Healthc Inform Res.
2022 Jul;28(3):210-221. 10.4258/hir.2022.28.3.210.
Machine Learning Smart System for Parkinson Disease Classification Using the Voice as a Biomarker
- Affiliations
-
- 1E2SN, ENSIAS, Mohammed V University in Rabat, Rabat, Morocco
- KMID: 2532448
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2022.28.3.210
Abstract
Objectives
This study presents PD Predict, a machine learning system for Parkinson disease classification using voice as a biomarker.
Methods
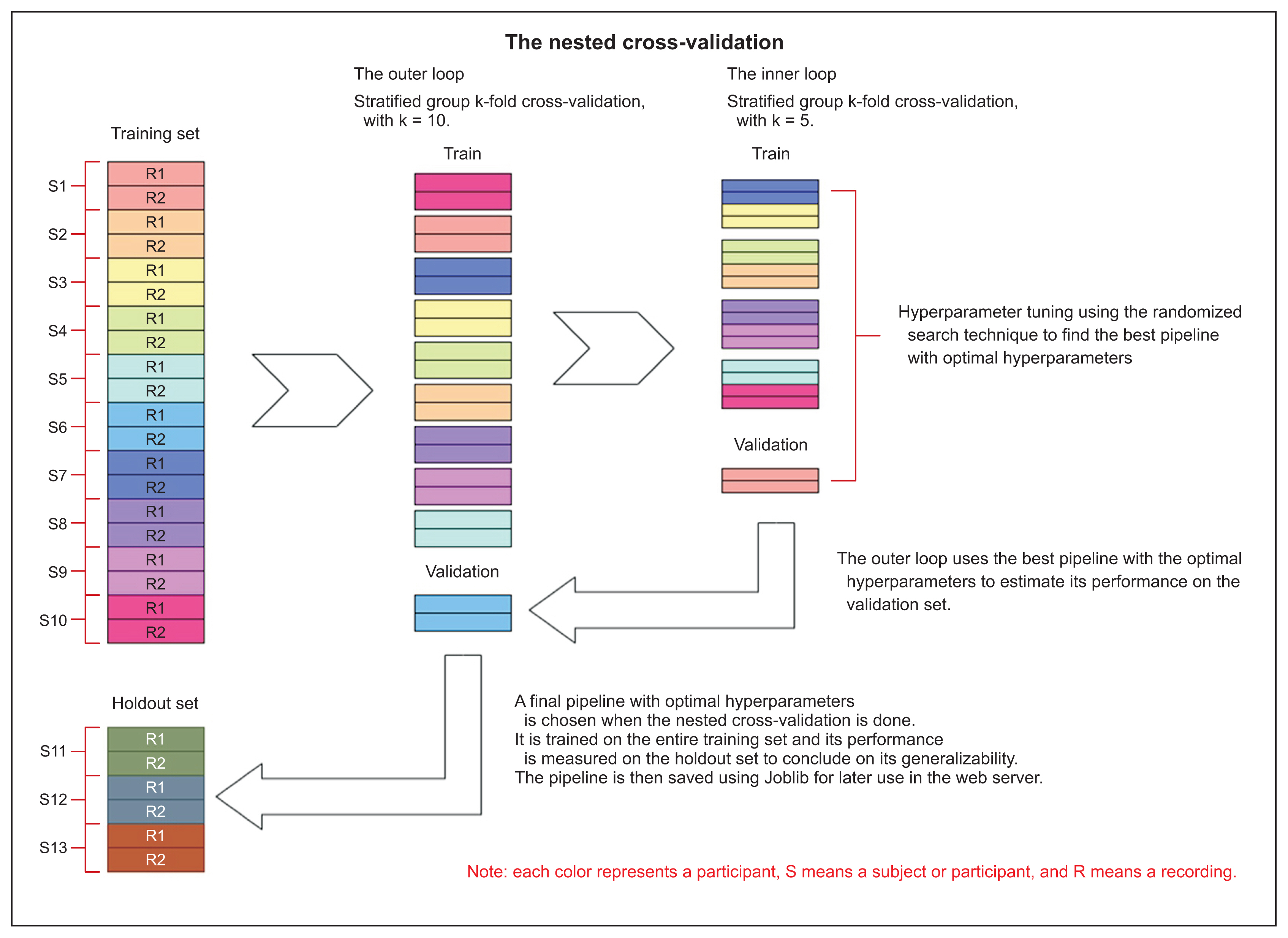
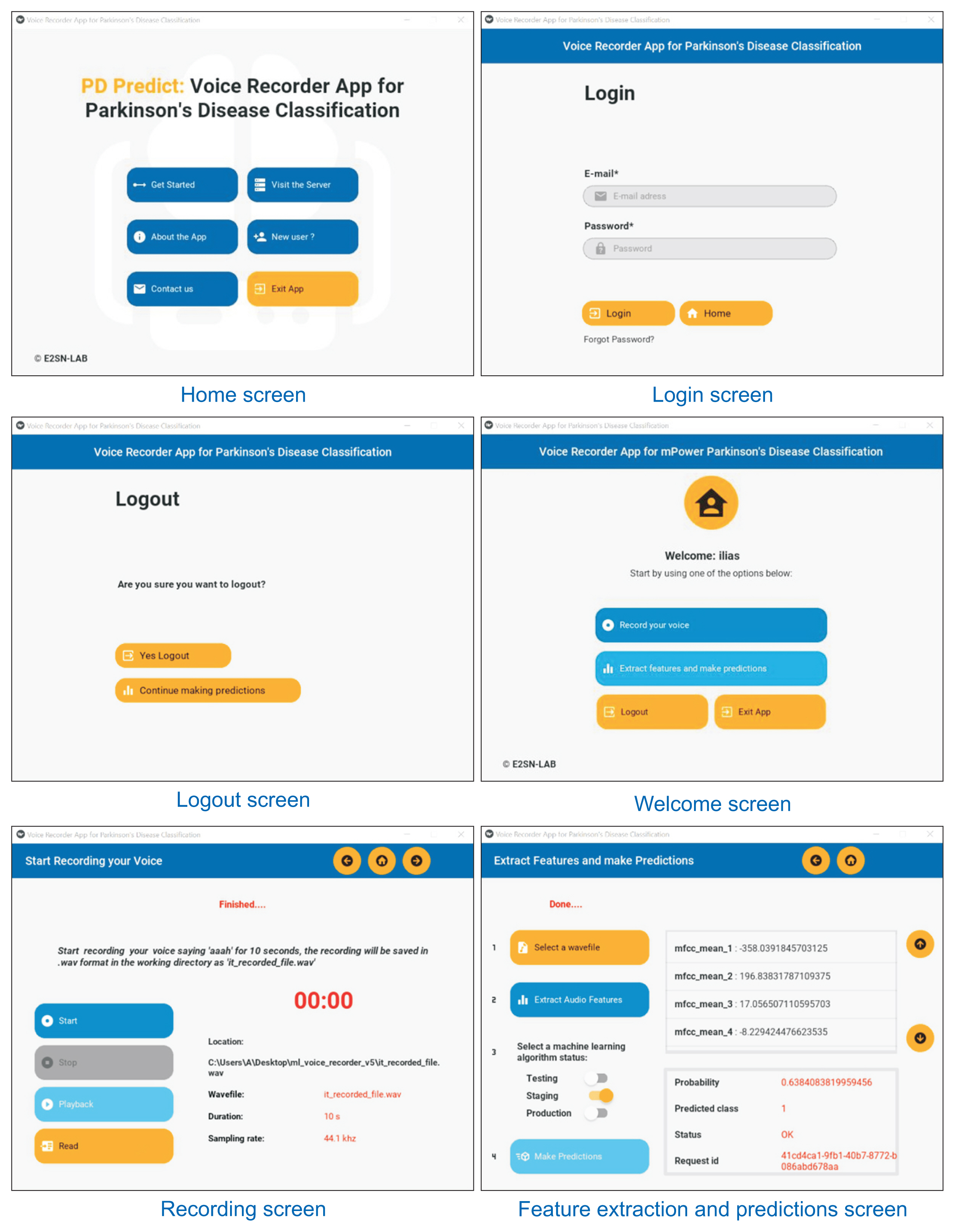
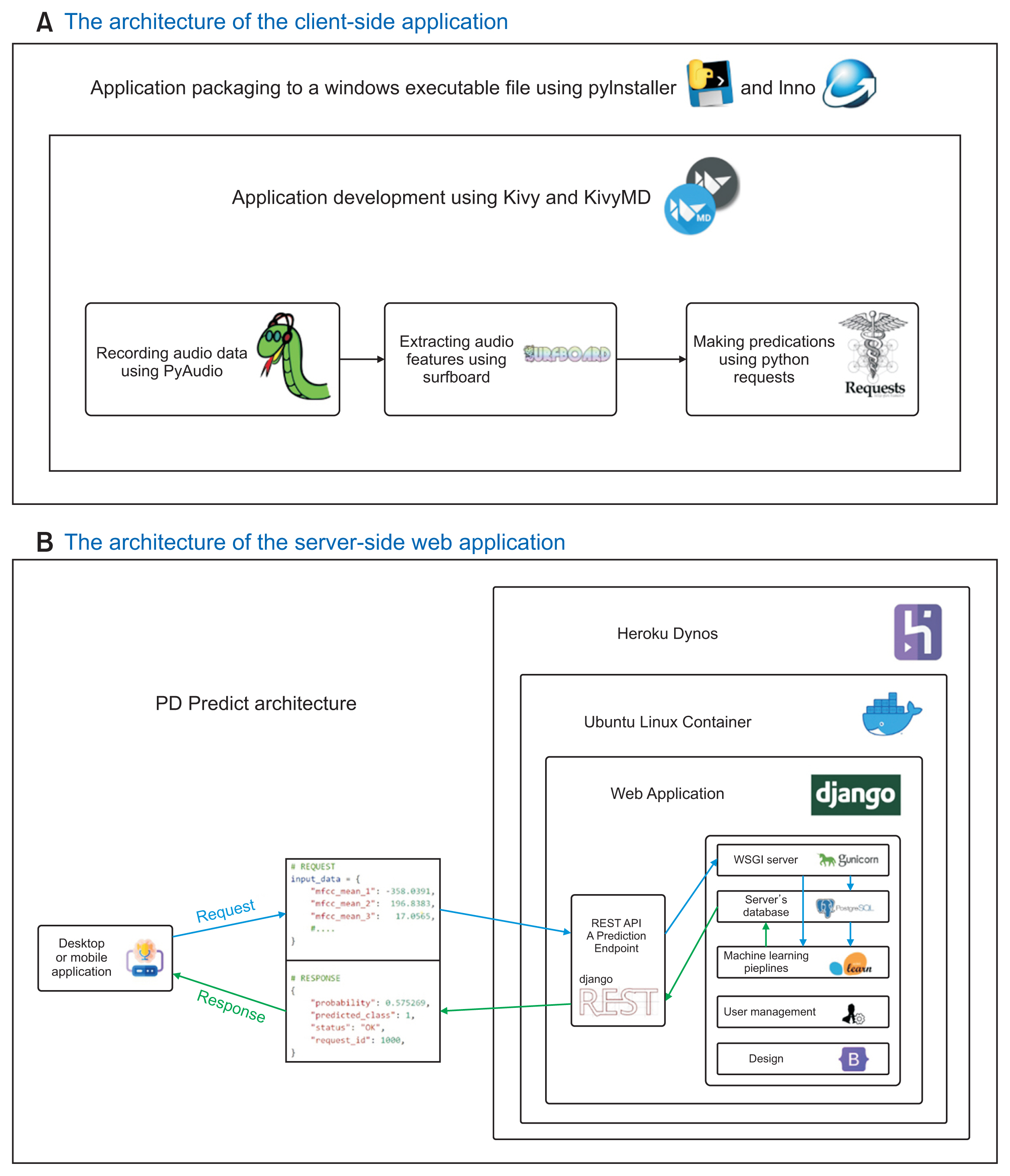
We first created an original set of recordings from the mPower study, and then extracted several audio features, such as mel-frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC) components and other classical speech features, using a windowing procedure. The generated dataset was then divided into training and holdout sets. The training set was used to train two machine learning pipelines, and their performance was estimated using a nested subject-wise cross-validation approach. The holdout set was used to assess the generalizability of the pipelines for unseen data. The final pipelines were implemented in PD Predict and accessed through a prediction endpoint developed using the Django REST Framework. PD Predict is a two-component system: a desktop application that records audio recordings, extracts audio features, and makes predictions; and a server-side web application that implements the machine learning pipelines and processes incoming requests with the extracted audio features to make predictions. Our system is deployed and accessible via the following link: https://pdpredict.herokuapp.com/.
Results
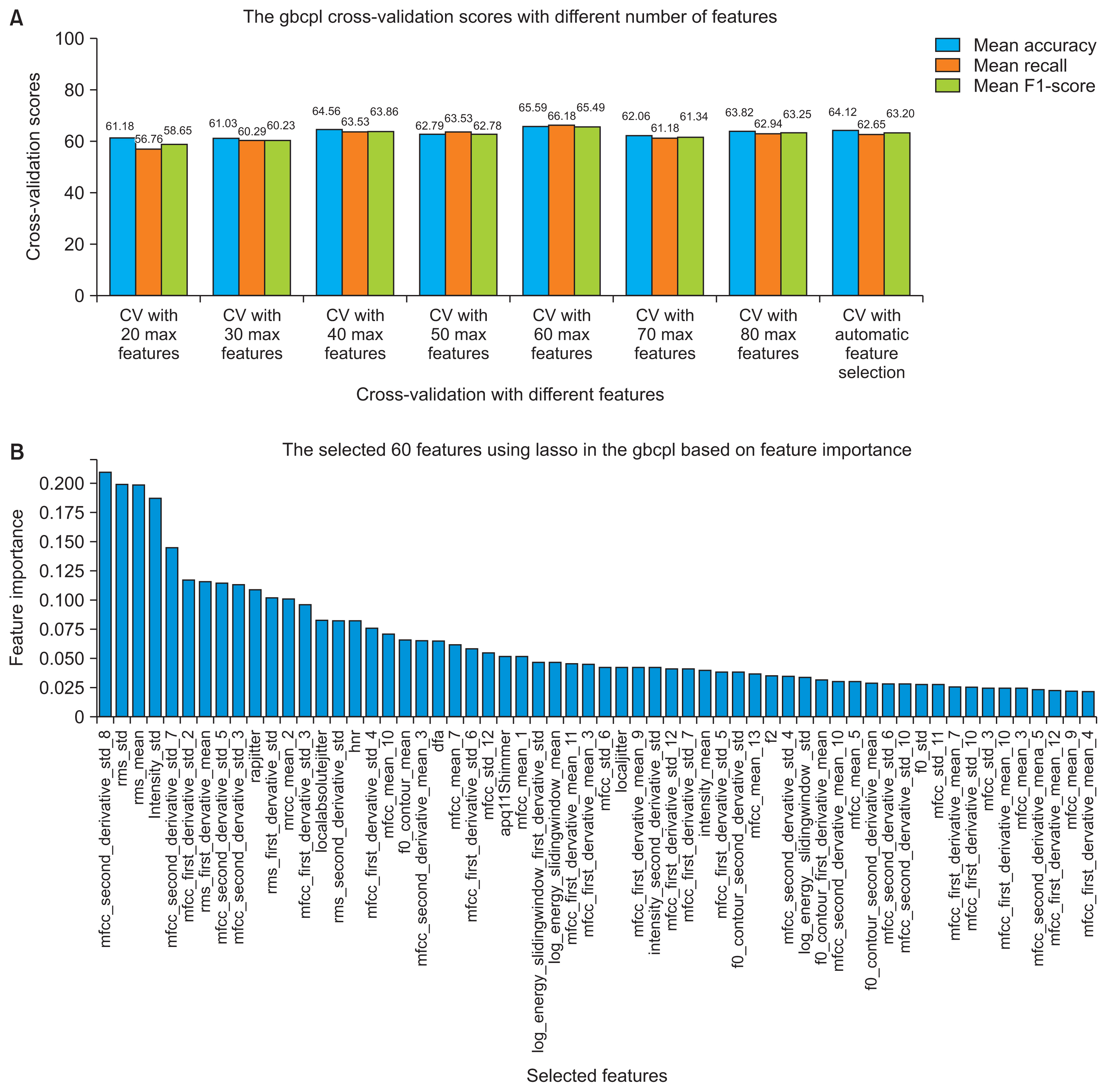
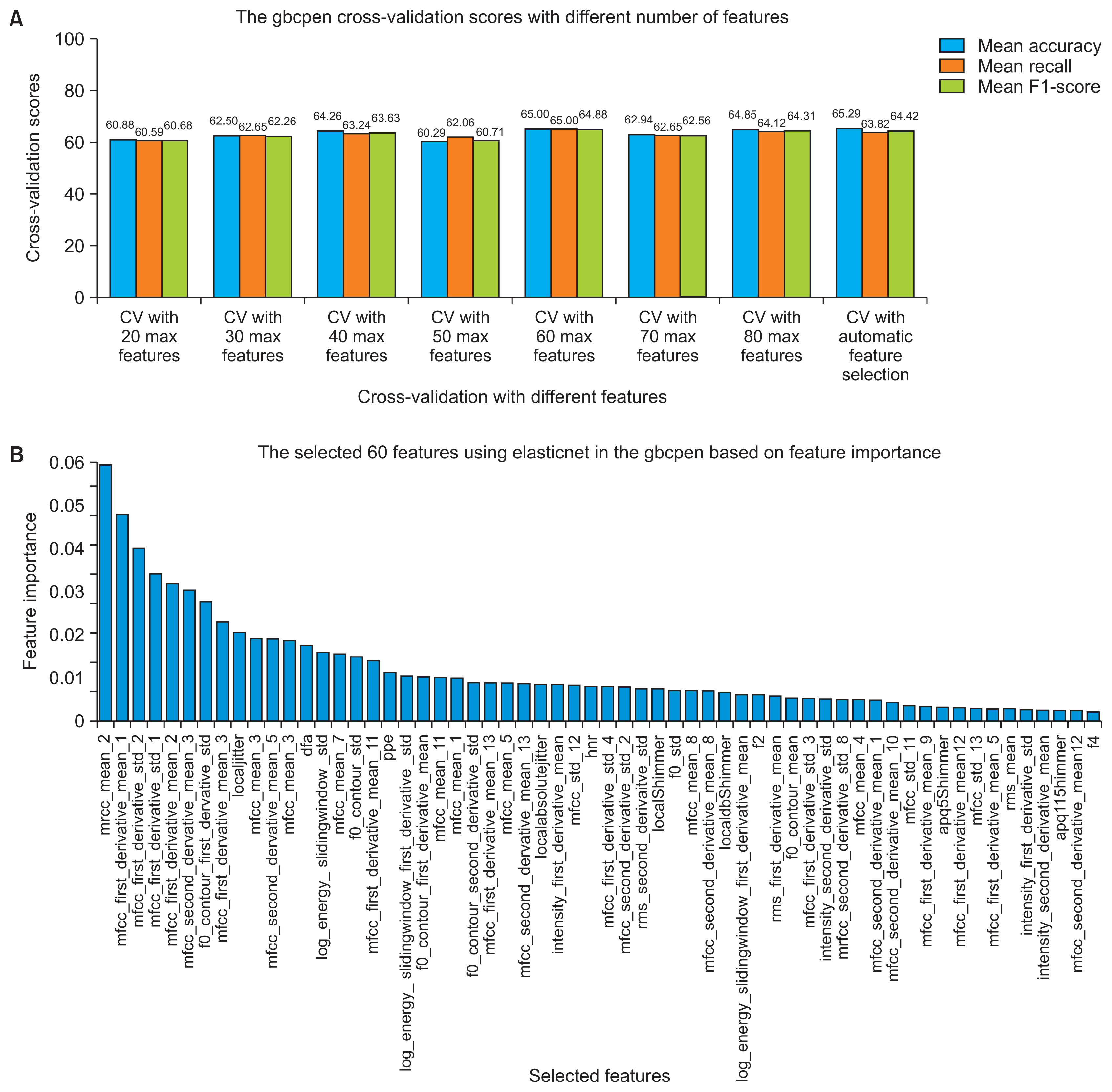
Both machine learning pipelines showed moderate performance, between 65% and 75% using the nested subject-wise cross-validation approach. Furthermore, they generalized well to unseen data and they did not overfit the training set.
Conclusions
The architecture of PD Predict is clear, and the performance of the implemented machine learning pipelines is promising and confirms the usability of smartphone microphones for capturing digital biomarkers of disease.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Weintraub D, Comella CL, Horn S. Parkinson’s disease: Part 1: pathophysiology, symptoms, burden, diagnosis, and assessment. Am J Manag Care. 2008; 14(2 Suppl):S40–8.2. Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C. Evidence-based medical review update: pharmacological and surgical treatments of Parkinson’s disease: 2001 to 2004. Mov Disord. 2005; 20(5):523–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20464.
Article3. Ho AK, Iansek R, Marigliani C, Bradshaw JL, Gates S. Speech impairment in a large sample of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Behav Neurol. 1998; 11(3):131–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/1999/327643.
Article4. Perry B, Herrington W, Goldsack JC, Grandinetti CA, Vasisht KP, Landray MJ, et al. Use of mobile devices to measure outcomes in clinical research, 2010–2016: a systematic literature review. Digit Biomark. 2018; 2(1):11–30. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486347.
Article5. Sakar CO, Serbes G, Gunduz A, Tunc HC, Nizam H, Sakar BE, et al. A comparative analysis of speech signal processing algorithms for Parkinson’s disease classification and the use of the tunable Q-factor wavelet transform. Appl Soft Comput. 2019; 74:255–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.10.022.
Article6. Gunduz H. Deep learning-based Parkinson’s disease classification using vocal feature sets. IEEE Access. 2019; 7:115540–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936564.
Article7. Haq AU, Li JP, Memon MH, Malik A, Ahmad T, Ali A, et al. Feature selection based on L1-norm support vector machine and effective recognition system for Parkinson’s disease using voice recordings. IEEE Access. 2019; 7:37718–34. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2906350.
Article8. Almeida JS, Reboucas Filho PP, Carneiro T, Wei W, Damasevicius R, Maskeliunas R, et al. Detecting Parkinson’s disease with sustained phonation and speech signals using machine learning techniques. Pattern Recognit Lett. 2019; 125:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.04.005.
Article9. Berus L, Klancnik S, Brezocnik M, Ficko M. Classifying Parkinson’s disease based on acoustic measures using artificial neural networks. Sensors (Basel). 2018; 19(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010016.
Article10. Benba A, Jilbab A, Hammouch A. Analysis of multiple types of voice recordings in cepstral domain using MFCC for discriminating between patients with Parkinson’s disease and healthy people. Int J Speech Technol. 2016; 19(3):449–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9338-4.
Article11. Bot BM, Suver C, Neto EC, Kellen M, Klein A, Bare C, et al. The mPower study, Parkinson disease mobile data collected using ResearchKit. Sci Data. 2016; 3:160011. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.11.
Article12. mPower: mobile Parkinson disease study [Internet]. Seattle (WA): Sage Bionetworks;2019. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://www.synapse.org/#!Synapse:syn4993293/wiki/247859.13. Synapse REST API: basics table query [Internet]. Seattle (WA): Sage Bionetworks;2020. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://docs.synapse.org/rest/org/sagebionetworks/repo/web/controller/TableExamples.html.14. Wong SL, Gilmour HL, Ramage-Morin PL. Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, diagnosis and impact. Health Rep. 2014; 25(11):10–4.15. Bonet-Sola D, Alsina-Pages RM. A comparative survey of feature extraction and machine learning methods in diverse acoustic environments. Sensors (Basel). 2021; 21(4):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041274.
Article16. Giannakopoulos T, Pikrakis A. Introduction to audio analysis: a MATLAB approach. Kidlington, UK: Academic Press;2014.17. Lenain R, Weston J, Shivkumar A, Fristed E. Surfboard: audio feature extraction for modern machine learning. arXiv [Preprint]. 2020. May. 18. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.08848.
Article18. Tougui I, Jilbab A, Mhamdi JE. Impact of the choice of cross-validation techniques on the results of machine learning-based diagnostic applications. Healthc Inform Res. 2021; 27(3):189–99. https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2021.27.3.189.19. Kotsiantis SB, Kanellopoulos D, Pintelas PE. Data preprocessing for supervised leaning. Int J Comput Sci. 2006; 1(2):111–7.20. Chandrashekar G, Sahin F. A survey on feature selection methods. Comput Electr Eng. 2014; 40(1):16–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.11.024.21. Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 2005; 67(2):301–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00503.x.22. Bergstra J, Bengio Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res. 2012; 13(2):281–305.23. Vabalas A, Gowen E, Poliakoff E, Casson AJ. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS One. 2019; 14(11):e0224365. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224365.
Article24. Virbel M, Hansen T, Lobunets O. Kivy: a framework for rapid creation of innovative user interfaces. In : Workshop-Proceedings der Tagung Mensch & Computer 2011; 2011 Sep 11–14; Chemnitz, Germany. p. 69–73.25. Pham H. PyAudio [Internet]. Cambridge (MA): MIT;2006. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://people.csail.mit.edu/hubert/pyaudio/.26. Cortesi D. PyInstaller Manual [Internet]. [place unknown]: PyInstaller.org;c2020. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://pyinstaller.org/en/stable/.27. jrsoftware. Inno Setup [Internet]. [place unknown]: jrsoftware.org;2022. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://jrsoftware.org/isinfo.php.28. Django: the web framework for perfectionists with deadlines [Internet]. [place unknown]: Django Software Foundation;c2022. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from: https://www.djangoproject.com/.29. Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, et al. Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2011; 12:2825–30.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Research in Voice Disease
- Analysis of Smartphone Recordings in Time, Frequency, and Cepstral Domains to Classify Parkinson’s Disease
- Performance of machine learning methods in diagnosing Parkinson's disease based on dysphonia measures
- Accuracy of Machine Learning Using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment for the Diagnosis of Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease
- Novel Method of Classification in Knee Osteoarthritis: Machine Learning Application Versus Logistic Regression Model