Endocrinol Metab.
2022 Aug;37(4):701-702. 10.3803/EnM.2022.401.
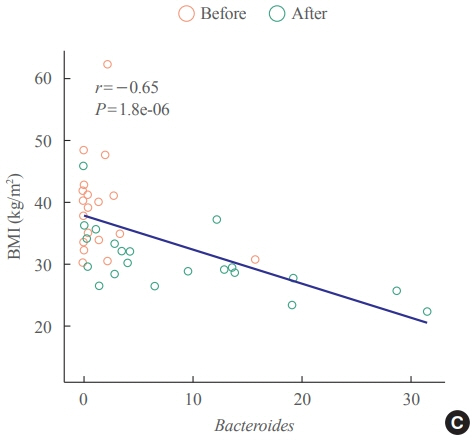
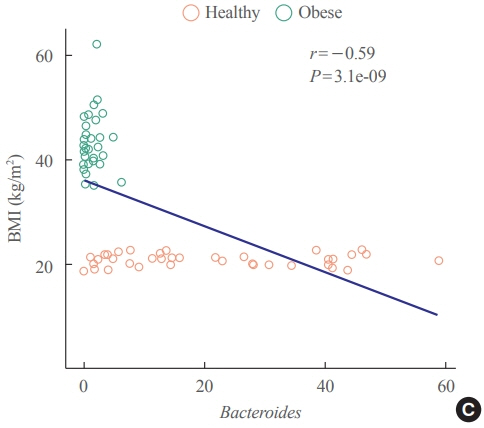
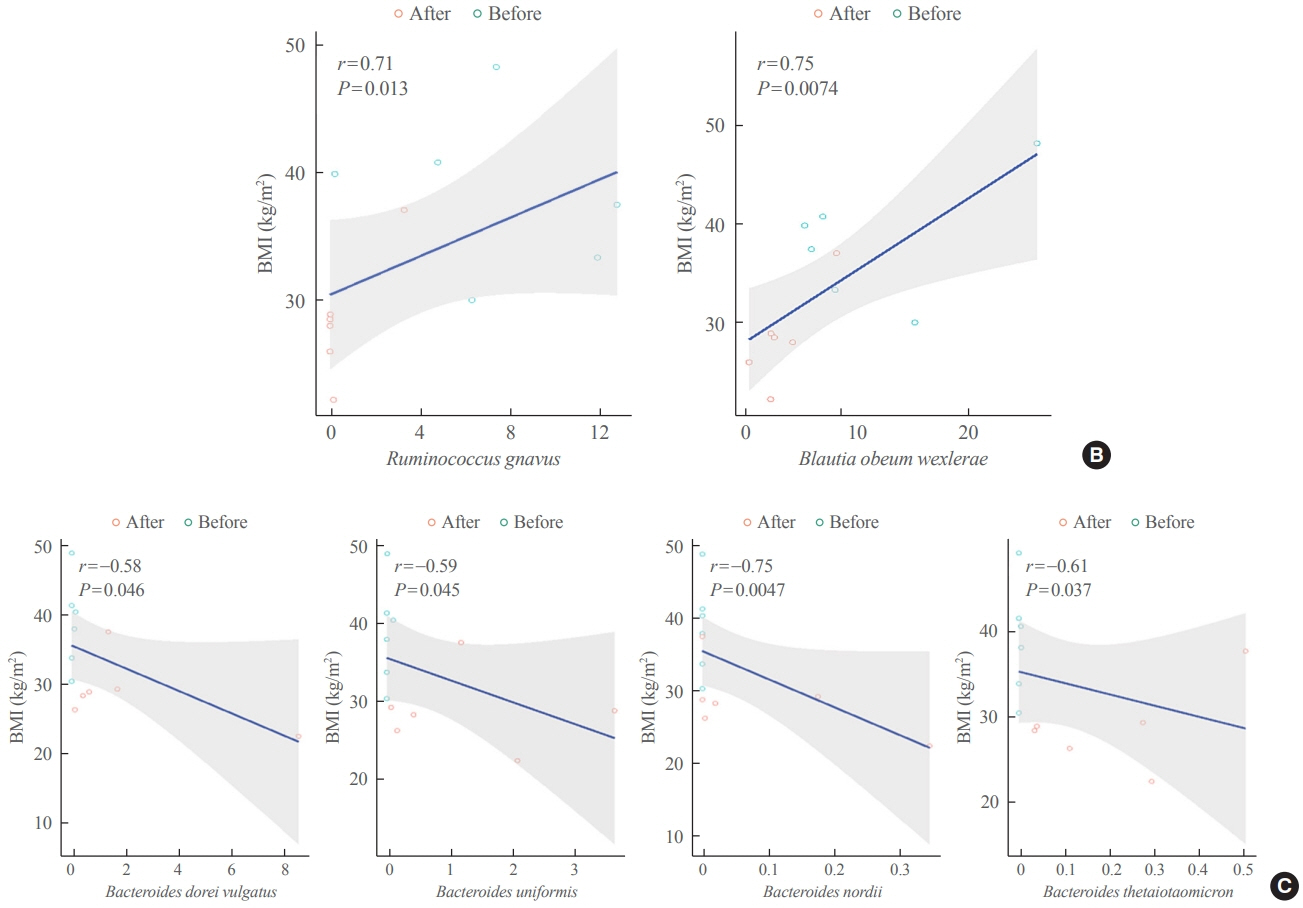
Association between the Blautia/Bacteroides Ratio and Altered Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Cell Biotech Co. Ltd., Gimpo, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2532870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.401
Figure
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association between the Blautia/Bacteroides Ratio and Altered Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery
- Assessment Parameters after Bariatric Surgery
- Current Status of Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery in Korea
- Bariatric Surgery
- Changes of Guidelines in the Management of Obese Patients With Diabetes in the Metabolic Surgery Perspective