Clin Endosc.
2013 May;46(3):230-234. 10.5946/ce.2013.46.3.230.
Endoscopic Treatment of Refractory Gastroesohageal Reflux Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Disease Center, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. sphong@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2048925
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.3.230
Abstract
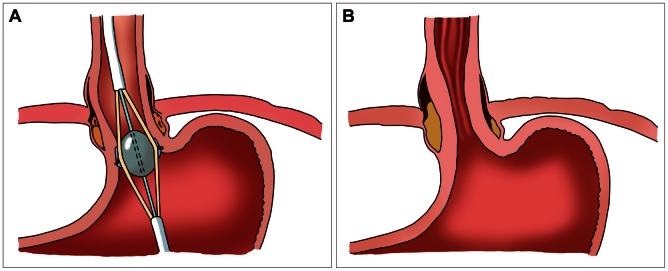
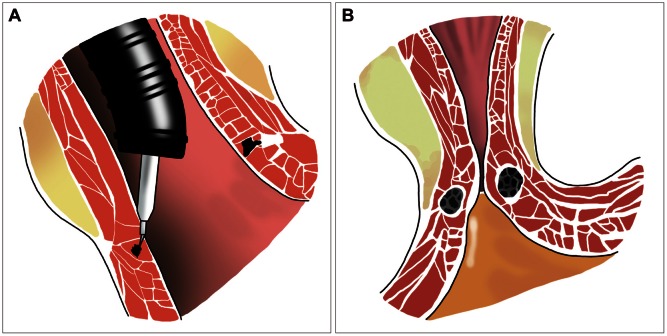
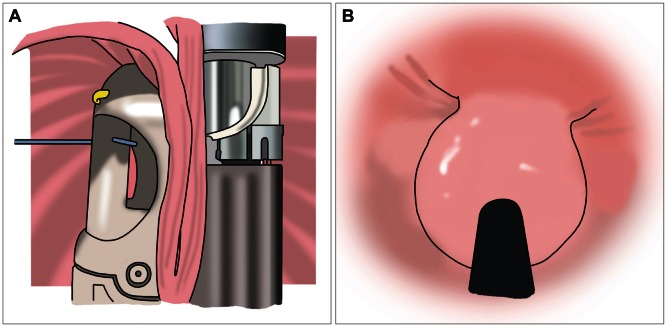
- Though efficient acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) remains the mainstay of treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), some of the patients showed refractory response to PPIs, necessitating further intervention. After increasing dose of PPIs and other kinds of pharmacological intervention adopting prokinetics or others, variable endoscopic treatments are introduced for the treatment of these refractory cases. The detailed introduction regarding endoscopic treatment for GERD is forwarded in this review article. Implantation of reabsorbable or synthetic materials in the distal esophagus was tried in vain and is expelled from the market due to limited efficacy and serious complication. Radiofrequency energy delivery (Stretta) and transoral incisionless fundoplication (EsophyX) are actively tried currently.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S. Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2005; 54:710–717. PMID: 15831922.
Article2. Lee ES, Kim N, Lee SH, et al. Comparison of risk factors and clinical responses to proton pump inhibitors in patients with erosive oesophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:154–164. PMID: 19392871.
Article3. Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:308–328. PMID: 23419381.
Article4. Sifrim D, Zerbib F. Diagnosis and management of patients with reflux symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitors. Gut. 2012; 61:1340–1354. PMID: 22684483.
Article5. Carlson MA, Frantzides CT. Complications and results of primary minimally invasive antireflux procedures: a review of 10,735 reported cases. J Am Coll Surg. 2001; 193:428–439. PMID: 11584971.
Article6. Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S, et al. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery vs esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011; 305:1969–1977. PMID: 21586712.
Article7. Lee SK, Kim EK. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in Korean patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:89–94. PMID: 19259354.
Article8. Fry LC, Mönkemüller K, Malfertheiner P. Systematic review: endoluminal therapy for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: evidence from clinical trials. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 19:1125–1139. PMID: 17998840.
Article9. Triadafilopoulos G. Stretta: an effective, minimally invasive treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Med. 2003; 115(Suppl 3A):192S–200S. PMID: 12928101.
Article10. Go MR, Dundon JM, Karlowicz DJ, Domingo CB, Muscarella P, Melvin WS. Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the lower esophageal sphincter improves symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Surgery. 2004; 136:786–794. PMID: 15467663.
Article11. Cipolletta L, Rotondano G, Dughera L, et al. Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the gastroesophageal junction (Stretta procedure) for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc. 2005; 19:849–853. PMID: 15868272.
Article12. Tam WC, Schoeman MN, Zhang Q, et al. Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the lower oesophageal sphincter and gastric cardia inhibits transient lower oesophageal sphincter relaxations and gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with reflux disease. Gut. 2003; 52:479–485. PMID: 12631654.
Article13. Reymunde A, Santiago N. Long-term results of radiofrequency energy delivery for the treatment of GERD: sustained improvements in symptoms, quality of life, and drug use at 4-year follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:361–366. PMID: 17321231.
Article14. Perry KA, Banerjee A, Melvin WS. Radiofrequency energy delivery to the lower esophageal sphincter reduces esophageal acid exposure and improves GERD symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012; 22:283–288. PMID: 22874675.15. Chen D, Barber C, McLoughlin P, Thavaneswaran P, Jamieson GG, Maddern GJ. Systematic review of endoscopic treatments for gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg. 2009; 96:128–136. PMID: 19160349.
Article16. Louis H, Closset J, Devière J. Enteryx. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2004; 18:49–59. PMID: 15123084.
Article17. Edmundowicz SA. Injection therapy of the lower esophageal sphincter for the treatment of GERD. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:545–552. PMID: 15044897.
Article18. Cohen LB, Johnson DA, Ganz RA, et al. Enteryx implantation for GERD: expanded multicenter trial results and interim postapproval follow-up to 24 months. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:650–658. PMID: 15855967.
Article19. Domagk D, Menzel J, Seidel M, et al. Endoluminal gastroplasty (EndoCinch) versus endoscopic polymer implantation (Enteryx) for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: 6-month results of a prospective, randomized trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:422–430. PMID: 16542275.20. Wong RF, Davis TV, Peterson KA. Complications involving the mediastinum after injection of Enteryx for GERD. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:753–756. PMID: 15855987.
Article21. Tintillier M, Chaput A, Kirch L, Martinet JP, Pochet JM, Cuvelier C. Esophageal abscess complicating endoscopic treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease by Enteryx injection: a first case report. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1856–1858. PMID: 15330928.
Article22. Noh KW, Loeb DS, Stockland A, Achem SR. Pneumomediastinum following Enteryx injection for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:723–726. PMID: 15743374.
Article23. Feretis C, Benakis P, Dimopoulos C, et al. Endoscopic implantation of Plexiglas (PMMA) microspheres for the treatment of GERD. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:423–426. PMID: 11275880.
Article24. Mahmood Z, Ang YS. EndoCinch treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 2007; 76:241–247. PMID: 18176078.
Article25. Jafri SM, Arora G, Triadafilopoulos G. What is left of the endoscopic antireflux devices? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009; 25:352–357. PMID: 19342950.
Article26. Zagol B, Mikami D. Advances in transoral fundoplication for oesophageal reflux. Dig Liver Dis. 2011; 43:361–364. PMID: 21382755.
Article27. Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Lo S, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: 12-month follow-up for the North American open-label trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:643–649. PMID: 15855966.
Article28. von Renteln D, Schiefke I, Fuchs KH, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD by application of multiple Plicator implants: a multicenter study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:833–844. PMID: 18534586.
Article29. Testoni PA, Vailati C. Transoral incisionless fundoplication with EsophyX(R) for treatment of gastro-oesphageal reflux disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2012; 44:631–635. PMID: 22622203.30. Barnes WE, Hoddinott KM, Mundy S, Williams M. Transoral incisionless fundoplication offers high patient satisfaction and relief of therapy-resistant typical and atypical symptoms of GERD in community practice. Surg Innov. 2011; 18:119–129. PMID: 21307014.
Article31. Trad KS, Turgeon DG, Deljkich E. Long-term outcomes after transoral incisionless fundoplication in patients with GERD and LPR symptoms. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:650–660. PMID: 21959689.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Diagnosis and Management
- A Case of Postfundoplication Dysphagia without Symptomatic Improvement after Endoscopic Dilatation
- Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Where Do We Stand?
- Endoscopic teflon injection in vesicoureteral reflux
- Unmet Needs in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease