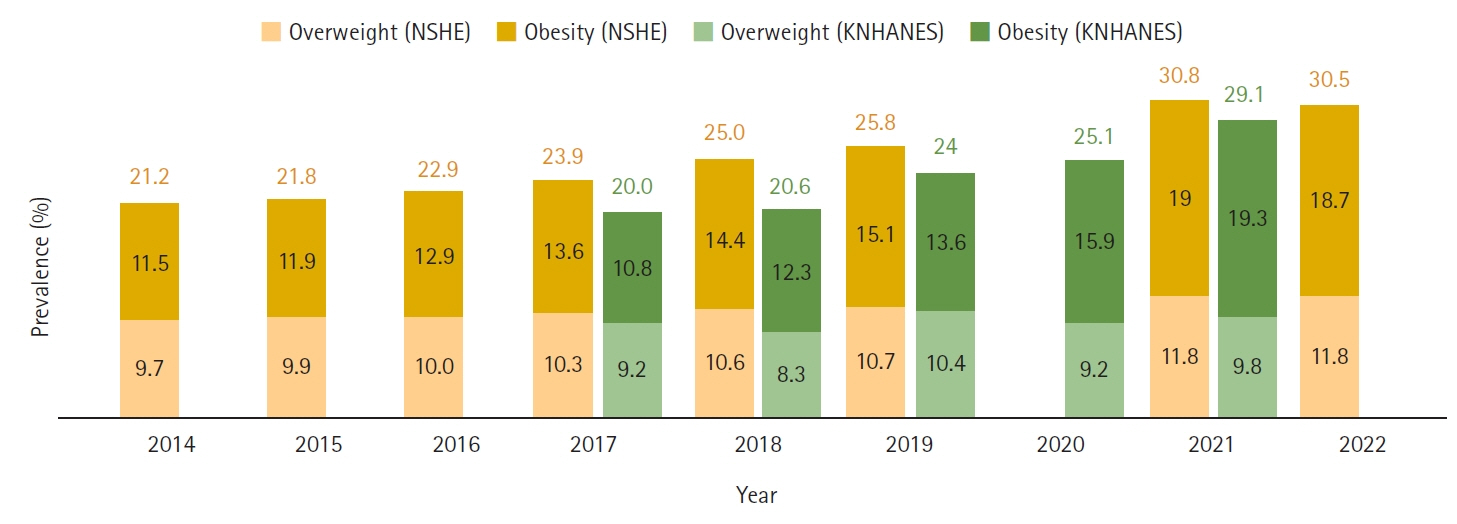
- Pediatric obesity has rapidly increased globally over the past few decades, including in Korea. We aimed to discuss trends in the prevalence of pediatric obesity and effective prevention strategies. Its prevalence has markedly increased in most high-income nations. According to recent reports, this increase has slowed in developed countries, but the levels remain alarmingly high. In Korea, the rate of pediatric obesity has surged notably since the 1990s; however, since the 2000s, this increase has become more gradual. According to recently published 2017 growth charts, the prevalence of pediatric obesity in Korea varies slightly depending on the data source. The National School Health Examination data showed that pediatric obesity gradually increase from 11.5% in 2014 to 15.1% in 2019, and after the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, it sharply increased to 19% in 2021. Based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the prevalence of pediatric obesity gradually increased from 10.8% in 2017 to 13.6% in 2019. This trend, which accelerated sharply to 15.9% in 2020 and 19.3% in 2021, was especially severe in boys and older children. Pediatric obesity not only affects health during childhood but also increases the risk of developing obesity and associated health conditions in adulthood. Despite ongoing research on treatment options, obesity prevention and control remain challenging. Hence, prioritizing early intervention and prevention of pediatric obesity through healthy eating habits and lifestyles is crucial. This requires intervention at the individual, family, school, and community levels.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lobstein T, Jackson-Leach R, Moodie ML, Hall KD, Gortmaker SL, Swinburn BA, et al. Child and adolescent obesity: part of a bigger picture. Lancet. 2015; 385:2510–20.2. Di Cesare M, Sorić M, Bovet P, Miranda JJ, Bhutta Z, Stevens GA, et al. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: a worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019; 17:212.3. Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Zeltser LM, Drewnowski A, Ravussin E, Redman LM, et al. Obesity pathogenesis: an endocrine society scientific statement. Endocr Rev. 2017; 38:267–96.4. Grandone A, Di Sessa A, Umano GR, Toraldo R, Miraglia Del Giudice E. New treatment modalities for obesity. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 32:535–49.5. Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev. 2008; 9:474–88.6. Simmonds M, Llewellyn A, Owen CG, Woolacott N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2016; 17:95–107.7. Sonntag D. Why early prevention of childhood obesity is more than a medical concern: a health economic approach. Ann Nutr Metab. 2017; 70:175–8.8. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128•9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017; 390:2627–42.9. World Health Organization (WHO). WHO fact sheet: Obesity and overweight [Internet]. Geneva: WHO;2024. [cited 2024 Mar 29]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.10. Skinner AC, Ravanbakht SN, Skelton JA, Perrin EM, Armstrong SC. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children, 1999-2016. Pediatrics. 2018; 141:e20173459.11. Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K, et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011; 6:342–60.12. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. JAMA. 2014; 311:806–14.13. Skinner AC, Skelton JA. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United States, 1999-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2014; 168:561–6.14. Kim DU, Rie KC. Studies on height, sitting height and relative sitting height of Korean primary school children in urban areas. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1967; 10:585–98.15. Moon HR, Yun DJ. Height and weight (and other measurements) of children in Korea 1975. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1978; 21:183–97.16. Shim TS, Ko KW. Physical growth of children in Korean, 1985. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1985; 29:1–22.17. Lee DH, Hong YM, Lee KY; The Committee for Public Health Statistics; The Committee for Nutrition. 1998 Korean National Growth Charts. Seoul: The Korean Pediatric Society;1999.18. Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, et al. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:1–25.19. Kim JH, Yun S, Hwang SS, Shim JO, Chae HW, Lee YJ, et al. The 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents: development, improvement, and prospects. Korean J Pediatr. 2018; 61:135–49.20. Park YS, Lee DH, Choi JM, Kang YJ, Kim CH. Trend of obesity in school age children in Seoul over the past 23 years. Korean J Pediatr. 2004; 47:247–57.21. Oh K, Jang MJ, Lee NY, Moon JS, Lee CG, Yoo MH, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among Korean children and adolescents in 1997 and 2005. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:950–5.22. Kim JH, Moon JS. Secular trends in pediatric overweight and obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2020; 29:12–7.23. Nam HK, Kim HR, Rhie YJ, Lee KH. Trends in the prevalence of extreme obesity among Korean children and adolescents from 2001 to 2014. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 30:517–23.24. Choe J, Kim J, Moon JS. Cutoff values of body mass index for severe obesity in Korean children and adolescents: the 99th percentile versus 120% of the 95th percentile. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023; 28:131–7.25. Student Health Information Center, Ministry of Education. Student Health Information Center Website [Internet]. Cheongju, Korea: Student Health Information Center, Ministry of Education;2024. [cited 2024 Mar 18]. https://schoolhealth.kr/index.do.26. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2010-2022 [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;2024. [cited 2024 Mar 19]. https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_04_01.do.27. Park HK, Seo JY, Jung HW, Lim JS. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity in Korean children and adolescents, 2007-2020: a population-based study. Pediatr Int. 2023; 65:e15472.28. Kang S, Seo MY, Kim SH, Park MJ. Changes in lifestyle and obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korean adolescents: based on the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey 2019 and 2020. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 27:281–8.29. Abbasi A, Juszczyk D, van Jaarsveld CH, Gulliford MC. Body mass index and incident type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and young adults: a retrospective cohort study. J Endocr Soc. 2017; 1:524–37.30. Kim HY, Kim JH. Temporal trends in the prevalence of metabolically healthy overweight and obesity in Korean youth: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2019. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 27:134–41.31. Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, Caprio S, Daniels SR, Kohli R, et al. NASPGHAN clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017; 64:319–34.32. Wühl E. Hypertension in childhood obesity. Acta Paediatr. 2019; 108:37–43.33. Calcaterra V, Klersy C, Muratori T, Telli S, Caramagna C, Scaglia F, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) in children and adolescents with varying degrees of obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008; 68:868–72.34. Chung YL, Rhie YJ. Severe Obesity in children and adolescents: metabolic effects, assessment, and treatment. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021; 30:326–35.35. Kim M, Kim J. Cardiometabolic risk factors and metabolic syndrome based on severity of obesity in Korean children and adolescents: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2018. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 27:289–99.36. Li S, Chen W, Srinivasan SR, Bond MG, Tang R, Urbina EM, et al. Childhood cardiovascular risk factors and carotid vascular changes in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. JAMA. 2003; 290:2271–6.37. Twig G, Yaniv G, Levine H, Leiba A, Goldberger N, Derazne E, et al. Body-mass index in 2.3 million adolescents and cardiovascular death in adulthood. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:2430–40.38. Kim JH. Overview of pediatric obesity: diagnosis, epidemiology, and significance. J Korean Med Assoc. 2021; 64:401–9.39. Brown V, Ananthapavan J, Sonntag D, Tan EJ, Hayes A, Moodie M. The potential for long-term cost-effectiveness of obesity prevention interventions in the early years of life. Pediatr Obes. 2019; 14:e12517.40. Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, Farooqi IS, Murad MH, Silverstein JH, et al. Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:709–57.41. Masood B, Moorthy M. Causes of obesity: a review. Clin Med (Lond). 2023; 23:284–91.42. Kyler KE, Hall M, Halvorson EE, Davis AM. Associations between obesity and adverse childhood experiences in the United States. Child Obes. 2021; 17:342–8.43. Bleich SN, Segal J, Wu Y, Wilson R, Wang Y. Systematic review of community-based childhood obesity prevention studies. Pediatrics. 2013; 132:e201–10.44. James J, Thomas P, Cavan D, Kerr D. Preventing childhood obesity by reducing consumption of carbonated drinks: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2004; 328:1237.45. Dietz WH. Sugar-sweetened beverages, milk intake, and obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2006; 148:152–4.46. Shefferly A, Scharf RJ, DeBoer MD. Longitudinal evaluation of 100% fruit juice consumption on BMI status in 2-5-year-old children. Pediatr Obes. 2016; 11:221–7.47. Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Beecher MD, Roemmich JN. Increasing healthy eating vs. reducing high energy-dense foods to treat pediatric obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008; 16:318–26.48. Kang E, Hong YH, Kim J, Chung S, Kim KK, Haam JH, et al. Obesity in children and adolescents: 2022 update of clinical practice guidelines for obesity by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024; 33:11–9.49. Rolls BJ. Plenary lecture 1: dietary strategies for the prevention and treatment of obesity. Proc Nutr Soc. 2010; 69:70–9.50. DiSantis KI, Birch LL, Davey A, Serrano EL, Zhang J, Bruton Y, et al. Plate size and children’s appetite: effects of larger dishware on self-served portions and intake. Pediatrics. 2013; 131:e1451–8.51. Crespo CJ, Smit E, Troiano RP, Bartlett SJ, Macera CA, Andersen RE. Television watching, energy intake, and obesity in US children: results from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001; 155:360–5.52. Erçelik ZE, Çağlar S. Effectiveness of active video games in overweight and obese adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 27:98–104.53. Andersen RE, Crespo CJ, Bartlett SJ, Cheskin LJ, Pratt M. Relationship of physical activity and television watching with body weight and level of fatness among children: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 1998; 279:938–42.54. Robinson TN, Banda JA, Hale L, Lu AS, Fleming-Milici F, Calvert SL, et al. Screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2017; 140(Suppl 2):S97–101.55. LeBourgeois MK, Hale L, Chang AM, Akacem LD, Montgomery-Downs HE, Buxton OM. Digital media and sleep in childhood and adolescence. Pediatrics. 2017; 140(Suppl 2):S92–6.56. Fang K, Mu M, Liu K, He Y. Screen time and childhood overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Child Care Health Dev. 2019; 45:744–53.57. Council on Communications and Media. Media and young minds. Pediatrics. 2016; 138:e20162591.58. Yan J, Liu L, Zhu Y, Huang G, Wang PP. The association between breastfeeding and childhood obesity: a meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2014; 14:1267.59. Harder T, Bergmann R, Kallischnigg G, Plagemann A. Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 162:397–403.60. Kramer MS, Matush L, Vanilovich I, Platt RW, Bogdanovich N, Sevkovskaya Z, et al. Effects of prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding on child height, weight, adiposity, and blood pressure at age 6.5 y: evidence from a large randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 86:1717–21.61. Fatima Y, Doi SA, Mamun AA. Longitudinal impact of sleep on overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a systematic review and bias-adjusted meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2015; 16:137–49.62. Kjeldsen JS, Hjorth MF, Andersen R, Michaelsen KF, Tetens I, Astrup A, et al. Short sleep duration and large variability in sleep duration are independently associated with dietary risk factors for obesity in Danish school children. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014; 38:32–9.63. Weng SF, Redsell SA, Swift JA, Yang M, Glazebrook CP. Systematic review and meta-analyses of risk factors for childhood overweight identifiable during infancy. Arch Dis Child. 2012; 97:1019–26.64. Ahn SN, Zhang H, Berlin KS, Levy M, Kabra R. Adverse childhood experiences and childhood obesity: a path analysis approach. Child Health Care. 2020; 49:247–66.65. Danielzik S, Langnäse K, Mast M, Spethmann C, Müller MJ. Impact of parental BMI on the manifestation of overweight 5-7 year old children. Eur J Nutr. 2002; 41:132–8.66. Whitaker KL, Jarvis MJ, Beeken RJ, Boniface D, Wardle J. Comparing maternal and paternal intergenerational transmission of obesity risk in a large population-based sample. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010; 91:1560–7.67. Chai LK, Collins C, May C, Brain K, Wong See D, Burrows T. Effectiveness of family-based weight management interventions for children with overweight and obesity: an umbrella review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019; 17:1341–427.68. van der Kruk JJ, Kortekaas F, Lucas C, Jager-Wittenaar H. Obesity: a systematic review on parental involvement in long-term European childhood weight control interventions with a nutritional focus. Obes Rev. 2013; 14:745–60.69. Ickovics JR, Duffany KO, Shebl FM, Peters SM, Read MA, Gilstad-Hayden KR, et al. Implementing school-based policies to prevent obesity: cluster randomized trial. Am J Prev Med. 2019; 56:e1–11.70. Mei H, Xiong Y, Xie S, Guo S, Li Y, Guo B, et al. The impact of long-term school-based physical activity interventions on body mass index of primary school children: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Public Health. 2016; 16:205.71. Teng AM, Jones AC, Mizdrak A, Signal L, Genç M, Wilson N. Impact of sugar-sweetened beverage taxes on purchases and dietary intake: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019; 20:1187–204.72. Goiana-da-Silva F, Severo M, Cruz E Silva D, Gregório MJ, Allen LN, Muc M, et al. Projected impact of the Portuguese sugar-sweetened beverage tax on obesity incidence across different age groups: a modelling study. PLoS Med. 2020; 17:e1003036.73. Anastasiou K, Miller M, Dickinson K. The relationship between food label use and dietary intake in adults: a systematic review. Appetite. 2019; 138:280–91.74. Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM. Patterns and trends in food portion sizes, 1977-1998. JAMA. 2003; 289:450–3.75. Díez J, Gullón P, Sandín Vázquez M, Álvarez B, Martín MD, Urtasun M, et al. A community-driven approach to generate urban policy recommendations for obesity prevention. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018; 15:635.76. Park SJ, Chung SC, Jeong HS, Noh YM, Kang EG, Hong YH. Policy suggestion on empowerment of prevention and management of pediatric obesity. Public Health Weekly Report. 2024; 17:840–58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Suggestions for the management of pediatric obesity in Korea
- Prevention strategies for obesity in children and adolescents
- Sarcopenic Obesity: A Comprehensive Approach for Postmenopausal Women
- An Update on Mental Health Problems and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Pediatric Obesity
- Weightism in Asia: A Narrative Review and Implications for Practice