Clin Endosc.
2022 Sep;55(5):630-636. 10.5946/ce.2022.003.
Safe implementation of transoral incisionless fundoplication as a new technique in a tertiary care center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Digestive Health, Virginia Mason Franciscan Health, Seattle, WA, USA
- KMID: 2533302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.003
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) is an accepted anatomic treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease in selected patients. In this report, we analyze our institution’s programmatic allocation of resources during the safe implementation of TIF as a new procedure.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of all patients who underwent TIF from January 2020 to February 2021 at our institution was performed. The process of initially allocating the operating room (OR) with overnight admission and postoperative esophagram for added safety, and subsequently transitioning TIF to the endoscopy suite (ES) as an outpatient procedure was described. Patient safety and outcomes were evaluated during transition.
Results
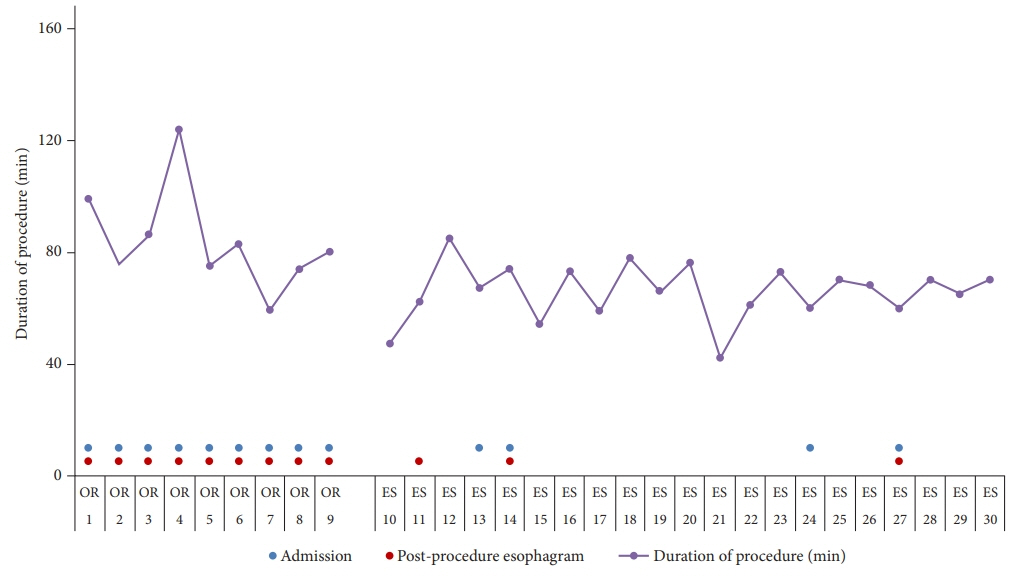
Thirty patients who underwent TIF were identified. The mean age was 51.2±16.0 years. TIF was performed in an OR in nine patients (30%) and 21 (70%) in the ES. All the OR patients were admitted overnight and had routine EG. In contrast, four (19%) from the ES group required clinically-indicated admission and three (14.2%) required esophagram. The mean procedure duration was significantly lower in the ES group (65.7 min vs. 84 min, p=0.02).
Conclusions
A stepwise, resource-efficient process was described that allowed safe initiation of TIF as a new technique and its effective transition to a fully outpatient procedure.
Keyword
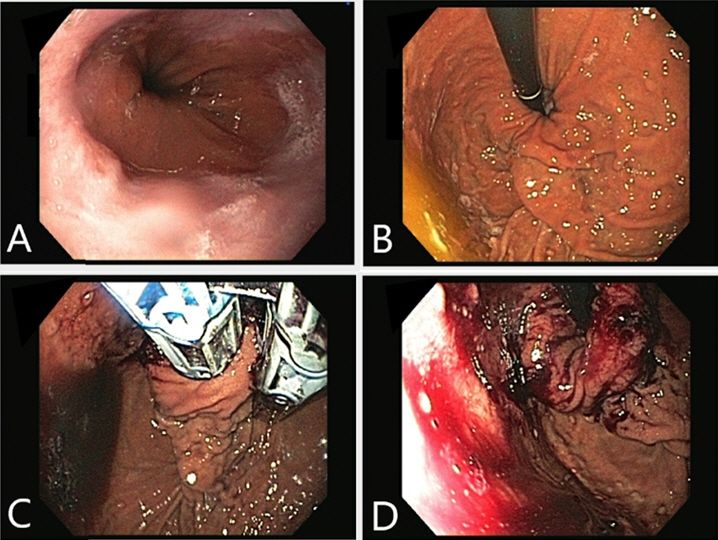
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Assessing implementation strategy and learning curve for transoral incisionless fundoplication as a new technique
Muhammad Haseeb, Christopher C. Thompson
Clin Endosc. 2022;55(6):751-752. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.280.
Reference
-
1. Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, et al. Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: update 2018. Gastroenterology. 2019; 156:254–272.2. Camilleri M, Dubois D, Coulie B, et al. Prevalence and socioeconomic impact of upper gastrointestinal disorders in the United States: results of the US Upper Gastrointestinal Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3:543–552.3. Maret-Ouda J, Markar SR, Lagergren J. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: a review. JAMA. 2020; 324:2536–2547.4. Spechler SJ, Souza RF. Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:836–845.5. Gyawali CP, Fass R. Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2018; 154:302–318.6. El-Serag H, Becher A, Jones R. Systematic review: persistent reflux symptoms on proton pump inhibitor therapy in primary care and community studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 32:720–737.7. Keszthelyi D, Jansen SV, Schouten GA, et al. Proton pump inhibitor use is associated with an increased risk for microscopic colitis: a case-control study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 32:1124–1128.8. Kwok CS, Arthur AK, Anibueze CI, et al. Risk of Clostridium difficile infection with acid suppressing drugs and antibiotics: meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1011–1019.9. Jafri SM, Arora G, Triadafilopoulos G. What is left of the endoscopic antireflux devices? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009; 25:352–357.10. Trad KS, Barnes WE, Prevou ER, et al. The TEMPO trial at 5 years: transoral fundoplication (TIF 2.0) is safe, durable, and cost-effective. Surg Innov. 2018; 25:149–157.11. Toomey P, Teta A, Patel K, et al. Transoral incisionless fundoplication: is it as safe and efficacious as a Nissen or Toupet fundoplication? Am Surg. 2014; 80:860–867.12. Richter JE, Kumar A, Lipka S, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic nissen fundoplication vs transoral incisionless fundoplication or proton pump inhibitors in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2018; 154:1298–1308.13. Ihde GM. The evolution of TIF: transoral incisionless fundoplication. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020; 13:1756284820924206.14. Chang KJ, Bell R. Transoral incisionless fundoplication. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020; 30:267–289.15. Brewer Gutierrez OI, Dbouk M, Kannadath BS, et al. Mo1283 Learning curve of transoral incisionless fundoplication: a single endoscopist experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91Suppl:AB416.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessing implementation strategy and learning curve for transoral incisionless fundoplication as a new technique
- Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication Leads to Esophageal Mucosa Healing in Responder Patients Followed up to 2 Years, as Documented by Esophageal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance
- Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Where Do We Stand?
- Esophgeal Perforation and Bilateral Empyema Following Endoscopic EsophyX Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication
- Endoscopic Treatment of Refractory Gastroesohageal Reflux Disease