Endocrinol Metab.
2022 Jun;37(3):475-486. 10.3803/EnM.2022.1481.
Association between the Blautia/Bacteroides Ratio and Altered Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Cell Biotech Co. Ltd., Gimpo, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2531391
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1481
Abstract
- Background
Current evidence support that the gut microbiota plays a potential role in obesity. Bariatric surgery can reduce excess weight and decrease the risk of life-threatening weight-related health problems and may also influence gut microbiota. In this study, we aimed to investigate the changes in gut microbiota before and after bariatric surgery and evaluate the association of the gut microbial shift and altered body mass index (BMI) after bariatric surgery.
Methods
Between January 2019 and July 2020, stools from 58 patients scheduled for bariatric surgery were collected. Six months after bariatric surgery, stools from 22 of these patients were re-collected, and the changes in gut microbiota before and after bariatric surgery were evaluated. In addition, the differences in gut microbiota between patients with severe obesity (BMI >35 kg/m2, n=42) and healthy volunteers with normal BMI (18.8 to 22.8 kg/m2, n=41) were investigated.
Results
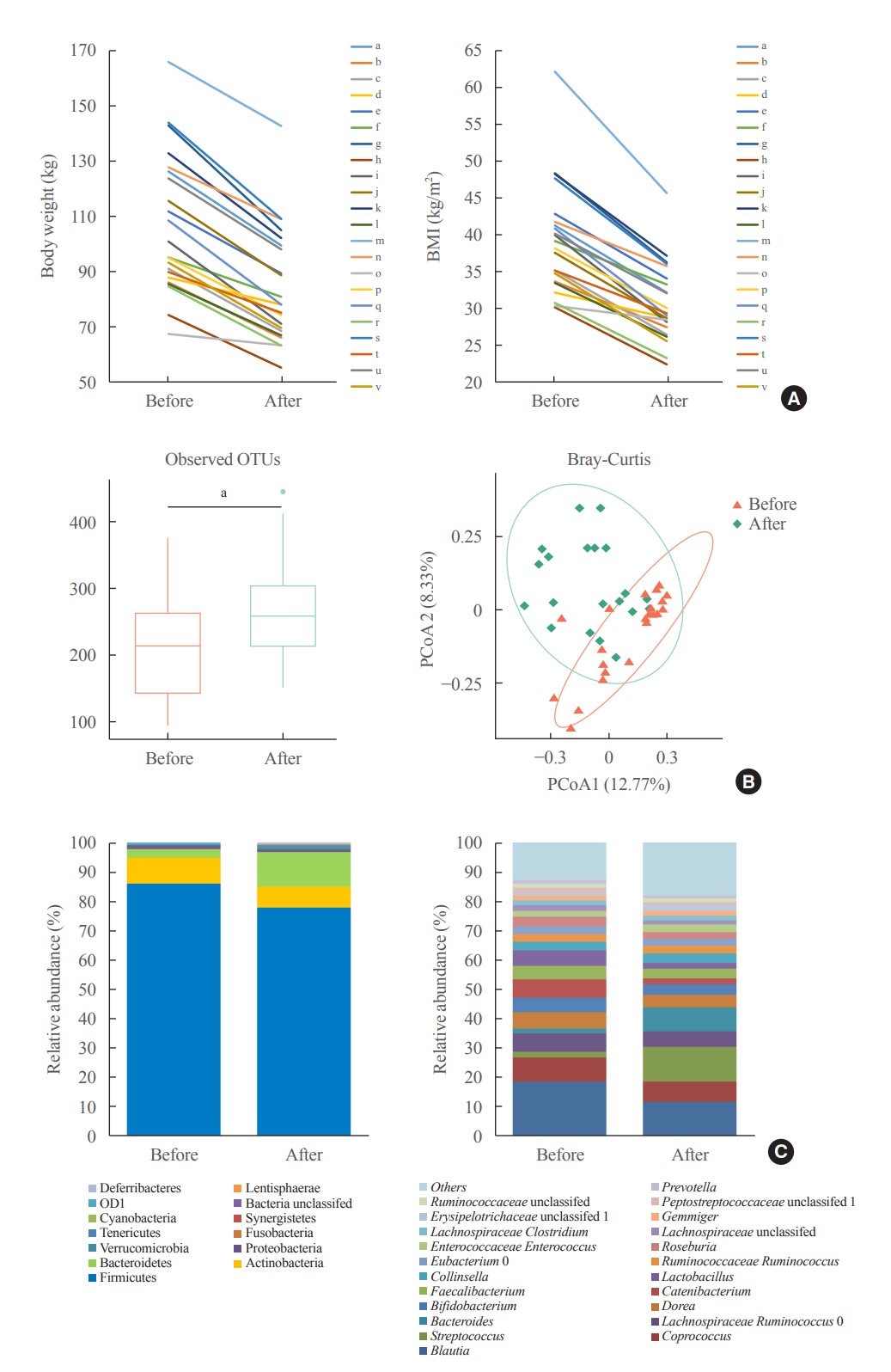
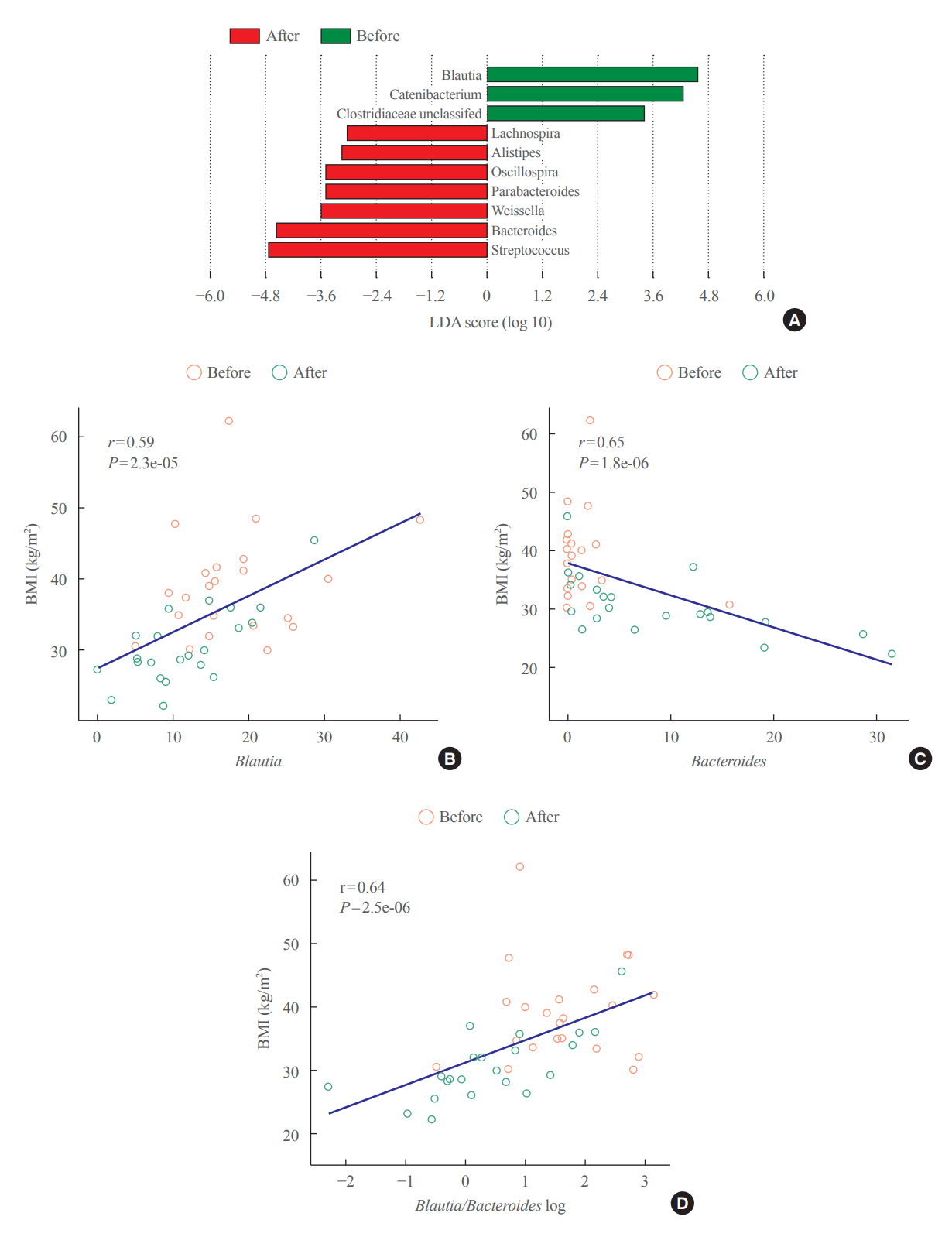
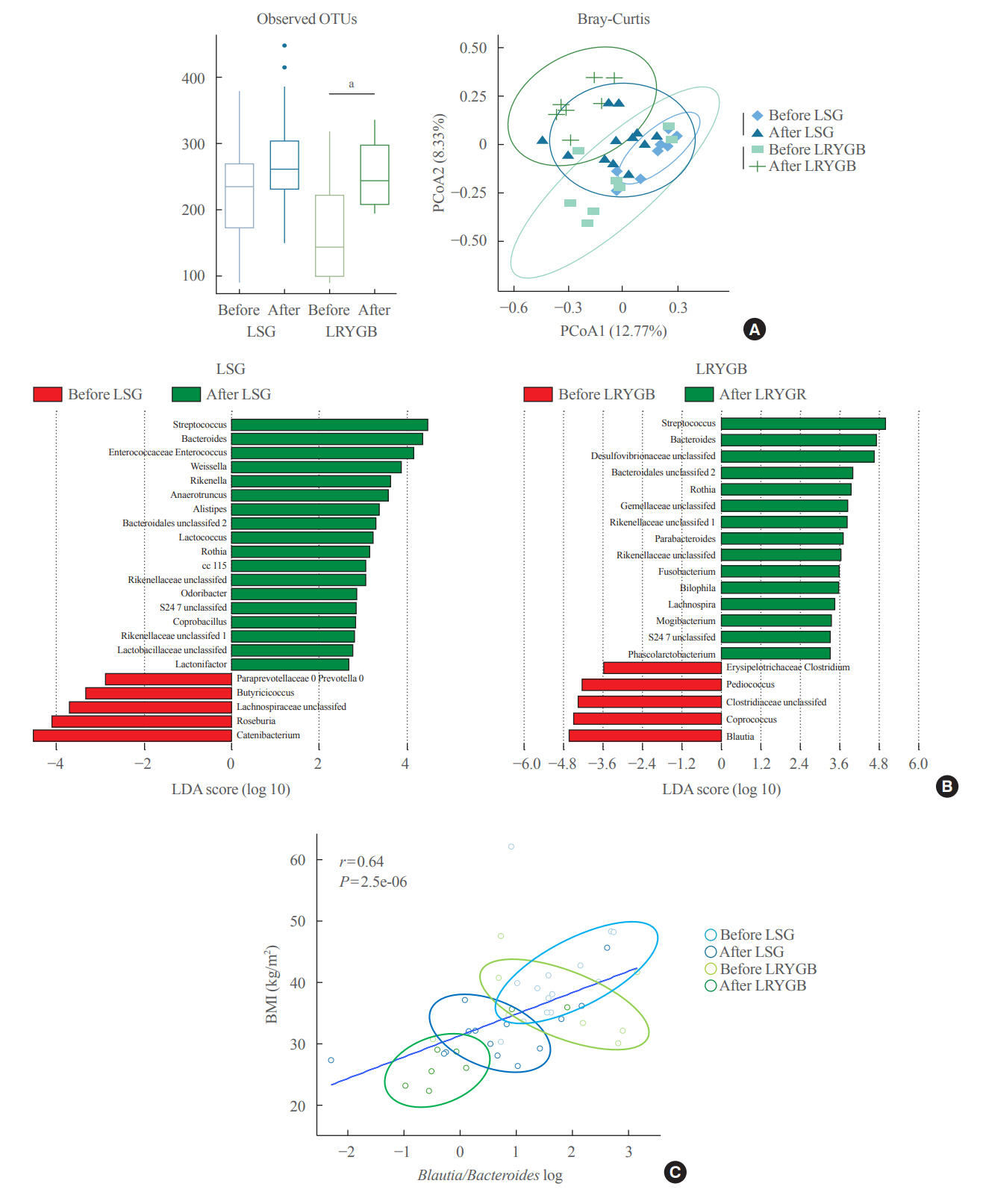
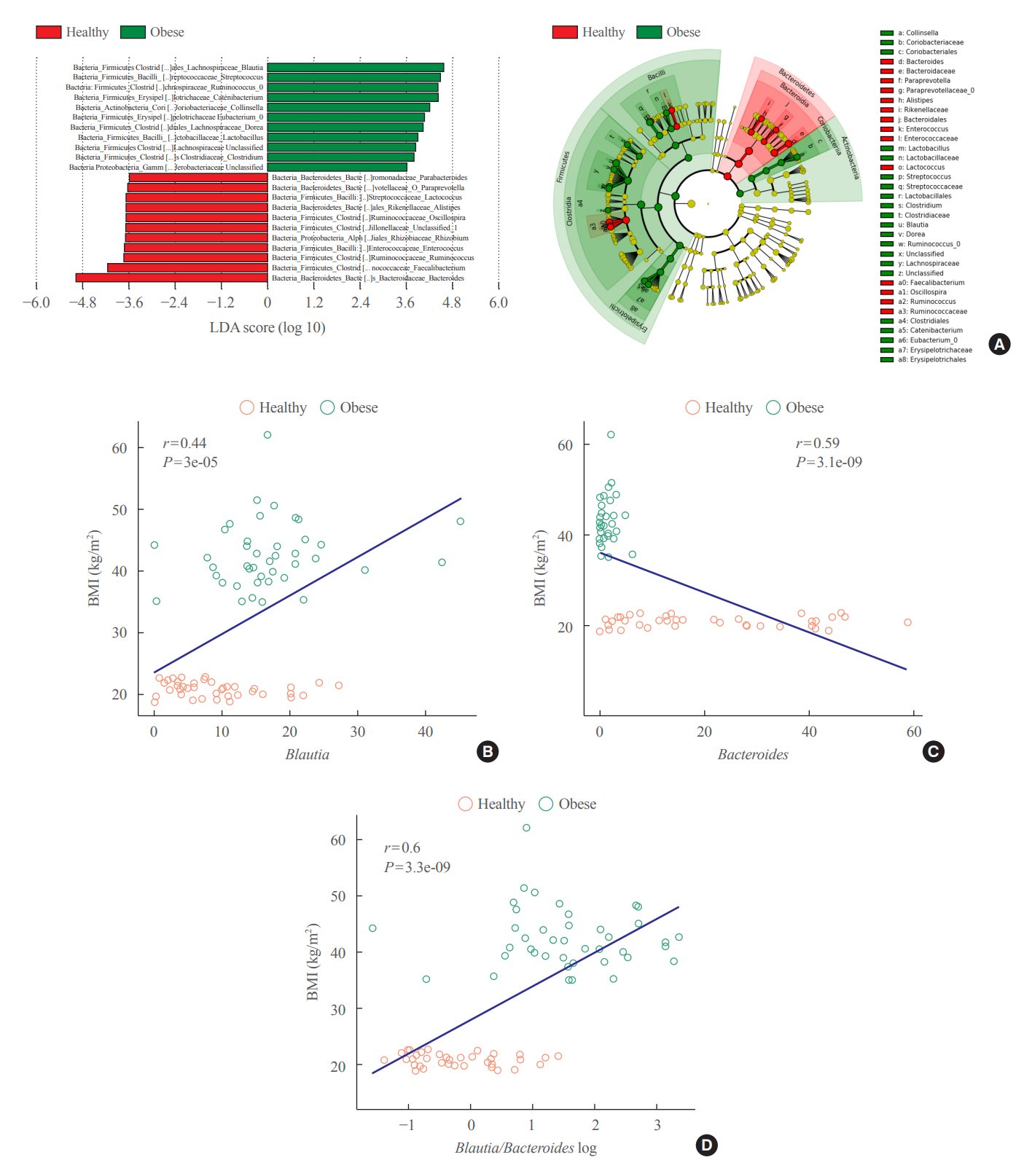
The gut microbiota of patients who underwent bariatric surgery showed increased α-diversity and differed β-diversity compared with those before surgery. Interestingly, Blautia was decreased and Bacteriodes was increased at the genus level after bariatric surgery. Further, the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio showed a positive correlation with BMI. To validate these results, we compared the gut microbiota from severely obese patients with high BMI with those from healthy volunteers and demonstrated that the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio correlated positively with BMI.
Conclusion
In the gut microbial analysis of patients who underwent bariatric surgery, we presented that the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio had changed after bariatric surgery and showed a positive correlation with BMI.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Boyeon Kim, Bukyung Kim
Kosin Med J. 2023;38(3):169-175. doi: 10.7180/kmj.23.138.
Reference
-
1. Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019; 92:6–10.
Article2. Singh GM, Danaei G, Farzadfar F, Stevens GA, Woodward M, Wormser D, et al. The age-specific quantitative effects of metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: a pooled analysis. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e65174.
Article3. Lauby-Secretan B, Scoccianti C, Loomis D, Grosse Y, Bianchini F, Straif K, et al. Body fatness and cancer: viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:794–8.
Article4. Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Budge M, Young J. Body mass index in midlife and late-life as a risk factor for dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Obes Rev. 2011; 12:e426–37.
Article5. Anandacoomarasamy A, Caterson I, Sambrook P, Fransen M, March L. The impact of obesity on the musculoskeletal system. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:211–22.
Article6. Racette SB, Deusinger SS, Deusinger RH. Obesity: overview of prevalence, etiology, and treatment. Phys Ther. 2003; 83:276–88.
Article7. Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006; 444:1027–31.
Article8. Magne F, Gotteland M, Gauthier L, Zazueta A, Pesoa S, Navarrete P, et al. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio: a relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients. 2020; 12:1474.
Article9. Koliada A, Syzenko G, Moseiko V, Budovska L, Puchkov K, Perederiy V, et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017; 17:120.
Article10. Bervoets L, Van Hoorenbeeck K, Kortleven I, Van Noten C, Hens N, Vael C, et al. Differences in gut microbiota composition between obese and lean children: a cross-sectional study. Gut Pathog. 2013; 5:10.
Article11. Andoh A, Nishida A, Takahashi K, Inatomi O, Imaeda H, Bamba S, et al. Comparison of the gut microbial community between obese and lean peoples using 16S gene sequencing in a Japanese population. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2016; 59:65–70.
Article12. Iqbal Z, Adam S, Ho JH, Syed AA, Ammori BJ, Malik RA, et al. Metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes of bariatric surgery. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2020; 31:246–56.
Article13. Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013; 23:427–36.
Article14. Hutch CR, Sandoval D. The role of GLP-1 in the metabolic success of bariatric surgery. Endocrinology. 2017; 158:4139–51.
Article15. Palleja A, Kashani A, Allin KH, Nielsen T, Zhang C, Li Y, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery of morbidly obese patients induces swift and persistent changes of the individual gut microbiota. Genome Med. 2016; 8:67.
Article16. Li JV, Ashrafian H, Sarafian M, Homola D, Rushton L, Barker G, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass-induced bacterial perturbation contributes to altered host-bacterial co-metabolic phenotype. Microbiome. 2021; 9:139.
Article17. Fouladi F, Carroll IM, Sharpton TJ, Bulik-Sullivan E, Heinberg L, Steffen KJ, et al. A microbial signature following bariatric surgery is robustly consistent across multiple cohorts. Gut Microbes. 2021; 13:1930872.
Article18. Furet JP, Kong LC, Tap J, Poitou C, Basdevant A, Bouillot JL, et al. Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes. 2010; 59:3049–57.19. Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. 2013; 341:1241214.
Article20. Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature. 2009; 457:480–4.
Article21. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006; 444:1022–3.22. Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:11070–5.
Article23. Kasai C, Sugimoto K, Moritani I, Tanaka J, Oya Y, Inoue H, et al. Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between obese and non-obese individuals in a Japanese population, as analyzed by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism and next-generation sequencing. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015; 15:100.
Article24. Ozato N, Saito S, Yamaguchi T, Katashima M, Tokuda I, Sawada K, et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20-76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019; 5:28.
Article25. Jie Z, Yu X, Liu Y, Sun L, Chen P, Ding Q, et al. The baseline gut microbiota directs dieting-induced weight loss trajectories. Gastroenterology. 2021; 160:2029–42.
Article26. Liu X, Mao B, Gu J, Wu J, Cui S, Wang G, et al. Blautia: a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes. 2021; 13:1–21.27. Farin W, Onate FP, Plassais J, Bonny C, Beglinger C, Woelnerhanssen B, et al. Impact of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy on gut microbiota: a metagenomic comparative analysis. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020; 16:852–62.
Article28. Paganelli FL, Luyer M, Hazelbag CM, Uh HW, Rogers M, Adriaans D, et al. Roux-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy directly change gut microbiota composition independent of surgery type. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:10979.
Article29. Pucci A, Batterham RL. Mechanisms underlying the weight loss effects of RYGB and SG: similar, yet different. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019; 42:117–28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association between the Blautia/Bacteroides Ratio and Altered Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery
- Assessment Parameters after Bariatric Surgery
- Current Status of Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery in Korea
- Bariatric Surgery
- Changes of Guidelines in the Management of Obese Patients With Diabetes in the Metabolic Surgery Perspective