Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Sep;55(3):384-389. 10.5115/acb.22.012.
Cadaveric findings of a duplicated superior petrosal sinus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Tulane Center for Clinical Neurosciences, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
- 2Department of Anatomical Dissection and Donation, Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland.
- 3Department of Neurology, Tulane Center for Clinical Neurosciences, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
- 4Department of Anatomical Sciences, St. George's University, St. George's, Grenada, West Indies.
- 5Department of Structural & Cellular Biology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
- 6Department of Neurosurgery and Ochsner Neuroscience Institute, Ochsner Health System, New Orleans, LA, USA.
- 7Department of Surgery, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
- 8University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
- KMID: 2533367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.012
Abstract
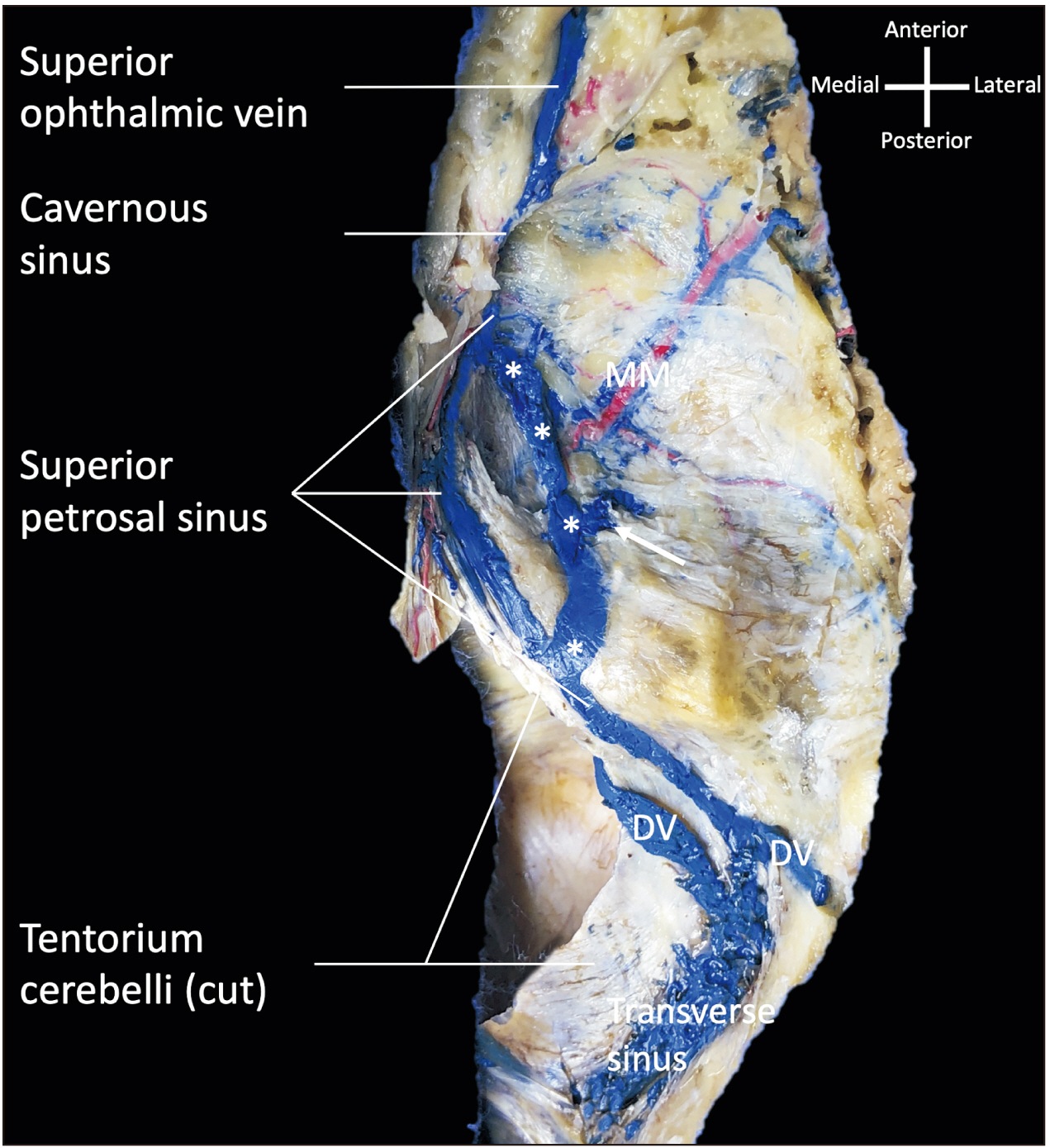
- Knowledge of the intracranial dural venous sinuses and their variations is important in the diagnosis and management of many cranial pathologies. We report a unique duplication of the right-sided superior petrosal sinus identified during routine dissection of the skull base.. Lateral to this sinus, a separate and more curvilinear superior petrosal sinus left the normally positioned superior petrosal sinus and traveled posteriorly near the foramen spinosum and then turned medially to drain into the normally positioned superior petrosal sinus. Anteriorly, the two sinuses joined together and drained into the cavernous sinus. Posteriorly, the laterally positioned sinus drained into the normally positioned sinus which then traveled in normal fashion along the petrous ridge to end in the transverse sinus. To our knowledge, such a duplication has not been previously reported in the extant medical literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Akobo S, Tubbs RS. Tubbs RS, editor. 2020. The superior petrosal sinus. Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses. Elsevier;St. Louis: p. 117–24. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-323-65377-0.00012-X.
Article2. Egemen E, Solaroglu I. Caplan LR, Biller J, Leary MC, Lo EH, Thomas AJ, Yenari MA, Zhang JH, editors. 2017. Anatomy of cerebral veins and dural sinuses. Primer on Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2nd ed. Elsevier, Academic Press;London: p. 32–6. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-803058-5.00005-9.
Article3. Patel N. 2009; Venous anatomy and imaging of the first centimeter. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 30:513–24. DOI: 10.1053/j.sult.2009.08.003. PMID: 20099637.
Article4. Butler H. 1957; The development of certain human dural venous sinuses. J Anat. 91:510–26. PMID: 13475149. PMCID: PMC1244905.5. Matsushima K, Ribas ES, Kiyosue H, Komune N, Miki K, Rhoton AL. 2015; Absence of the superior petrosal veins and sinus: surgical considerations. Surg Neurol Int. 6:34. DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.152147. PMID: 25745589. PMCID: PMC4348801.
Article6. Streeter GL. 1915; The development of the venous sinuses of the dura mater in the human embryo. Am J Anat. 18:145–78. DOI: 10.1002/aja.1000180202.
Article7. Swedenborg E, Tafel RL. 1887. The brain considered anatomically, physiologically and philosophically. The pituitary gland, the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata. Vol. II:James Speirs;London: p. 490–8.8. Narayan V, Savardekar AR, Patra DP, Mohammed N, Thakur JD, Riaz M, Nanda A. 2018; Safety profile of superior petrosal vein (the vein of Dandy) sacrifice in neurosurgical procedures: a systematic review. Neurosurg Focus. 45:E3. DOI: 10.3171/2018.4.FOCUS18133. PMID: 29961377.
Article9. Jinkins JR. 2000. Atlas of neuroradiologic embryology, anatomy, and variants. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: p. 374–81. DOI: 10.3171/2018.4.focus18133.10. Kiliç T, Akakin A. 2008; Anatomy of cerebral veins and sinuses. Front Neurol Neurosci. 23:4–15. DOI: 10.1159/000111256. PMID: 18004050.11. Basamh M, Sinning N, Kehler U. 2020; Individual variations of the superior petrosal vein complex and their microsurgical relevance in 50 cases of trigeminal microvascular decompression. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 162:197–209. DOI: 10.1007/s00701-019-04109-7. PMID: 31768757. PMCID: PMC6942005.
Article12. Huang YP, Wolf BS, Antin SP, Okudera T. 1968; The veins of the posterior fossa--anterior or petrosal draining group. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 104:36–56. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.104.1.36. PMID: 5672774.
Article13. Koh M, Boo SH. c2021. Neuroanatomy, superior petrosal sinus [Internet]. StatPearls;Treasure Island, FL: Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547681/. cited 2022 Jan 2.14. Kaplan HA, Browder J, Krieger AJ. 1975; Venous channels within the intracranial dural partitions. Radiology. 115:641–5. DOI: 10.1148/15.3.641. PMID: 1129477.
Article15. Mortazavi MM, Cox MA, Saker E, Krishnamurthy S, Verma K, Griessenauer CJ, Loukas M, Oskouian RJ, Tubbs RS. 2018; The superior petrosal sinus: a review of anatomy, embryology, pathology, and neurosurgical relevance. Neurosurg Rev. 41:713–8. DOI: 10.1007/s10143-016-0785-9. PMID: 27647276.
Article16. Tubbs RS, Mortazavi MM, Krishnamurthy S, Verma K, Griessenauer CJ, Cohen-Gadol AA. 2013; The relationship between the superior petrosal sinus and the porus trigeminus: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg. 119:1221–5. DOI: 10.3171/2013.4.JNS122062. PMID: 23706047.
Article17. Shimada R, Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Mori H, Abe T. 2013; Superior petrosal sinus: hemodynamic features in normal and cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:609–15. DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A3252. PMID: 22954738. PMCID: PMC7964905.
Article18. Knott JF. 1881; On the cerebral sinuses and their variations. J Anat Physiol. 16(Pt 1):27–42. PMID: 17231415. PMCID: PMC1310067.19. Williams HL. 1930; Apparent unilateral absence of the sigmoid sinus noted at operation. Arch Otolaryngol. 12:339–41. DOI: 10.1001/archotol.1930.03570010385006.
Article20. Waltner J. 1944; Anatomic variations of the lateral and sigmoid sinuses. Arch Otolaryngol. 39:307–12. DOI: 10.1001/archotol.1944.00680010321002.
Article21. Lv X, Jiang C, Liang S, Wang J. 2019; The variant with the absence of the superior petrosal venous and sinus: a potential pitfall of transvenous balloon-assisted embolisation of Borden type II transverse-sigmoid dural arteriovenous fistula. Interv Neuroradiol. 25:474–7. DOI: 10.1177/1591019919841929. PMID: 30997861. PMCID: PMC6607615.
Article22. Gutierrez S, Iwanaga J, Dumont AS, Tubbs RS. 2020; Direct drainage of the basal vein of Rosenthal into the superior petrosal sinus: a literature review. Anat Cell Biol. 53:379–84. DOI: 10.5115/acb.20.199. PMID: 33148874. PMCID: PMC7769095.
Article23. Padget DH. 1956; The cranial venous system in man in reference to development, adult configuration, and relation to the arteries. Am J Anat. 98:307–55. DOI: 10.1002/aja.1000980302. PMID: 13362118.
Article24. Avci E, Dagtekin A, Akture E, Uluc K, Baskaya MK. 2011; Microsurgical anatomy of the vein of Labbé. Surg Radiol Anat. 33:569–73. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-011-0782-1. PMID: 21279640.
Article25. Bergman AR, Thompson SA, Afifi AK, Saadeh FA. Bergman R, editor. 1988. Cardiovascular system. Compendium of Human Anatomic Variation: Text, Atlas, and World Literature. Urban & Schwarzenberg;Baltimore: p. 63. DOI: 10.1201/9781482264463-26.26. Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Okahara M, Sagara Y, Hori Y, Kashiwagi J, Mori H. 2006; Para-cavernous sinus venous structures: anatomic variations and pathologic conditions evaluated on fat-suppressed 3D fast gradient-echo MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 27:1083–9. PMID: 16687548. PMCID: PMC7975714.27. Coates AE. 1934; A note on the superior petrosal sinus and its relation to the sensory root of the trigeminal nerve. J Anat. 68(Pt 3):428. PMID: 17104494. PMCID: PMC1249045.28. Benndorf G. Benndorf G, editor. 2010. Classification of cavernous sinus fistulas (CSFs) and dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs). Dural Cavernous Sinus Fistulas: Diagnostic and Endovascular Therapy. Springer;Berlin: p. 51–63. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-68889-1_4.
Article29. Tanriover N, Abe H, Rhoton AL Jr, Kawashima M, Sanus GZ, Akar Z. 2007; Microsurgical anatomy of the superior petrosal venous complex: new classifications and implications for subtemporal transtentorial and retrosigmoid suprameatal approaches. J Neurosurg. 106:1041–50. DOI: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.6.1041. PMID: 17564177.
Article30. Pathmanaban ON, O'Brien F, Al-Tamimi YZ, Hammerbeck-Ward CL, Rutherford SA, King AT. 2017; Safety of superior petrosal vein sacrifice during microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve. World Neurosurg. 103:84–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.03.117. PMID: 28377255.
Article31. da Silva OT, de Almeida CC, Iglesio RF, de Navarro JM, Teixeira MJ, Duarte KP. 2016; Surgical variation of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: a technical note and anatomical study. Surg Neurol Int. 7(Suppl 21):S571–6. DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.188916. PMID: 27625893. PMCID: PMC5009571.
Article32. McKenna MJ. Nadol JB, McKenna MJ, editors. 2005. Transtemporal and transpetrous approach to the cranial base. Surgery of the Ear and Temporal Bone. 2nd ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: p. 135–54.33. ijit D Sr, Shipra P. 2007; Unusual venous sinuses. Bratisl Lek Listy. 108:104–6. PMID: 17685011.34. Iwanaga J, Singh V, Ohtsuka A, Hwang Y, Kim HJ, Moryś J, Ravi KS, Ribatti D, Trainor PA, Sañudo JR, Apaydin N, Şengül G, Albertine KH, Walocha JA, Loukas M, Duparc F, Paulsen F, Del Sol M, Adds P, Hegazy A, Tubbs RS. 2021; Acknowledging the use of human cadaveric tissues in research papers: recommendations from anatomical journal editors. Clin Anat. 34:2–4. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23671. PMID: 32808702.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent fetal superficial middle cerebral vein: an anatomical study
- Surgical Obliteration in Superior Petrosal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
- Petrosal Approach to Petroclival Meningiomas: Experience with 3 Cases
- Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Using the Direct Superior Ophthalmic Vein Approach: A Case Report
- Direct drainage of the basal vein of Rosenthal into the superior petrosal sinus: a literature review