Clin Endosc.
2022 Sep;55(5):645-654. 10.5946/ce.2022.048.
Optical diagnosis by near-focus versus normal-focus narrow band imaging colonoscopy in colorectal polyps based on combined NICE and WASP classification: a randomized controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Songkhla, Thailand
- 2Division of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Songkhla, Thailand
- KMID: 2533304
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.048
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE) and Workgroup Serrated Polyps and Polyposis (WASP) classifications were developed for optical diagnosis of neoplastic and sessile serrated polyps, respectively. Near-focus NBI with NICE combined with WASP criteria for optical diagnosis of colonic polyps has not yet been evaluated. We aimed to compare the accuracy of near-focus NBI (group A) with normal-focus NBI (group B) in real-time optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps using combined NICE and WASP criteria.
Methods
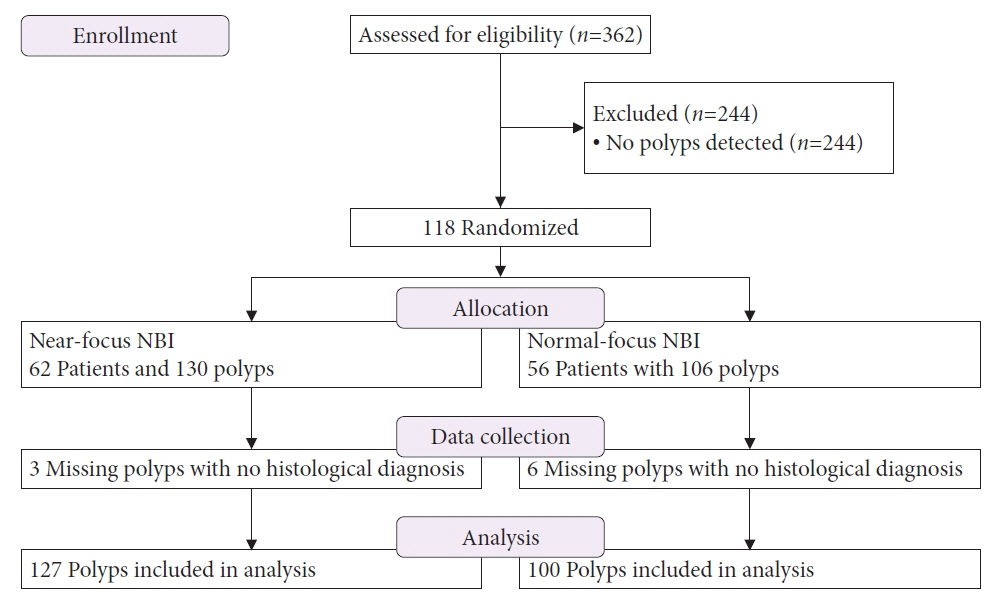
Among 362 patients, 118 with 227 polyps were recruited. Groups A and B included 62 patients with 130 polyps (three lost polyps) and 56 patients with 106 polyps (six lost polyps), respectively. Optical diagnoses were compared with pathological reports.
Results
The accuracy of optical diagnosis of neoplastic polyps in groups A and B was not significantly different (76% vs. 71%, p=0.52). WASP criteria provided all false positive diagnoses of sessile polyps as serrated polyps in 31 (16.2%) patients.
Conclusions
Near-focus NBI was not superior to normal-focus NBI in optical diagnostics of neoplastic polyps using NICE criteria. In our study, WASP classification yielded all false positives in the diagnosis of sessile serrated adenomas/polyps. Routine real-life optical diagnosis of polyps is still unadvisable.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:687–696.2. Ignjatovic A, East JE, Suzuki N, et al. Optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps at routine colonoscopy (Detect InSpect ChAracterise Resect and Discard; DISCARD trial): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:1171–1178.3. Rees CJ, Rajasekhar PT, Wilson A, et al. Narrow band imaging optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps in routine clinical practice: the Detect Inspect Characterise Resect and Discard 2 (DISCARD 2) study. Gut. 2017; 66:887–895.4. ASGE Technology Committee, Manfredi MA, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Electronic chromoendoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:249–261.5. Komeda Y, Kashida H, Sakurai T, et al. Magnifying narrow band imaging (NBI) for the diagnosis of localized colorectal lesions using the Japan NBI Expert Team (JNET) Classification. Oncology. 2017; 93 Suppl 1:49–54.6. Repici A, Hassan C, Radaelli F, et al. Accuracy of narrow-band imaging in predicting colonoscopy surveillance intervals and histology of distal diminutive polyps: results from a multicenter, prospective trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:106–114.7. Machida H, Sano Y, Hamamoto Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of colorectal mucosal lesions: a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1094–1098.8. Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Evaluation of microvessels in colorectal tumors by narrow band imaging magnification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:945–952.9. Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for diagnosis of colorectal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:988–995.10. Wanders LK, East JE, Uitentuis SE, et al. Diagnostic performance of narrowed spectrum endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging, and confocal laser endomicroscopy for optical diagnosis of colonic polyps: a meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:1337–1347.11. Backes Y, Moss A, Reitsma JB, et al. Narrow band imaging, magnifying chromoendoscopy, and gross morphological features for the optical diagnosis of T1 colorectal cancer and deep submucosal invasion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112:54–64.12. Picot J, Rose M, Cooper K, et al. Virtual chromoendoscopy for the real-time assessment of colorectal polyps in vivo: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2017; 21:1–308.13. Mason SE, Poynter L, Takats Z, et al. Optical technologies for endoscopic real-time histologic assessment of colorectal polyps: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019; 114:1219–1230.14. ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Thosani N, et al. ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:502.15. Hewett DG, Kaltenbach T, Sano Y, et al. Validation of a simple classification system for endoscopic diagnosis of small colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:599–607.16. Hayashi N, Tanaka S, Hewett DG, et al. Endoscopic prediction of deep submucosal invasive carcinoma: validation of the narrow-band imaging international colorectal endoscopic (NICE) classification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:625–632.17. Rastogi A, Bansal A, Wani S, et al. Narrow-band imaging colonoscopy: a pilot feasibility study for the detection of polyps and correlation of surface patterns with polyp histologic diagnosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:280–286.18. Uraoka T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, et al. Detectability of colorectal neoplastic lesions using a narrow-band imaging system: a pilot study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:1810–1815.19. Snover DC. Update on the serrated pathway to colorectal carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2011; 42:1–10.20. Leggett B, Whitehall V. Role of the serrated pathway in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:2088–2100.21. Kumar S, Fioritto A, Mitani A, et al. Optical biopsy of sessile serrated adenomas: do these lesions resemble hyperplastic polyps under narrow-band imaging? Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:902–909.22. Parikh ND, Chaptini L, Njei B, et al. Diagnosis of sessile serrated adenomas/polyps with image-enhanced endoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:731–739.23. Hazewinkel Y, López-Cerón M, East JE, et al. Endoscopic features of sessile serrated adenomas: validation by international experts using high-resolution white-light endoscopy and narrow-band imaging. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:916–924.24. IJspeert JE, Bastiaansen BA, van Leerdam ME, et al. Development and validation of the WASP classification system for optical diagnosis of adenomas, hyperplastic polyps and sessile serrated adenomas/polyps. Gut. 2016; 65:963–970.25. Castela J, Mão de Ferro S, Rosa I, et al. Real-time optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps in the routine clinical practice using the NICE and WASP classifications in a nonacademic setting. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2019; 26:314–323.26. Wallace MB, Crook JE, Coe S, et al. Accuracy of in vivo colorectal polyp discrimination by using dual-focus high-definition narrow-band imaging colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1072–1087.27. Wiessner JR, Brown H, Haller B, et al. Near focus NBI endoscopy plus acetic acid for optical polyp characterization in the colorectum: a proof of principle study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019; 54:377–383.28. Kaltenbach T, Rastogi A, Rouse RV, et al. Real-time optical diagnosis for diminutive colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging: the VALID randomised clinical trial. Gut. 2015; 64:1569–1577.29. Szura M, Pasternak A, Bucki K, et al. Two-stage optical system for colorectal polyp assessments. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:204–214.30. Singh R, Jayanna M, Navadgi S, et al. Narrow-band imaging with dual focus magnification in differentiating colorectal neoplasia. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25 Suppl 2:16–20.31. Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, et al. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(3 Pt 2):620–625.32. The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58(6 Suppl):S3–S43.33. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, et al. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4th ed. Geneva: World Heath Organization;2010.34. Kuiper T, Marsman WA, Jansen JM, et al. Accuracy for optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps in nonacademic settings. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:1016–1020.35. Ciocâlteu AM, CârŢână ET, Florescu DN, et al. Narrow band imaging with near-focus mode for colorectal polyps’ characterization. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016; 57(2 Suppl):619–626.36. Hattori S, Iwatate M, Sano W, et al. Narrow-band imaging observation of colorectal lesions using NICE classification to avoid discarding significant lesions. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 6:600–605.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Optical Diagnosis for Colorectal Polyps: A Useful Technique Now or in the Future?
- Classification and endoscopic diagnosis of colorectal polyps
- Introduction: What Are New Roles of Current Colonoscopy?
- Artificial Intelligence-Based Colorectal Polyp Histology Prediction by Using Narrow-Band Image-Magnifying Colonoscopy
- Classification of image-enhanced endoscopy in colon tumors